0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 viewsNCP Risk
NCP Risk
Uploaded by
Paolo Vittorio Perdigueros Gonzales
1. Monitor intake and 1. Monitor intake and
output. output to determine
fluid and electrolyte
balance.
2. Monitor vital signs 2. Vital signs changes
and level of may indicate fluid
consciousness. volume deficit or
excess.
3. Monitor lab values 3. Laboratory values
for electrolytes. provide objective
data to determine
effectiveness of
interventions.
Evaluation:
1. Compare lab values 1. Laboratory values
to baseline and provide quantitative
normal range. data to evaluate
effectiveness of
interventions.
2. Note changes in 2. Subjective changes
subjective findings. may indicate need
for modification of
plan of care.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
NCP Risk
NCP Risk
Uploaded by
Paolo Vittorio Perdigueros Gonzales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views2 pages
1. Monitor intake and 1. Monitor intake and
output. output to determine
fluid and electrolyte
balance.
2. Monitor vital signs 2. Vital signs changes
and level of may indicate fluid
consciousness. volume deficit or
excess.
3. Monitor lab values 3. Laboratory values
for electrolytes. provide objective
data to determine
effectiveness of
interventions.
Evaluation:
1. Compare lab values 1. Laboratory values
to baseline and provide quantitative
normal range. data to evaluate
effectiveness of
interventions.
2. Note changes in 2. Subjective changes
subjective findings. may indicate need
for modification of
plan of care.
Original Title
ncp risk
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
1. Monitor intake and 1. Monitor intake and
output. output to determine
fluid and electrolyte
balance.
2. Monitor vital signs 2. Vital signs changes
and level of may indicate fluid
consciousness. volume deficit or
excess.
3. Monitor lab values 3. Laboratory values
for electrolytes. provide objective
data to determine
effectiveness of
interventions.
Evaluation:
1. Compare lab values 1. Laboratory values
to baseline and provide quantitative
normal range. data to evaluate
effectiveness of
interventions.
2. Note changes in 2. Subjective changes
subjective findings. may indicate need
for modification of
plan of care.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views2 pagesNCP Risk
NCP Risk
Uploaded by
Paolo Vittorio Perdigueros Gonzales
1. Monitor intake and 1. Monitor intake and
output. output to determine
fluid and electrolyte
balance.
2. Monitor vital signs 2. Vital signs changes
and level of may indicate fluid
consciousness. volume deficit or
excess.
3. Monitor lab values 3. Laboratory values
for electrolytes. provide objective
data to determine
effectiveness of
interventions.
Evaluation:
1. Compare lab values 1. Laboratory values
to baseline and provide quantitative
normal range. data to evaluate
effectiveness of
interventions.
2. Note changes in 2. Subjective changes
subjective findings. may indicate need
for modification of
plan of care.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
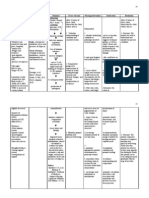
ASSESSMENT NURSING RATIONALE DESIRED NURSING JUSTIFICATIONS EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS OUTCOMES INTERVENTIONS
Subjective Cues: Risk for electrolyte Profuse sweating After 16 hrs of nursing Independent: After 16 hours of
Patient has verbalized, imbalance related to without adequate intervention the client nursing intervention,
“gasakit pa ulo ko.” decrease potassium intake or folks will be able 1. Review laboratory 1. electrolytes include, the patient was able to:
levels, high sodium to: results for abnormal calcium, potassium, etc.
Objective Cues: diet and profuse findings. These chemicals are 1. Display Laboratory
Compromised sweating. electrolyte 1. Display laboratory essential in many bodily results close to normal
concentration wasting results within functions including fluid range for individual.
Assisted activities of Definition: For normal range for balance, movement of Goal Partially met.
daily living change in serum individual. fluid within and between
Confusion electrolyte levels tha 2. Be free of body compartment, nerve 2. Be free of
Restless may compromise internal complications conduction, and muscle complications resulting
Slow movement health. imbalance resulting from contraction. from electrolyte
Lack of energy electrolyte imbalance. Goal met.
imbalance. 2. Discuss preventable 2. Provide opportunity for
Source: electrolyte 3. Identify individual causes of condition client to prevent 3. Identify individual
Wellness/Strengths Doenges, M. et. Al., imbalance risks and engage in such as nutritional recurrence. Also, dietary risks and engage in
Good compliance to (2010). Nurse’s participate choices and the control is more palatable participate behaviors or
medication Pocket Guide: behaviors or proper use of than oral replacement lifestyle changes to
Cooperative behavior Diagnoses, lifestyle changes to laxatives. medications. prevent or reduce
of the patient Interventions and prevent or reduce frequency of electrolyte
th
Strong family support. Rationales. (12 frequency of 3. Encourage intake of 3. Potassium may be imbalances. Goal met.
Compliance to diet. ed.). Philadelphia, electrolyte foods and fluids replaced and level
F.A. Davis imbalances. high in potassium maintained through the
Company. pp 320 such as bananas, diet when the client is
Doenges, et al. Nurses oranges, dried allowed oral food and Doenges, et al. Nurses
Pocket Guide. F.A fruits, red meat, fluids. Dietary Pocket Guide. F.A
Davis Company 2010. leafy vegetables, replacement of 40- Davis Company 2010.
P. 312-313 peas, baked 60mEq/L/day is typically P. 313-319.
potatoes and sufficient if no abnormal
tomatoes. losses are occurring.
4. Maintain accurate 4. Guide for calculating
record of urinary, fluid and potassium
gastric, and wound replacement needs.
losses.
Collaborative:
1. Assist treatment of 1. Refer to listing of
underlying cause. predisposing factors
or contributing factors
to determine
treatment needs.
Note: Hypokalemia is
life threatening,
therefore early
detection is crucial.
2. Administer oral 2. May be required to
and/or IV correct deficiencies
potassium. when changes in
medication, therapy,
and/or dietary intake
are insufficient.
You might also like
- Mitsubishi Service Manual V41 ChassisDocument69 pagesMitsubishi Service Manual V41 ChassisJames Jackson100% (3)
- Mozart's Requiem Historical and Analytical Studies, Documents, Score by Christoph WolffDocument276 pagesMozart's Requiem Historical and Analytical Studies, Documents, Score by Christoph WolffMirko Zambelli100% (3)
- As Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ADocument2 pagesAs Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ATanya Alyssa Untalan AquinoNo ratings yet
- "Nagsusuka Ang Anak Ko.": Nursing Care ProcessDocument2 pages"Nagsusuka Ang Anak Ko.": Nursing Care Processgeorgia50% (2)
- WP Integrating Active Directory MLDocument14 pagesWP Integrating Active Directory MLFarid BouNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermKenneth PoncialNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentDocument10 pagesCase Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentChristine EmanNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN (Electrolyte Imbalance)Document2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN (Electrolyte Imbalance)audsNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea What To Look Out ForDocument15 pagesDiarrhea What To Look Out ForSiraf IldaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Saint Louis University School of Nursing Bonifacio Street, Baguio CityDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Saint Louis University School of Nursing Bonifacio Street, Baguio CitySoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- GI1026Document3 pagesGI10262pwtqbcynjNo ratings yet
- Risk NCP - PESCADERO 4CDocument1 pageRisk NCP - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- A Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementDocument6 pagesA Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementakoitsmeNo ratings yet
- Health Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareDocument8 pagesHealth Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareMyrshaida IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 NCPDocument5 pagesActivity 5 NCPAl-Mujib TanogNo ratings yet
- Rle Worksheet Nursing ProcessDocument6 pagesRle Worksheet Nursing ProcessMARVIE JOY BALUMA CABIOCNo ratings yet
- المستند (7) Document3 pagesالمستند (7) Mawadh AlsbhiNo ratings yet
- Casestudy 2 BurnsDocument16 pagesCasestudy 2 BurnsNOOR QASIMNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management of Gastrointestinal Stasis in Rabbits - Final - PublishDocument10 pagesGuidelines For The Management of Gastrointestinal Stasis in Rabbits - Final - PublishHouse HuntingNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Related To Altered Image, Inadequate Nutrient Intake, and Chronic Vomiting.Document2 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Related To Altered Image, Inadequate Nutrient Intake, and Chronic Vomiting.Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- GASTRITISDocument11 pagesGASTRITIStamannaNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Activity # 7 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance (WITH NCP)Document15 pagesActivity # 7 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance (WITH NCP)Louise OpinaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolye HTDocument7 pagesFluid and Electrolye HT421Karanbir KaurNo ratings yet
- Health Education - DiarrheaDocument7 pagesHealth Education - DiarrheaRashmi Devrani VyasNo ratings yet
- Risk For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesRisk For Deficient Fluid VolumeALEKS MONTECINO JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Nutri Lec Q3 Finals QuizletDocument3 pagesNutri Lec Q3 Finals QuizletArianne Courtney NacarNo ratings yet
- F and E ReviewerDocument9 pagesF and E Revieweralifah.macabagoNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Report. VVVVVVVDocument7 pagesPreliminary Report. VVVVVVVAnonymous 19KBW1yNo ratings yet
- NCPs (ABRIAN)Document23 pagesNCPs (ABRIAN)Rouie Björn ABrianNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CP - 054923Document5 pagesAntenatal CP - 054923shabnumshowkat58No ratings yet
- NCP of Patient With GastritisDocument4 pagesNCP of Patient With GastritisBer AnneNo ratings yet
- Decoding Stools - Guide To Infant Wellbeing - FinalDocument45 pagesDecoding Stools - Guide To Infant Wellbeing - FinalRaj WardhanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- JVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesJVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitvicenteturasNo ratings yet
- NRS456 - Malnutrition - Written Assignment-2Document12 pagesNRS456 - Malnutrition - Written Assignment-2najwaNo ratings yet
- U2 Nutritional ToxicologyDocument29 pagesU2 Nutritional Toxicologykuppala himachandanaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Stress Case StudyDocument10 pagesMetabolic Stress Case StudydakotaNo ratings yet
- Anti Hyperlipidemic Activities of Annona Muricata (Linn)Document8 pagesAnti Hyperlipidemic Activities of Annona Muricata (Linn)Danny. JayNo ratings yet
- Adams4e Tif Ch41Document19 pagesAdams4e Tif Ch41fbernis1480_11022046100% (1)
- (Solved) - Task 1 - Criticise The Effectiveness of Healthcare Provision In..Document5 pages(Solved) - Task 1 - Criticise The Effectiveness of Healthcare Provision In..sesaeedhaniyah.dNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermDocument2 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- NCP-CKD LabcoDocument5 pagesNCP-CKD Labcojay kusainNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (AGE)Document2 pagesDiarrhea (AGE)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiologic Basis/Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiologic Basis/Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- Name: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralDocument2 pagesName: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Session #9 SAS - Nutrition (Lecture)Document9 pagesSession #9 SAS - Nutrition (Lecture)Mariel Gwen RetorcaNo ratings yet
- Briend 1999Document2 pagesBriend 1999edith rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Prado NCPDocument4 pagesPrado NCPalleah pradoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanperezNo ratings yet
- MDH_Nursing Care Plan_RetiradoDocument3 pagesMDH_Nursing Care Plan_Retiradosretirado02No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: IndependentgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CP - 064226Document6 pagesAntenatal CP - 064226shabnumshowkat58No ratings yet
- MediUnite Journal Monthly Magasine Vital - July 2024Document22 pagesMediUnite Journal Monthly Magasine Vital - July 2024MediUnite JournalNo ratings yet
- KUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE ConstipationDocument2 pagesKUSAIN - NCP IN NCM 112 RLE Constipationjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Dr. Greer Parasites in Dogs HandoutDocument18 pagesDr. Greer Parasites in Dogs HandoutacslindaNo ratings yet
- Control of DiarrheaDocument2 pagesControl of DiarrheaNikhil Jose KNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea New Edited 2Document82 pagesDiarrhea New Edited 2bharath100% (1)
- Problem Scientific Basis Goals/ Objectives Criteria Nursing Intervention S Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesProblem Scientific Basis Goals/ Objectives Criteria Nursing Intervention S Rationale Evaluationmjoycerobin16No ratings yet
- Discharge Planning and NCP SDocument8 pagesDischarge Planning and NCP SRainier RamosNo ratings yet
- Diet & Supplementation: Keys To Optimal HealthDocument10 pagesDiet & Supplementation: Keys To Optimal HealthSteveNo ratings yet
- Dapus 30Document25 pagesDapus 30Titi SulistiowatiNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid Reset Diet: Reverse Hypothyroidism and Hashimoto's Symptoms with a Proven Iodine-Balancing PlanFrom EverandThe Thyroid Reset Diet: Reverse Hypothyroidism and Hashimoto's Symptoms with a Proven Iodine-Balancing PlanNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study For Case in SleDocument34 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Case in SlePaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument10 pagesHealth Teaching PlanPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain NCSDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain NCSPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies and Health Teaching PlanDocument28 pagesDrug Studies and Health Teaching PlansfkjalkhsafgNo ratings yet
- Jurisprudence 2 NotesDocument5 pagesJurisprudence 2 NotesPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- X. Pathophysiology Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesX. Pathophysiology Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- HemophiliaDocument4 pagesHemophiliaPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP Actual 1Document2 pagesNCP Actual 1Paolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PPG - Module 2 - 2ND Sem - 2ND Quarter - Grade 11 - Humss Bonifacio-Agoncillo - MR - Paombong - MRS CuencaDocument12 pagesPPG - Module 2 - 2ND Sem - 2ND Quarter - Grade 11 - Humss Bonifacio-Agoncillo - MR - Paombong - MRS CuencaArnold Paombong100% (1)
- Max Dupain ModernistDocument32 pagesMax Dupain ModernistFrancisco FernandezNo ratings yet
- Get (eBook PDF) Temperate and Subtropical Fruit Production 3rd Edition free all chaptersDocument51 pagesGet (eBook PDF) Temperate and Subtropical Fruit Production 3rd Edition free all chaptersthombabiyasi100% (2)
- Gen - Ranjeet Dilshan - 20201016 - 000356Document1 pageGen - Ranjeet Dilshan - 20201016 - 000356Shaashwat SinghNo ratings yet
- Allantoin Soothing Effect 2Document8 pagesAllantoin Soothing Effect 2Valentina CarreroNo ratings yet
- Final Ism PresentationDocument31 pagesFinal Ism Presentationapi-250164151No ratings yet
- Mcts Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesMcts Questions and AnswersKaveesha AnginthayaNo ratings yet
- 1503971634VIVO Basic Emergency Medical Technician (EMT B) 2 M PDFDocument1 page1503971634VIVO Basic Emergency Medical Technician (EMT B) 2 M PDFRiya SachanNo ratings yet
- 4281 - 03 Stiffened Shear WebDocument26 pages4281 - 03 Stiffened Shear WebAndrew GilbrideNo ratings yet
- Yashica FX-D Se PDFDocument46 pagesYashica FX-D Se PDFheraasku7194No ratings yet
- Black Arabs in Macadomian ArtDocument10 pagesBlack Arabs in Macadomian ArtWesley MuhammadNo ratings yet
- SMC Datalinks Ethernet OptionDocument9 pagesSMC Datalinks Ethernet Optionisraelalmaguer0% (1)
- Design of Concrete Bridges: Praveen NagarajanDocument18 pagesDesign of Concrete Bridges: Praveen NagarajanSSNo ratings yet
- A Manual For Writers of Research Papers Theses and Dissertations PDF DownloadDocument8 pagesA Manual For Writers of Research Papers Theses and Dissertations PDF DownloadWriteMyPaperForMeIn3HoursMilwaukeeNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Surface Anatomy and Surface Landmarks For Thoracic SurgeryDocument13 pages1.1 Surface Anatomy and Surface Landmarks For Thoracic SurgeryResidentes CirugíaNo ratings yet
- Audiovox Vme-9120tsDocument32 pagesAudiovox Vme-9120tsadrianNo ratings yet
- Effect of High Pressure On Cooking Losses and Functional Properties of Reduced-Fat and Reduced-Salt Pork Sausage EmulsionsDocument9 pagesEffect of High Pressure On Cooking Losses and Functional Properties of Reduced-Fat and Reduced-Salt Pork Sausage EmulsionstavibastiNo ratings yet
- Dua e YastasheerDocument3 pagesDua e YastasheerSyed Azhar Alam NaqviNo ratings yet
- PDF List of HR Persons Companies Ascending OrderDocument13 pagesPDF List of HR Persons Companies Ascending OrderRainwaterNo ratings yet
- MathPracticeTestsfortheACT - 2024 - SAMPLEDocument32 pagesMathPracticeTestsfortheACT - 2024 - SAMPLEVibrant PublishersNo ratings yet
- Treasury Management in BankingDocument5 pagesTreasury Management in Bankingbhupendra mehraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - SEPARATIONDocument41 pagesChapter 1 - SEPARATIONhafizulhakim02No ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Solar EnergyDocument81 pagesLecture 11 - Solar Energyglenlcy100% (1)
- SCIENCE 9 MODULE 2 WEEKS 3 4 For Offline ClassDocument48 pagesSCIENCE 9 MODULE 2 WEEKS 3 4 For Offline ClassPearl Ann Arbuis ParameNo ratings yet
- High AvailabilityDocument38 pagesHigh AvailabilityathulyabeenaraniNo ratings yet
- Brother Filtration, New Era PartnerDocument16 pagesBrother Filtration, New Era PartnerCarlos BarriosNo ratings yet
- (11-16) 3A-Ch.4-Quadrilaterals - CQDocument8 pages(11-16) 3A-Ch.4-Quadrilaterals - CQpatrickNo ratings yet