Powder Metallurgy: Applications
Powder Metallurgy: Applications
Uploaded by
MhamedCopyright:
Available Formats
Powder Metallurgy: Applications
Powder Metallurgy: Applications
Uploaded by
MhamedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Powder Metallurgy: Applications
Powder Metallurgy: Applications
Uploaded by
MhamedCopyright:
Available Formats
Powder Metallurgy p.
460
Metal parts are made by compacting fine metal powder in suitable dies
and sintering that by heating without melting, the process is called
powder metallurgy.
Applications
Tiny ball of ball-point pens, abrasive wheels, gears, cams, bushing, 70%
automotive components and diode heat sinks (table 17.1)
The most commonly metals in P/M are (Iron, Copper, aluminum, Tin,
Nickel and Titanium).
Advantages
1. Complex parts made of high - strength and hard alloys.
2. Although most parts weight less than 2.5 Kg, they can weigh as
much as 50 Kg.
3. Advantages in technology now permit structural parts of air craft.
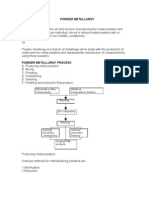
Production of Metal powders
The powder metallurgy process basically consists of the following
operation in sequence:
i. Powder Production
ii. Blending
iii. Compaction
iv. Sintering
v. Finishing Operation
i- Powder Production
Particle size range from 0.1 μm to 1000 μm metal sources are generally
bulk metals and alloys ores, salts and other compounds.
Particle size is usually measured by screening that, by passing the metal
powder through screens (sieves) of various mesh size.
ii- Blending Metal Powder
Blending (mixing) powder is the second step in powder metallurgy
processing; it is carried out for the following purpose:
1. Because the powder made by various processes have different sizes
and shapes.
2. Powder of different metals and other materials can be mixed in
order to import special physical and mechanical properties.
3. Lubricant can be mixed with the powder to import their flow
characteristics.
iii- Compaction of metal Powder
Compaction is the step in which the blended powder are pressed
(hydraulically or mechanically) into shapes in dies.
The purposes of compaction are:
1. To obtain the required shape.
2. To obtain the required density.
3. Particle to particle contact.
4. Make the parts sufficiently strong.
The density of green compact depends on:
A. Pressure applied.
B. Size distribution of the particle.
iv- Sintering
Sintering is the process whereby green compacts are heated in a
controlled atmosphere furnace to a temperature below the melting point.
Notes
The principal variables in sintering are temperature, time and
furnace atmosphere.
Sintering temperature are generally within 70% to 90% melting
point of the metal or alloys.
Sintering time range from minimum of about 10 minutes for iron
and copper to as 8 hours for tungsten and tantalum.
Example of Powder metallurgy
Production of tungsten Carbide for tools and dies
Tungsten carbide is an important tool and dies materials, mostly because
of its hardness, strength and wears resistance over a wide range of
temperature.
Below the procedure of producing Tungsten carbide material:
1. Powder of tungsten and carbon are blended (94% tungsten and 6%
carbon).
2. Heating the mixture approximately to 1500 ℃ (vacuumed
furnace).
3. Powder of tungsten carbide produce.
4. A binding agent (usually Cobalt) is added to tungsten carbide
powder with hexane.
5. Mixing the components (several hours or days).
6. Drying the mixture by cold compaction under pressure (200 Mpa).
7. The part is then sintered in a hydrogen atmosphere or vacuum
furnace at temperature (1350 ℃ to 1600℃ ).
Video Powder Metallurgy
You might also like
- Lecture - Notes - Materials Science and Engineering - 9282018 PDFDocument129 pagesLecture - Notes - Materials Science and Engineering - 9282018 PDFAlvin Deliro75% (4)
- Design of Superstructure - 25mDocument243 pagesDesign of Superstructure - 25mmrinal kayal0% (1)
- Powder MetallurgyDocument9 pagesPowder MetallurgysrpyrhlNo ratings yet
- MSM Experiment No 8Document9 pagesMSM Experiment No 8zakariyasheikh22No ratings yet
- Powder Technology (POWDER TECHNOL)Document8 pagesPowder Technology (POWDER TECHNOL)Dappa DavidNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument5 pagesPowder Metallurgyমুকসেতিন আল রাজী রিফাতNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument7 pagesPowder Metallurgykawsar_002100% (3)
- ميحرلا نمحرلا الله مسب Manufacturing Techniques 0703314: Powder MetallurgyDocument33 pagesميحرلا نمحرلا الله مسب Manufacturing Techniques 0703314: Powder MetallurgyAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument7 pagesPowder MetallurgyAnkur KumarNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument44 pagesPowder MetallurgyjrvinodNo ratings yet
- Powder Composite Related To Powder Metallurgy: Ordinance Factory Institute of LearningDocument72 pagesPowder Composite Related To Powder Metallurgy: Ordinance Factory Institute of LearningriyamondalNo ratings yet
- 202004160626023155prashant Engg Powder Metrollpgy 1Document8 pages202004160626023155prashant Engg Powder Metrollpgy 1Rabi Narayana SahuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Plastics PDFDocument17 pagesUNIT 4 Plastics PDFRITESH KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy PDFDocument9 pagesPowder Metallurgy PDFetamil87No ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument11 pagesPowder MetallurgyChandan PathakNo ratings yet
- محاضرات بودر دزعراقيDocument5 pagesمحاضرات بودر دزعراقيMohammed GhisheerNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument6 pagesPowder Metallurgyjayadevakodi100% (1)
- Powder Metallurgy PDF - Amrita UniversityDocument44 pagesPowder Metallurgy PDF - Amrita UniversityAkshay RajanNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy Process (E-2 Batch)Document13 pagesPowder Metallurgy Process (E-2 Batch)Manu DubeyNo ratings yet
- The Sintering Process of Iron Ore FinesDocument5 pagesThe Sintering Process of Iron Ore FinesRanggaa RamandanaNo ratings yet
- Msem Unit 3 FinalDocument14 pagesMsem Unit 3 FinalAditya BishtNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Manufacturing-Process Powder-Metallurgy NotesDocument14 pagesMechanical Engineering Manufacturing-Process Powder-Metallurgy NotesSiddheswar BiswalNo ratings yet
- Sinter Plant: Agglomerate FinesDocument7 pagesSinter Plant: Agglomerate FinesDinta PratiwiNo ratings yet
- InternshipDocument19 pagesInternshipRitwik TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Powder MetallurgyDocument30 pagesLecture 11 - Powder MetallurgySatyam JhaNo ratings yet
- The Sintering Process of Iron Ore FinesDocument6 pagesThe Sintering Process of Iron Ore FinesAbdullah Aljabir100% (1)
- Powder Metallurgy WikDocument11 pagesPowder Metallurgy WiksiswoutNo ratings yet
- Powder 1Document84 pagesPowder 1Nyanda MadiliNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument24 pagesPowder MetallurgyNitin Gupta100% (1)
- Powder MetallurgyDocument34 pagesPowder MetallurgySports GloballyNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy Is The Process of Blending Fine Powdered MaterialsDocument13 pagesPowder Metallurgy Is The Process of Blending Fine Powdered MaterialsLalit RanaNo ratings yet
- FoundryDocument10 pagesFoundryAnjana_EdathadanNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument21 pagesPowder MetallurgyHamed MeghNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument10 pagesPowder MetallurgynoelmbondeNo ratings yet
- E Sintering Process of Iron Ore FinesDocument6 pagesE Sintering Process of Iron Ore FinesJose Marval RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Design Considerations For Powder MetallurgyDocument4 pagesDesign Considerations For Powder Metallurgyrr1998773No ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument79 pagesPowder MetallurgyhavalNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument79 pagesPowder MetallurgyTrevor Menezes100% (1)
- Powder MetallurgyDocument18 pagesPowder MetallurgyBhupendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy: Adapted From Jenna Justice LectureDocument11 pagesPowder Metallurgy: Adapted From Jenna Justice LectureIhsanNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument3 pagesPowder Metallurgysrinivas100% (1)
- POWDERMETTRALUGYDocument9 pagesPOWDERMETTRALUGYNeel PatelNo ratings yet
- POWDER METALLURGYDocument4 pagesPOWDER METALLURGYrashidulislamra4090No ratings yet
- Iron Making MM 321Document16 pagesIron Making MM 321Sanjeev SahuNo ratings yet
- Powder Matullargy MSDocument36 pagesPowder Matullargy MSvinay12016070No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document59 pagesChapter 9amonmeizNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument16 pagesPowder MetallurgySwaraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument65 pagesPowder MetallurgyritikssvNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Aircraft Engineering MaterialsDocument75 pagesUnit-I Aircraft Engineering MaterialsSiddhesh AvhadNo ratings yet
- Sintering of Iron Ore PDFDocument32 pagesSintering of Iron Ore PDFDhiraj KadheNo ratings yet
- Alloys: An Alloy Is A Solid Mixture of Two or More Metals or Non-MetalsDocument9 pagesAlloys: An Alloy Is A Solid Mixture of Two or More Metals or Non-MetalsnuraliashahiraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials II - 2Document67 pagesEngineering Materials II - 2DANIEL WELDAYNo ratings yet
- Steel PlantDocument20 pagesSteel PlantRohith KancherlaNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument8 pagesPowder MetallurgyPritamNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument15 pagesPowder Metallurgypankajsinghbaghel100% (2)
- Advanced Metal Casting Technology (MAT515) Test One .Document18 pagesAdvanced Metal Casting Technology (MAT515) Test One .Bizuayehu TadesseNo ratings yet
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonNo ratings yet
- Thixoforming: Semi-solid Metal ProcessingFrom EverandThixoforming: Semi-solid Metal ProcessingGerhard HirtNo ratings yet
- Supercharging Supercharging: Is The Process of Increasing The Weight Density of The Charge Induced Into TheDocument4 pagesSupercharging Supercharging: Is The Process of Increasing The Weight Density of The Charge Induced Into TheMhamedNo ratings yet
- Example 5.3: Engine Oil at 20Document1 pageExample 5.3: Engine Oil at 20MhamedNo ratings yet
- University of Kirkuk College of EngineeringDocument7 pagesUniversity of Kirkuk College of EngineeringMhamedNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution From Internal Combustion Engines and It's ControlDocument4 pagesAir Pollution From Internal Combustion Engines and It's ControlMhamedNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution From Internal Combustion Engines and It's Control PollutantsDocument4 pagesAir Pollution From Internal Combustion Engines and It's Control PollutantsMhamedNo ratings yet
- Principles of ConvectionDocument6 pagesPrinciples of ConvectionMhamedNo ratings yet
- University of Kirkuk College of EngineeringDocument13 pagesUniversity of Kirkuk College of EngineeringMhamedNo ratings yet
- CH 8Document3 pagesCH 8MhamedNo ratings yet
- Engine Testing and Performance 1-Indicated Power (IP) : It's The Power Developed Inside The Cylinder and It Is ProportionalDocument5 pagesEngine Testing and Performance 1-Indicated Power (IP) : It's The Power Developed Inside The Cylinder and It Is ProportionalMhamedNo ratings yet
- Supercharging: Fig.7.1 (A) Naturally Aspirated Engine and (B) Supercharged EngineDocument4 pagesSupercharging: Fig.7.1 (A) Naturally Aspirated Engine and (B) Supercharged EngineMhamedNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document8 pagesCH 3MhamedNo ratings yet
- Types of SentencesDocument4 pagesTypes of SentencesMhamedNo ratings yet
- Normal Shock WaveDocument10 pagesNormal Shock WaveMhamedNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document9 pagesCH 10MhamedNo ratings yet
- Combustion in Spark-Ignition Engines 1-A Normal Combustion: in A Gaseous Fuel-Air Mixture Ignited by A Spark IsDocument8 pagesCombustion in Spark-Ignition Engines 1-A Normal Combustion: in A Gaseous Fuel-Air Mixture Ignited by A Spark IsMhamedNo ratings yet
- 5 6170476391998423952Document3 pages5 6170476391998423952MhamedNo ratings yet
- University of Kirkuk - College of Engineering Mechanical Department Third Stage - Morning StudyDocument4 pagesUniversity of Kirkuk - College of Engineering Mechanical Department Third Stage - Morning StudyMhamedNo ratings yet
- Engineering AnalysisDocument11 pagesEngineering AnalysisMhamedNo ratings yet
- 5 6170236483715203319Document6 pages5 6170236483715203319MhamedNo ratings yet
- MIG Welding: University of Kirkuk College of Engineering Mechanical Dept. - Third StageDocument5 pagesMIG Welding: University of Kirkuk College of Engineering Mechanical Dept. - Third StageMhamed100% (1)
- Industrial Safety: University of Kirkuk College of Engineering Mechanical Dept. - Third StageDocument3 pagesIndustrial Safety: University of Kirkuk College of Engineering Mechanical Dept. - Third StageMhamedNo ratings yet
- University of Kirkuk - College of Engineering Mechanical Department Third Stage - Morning StudyDocument4 pagesUniversity of Kirkuk - College of Engineering Mechanical Department Third Stage - Morning StudyMhamedNo ratings yet
- Sheet Naixo 1Document1 pageSheet Naixo 1MhamedNo ratings yet
- 2 5260552733861086944Document302 pages2 5260552733861086944Mhamed100% (1)
- External Electrical Boq R2Document15 pagesExternal Electrical Boq R2mudassir mNo ratings yet
- Bifunctional Nanoprecipitates StrengthenDocument26 pagesBifunctional Nanoprecipitates StrengthenmichaelNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification of Utp Cat 6E 4X2X23 Awg CableDocument1 pageTechnical Specification of Utp Cat 6E 4X2X23 Awg CableRasel AhmedNo ratings yet
- SMART-MASONRY-INSTALLATION-MANUAL EnglishDocument18 pagesSMART-MASONRY-INSTALLATION-MANUAL EnglishMichael Davies100% (2)
- GB Grade ASP-2030Document2 pagesGB Grade ASP-2030Nabeel AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Construction Materials & MethodsDocument6 pagesAssignment 2: Construction Materials & MethodsYeasfi ArafNo ratings yet
- Physics 2nd Year (CH 17)Document1 pagePhysics 2nd Year (CH 17)sanaaliakhter93No ratings yet
- Brosur Glazing N10Document1 pageBrosur Glazing N10RND KencanaNo ratings yet
- Current Refractory Technology and Practices in The Steel IndustryDocument25 pagesCurrent Refractory Technology and Practices in The Steel IndustrySebastian SolanoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Lateral Quasi-Static Load On Nonlinear Behaviour and Damage Indexes of Retrofitted RC Frame ModelDocument26 pagesEffect of Lateral Quasi-Static Load On Nonlinear Behaviour and Damage Indexes of Retrofitted RC Frame ModelVladekNo ratings yet
- Martina: Available Colors For This VersionDocument2 pagesMartina: Available Colors For This VersionUmeshNo ratings yet
- Flashguard Flyer 6 - 15 WEBDocument2 pagesFlashguard Flyer 6 - 15 WEBhenrik70No ratings yet
- Elastic Deformations Basic Knowledge - English PDFDocument1 pageElastic Deformations Basic Knowledge - English PDFMuhammad Naseem Ishaq /ME Lab EngineerNo ratings yet
- Marmox Wetroom 2021Document55 pagesMarmox Wetroom 2021Salma Tarek KamalNo ratings yet
- Mar 2021Document32 pagesMar 2021Lai Kok UeiNo ratings yet
- LG Medistep UN Studio PDFDocument3 pagesLG Medistep UN Studio PDFlendang endaNo ratings yet
- Masterglenium Sky 8788 - Asean-0717Document2 pagesMasterglenium Sky 8788 - Asean-0717Khin Sandi KoNo ratings yet
- DR SamsonDocument63 pagesDR Samsonbright consultingNo ratings yet
- Trabelsi 2019Document10 pagesTrabelsi 2019Հեղինե ՂազոյանNo ratings yet
- EPC Contractor Consultant Client: SIL/DMP/PQP CONC-01 Rev 0Document9 pagesEPC Contractor Consultant Client: SIL/DMP/PQP CONC-01 Rev 0Biplab dattaNo ratings yet
- Mrai SteelDocument495 pagesMrai SteelSharon SusmithaNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study On The Production of Eco Blocks and Paver in The Municipality of SurallahDocument13 pagesFeasibility Study On The Production of Eco Blocks and Paver in The Municipality of SurallahJeniffer NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Building Construciton Sample Exit Exam QuestionsDocument156 pagesBuilding Construciton Sample Exit Exam QuestionsascendancyyfirisaNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument16 pagesMetal CastingsathishNo ratings yet
- Rheological Properties of PolymersDocument23 pagesRheological Properties of PolymersAbdullah AlkalaliNo ratings yet
- 4PB1-PK5 - (W-X) SDL0.75LL5.4Document19 pages4PB1-PK5 - (W-X) SDL0.75LL5.4Phạm Tiến ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document3 pagesLesson 1Donna Shane ReyesNo ratings yet
- 2022 10 Xepox enDocument14 pages2022 10 Xepox enGNo ratings yet