100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
197 viewsBombay Settlement
Bombay Settlement
Uploaded by
Satyam OjhaThe document summarizes the history of Bombay Settlement from 1668-1728 in three phases:
1) In 1668, the British East India Company was given control of Bombay island by the King of England at an annual rent of £10. This established the Company's territorial authority and empowered it to legislate and administer justice.
2) The first phase from 1668-1683 saw the introduction of a regular system of laws and division of Bombay into judicial districts. However, the legal system was imperfect with vague laws and reliance on native customs.
3) This was evident in the controversial 1720 trial of Rama Kamati, a wealthy merchant, who was convicted based
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Bombay Settlement
Bombay Settlement
Uploaded by
Satyam Ojha100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
197 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the history of Bombay Settlement from 1668-1728 in three phases:
1) In 1668, the British East India Company was given control of Bombay island by the King of England at an annual rent of £10. This established the Company's territorial authority and empowered it to legislate and administer justice.
2) The first phase from 1668-1683 saw the introduction of a regular system of laws and division of Bombay into judicial districts. However, the legal system was imperfect with vague laws and reliance on native customs.
3) This was evident in the controversial 1720 trial of Rama Kamati, a wealthy merchant, who was convicted based
Original Description:
Bombay settlement legal history
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document summarizes the history of Bombay Settlement from 1668-1728 in three phases:
1) In 1668, the British East India Company was given control of Bombay island by the King of England at an annual rent of £10. This established the Company's territorial authority and empowered it to legislate and administer justice.
2) The first phase from 1668-1683 saw the introduction of a regular system of laws and division of Bombay into judicial districts. However, the legal system was imperfect with vague laws and reliance on native customs.
3) This was evident in the controversial 1720 trial of Rama Kamati, a wealthy merchant, who was convicted based
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
197 views2 pagesBombay Settlement
Bombay Settlement
Uploaded by
Satyam OjhaThe document summarizes the history of Bombay Settlement from 1668-1728 in three phases:
1) In 1668, the British East India Company was given control of Bombay island by the King of England at an annual rent of £10. This established the Company's territorial authority and empowered it to legislate and administer justice.
2) The first phase from 1668-1683 saw the introduction of a regular system of laws and division of Bombay into judicial districts. However, the legal system was imperfect with vague laws and reliance on native customs.
3) This was evident in the controversial 1720 trial of Rama Kamati, a wealthy merchant, who was convicted based
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Bombay Settlement
1. Bombay got name- Deity Mumbadevi
a. Goddess was worshipped by Lord Ram- when asked for victory over Ravana- to get
Sita back- performed a yajna- to please the deity
2. Portuguese gave this island in dowry to English King- in turn gave this to Brit EIC @ annual
rent of £10
a. 1534:This island of Bombay was acquired by Portuguese from King of Gujarat, Sultan
Bahadur Shah
b. King of Portugal Alphonso VI gave this dowry to King of England Charles II- when
Charles married Alphonso’s sister, Catherine of Briganza
3. 1668:Became difficult for Charles II to exercise control- from England- so transferred
BOMBAY to EIC @ 10 bucks per annum rent
4. Position of Bombay changed with transfer- by new charter of 1668
5. Charter authorised company to legislate & exercise judicial authority in island of Bombay.
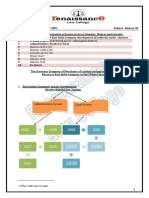
6. Phases of Bombay Settlement
a. 1668-83
b. 1684-90
c. 1718-26
7. In first phase- Charter of 1668- empowered company to frame laws & ordinances to admin
Bombay
a. Impose punishment- fine, imprisonment & death sentence
8. Company was given right to make money from Bombay
9. Initially-bombay was under control of Prez. And Council of Surat factory
10. Governor of Surat- ex officio gov. of Bombay
11. 1669: Sir George Oxendin- prez of Surat Factory- visited Bombay- est. government under
Deputy Governor and Council.
12. Provision mentioned in ’68 charter led to incorporation of two peeps,Thomas Papillion and
Moses – deputed to introduce laws for admin of justice categorised into 6 divisions:
a. Worship/religion
b. Common rights of man
c. Legal procedure
d. Registration of Sale & purchase of land & houses
e. Penal Offence
f. Military Discipline
13. As effect of Charter of 1668: transition of company- trading association to territorial
authority in Bombay was convened
14. 1670: Regular system of law in Bombay- introduced by Gerard Aunger.
15. Deputy Governor of Surat factory divided Bombay into 2 territorial division
a. Bombay, mazagaon & Gurgaon
b. Mahim, Parel, Sion, Worli
16. He improved judicial system gradually- was aware- it is not possible to supercede old pattern
of admin given by Portuguese law
17. In judicial system- separate court of judicature was est.- one for each division for these
areas- court had judges- decided civil cases- custom officers was prez for each court- held
once a week- decided civil disputes upto 200 xerophenes
18. Aunger was not satisfied with judges- wanted people who were well versed in law- request
was denied- asked to choose among company
19. Judicial Scheme of 1672: George Wilcox was appointed by Aunger- new judicial English law
was introduced-court’s jurisdiction in all cases- civil and criminal- civil was dealt once a
week- with help of judges who acted as Registrar- handled Probate, Admin & Registration
of Wills related to property.
20. Bombay was now categorised in 4 division
a. Bombay
b. Mahe
c. Mazagaon
d. Sion
21. For each division, justice of peace was appointed- was an Englishman
a. Main power was to apprehend the offender- to hold enquiry to examine witness-
to send record to court of judicature for the final trial of the case.
b. Court of Judicature was to sit once in a month- and it was to decide criminal case
with help of justices of peace
22. Highest Court of appeal – Court of Deputy Governor & Council of Bombay
a. Decided civil cases upto value less than 20 xerophenes
b. Purpose: to impart justice to the poor free of cost
23. Other Court that existed
a. Panchayat(village)- reorganised in 1672
i. Decided case of their own castes or they were brought to Court of
Judicature to discuss the case
24. This system of admin continued upto 1683 until Keigwin’s rebellion took place- after this it
ceased to function for one year
25. 1684: Island of Bombay came back to English Company.
RAMAKAMATI CASE
1. Laws applied were vague in nature, uncertain, evident from trial of Rama kamati
2. Wealthy Hindu merchant of Bombay- Chief Justice was Lawrence Parker
3. Charges inflicted upon him was that he communicated with dacoit Angeera through letter
4. Case was based on hearsay evidence of a dancer who told court- Angeera himself told her-
Rama Kamati had written letters to him
5. It’s believed that it was conspired by Governor Boone
6. Kamati was convicted- sentenced to imprisonment of life- confiscation of all properties- 8
years later in jail he died(1728)- Case started in 1720
You might also like
- Settlement at Surat-Madras-1ADocument11 pagesSettlement at Surat-Madras-1AGunjan Joshi0% (1)
- 8 Odyssey Park, Inc. vs. Court of AppealsDocument2 pages8 Odyssey Park, Inc. vs. Court of AppealsJemNo ratings yet
- EIC IN BOMBAY and CalcuttaDocument29 pagesEIC IN BOMBAY and CalcuttaGaureeka NathNo ratings yet
- Adm of Justice-BombayDocument4 pagesAdm of Justice-BombayRutuja PawarNo ratings yet
- Administration of Justice in BombayDocument5 pagesAdministration of Justice in Bombaytanishqrana553No ratings yet
- The Bombay SettlementDocument9 pagesThe Bombay SettlementMohandas PeriyasamyNo ratings yet
- Administration of Justice in BombayDocument13 pagesAdministration of Justice in BombayDinesh PKNo ratings yet
- Overview of Legal HistoryDocument7 pagesOverview of Legal HistoryNikhil ThakurNo ratings yet
- Bombay Judical System On 15th December, 2015Document27 pagesBombay Judical System On 15th December, 2015BhanuNo ratings yet
- Administration of Justice in Bombay and CalcuttaDocument6 pagesAdministration of Justice in Bombay and CalcuttaAjay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Legal History NotesDocument40 pagesLegal History NotesMadhav VyasNo ratings yet
- (PERIOD 1639-1726) Administration of Justice in BombayDocument7 pages(PERIOD 1639-1726) Administration of Justice in BombayAayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Administration of Justice (Madras, Bombay & Calcutta) 2024219154140Document45 pagesAdministration of Justice (Madras, Bombay & Calcutta) 2024219154140Aditya RathiNo ratings yet
- Administration of Justice in MadrasDocument11 pagesAdministration of Justice in MadrasVIDYARTHI VNo ratings yet
- Madras Bombay, CalcuttaDocument46 pagesMadras Bombay, CalcuttaSWETCHCHA MISKANo ratings yet
- Madras Mayors Court (1688)Document4 pagesMadras Mayors Court (1688)SOHAM DASNo ratings yet
- (PPT 2) Unit - I Settlement at Surat, MadrasDocument29 pages(PPT 2) Unit - I Settlement at Surat, Madrasgandla.varshaNo ratings yet
- Adm. of Justice in Madras Bombay and CalcuttaDocument65 pagesAdm. of Justice in Madras Bombay and CalcuttaArrowhead GamingNo ratings yet
- Justice in Presidencies - Company RajDocument13 pagesJustice in Presidencies - Company RajIshan LakhanNo ratings yet
- Administration of Justice in Bombay: Admiralty CourtDocument4 pagesAdministration of Justice in Bombay: Admiralty Courttanishqrana553No ratings yet
- Hoc 1Document16 pagesHoc 1Satyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- LegalhistoryDocument123 pagesLegalhistoryVidushi SatijaNo ratings yet
- Administration of Justice in MadrasDocument16 pagesAdministration of Justice in MadrasYasharth Tripathi80% (5)
- Adminisration of Madras, Surat, BombayDocument18 pagesAdminisration of Madras, Surat, BombayDevanshu Vashishtha100% (1)
- Main Philosophical Trends in Early 19 CenturyDocument59 pagesMain Philosophical Trends in Early 19 CenturyGunjan JoshiNo ratings yet
- Adminisration of Madras, Surat, BombayDocument18 pagesAdminisration of Madras, Surat, BombayAyushman DubeyNo ratings yet
- History Unit 1Document15 pagesHistory Unit 1amritagulati22No ratings yet
- Judicial System Before 1947Document9 pagesJudicial System Before 1947Arslan ButtarNo ratings yet
- Judicial System of East India CompanyDocument14 pagesJudicial System of East India CompanymahuanarayanNo ratings yet
- Legal and Constitutional HistoryDocument117 pagesLegal and Constitutional HistoryPurnima ShekharNo ratings yet
- Legal History III ALDocument72 pagesLegal History III ALAakashBaghNo ratings yet
- Legal & Constitutional History of IndiaDocument152 pagesLegal & Constitutional History of IndiasmssubhamNo ratings yet
- Settlement in Madras Before 1726Document6 pagesSettlement in Madras Before 1726Sneh GadaNo ratings yet
- Indian Legal and Constitutional History: Dr. Saurabh ChaturvediDocument45 pagesIndian Legal and Constitutional History: Dr. Saurabh ChaturvediHari Harul VullangiNo ratings yet
- As Mayor and Alderman Did Not Have Legal Knowledge The Provision Was Made For The Appointment of The Recorder of The CourtDocument1 pageAs Mayor and Alderman Did Not Have Legal Knowledge The Provision Was Made For The Appointment of The Recorder of The Courtudit rajNo ratings yet
- Legal HistoryDocument23 pagesLegal HistoryAryan DashNo ratings yet
- British Settlement BombayDocument13 pagesBritish Settlement BombayAnish KartikNo ratings yet
- British Settlement BombayDocument13 pagesBritish Settlement BombayAnish KartikNo ratings yet
- Indian Legal HistoryDocument31 pagesIndian Legal HistoryKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hoc NotesDocument23 pagesHoc Notesprisha.goel16838No ratings yet
- Development of Administration by The British in India (PERIOD 1639-1726)Document6 pagesDevelopment of Administration by The British in India (PERIOD 1639-1726)himanshu52143No ratings yet
- ILCH NotesDocument5 pagesILCH NotesJefferson PaulNo ratings yet
- Court of JudicatureDocument1 pageCourt of JudicatureoneNo ratings yet
- Split 20241005 1842Document42 pagesSplit 20241005 1842smyr.080004No ratings yet
- Legal History Unit 1 AdobeDocument75 pagesLegal History Unit 1 AdobeLochana HegdeNo ratings yet
- 2020-11-03 Legal History Lecture-7Document3 pages2020-11-03 Legal History Lecture-7nazmunnaharsupti01No ratings yet
- Political Changes in Madras (September 1746 To AUGUST 1749)Document5 pagesPolitical Changes in Madras (September 1746 To AUGUST 1749)ishusharma82699No ratings yet
- Judicial System in Madras Before 1726 - Law ColumnDocument6 pagesJudicial System in Madras Before 1726 - Law ColumnJoyNo ratings yet
- Legal History Notes by Neil AryanDocument75 pagesLegal History Notes by Neil Aryanwogec16512No ratings yet
- Objective Legal MCQDocument3 pagesObjective Legal MCQdukeishtarNo ratings yet
- Schematic Representation of Courts Under East India Company 1. Court Under Settlement at SuratDocument8 pagesSchematic Representation of Courts Under East India Company 1. Court Under Settlement at SuratGunjan JoshiNo ratings yet
- Judicial Development During British PeriodDocument7 pagesJudicial Development During British PeriodSrinibash DashNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument49 pagesQuestionsGitika TiwariNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court at Calcutta, Madras and BombayDocument34 pagesSupreme Court at Calcutta, Madras and BombayGunjan JoshiNo ratings yet
- HistoryfDocument70 pagesHistoryfpadapradeepdas862000No ratings yet
- One 2Document23 pagesOne 2Mohammad Ikhlas100% (1)
- Chapter - I: The Laws in Operation in IndiaDocument11 pagesChapter - I: The Laws in Operation in IndiaVatsal GalaNo ratings yet
- Madras: Admiralty Court in BombayDocument5 pagesMadras: Admiralty Court in Bombaygaurav singhNo ratings yet
- Philamlife v. Ansalado 234 SCRA 509 (1994)Document5 pagesPhilamlife v. Ansalado 234 SCRA 509 (1994)Joena GeNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property Code Case DigestDocument12 pagesIntellectual Property Code Case DigestJerica MercadoNo ratings yet
- People of The Philippines vs. Malmstedt, G.R. No. 91107, June 19, 1991.Document27 pagesPeople of The Philippines vs. Malmstedt, G.R. No. 91107, June 19, 1991.Joshua RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Dabuet Vs Roche 149 SCRA 386Document2 pagesDabuet Vs Roche 149 SCRA 386Denee Vem MatorresNo ratings yet
- SUPREME COURT REPORTS ANNOTATED VOLUME 546 Case1Document12 pagesSUPREME COURT REPORTS ANNOTATED VOLUME 546 Case1Marie Bernadette BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Guillermo Salvador Vs Patricia, Inc. (Jurisdiction Is Conferred by Law)Document15 pagesGuillermo Salvador Vs Patricia, Inc. (Jurisdiction Is Conferred by Law)Zyrene CabaldoNo ratings yet
- 2017 Spouses - Williams - v. - Zerda20220613 11 582xgcDocument6 pages2017 Spouses - Williams - v. - Zerda20220613 11 582xgcRubierosseNo ratings yet
- Carino vs. Insular GovernmentDocument3 pagesCarino vs. Insular GovernmentRyan Cruz IINo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 173120 & 173141Document40 pagesG.R. No. 173120 & 173141ChatNo ratings yet
- Land Law Historical Through YearsDocument15 pagesLand Law Historical Through YearsIbrahim SaidNo ratings yet
- SQE 1 SpecDocument28 pagesSQE 1 SpecKishan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Evidence Exam FinalDocument5 pagesEvidence Exam FinalJoshua PeraltaNo ratings yet
- DRT JudgementDocument25 pagesDRT JudgementNatasha Sharma100% (1)
- 2 (EDITED) Yap SR V SiaoDocument4 pages2 (EDITED) Yap SR V SiaoRioNo ratings yet
- 2020BALLB19 (Family Law)Document14 pages2020BALLB19 (Family Law)Hrithik ChormareNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT 4 Abdul Moaiz V State. FIR No. 15 2023. Offence 376iii 511 P.S Bhagat.. Allowed. 29.03.2023Document19 pagesChatGPT 4 Abdul Moaiz V State. FIR No. 15 2023. Offence 376iii 511 P.S Bhagat.. Allowed. 29.03.2023hamad shahNo ratings yet
- Flavia Agnes - Law, Ideology and Female SexualityDocument4 pagesFlavia Agnes - Law, Ideology and Female SexualityAkash Kumar SuryaNo ratings yet
- Rera Case LawsDocument3 pagesRera Case LawsAkshitNo ratings yet
- Rule On CICLDocument2 pagesRule On CICLTori PeigeNo ratings yet
- Tan V PeopleDocument8 pagesTan V PeopleGol LumNo ratings yet
- Equiv Alent Citation: AIR2021SC 1391, 2021 (2) ALD294, 2021 (3) ALT65, 2021 (2) ARBLR27 (SC), 132 (2021) C LT1, (2021) 5SC C 705, 2021 (3) SC J 120Document14 pagesEquiv Alent Citation: AIR2021SC 1391, 2021 (2) ALD294, 2021 (3) ALT65, 2021 (2) ARBLR27 (SC), 132 (2021) C LT1, (2021) 5SC C 705, 2021 (3) SC J 120Rohan D'cruzNo ratings yet
- In The High Court of The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Court of AppealDocument14 pagesIn The High Court of The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Court of AppealTPNo ratings yet
- Court Fees Rules 2018Document15 pagesCourt Fees Rules 2018Bongani SaidiNo ratings yet
- PLDT V City of Davao August 2001Document3 pagesPLDT V City of Davao August 2001owenNo ratings yet
- GR No 168661Document2 pagesGR No 168661GENEVIE TALANGNo ratings yet
- Sunga vs. National Labor Relations CommissionDocument8 pagesSunga vs. National Labor Relations CommissionEnzoNo ratings yet
- Ibm Vs NestleDocument2 pagesIbm Vs NestleCamille GrandeNo ratings yet
- FEBRUARY 2017 CASES-paleDocument4 pagesFEBRUARY 2017 CASES-paleScarlette CooperaNo ratings yet
- Jose Antonio Leviste v. The Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 189122, May 17, 2010Document2 pagesJose Antonio Leviste v. The Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 189122, May 17, 2010Greta Fe DumallayNo ratings yet