Activity 1 - The Plant Kingdom (6th Grade)
Activity 1 - The Plant Kingdom (6th Grade)
Uploaded by
David JustinicoCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity 1 - The Plant Kingdom (6th Grade)
Activity 1 - The Plant Kingdom (6th Grade)
Uploaded by
David JustinicoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Activity 1 - The Plant Kingdom (6th Grade)
Activity 1 - The Plant Kingdom (6th Grade)
Uploaded by
David JustinicoCopyright:
Available Formats
GIMNASIO LA ARBOLEDA
PROCESO GESTIÓN ACADÉMICA Y DESARROLLO CURRICULAR Código: GADC-F-019
PROCEDIMIENTO SEGUIMIENTO ACADÉMICO Versión: 001
FORMATO PLANT KINGDOM
TERCER PERIODO PROFESOR: M.sc. David L. Justinico Castro Asignatura: Biology Grado 6°
The Plant Kingdom
Plants are members of the kingdom PLANTAE
Characteristics of most plants:
• Most plants make their own food through a process called
_______PHOTOSYNTHESIS_________________.
• Plants have a _________CUTICULE____________, meaning they have a
_____WAXY________ layer on their surface that protects them and keeps them from
_____DRYING_____________ out.
• They have _____EUKARYOTIC____ cells with rigid cell walls.
• They reproduce with ____SPORES___________ or with ____POLLEN ______ cells.
There are four main plant groups:
Bryophytes: MOSS, LIVERWORTS Pteridophytes: FERNS
Gymnosperms: COIFERS, PINES
Angiosperms: FLOWERING PLANTS
Overview of the Plant Kingdom
Botanists divide the plant kingdom into four groups based on several important features:
1. ________BRYOPHYTES________________________________
2. ____PTERIDOPHYTES_________________________
3. ____GIMNOSPERMS____________
4. ___ANGIOSPERMS_____________
Since 1994, a team of biologists has been studying the __DNA______ sequences of various plant
species. This project has provided strong evidence that the first plants evolved from
_____GREEN________ ______ALGAE_______ that lived in _____FRESH_______ water.
What do plants need to survive?
1. ____SUNLIGHT____________
2. _WATER___________ and ___MINERALS_________
3. ____CO2_____________________________
4. __MOVEMENT OF WATER AND NUTRIENTS _______________________________
Plant Life Cycle
Plants have life cycles that are characterized by alternation of
generations. The two generations are the haploid (N) gametophyte (or
gamete-producing plant), and the diploid (2N) sporophyte or spore-producing plant.
Gametes – the egg and sperm – are haploid cells that fuse together to form a new diploid individual. Spores are
reproductive cells that produce a new individual by mitosis. Some plants spend more time in the sporophyte
stage, others spend more time in the gametophyte stage.
Vascular Plants
Vascular plants are also known as tracheophytes.
What is a vascular plant?
Vascular plants have vascular tissues which distribute water and minerals through the
plant.
Plants with vascular tissue can grow taller because they have a mechanism for the
transport of water and nutrients to plant tissues.
Tall vascular plants can compete better for sunlight.
What is xylem and phloem?
The basic function of xylem (in blue below) is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves, but it
also transports nutrients.
Phloem (orange) transports products of photosynthesis to various parts of the plant.
Plants: Cohesion and Capillary Action
Plants have tiny tubes called _____XYLEM______ that help transport
_Water and nutrients___________ up the plant’s stem. Xylem transports water
and soluble mineral nutrients from __root____ to
various parts of the plant. It is responsible for replacing water
lost through transpiration and photosynthesis.
[Note: ___PHLOEM___________ is the tissue in vascular plants that
transports sugars
and other products made during photosynthesis to parts of the plant where it is
needed.]
Water moves through plants due to three main factors:
1) TRANSPIRATION: As water evaporates through the
stomata in the leaves (or any part of the plant exposed to
air), it creates a negative pressure (also called tension or
suction) in the leaves and tissues of the xylem. This is called
transpiration. (We learned this word when we studied the
water cycle!) The negative pressure exerts a pulling force on the water in the plant’s xylem
and draws the water upward.
2) COHESION: When water molecules stick to one another through Cohesion they fill the
column in the xylem and act as a huge single molecule of water.
3) CAPILLARY ACTION: This is the movement of a liquid across the surface of a
solid caused by adhesion between the two. When you a place a tube in water, water
automatically moves up the sides of the tube because of Adhesion. The
narrower the tube, the higher the water climbs on its own. In plants, adhesion forces
water up the columns of cells in the xylem and through fine tubes in the cell wall.
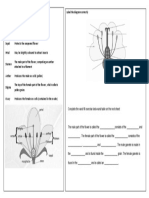
Here is another illustration of the process of the movement of water in a plant:
1. Water is passively transported into the
___roots________ and then into the ___xylem________.
2. The forces of ____cohesion_________ and
____adhesion_________ cause the water molecules to
form a column in the xylem.
3. Water moves from the ___xylem________ into the mesophyll
cells (in the leaves), ___evaporates___ from their surfaces and
leaves the plant by diffusion through the ___the stomata____
Plant Cladogram
Bryophytes Pteridophytes Gymnosperms Angiosperms
(mooses) (ferns)
flowers
seeds
Vascular tissues
roots
Bryophytes: moss, liverworts _are non-vascular plants that use
______water______ for fertilization. These are __low____-growing plants that can be
found in _____moist______, shaded areas. The most common bryophytes are
________mosses______. In bryophytes, the _____gametophyte_____________ is the dominant,
recognizable stage of the life cycle. This stage carries out most of the
plant’s photosynthesis.
Ferns & Lycophytes _are vascular plants that lack seeds, wood, fruit and
flowers. Ferns and their relatives have true ______roots______, ____leaves______, and
_____stems__________. Lychophytes are vascular plants similar to ferns but have
unique leaves called microphylls. Ferns have a life cycle in which the diploid
____sporophyte____________is the dominant phase.
Gymnosperms: conifers, cycads _____vascular__ plant. These are the most
ancient surviving ____seed_______ plant. These plants all reproduce with seeds that
are exposed – gymnosperm means “_____naked______ seed.”
Angiosperms: flowering plants Vascular plant with unique reproductive organs
known as _____flower______. Flowers attract animals which transport _____pollen_________
from flower to flower. This means of pollination is more efficient. Flowers contain
____ovaries_______, which surround and ___protects________ the seeds.
Angiosperm
means “_enclosed__________ seed.” After pollination, the ovary develops into a
___fruit________. These are members of the phylum Anthophyta.
You might also like
- 6th Grade-Post-Assessment Directions and Answer KeyDocument7 pages6th Grade-Post-Assessment Directions and Answer KeySULTAN SURGANo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Animal Adaptations Final VersionDocument78 pages4th Grade Animal Adaptations Final VersionTGNo ratings yet
- Natural Science 5 Pupil S Book PDFDocument108 pagesNatural Science 5 Pupil S Book PDFaliciaNo ratings yet
- L - 16.3 Review WorksheetDocument3 pagesL - 16.3 Review WorksheetHexagon LyricsNo ratings yet
- Plant WorksheetDocument21 pagesPlant WorksheetKyo Toey100% (2)
- Macmillan English 2 Unit 6 Worksheet Teaching Notes: 3 MarksDocument1 pageMacmillan English 2 Unit 6 Worksheet Teaching Notes: 3 MarksBidesh DeyNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and Function: Interpreting DiagramsDocument4 pagesPlant Structure and Function: Interpreting DiagramsWayne CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Worksheet 9.1Document2 pagesEcosystem Worksheet 9.1puchiti1234No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Adaptaion in PlantsDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Adaptaion in PlantsRama NathanNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Final Revision (Answers) )Document6 pagesYear 5 Final Revision (Answers) )M7G Royal100% (1)
- Unit 5 WorksheetsDocument4 pagesUnit 5 WorksheetsenkarniNo ratings yet
- Science PH Grade 3Document3 pagesScience PH Grade 3Nemsi Prisda TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Pre - IGCSE (0.13) - Biology - Term TestDocument11 pagesPre - IGCSE (0.13) - Biology - Term TestKaung Khant ZawNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures: Gen. ScienceDocument31 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures: Gen. ScienceMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Forms: Name: - DateDocument2 pagesWater and Its Forms: Name: - DateNutrionist Preet PatelNo ratings yet
- The Amazing Amazon Reading ComprehensionDocument4 pagesThe Amazing Amazon Reading ComprehensionIrina BodeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-Solid Liquid and GasesDocument4 pagesWorksheet-Solid Liquid and Gasesrachna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Food Pyramid Activity 1Document4 pagesFood Pyramid Activity 1El mishiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of FlowerDocument1 pageStructure and Function of Flowersuma devi100% (1)
- Name: Air, Water and Weather Subject:Science Grade & Section: Practice Work DateDocument2 pagesName: Air, Water and Weather Subject:Science Grade & Section: Practice Work DateSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- 5 Test A: Waste Recycle Plant SaveDocument4 pages5 Test A: Waste Recycle Plant SavePaula Loureiro FagulhaNo ratings yet
- Hassan Nouns PracticeDocument5 pagesHassan Nouns PracticeIsaac EscobedoNo ratings yet
- Class 4 SSTDocument2 pagesClass 4 SSTfgh ijkNo ratings yet
- STD IV Science Ws1 Adaptations in Plants 2018Document2 pagesSTD IV Science Ws1 Adaptations in Plants 2018smileNo ratings yet
- °C 9. Heating of ButterDocument1 page°C 9. Heating of ButterShiela AcevedaNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Science TestDocument2 pagesGrade 4 Science Testnakeshia.stapletonNo ratings yet
- 4-3 ReadyDocument5 pages4-3 Readyisabella gonzalez0% (1)
- Living Vs Non Living Things Worksheet GGDocument1 pageLiving Vs Non Living Things Worksheet GGUzie MidinNo ratings yet
- Diet Worksheet 1Document4 pagesDiet Worksheet 1L NarineNo ratings yet
- Anagram Sheet Fun DayDocument2 pagesAnagram Sheet Fun DayMarzenaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument18 pagesClassification of Living Thingsbeatrizgi100% (1)
- Descriptive WritingDocument4 pagesDescriptive WritingKarleen DouglasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Anaerobic Respiration ks3Document2 pagesWorksheet Anaerobic Respiration ks3Aigerim ImanayevaNo ratings yet
- Class 5 EVS Chapter 13 Amazing EnergyDocument5 pagesClass 5 EVS Chapter 13 Amazing EnergyragharikaNo ratings yet
- C8 CH2 WoeksheetDocument2 pagesC8 CH2 WoeksheetSheena RizviNo ratings yet
- Adaptations of Plants and Animals LessonDocument40 pagesAdaptations of Plants and Animals LessonBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Food Worksheet SolutionsDocument3 pagesFood Worksheet SolutionsPNG networksNo ratings yet
- Science 5 ST 1Document3 pagesScience 5 ST 1Nila Mae CalpoNo ratings yet
- Food Factory of Plants CDocument3 pagesFood Factory of Plants CNachammai SNo ratings yet
- GR - 4 - Science Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesGR - 4 - Science Revision WorksheetRaihana ReemNo ratings yet
- Human Body System WorksheetDocument2 pagesHuman Body System WorksheetRPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Vocabulary - Physical AppearanceDocument15 pagesUnit 1 - Vocabulary - Physical AppearanceValeska NatNo ratings yet
- Living Things - Unit Test 1Document7 pagesLiving Things - Unit Test 1Rhonda BladesNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 4 Science Food For PlantsDocument1 pageCBSE Class 4 Science Food For PlantsSuvashreePradhanNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Solid, Liquid, Gas, and Plasma. Solids LiquidsDocument6 pagesStates of Matter Solid, Liquid, Gas, and Plasma. Solids LiquidsWaleedSubhanNo ratings yet
- Mammal Fish Bird Insect Reptile AmphibianDocument1 pageMammal Fish Bird Insect Reptile AmphibianJamie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- 7 Life Processes Unit 1Document22 pages7 Life Processes Unit 1Prasad Swaminathan100% (1)
- Study Guide Fronts KeyDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Fronts Keyapi-262318021100% (1)
- Grade3 Worksheet (Answer) SOME PROPERTIES of WATER - PDF - Ic43211Document2 pagesGrade3 Worksheet (Answer) SOME PROPERTIES of WATER - PDF - Ic43211Vikas MahurkarNo ratings yet
- Science Test - 1 QuarterDocument3 pagesScience Test - 1 QuarterCeeKay0% (1)
- UNIT 1 NATURAL SCIENCE 6th GRADE, TEACHER PILAR CARRASCO PDFDocument6 pagesUNIT 1 NATURAL SCIENCE 6th GRADE, TEACHER PILAR CARRASCO PDFVicenteAguilarSanchezNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 4 Science Worksheet - RevisionDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 4 Science Worksheet - RevisionAnishka Gupta100% (1)
- Grade 07 Science 2nd Term Test Paper 2019 English Medium - North Western ProvinceDocument8 pagesGrade 07 Science 2nd Term Test Paper 2019 English Medium - North Western ProvinceRithaj HarunNo ratings yet
- Montessori Gading Permata School Science Worksheet Name: - Level: - TOPIC: Life Cycle of Animals A. Maggot Wriggler Tadpole Caterpillar NymphDocument2 pagesMontessori Gading Permata School Science Worksheet Name: - Level: - TOPIC: Life Cycle of Animals A. Maggot Wriggler Tadpole Caterpillar NymphCamille HugoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - 8ae AbsorptionDocument12 pagesLesson 5 - 8ae AbsorptionarnavprajeetNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Final WorksheetDocument4 pagesStates of Matter Final Worksheetrubina khatriNo ratings yet
- Compound AdjectiveDocument5 pagesCompound AdjectiveSari SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Plant Worksheet A. Vascular Plant B. Nonvascular Plant C. Xylem D. Phloem E. Photosynthesis F. Spores G. Dicot H. Monocot I. Embryo J. SeedsDocument1 pagePlant Worksheet A. Vascular Plant B. Nonvascular Plant C. Xylem D. Phloem E. Photosynthesis F. Spores G. Dicot H. Monocot I. Embryo J. Seedsstephanie hufanaNo ratings yet
- Acids and AlkaliDocument20 pagesAcids and Alkalirafay.6942cNo ratings yet
- '12 3Q Poqewkl ' Plant Tissue Dermal Tissue Vascular TissueDocument4 pages'12 3Q Poqewkl ' Plant Tissue Dermal Tissue Vascular TissueWILMA MUNOZNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Unit 1: Mansi Damani BNCPDocument73 pagesMicrobiology Unit 1: Mansi Damani BNCPSiddhant BanwatNo ratings yet
- Perigastric Organ" A Replacement Name For The "Hepatopancreas" of DecapodaDocument3 pagesPerigastric Organ" A Replacement Name For The "Hepatopancreas" of DecapodaHafez A MabroukNo ratings yet
- L2 - Neuroanatomy Lecture BootcampDocument52 pagesL2 - Neuroanatomy Lecture Bootcampdedhomosapien2No ratings yet
- Biology 1-3 Class 10Document3 pagesBiology 1-3 Class 10Binode SarkarNo ratings yet
- Concept 3 Notes - Endocrine System For StudentsDocument14 pagesConcept 3 Notes - Endocrine System For StudentsKaranNo ratings yet
- S4 - Ojo FisiologiaDocument6 pagesS4 - Ojo FisiologiaLUIS FERNANDO MEZA GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Uncaria Tomentosa Reduces Osteoclastic Bone Loss in Vivo: PhytomedicineDocument9 pagesUncaria Tomentosa Reduces Osteoclastic Bone Loss in Vivo: PhytomedicineGallardo JahseNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWDocument35 pagesPlant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Patogenesis Infeksi Bakteri, Infeksi Lokal, Dan SepsisDocument52 pagesPatogenesis Infeksi Bakteri, Infeksi Lokal, Dan SepsisNia AnestyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review Clinical Immunology and SerologyDocument68 pagesChapter Review Clinical Immunology and Serologyterah debuyanNo ratings yet
- Medical Physiology: Integration Using Clinical Cases: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument14 pagesMedical Physiology: Integration Using Clinical Cases: Multiple Choice QuestionswanderagroNo ratings yet
- Cellu Coelenterata Cnldarla) : L e V C L - J o R I F e R ADocument9 pagesCellu Coelenterata Cnldarla) : L e V C L - J o R I F e R AThe Dream HackerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Muscular SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology: The Muscular SystemEliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Korotkoff SoundsDocument25 pagesKorotkoff SoundsaftaabkhankhichiNo ratings yet
- APC Free Journal List External-Embargo-List - ElsevierDocument47 pagesAPC Free Journal List External-Embargo-List - ElsevierSYED ALI HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Chapter 1 Revision Worksheet - 1Document3 pagesGrade 9 Chapter 1 Revision Worksheet - 1Abdullah AkmalNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument9 pagesCell CycleCrystal Joy RebelloNo ratings yet
- 73 DR Wendy Suzuki Boost Attention & Memory With ScienceBased Tools Huberman Lab Podcast 73Document38 pages73 DR Wendy Suzuki Boost Attention & Memory With ScienceBased Tools Huberman Lab Podcast 73Bartis Réka RáhelNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Facilitation Techniques: Miss Rojaramani Vasamshetty MPT Ii YrDocument24 pagesNeuromuscular Facilitation Techniques: Miss Rojaramani Vasamshetty MPT Ii YrdeepuphysioNo ratings yet
- Inhalational Anesthetics: Patigas, Requinta, ResuelloDocument88 pagesInhalational Anesthetics: Patigas, Requinta, Resuellosarguss140% (1)
- Learning Module For Science 9 First Quarter: Camarines Norte College IncDocument24 pagesLearning Module For Science 9 First Quarter: Camarines Norte College IncCrisanto VelascoNo ratings yet
- Imaging in ORLDocument46 pagesImaging in ORLKelvin ChanNo ratings yet
- ISC Class 12 Biology Practical SyllabusDocument3 pagesISC Class 12 Biology Practical SyllabusNAATU NAATUNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Thyroid Hormone MBBS 2024Document23 pagesPhysiology of Thyroid Hormone MBBS 2024gurungprajwal758No ratings yet
- GRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewDocument9 pagesGRADE-7 RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-NOTES-NewsabariqaNo ratings yet
- Birla Public School, Doha-Qatar: Class Xi-Holiday Homework-Biology Record CompletionDocument1 pageBirla Public School, Doha-Qatar: Class Xi-Holiday Homework-Biology Record CompletionRajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- Alvarez Duran Priscilla Jacqueline: ExercisesDocument1 pageAlvarez Duran Priscilla Jacqueline: ExercisesPRISCILLA JACQUELINE ALVAREZ DURANNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument22 pagesBotanyaccountcmts100% (3)
- Onion and Human Cheek CellDocument3 pagesOnion and Human Cheek CellAnjehyn Elle100% (1)
- Organ SystemDocument9 pagesOrgan SystemMaycee ʚĭɞNo ratings yet