0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
231 viewsFolk Literature
Folk Literature
Uploaded by
Lovie FuentesFolk literature is characterized by oral tradition, themes that convey insights into life, and purposes like explaining cultural perspectives or entertaining. Common elements include heroes and heroines who overcome obstacles, tricksters who get into trouble, personification of nonhuman subjects, and hyperbole or exaggerated language. Forms of folk literature are myths about gods and goddesses, legends based on real events, tall tales about central heroes' feats, folk tales reflecting cultural values, fables with animals and morals, and epics telling of heroes' quests.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Folk Literature
Folk Literature
Uploaded by
Lovie Fuentes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
231 views1 pageFolk literature is characterized by oral tradition, themes that convey insights into life, and purposes like explaining cultural perspectives or entertaining. Common elements include heroes and heroines who overcome obstacles, tricksters who get into trouble, personification of nonhuman subjects, and hyperbole or exaggerated language. Forms of folk literature are myths about gods and goddesses, legends based on real events, tall tales about central heroes' feats, folk tales reflecting cultural values, fables with animals and morals, and epics telling of heroes' quests.
Original Title
Folk Literature.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Folk literature is characterized by oral tradition, themes that convey insights into life, and purposes like explaining cultural perspectives or entertaining. Common elements include heroes and heroines who overcome obstacles, tricksters who get into trouble, personification of nonhuman subjects, and hyperbole or exaggerated language. Forms of folk literature are myths about gods and goddesses, legends based on real events, tall tales about central heroes' feats, folk tales reflecting cultural values, fables with animals and morals, and epics telling of heroes' quests.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
231 views1 pageFolk Literature
Folk Literature
Uploaded by
Lovie FuentesFolk literature is characterized by oral tradition, themes that convey insights into life, and purposes like explaining cultural perspectives or entertaining. Common elements include heroes and heroines who overcome obstacles, tricksters who get into trouble, personification of nonhuman subjects, and hyperbole or exaggerated language. Forms of folk literature are myths about gods and goddesses, legends based on real events, tall tales about central heroes' feats, folk tales reflecting cultural values, fables with animals and morals, and epics telling of heroes' quests.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
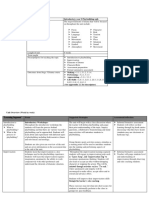
Folk Literature Characteristics of Folk Literature
1.Heroes and heroines – larger-than-life figures who
Elements of Folk Literature over-come obstacles or participate in exciting
1.The oral tradition – sharing of stories by word of adventures
mouth Often featured in….myths, legends, epics
2.The Importance of The Story Teller 2.Trickster – a clever character who can fool others but
– Stories in oral tradition were created thousands of often gets in trouble
years ago Often featured in….folk tales, fables
-No one knows the first storytellers 3.Personification – a type of figurative language in
-New storytellers add and change details which nonhuman subjects are given human qualities
-Cultural perspective – view of the world Often featured in….myth, fables
-Viewpoints are shaped by story teller’s background and 4.Hyperbole – a type of figurative language that uses
experiences extreme exaggeration
3.Theme – the central idea, message, or insight about Often featured in….tall tales, myths, epics
life that a story conveys 5.Dialect – language spoken by people in a particular
-universal themes – themes that are repeated across region or group
many cultures and over many time periods – express Often featured in….tall tales, folk tales
insights into life that many people understand
For example: the struggle of good against evil Additional Academic Vocabulary
-moral – a lesson about life that is stated directly, 1.Main Idea – what the text is mostly about
usually at end of story 2.Supporting Details – additional information that
4.Purpose of Folk Literature – the reason it was written explains, defines, proves, illustrates, clarifies and
For example: to explain or teach, to entertain describes more about a main idea. They can be facts,
examples, and statements.
Forms of Folk Literature 3.Textual Evidence – the details you get from your
1.Myths – tales that relate the action of gods, readings that support your answers and claims
goddesses, and the heroes who interact with them 4.Allusion – an implied or indirect reference in literature
For example: Greek mythology to a familiar person, place, or event
-mythology – collection of myths 5.Analysis – using a close reading of texts to examine
2.Legends – traditional stories based on real-life the relationships/connections among ideas, details,
events…as retold, fact often changes to fiction and/or examples
For example: Robin Hood, King Arthur, Knights of the 6.Inference – a judgment based on reasoning rather
round table than on a direct or explicit statement. An understanding
3.Tall tales – often focus on a central hero who based on “reading between the lines”.
performs impossible feats 7. Text Dependent Analysis – information based on
For example: Paul Bunyan, Pecos Bill, and Johnny specific evidence within a reading passage and being
Appleseed able to interpret the meaning
4.Folk Tales – may deal with real people or magical
characters, and they reflect the values & beliefs of the
culture
For example: Little Mermaid, Chinese folk tales about
respect, and Cinderella
5.Fables – brief stories or poems that often feature
animal characters who act and speak like humans, and
they usually end with a moral
For example: Aesop’s Fables
6.Epics – long narrative poems important to the history
of a nation or culture, and they tell of great hero going
on a dangerous journey, or quest
For example: Beowulf
You might also like
- Visual Rhetoric and The ResumeDocument11 pagesVisual Rhetoric and The Resumeapi-297089699No ratings yet
- Mythology and Folklore Sample SyllabusDocument19 pagesMythology and Folklore Sample SyllabusLarah BautistaNo ratings yet
- Verbal & Non-Verbal CommunicationDocument7 pagesVerbal & Non-Verbal CommunicationNoharaShinNo ratings yet
- Graphic OrganizersDocument20 pagesGraphic OrganizersdicasiveNo ratings yet
- Cony B.Lorica Beed The Process of Remedial Teaching Curriculum AdaptationDocument3 pagesCony B.Lorica Beed The Process of Remedial Teaching Curriculum AdaptationSweetcell LoricaNo ratings yet
- Bics Vs CalpDocument2 pagesBics Vs CalpAlassfar AbdelNo ratings yet
- Mother TongueDocument2 pagesMother Tongueapi-77420539No ratings yet
- The Writing Process PDFDocument23 pagesThe Writing Process PDFChristine GarciaNo ratings yet
- World Lit Report Arabian NightsDocument18 pagesWorld Lit Report Arabian NightsRoseAnnNooraNo ratings yet
- Language Shift and DeathDocument1 pageLanguage Shift and DeathHaeruddin RahmanNo ratings yet
- Using Pronouns EffectivelyDocument22 pagesUsing Pronouns EffectivelyStanley DulaliaNo ratings yet
- Gingoog City Colleges, Inc.: College/DepartmentDocument4 pagesGingoog City Colleges, Inc.: College/DepartmentJoevannie AceraNo ratings yet
- Drama Assessment 2Document25 pagesDrama Assessment 2api-357631525100% (1)
- Creation MythsDocument4 pagesCreation MythsKarissa YoungNo ratings yet
- Graphic OrganizersDocument27 pagesGraphic OrganizersCITCEducator0% (1)
- Speech and Theater Arts - Module 1Document6 pagesSpeech and Theater Arts - Module 1Trisha RiveraNo ratings yet
- Family Members PPT Fun Activities Games 41354Document24 pagesFamily Members PPT Fun Activities Games 41354Lesmes EduardoNo ratings yet
- Japanese LiteratureDocument3 pagesJapanese LiteratureRiza naagNo ratings yet
- 6 Suprasegmental Phonology Pp186 238Document27 pages6 Suprasegmental Phonology Pp186 238Bee BrightNo ratings yet
- Mythology and FolkloreDocument3 pagesMythology and FolkloreCristine AspirinNo ratings yet
- Lingg 1 - 70s LanguageDocument21 pagesLingg 1 - 70s LanguageJ Alexander Ines0% (1)
- Survey of English and American LiteratureDocument6 pagesSurvey of English and American Literaturecollegeofeducation161No ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Literature Why Literature LabDocument41 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Literature Why Literature LabNexty GamingNo ratings yet
- Approaches and Methods in EFLDocument45 pagesApproaches and Methods in EFLemo_transNo ratings yet
- Language and Literature AssessmentDocument6 pagesLanguage and Literature AssessmentPatricia Iris Villafuerte Razon100% (1)
- Structure of EnglishDocument6 pagesStructure of EnglishSandy Medyo GwapzNo ratings yet
- U1L1 - Definitions of Traditional LiteraciesDocument18 pagesU1L1 - Definitions of Traditional LiteraciesJerry Glenn Latorre CastilloNo ratings yet
- Language and Literature ArticleDocument2 pagesLanguage and Literature ArticleSare BaykalNo ratings yet
- Communicative CompetenceDocument14 pagesCommunicative CompetenceMira Joy Butiong100% (1)
- He Is More Than A Hero by Sappho: Activate Your Prior Knowledge. Share Your Thoughts On The Lines ProvidedDocument5 pagesHe Is More Than A Hero by Sappho: Activate Your Prior Knowledge. Share Your Thoughts On The Lines ProvidedUnnamed homosapien100% (1)
- Constructive and Destructive Feedback NotesDocument5 pagesConstructive and Destructive Feedback NotesSaisanthosh Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ogayon - Els 100 - Syllabus - ElsDocument8 pagesOgayon - Els 100 - Syllabus - ElspearlybethogayonNo ratings yet
- Origin and HistoryDocument31 pagesOrigin and HistoryJhazmine kale SerranoNo ratings yet
- Verbal and Non Verbal CommunicationDocument36 pagesVerbal and Non Verbal CommunicationMonica MarticioNo ratings yet
- Afro - Asian LiteratureDocument13 pagesAfro - Asian LiteratureAlona UrbiztondoNo ratings yet
- Social Dimension of EducationDocument39 pagesSocial Dimension of EducationEvelyn lopezNo ratings yet
- Translation and Editing of TextDocument7 pagesTranslation and Editing of Textjonard rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Assessment of Grammar Midterm CoverageDocument4 pagesTeaching and Assessment of Grammar Midterm CoverageRoselyn AlbisoNo ratings yet
- The Place of Literature in A Childs LifeDocument17 pagesThe Place of Literature in A Childs LifeJuvie Almazan UbilasNo ratings yet
- L3 Philippine Literature OverviewDocument16 pagesL3 Philippine Literature OverviewAlvin ObnialaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Teaching Prose 1Document12 pagesModule 4 Teaching Prose 1Liezl Coronado villaNo ratings yet
- PCED110 The Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipDocument6 pagesPCED110 The Teacher and The Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipPerly BarongNo ratings yet
- Language PolicyDocument25 pagesLanguage PolicyUmesh ThanaiNo ratings yet
- ReviewersDocument8 pagesReviewersAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Afro-Asian LiteratureDocument64 pagesAfro-Asian LiteratureShannara Ellise100% (2)
- Commmunicative Language Teaching (CLT) : I-IntroductionDocument6 pagesCommmunicative Language Teaching (CLT) : I-IntroductionHajer MrabetNo ratings yet
- The Speaking Process: Enged 317Document34 pagesThe Speaking Process: Enged 317Grezzly BearNo ratings yet
- English 13 Module 14-15Document8 pagesEnglish 13 Module 14-15Chemae Flora100% (1)
- Afro Asian LiteratureDocument9 pagesAfro Asian LiteratureJon Michael BoboyoNo ratings yet
- Audio-Lingual MethodDocument19 pagesAudio-Lingual MethodSoon Huong SiaNo ratings yet
- Bics and CalpDocument7 pagesBics and Calpapi-356630565No ratings yet
- (Subject/Course) : University of Caloocan CityDocument10 pages(Subject/Course) : University of Caloocan CityFudge FajardoNo ratings yet
- Traditional LiteratureDocument3 pagesTraditional LiteratureLorretta KongNo ratings yet
- ConjunctionDocument19 pagesConjunctionMuhammad Hafiz MansorNo ratings yet
- Elt 214 Week 4-5 Ulo A SimDocument9 pagesElt 214 Week 4-5 Ulo A SimELLEN JANE BARASOLIANo ratings yet
- Children and Adolescent LiteratureDocument5 pagesChildren and Adolescent Literaturejane lastNo ratings yet
- A Study Guide for Vishnu Sarma's "The Mice that Set the Elephants Free"From EverandA Study Guide for Vishnu Sarma's "The Mice that Set the Elephants Free"No ratings yet
- 2 Folk Literature PDFDocument16 pages2 Folk Literature PDFLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Phil Lit)Document6 pagesModule 3 (Phil Lit)Rowenalyn AndresNo ratings yet
- Definition of GenreDocument6 pagesDefinition of GenreJambres DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Monk's TaleDocument14 pagesMonk's TaleLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- TextualityDocument2 pagesTextualityLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument19 pagesThe Problem and Its BackgroundLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Books For KiddosDocument8 pagesBooks For KiddosLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Myth Title: The Story of Isis and Osiris: NAME: - Kenneth Drapite - Story Analysis TemplateDocument4 pagesMyth Title: The Story of Isis and Osiris: NAME: - Kenneth Drapite - Story Analysis TemplateLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Greek and Roman MythologyDocument106 pagesGreek and Roman MythologyLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I - Thesis TechnologyDocument6 pagesCHAPTER I - Thesis TechnologyLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Copy Reading and Headline WritinggDocument2 pagesCopy Reading and Headline WritinggLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Learning DifficultyDocument1 pageLearning DifficultyLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Copyreading and Headline WritingDocument1 pageCopyreading and Headline WritingLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Ethics: An Introduct IONDocument27 pagesEthics: An Introduct IONLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- FREEDOMDocument4 pagesFREEDOMLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- 2 Folk Literature PDFDocument16 pages2 Folk Literature PDFLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Learning ActivityDocument1 pageLearning ActivityLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Astronomy. This Era Began What Was Known As: Science May Be Defined As The System of Knowledge ofDocument2 pagesAstronomy. This Era Began What Was Known As: Science May Be Defined As The System of Knowledge ofLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- The Noun PowerPointDocument17 pagesThe Noun PowerPointLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document6 pagesGroup 2Lovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Prelim Lesson 2 Literary GenresDocument34 pagesPrelim Lesson 2 Literary GenresLovie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Formation and TransformationDocument1 pageFormation and TransformationLovie Fuentes100% (2)
- A 6a PlanificareDocument7 pagesA 6a PlanificareNicoleta AstefanoaieNo ratings yet
- Discurs OrganizationalDocument23 pagesDiscurs OrganizationalAndreea TudorNo ratings yet
- End of Term Test (Basic)Document5 pagesEnd of Term Test (Basic)phuongnhi08052009No ratings yet
- MPE720CntrllrSftwrApplGuide 1.0Document5 pagesMPE720CntrllrSftwrApplGuide 1.0ovNo ratings yet
- Powerview 3.0 Generic Tables and Fields Page 1 of 7: Field Name Field Description Data Type Relationship ClientsDocument7 pagesPowerview 3.0 Generic Tables and Fields Page 1 of 7: Field Name Field Description Data Type Relationship ClientsNéstor Raúl Pineda JaraNo ratings yet
- OrcaDocument13 pagesOrcaRoyce Dunhill Fortes Domondon50% (2)
- Runway RubricDocument2 pagesRunway Rubricapi-253897352No ratings yet
- Gallipoli Movie AnalysisDocument17 pagesGallipoli Movie Analysismamanda18No ratings yet
- Primary Readers: Black CatDocument20 pagesPrimary Readers: Black CatidoiaNo ratings yet
- Concessive ClauseDocument6 pagesConcessive ClauseCMarie Cachero PazNo ratings yet
- Y6 Unit 7 Listening & Speaking: Myths and LegendsDocument29 pagesY6 Unit 7 Listening & Speaking: Myths and Legendspoppy_90No ratings yet
- 剑桥新思维英语青少版 2级 语法与口语练习册答案Document9 pages剑桥新思维英语青少版 2级 语法与口语练习册答案shan wuNo ratings yet
- 1st-Summative-Test-in-Oral Communication SET BDocument2 pages1st-Summative-Test-in-Oral Communication SET Bfranciscoyen575No ratings yet
- College of Arts and Sciences: History of The English LanguageDocument11 pagesCollege of Arts and Sciences: History of The English LanguageKristine GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Rivera - TranspersonalDocument4 pagesRivera - TranspersonalJohn RiveraNo ratings yet
- Pgt-English LM Sir 12-07-2021Document49 pagesPgt-English LM Sir 12-07-2021gopalNo ratings yet
- Ingles Trabajo FinalDocument27 pagesIngles Trabajo FinalJoel AlbarracinNo ratings yet
- Admintjiss,+2 +Jurnal+Tebuireng+Hanif+FathoniDocument21 pagesAdmintjiss,+2 +Jurnal+Tebuireng+Hanif+FathoniatunkNo ratings yet
- Future Forms ExercisesDocument2 pagesFuture Forms Exerciseskastemania100% (3)
- Focus4 2E Grammar Quiz Unit1.2 GroupB 1kolDocument2 pagesFocus4 2E Grammar Quiz Unit1.2 GroupB 1koljustys05No ratings yet
- Buku Pedoman KKP FH - 2024Document41 pagesBuku Pedoman KKP FH - 2024suhendraaa208No ratings yet
- Anglican Church of South AmericaDocument7 pagesAnglican Church of South Americabrian2chrisNo ratings yet
- Summary of Noun ModifierDocument8 pagesSummary of Noun ModifierZeninda anggiNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSocial Studies Lesson Planapi-700564441No ratings yet
- LS M100 Easy Start GuideDocument14 pagesLS M100 Easy Start GuideKaan CanNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanAnimor-nocahc070824No ratings yet
- Javascript HTML Dom ElementsDocument26 pagesJavascript HTML Dom ElementsRajaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Mother-Tongue Based Instruction On Pupils Mathematical Word Problem Solving SkillsDocument20 pagesEffect of Mother-Tongue Based Instruction On Pupils Mathematical Word Problem Solving SkillsJemima DoyonganNo ratings yet
- Hsu Myat Htet (S-16860) CV FormDocument3 pagesHsu Myat Htet (S-16860) CV FormHsu Myat HtetNo ratings yet
- Book Title: Author NameDocument19 pagesBook Title: Author NameJuan R. Rodríguez SantanaNo ratings yet