0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Difficulty Voiding: Symptom Flow Chart
Difficulty Voiding: Symptom Flow Chart
Uploaded by
Jeff ZhouThis symptom flow chart compares benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and acute renal failure, both of which can cause difficulty voiding. For BPH, key symptoms include dribbling at the end of urination, intermittency, and bladder distention. Diagnostics involve history, physical exam, uroflowmetry, transrectal ultrasound, and serum creatinine. Treatments include encouraging urination, Foley catheter, medications, and TURP. Nursing implications are teaching self-care and monitoring for complications like urinary tract infection and acute urinary retention. For acute renal failure, symptoms include edema, weight gain, hematuria, mental status changes, and flank pain. Diagnostics involve history
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
Difficulty Voiding: Symptom Flow Chart
Difficulty Voiding: Symptom Flow Chart
Uploaded by
Jeff Zhou0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
This symptom flow chart compares benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and acute renal failure, both of which can cause difficulty voiding. For BPH, key symptoms include dribbling at the end of urination, intermittency, and bladder distention. Diagnostics involve history, physical exam, uroflowmetry, transrectal ultrasound, and serum creatinine. Treatments include encouraging urination, Foley catheter, medications, and TURP. Nursing implications are teaching self-care and monitoring for complications like urinary tract infection and acute urinary retention. For acute renal failure, symptoms include edema, weight gain, hematuria, mental status changes, and flank pain. Diagnostics involve history
Original Title
BPH
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This symptom flow chart compares benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and acute renal failure, both of which can cause difficulty voiding. For BPH, key symptoms include dribbling at the end of urination, intermittency, and bladder distention. Diagnostics involve history, physical exam, uroflowmetry, transrectal ultrasound, and serum creatinine. Treatments include encouraging urination, Foley catheter, medications, and TURP. Nursing implications are teaching self-care and monitoring for complications like urinary tract infection and acute urinary retention. For acute renal failure, symptoms include edema, weight gain, hematuria, mental status changes, and flank pain. Diagnostics involve history
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Difficulty Voiding: Symptom Flow Chart
Difficulty Voiding: Symptom Flow Chart
Uploaded by
Jeff ZhouThis symptom flow chart compares benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and acute renal failure, both of which can cause difficulty voiding. For BPH, key symptoms include dribbling at the end of urination, intermittency, and bladder distention. Diagnostics involve history, physical exam, uroflowmetry, transrectal ultrasound, and serum creatinine. Treatments include encouraging urination, Foley catheter, medications, and TURP. Nursing implications are teaching self-care and monitoring for complications like urinary tract infection and acute urinary retention. For acute renal failure, symptoms include edema, weight gain, hematuria, mental status changes, and flank pain. Diagnostics involve history
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1/ 2
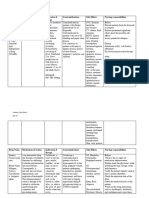
SYMPTOM FLOW CHART
Difficulty Voiding
Disease associated BPH Acute Renal Failure
with symptom
Symptom Cluster: dribbling at the end of fluid retention causing edema
minimum of 3 urination and weight gain
intermittency(stopping and hematuria
other associated
starting stream several times change in mental status
s/sx while voiding) flank pain
bladder distention
men
Diagnostics: History and physical History and physical
What will examination examination
Uroflowmetry Renal ultrasound
differentiate this
Transrectal ultrasound Renal scan
disease Serum creatinine Urinalysis
Lab tests Cystoscopy Serum creatinine and BUN level
Serum electrolytes
Treatment: Encourage pt to urinate Diuretic therapy: furosemide
Independent Fx when first having urge Antibiotic
Foley catheter dialysis
DependentFx
Meds: 5a-Reductase
Inhibitors(Proscar), a-
Adrenergic Receptor
Blockers
Herbal therapy: saw
palmetto
TURP
Nsg Implications: Teach pt to maintain fluid Teach pt to have a low-protein,
Patient/ family intake at a normal level to moderate-fat, high-
avoid dehydration or fluid carbohydrate diet
Education
overload Teach pt to prevent skin break
Potential Acute urinary retention down
complications UTI Take entire prescription as
directed
Hypokalemia
Dysrhythmias
Permanent kidney damage
You might also like
- Year 10 Biology - Plant Processes: Lesson 5 - Transpiration & TranslocationNo ratings yetYear 10 Biology - Plant Processes: Lesson 5 - Transpiration & Translocation4 pages
- Cebu Normal University College of Nursing: Drug StudyNo ratings yetCebu Normal University College of Nursing: Drug Study2 pages
- Diagnosa Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi TPG RRTNo ratings yetDiagnosa Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi TPG RRT56 pages
- Common Genitourinary Disease: Acute and Chronic Renal FailureNo ratings yetCommon Genitourinary Disease: Acute and Chronic Renal Failure15 pages
- Incontinentia Urine Kuliah Uniba 6-11-12. ANo ratings yetIncontinentia Urine Kuliah Uniba 6-11-12. A53 pages
- Post-Obstructive Diuresis: A Complication of Urinary RetentionNo ratings yetPost-Obstructive Diuresis: A Complication of Urinary Retention3 pages
- Lecture 15-16. BPH, Stricture Urethra, Varicocele, Spermatocele, Neonatal HidronefrosisNo ratings yetLecture 15-16. BPH, Stricture Urethra, Varicocele, Spermatocele, Neonatal Hidronefrosis64 pages
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Free Nursing LecturesNo ratings yetBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Free Nursing Lectures8 pages
- Signs & Symptoms: Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesNo ratings yetSigns & Symptoms: Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances3 pages
- Renal Insufficiency - Dialysis, Urinary Incontinence - CalculiNo ratings yetRenal Insufficiency - Dialysis, Urinary Incontinence - Calculi27 pages
- David's Drug Guide Tenth Edition Judith Hopfer April Hazard Vallerand pg.558-560No ratings yetDavid's Drug Guide Tenth Edition Judith Hopfer April Hazard Vallerand pg.558-56010 pages
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Module F Endocrine Roy Model-Protection, Rest, and ActivityNo ratings yetModule F Endocrine Roy Model-Protection, Rest, and Activity8 pages
- Module H Burns Roy Model-Alterations in Protection Required ReadingNo ratings yetModule H Burns Roy Model-Alterations in Protection Required Reading2 pages
- Module G Emergency Care Roy Model-Oxygenation-Perfusion Required Readings (See Syllabus For Detailed Readings)No ratings yetModule G Emergency Care Roy Model-Oxygenation-Perfusion Required Readings (See Syllabus For Detailed Readings)5 pages
- Module E Shock, MODS Roy Model-Oxygenation-Perfusion Required Readings (See Syllabus For Detailed Reading)No ratings yetModule E Shock, MODS Roy Model-Oxygenation-Perfusion Required Readings (See Syllabus For Detailed Reading)7 pages
- Module C Respiratory Roy Model-Oxygenation Required ReadingsNo ratings yetModule C Respiratory Roy Model-Oxygenation Required Readings6 pages
- Module A Introduction To Critical Care, Advanced Pain & Fluid N ElectrolytesNo ratings yetModule A Introduction To Critical Care, Advanced Pain & Fluid N Electrolytes2 pages
- Symptom Flow Chart Group #6: Sore ThroatNo ratings yetSymptom Flow Chart Group #6: Sore Throat2 pages
- Symptom Flow Chart (Difficulty Breathing)No ratings yetSymptom Flow Chart (Difficulty Breathing)2 pages
- VPN Interoperability Between SonicWALL TZ 170 SP SonicOS ENo ratings yetVPN Interoperability Between SonicWALL TZ 170 SP SonicOS E16 pages
- Kurdish-English Dictionary - (Michael L. Chyet)No ratings yetKurdish-English Dictionary - (Michael L. Chyet)894 pages
- PPP Reading Test 7 Parts BC Question PaperNo ratings yetPPP Reading Test 7 Parts BC Question Paper16 pages
- Canadian Tire Early Black Friday Week 3 1 Valid 21-11-24 - 28-11-24No ratings yetCanadian Tire Early Black Friday Week 3 1 Valid 21-11-24 - 28-11-243 pages
- PEOPLE v. MATIAS G.R. No. 186469, 13 June 2012100% (1)PEOPLE v. MATIAS G.R. No. 186469, 13 June 20121 page
- Smart Elevator Design With Scada System 1No ratings yetSmart Elevator Design With Scada System 18 pages
- Dynamic Physical Education For Secondary School Students Seventh Edition 1292020520 9781292020525 9781292033815 1292033819 - CompressNo ratings yetDynamic Physical Education For Secondary School Students Seventh Edition 1292020520 9781292020525 9781292033815 1292033819 - Compress493 pages
- SQL Server Replication - Full Overview and Step-By-Step ConfigurationNo ratings yetSQL Server Replication - Full Overview and Step-By-Step Configuration41 pages