Classroom Practice I: Amino Acids and Peptides Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Questions
Classroom Practice I: Amino Acids and Peptides Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Questions
Uploaded by
Valentina CretuCopyright:
Available Formats
Classroom Practice I: Amino Acids and Peptides Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Questions
Classroom Practice I: Amino Acids and Peptides Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Questions
Uploaded by
Valentina CretuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Classroom Practice I: Amino Acids and Peptides Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Questions
Classroom Practice I: Amino Acids and Peptides Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Questions
Uploaded by
Valentina CretuCopyright:
Available Formats
Classroom practice I 1
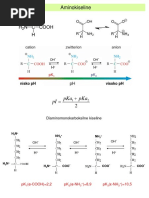
Classroom practice I: Amino acids and Dissociable group pKa
peptides α-COOH 2
R-COOH (Glu, Asp) 4
AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND α-NH 3
+
9
R-NH (Arg) +
12
PROTEINS QUESTIONS 2
9. a) Calculate the pI for the following oligopeptide:
Gly-Glu-Asp-Leu-Ala-Arg-Trp-Val.
Answer key provided at the end of the questionnaire b) Given 100 mL of a solution 1 mM of the above
peptide, at pH 4. How many milliliters of NaOH 0,1 M
1. a) Calculate the isoelectric point for glutamic acid. are required to adjust the pH of the solution to 5?
b) Indicate towards which pole this amino acid would Data:
migrate in an electric field at pH 3.22. Dissociable group pKa
c) What about at pH 8.2?. α-COOH 2
Data: pKa = 2.19; pKa = 9.67;. pKa = 4.25
1 2 R R-COOH (Glu, Asp) 4
α-NH 3
+
9
2. Indicate towards which pole the amino acid histidine R-NH (Arg)
2
+
12
would migrate in an electrophoresis performed at:
a) pH 5.0. 10. A protein has the following ionisable groups,
b) pH 7.6. besides the terminal α-amine y α-carboxile: 9 Asp or
Data: pKa = 1.82; pKa = 9.17; pKa = 6.0.
1 2 R
Glu, 3 His, 3 Lys and 3 Arg.
a) Calculate its pI.
3. Calculate the pI for the following amino acids: b) Towards which pole would the protein migrate in a
a) Gly. electrophoresis performed at pH 4?
b) Ser. c) Given 1 mol of the above protein, at pH 1, How
c) Gln. many equivalents of NaOH are required to titrate it?
d) Arg. Data:
Data: Dissociable group pKa
Amino acid pKa 1 pKa 2 pKa R
α-COOH 2
Glycine 2.34 9.60 --
Serine 2.21 9.15 -- α-NH 3
+
9
Glutamine 2.17 9.13 -- R-COOH (Asp, Glu) 4
Arginine 2.17 9.04 12.48 R-NH (His)
+
6
R-NH (Lys)
3
+
11
4. Given a mixture of the following amino acids: Glu, R-NH (Arg)
2
+
12
Ser and Arg,
a) Would it be possible to separate them by 11. Given a solution containing a mixture of the
electrophoresis? following peptides:
b) Which pH would be most suitable?. I) His-Asp-Glu-Glu-Leu
c) Towards which pole (+, -, o) would each amino acid II) Arg-His-Leu-Lys
migrate at that given pH? III) Gly-Ala-Leu-Trp
Data: Amino acid pKa pKa
1 2pKa R
a) Would it be possible to separate them by
Glutamic acid 2.19 9.67 4.25 electrophoresis?
Serine 2.21 9.15 b) Which pH would be most suitable?. Explain the
Arginine 2.17 9.04 12.48 reasoning behind your answer.
Data:
Dissociable group pKa
5. A mixture of Val, Arg, Glu and Ser is subjected to α-COOH 2
electrophoresis at pH 6.0. Predict towards which pole (+, α-NH 3
+
9
-, o) each amino acid would migrate. R-COOH (Asp, Glu) 4
Data: R-NH (His)+
6
Amino acid pKa pKa
1 2 pKa R
R-NH (Lys)3
+
11
Valine 2.32 9.62 -- R-NH (Arg)2
+
12
Arginine 2.17 9.04 12.48 12. Calculate the pI for the following oligopeptide:
Glutamic acid 2.19 9.67 4.25 Gly-Arg-Gly-His-Asp-Asp-Arg-Leu-Asp-Arg-Asp-
Serine 2.21 9,15 -- Asp-Ala.
Data:
6. If a mixture of hemoglobin (pI: 6.8) and Dissociable group pKa
chymotrysinogen (pI: 9.5) is subjected to electrophoresis, α-COOH 2
towards which pole (+, -, o) would every protein migrate R-COOH 4
at pH 6.8 and pH 8?. α-NH 3
+
9
R-NH +
6
7. Which pH would be most suitable to separate a R-NH 2
+
12
mixture of γ-globuline (pI = 6.6), myoglobin (pI = 7) and
hemoglobin (pI = 6.8) by electrophoresis? Explain the 13. a) Calculate the pI for the following oligopeptide:
reasoning behind your answer. Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Arg-Arg-Leu-Asp-Arg-Arg-Asp-
Ala.
8. Calculate the pI for the following oligopeptide: Asp- b) How many mL of a 0.2 M solution of HCl are
Arg-Arg-Gly-Arg-Asp-Arg. required to decrease the pH from 13 to 5, in a solution
Data: containing 10 millimoles of the above peptide?.
Degree in Veterinary Medicine. Biochemistry 1
Classroom practice I 2
Data:
Dissociable group pKa
α-COOH 2
R-COOH 4
α-NH 3
+
9
R-NH 2
+
12
14. a) Calculate the pI for the following oligopeptide:
Asp-Gly-Gly-Glu-Lys-Ile-His-Lys-Asp-Asp-Asp-Gln-
Asp
pKa α-COOH = 2; pKa R-COOH = 4; pKa R-His = 6;
pKa α-NH = 9; pKa R-Lys = 11
3
+
b) Which charge would the peptide have at pH 10?
15. a) Calculate the pI for the following oligopeptide:
Glu-Gly-Lys-Gln-Lys-Ile-His-Lys-Asp-Asn-Gly-Glu-
Ile-His-His
pKa α-COOH = 2; pKa R-COOH = 4; pKa R-His = 6;
pKa α-NH = 9; pKa R-NH = 11
3
+
3
+
b) How many mLs of a solution 0.5 M of NaOH is
required to increase the pH from 4 to 8, of a 200 mL of a
2 mM solution of the above peptide?
ANSWER KEY
1. a) pI=3.22; b) It will not move (no charge); c)
Towards the anode (- charged).
2. a) Towards the cathode; b) ) It will not move.
3. a) Gly: 5.97; b) Ser: 5.68; c) Gln: 5.65; d) Arg: 10.76.
4. a) Yes; b) pH 5.68; c) Glu: towards the anode; Ser: it
will not move; Arg: towards the cathode.
5. Val: it will not move; Arg: towards the cathode; Glu:
towards the anode; Ser: slight migration towards the
anode.
6. pH 6.8: Hb will not move and Chtr towards the
cathode; pH 8.0: Hb towards the anode and Chtr towards
the cathode.
7. pH 6.8.
8. pI = 11.52.
9. a) pI = 4; b) 1 ml of 0.1 M NaOH.
10. a) pI = 5.0; b) Towards the cathode; c) 20
equivalents.
11. a) Yes; b) pH 5.5.
12. a) pI = 4.6.
13. a) pI = 11.4; b) 300 mL.
14. a) pI = 4.0; b) Charge –5.
15. a) pI = 7.0; b) 3.6 mL.
Degree in Veterinary Medicine. Biochemistry 2
You might also like
- GMP GR: Reaction Chart For AlkanesDocument3 pagesGMP GR: Reaction Chart For AlkanesManoj DesaiNo ratings yet
- CPI - Aa and PeptidesDocument20 pagesCPI - Aa and PeptidesValentina CretuNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Lecture 1 and 2Document69 pagesBiomolecules Lecture 1 and 2Maryam DawoodNo ratings yet
- Handout 3a Peptide drawingDocument2 pagesHandout 3a Peptide drawingnafisa_buet00No ratings yet
- Aminoacid and Protein Structure (I)Document24 pagesAminoacid and Protein Structure (I)Game OverNo ratings yet
- Prebiotic synthesis of α-amino acids and orotate from α-ketoacids potentiates transition to extantDocument11 pagesPrebiotic synthesis of α-amino acids and orotate from α-ketoacids potentiates transition to extantjos.adi03No ratings yet
- Unit 1&2 Exercises Biochemistry 27.10.20Document56 pagesUnit 1&2 Exercises Biochemistry 27.10.20Nguyen Bao TranNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid and Peptide BondsDocument61 pagesAmino Acid and Peptide Bondsjessyemma081No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins: Dr. Clower Chem 4202Document55 pagesChapter 3: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins: Dr. Clower Chem 4202Vikas YadavNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument89 pagesProteinsResty De Guzman SoteloNo ratings yet
- Answer Assignment-01 Amino Acids (17-01-2024)Document3 pagesAnswer Assignment-01 Amino Acids (17-01-2024)parvkatiyarkviitNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids CNF HandoutDocument22 pagesAmino Acids CNF HandoutvhannzNo ratings yet
- 27 Amino Acids, ProteinsDocument73 pages27 Amino Acids, ProteinsRimisha NabeelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - The Amino Acids II - Acid-Base CharacteristicsDocument33 pagesLecture 9 - The Amino Acids II - Acid-Base CharacteristicsThomas JonesNo ratings yet
- Bchm2000 P1Document11 pagesBchm2000 P1Valine Cysteine MethionineNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 Solution Key 36 Points Total: PH Pka + Log RDocument3 pagesProblem Set 2 Solution Key 36 Points Total: PH Pka + Log RLani PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Summary and ReagentsDocument14 pagesSummary and Reagentsmchaubey181No ratings yet
- 6.2.2 Revision Guides Amino Acids AmidesDocument3 pages6.2.2 Revision Guides Amino Acids Amidessabarin.a.mahamudNo ratings yet
- (20672446 - Acta Chemica Iasi) Aldol Condensation Reactions Effectively Catalysed by Lewis AcidDocument10 pages(20672446 - Acta Chemica Iasi) Aldol Condensation Reactions Effectively Catalysed by Lewis AcidNurannisa NisaNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme ProteinDocument28 pagesMetabolisme ProteinFerlisan TabanciNo ratings yet
- Polyprotic Acid-Base EquilibriaDocument13 pagesPolyprotic Acid-Base EquilibriaNicos Rivera100% (1)
- Amino Acids & Its Buffer Function: DR Jaiprakash MohanrajDocument30 pagesAmino Acids & Its Buffer Function: DR Jaiprakash Mohanrajchoo zhen xingNo ratings yet
- Justine Chirichella - Lab 3 BiochemistryDocument7 pagesJustine Chirichella - Lab 3 Biochemistryapi-310022767No ratings yet
- Biokimia Asam Amino Dan Protein: Lucia Wiwid Wijayanti, M.SiDocument29 pagesBiokimia Asam Amino Dan Protein: Lucia Wiwid Wijayanti, M.SiindahsyetiaNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Stored EnergyDocument57 pagesHow Cells Release Stored EnergykylevNo ratings yet
- NYAW08-Unit Test 3 White)Document6 pagesNYAW08-Unit Test 3 White)Dr. Michael Lautman100% (1)
- L6 ElectronsDocument12 pagesL6 ElectronsCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Bchm2000 P1Document11 pagesBchm2000 P1cook88130No ratings yet
- Unit 7: Equilibria and Kinetics: Recommended Prior Knowledge: Context: OutlineDocument4 pagesUnit 7: Equilibria and Kinetics: Recommended Prior Knowledge: Context: OutlineHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio Oxidation Students CopyDocument17 pagesBio Oxidation Students Copyfrozenmail74No ratings yet
- Acidity of Organic MoleculesDocument1 pageAcidity of Organic MoleculesoreldysNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 13 THDocument20 pagesHydrocarbon 13 THRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Lec.4 Org IIDocument17 pagesLec.4 Org IItealempo80No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument36 pagesHydrocarbonUsha SherkhaneNo ratings yet
- SLG Chem 3 LG 5.4 Pka and The Isoelectric Point PiDocument5 pagesSLG Chem 3 LG 5.4 Pka and The Isoelectric Point PifranzachilleslindayagNo ratings yet
- Alkane: Preparation of Alkanes (6-Methods)Document17 pagesAlkane: Preparation of Alkanes (6-Methods)Uma KasyapNo ratings yet
- 10 01 Aminoacid 2012 ENDocument62 pages10 01 Aminoacid 2012 ENanthony.johNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument1 pageCellular RespirationDemonX01No ratings yet
- Macro-Molecule Analysis: Analysis of Amino Acids and CarbohydratesDocument50 pagesMacro-Molecule Analysis: Analysis of Amino Acids and CarbohydratesWu Ming-ShihNo ratings yet
- Notes For Amino AcidsDocument19 pagesNotes For Amino AcidspiriyalakanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 3A 3502 2005-06 Slide 3A-01: (See Eqn. 1.4 B)Document8 pagesLecture Notes 3A 3502 2005-06 Slide 3A-01: (See Eqn. 1.4 B)Neha MehraNo ratings yet
- Doc3Document16 pagesDoc3hadiimani1985No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08 Jan 2025Document16 pagesAdobe Scan 08 Jan 2025Timinesh SinghalNo ratings yet
- 556611269 Mind Map HydrocarbonsDocument3 pages556611269 Mind Map Hydrocarbonsmedookasha009No ratings yet
- Mind Map (Hydrocarbons)Document3 pagesMind Map (Hydrocarbons)Meenakshi Nair100% (1)
- Amino Acids and Peptide BondDocument61 pagesAmino Acids and Peptide Bondranger cleetusNo ratings yet
- Al Kane:: (A) DefinitionDocument17 pagesAl Kane:: (A) DefinitionsohamNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 6Document481 pagesBiochemistry 6baraahNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon (12th)Document22 pagesHydrocarbon (12th)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Problems - Acid Base EquilibriaDocument32 pagesProblems - Acid Base EquilibriaSulthoni AkmilNo ratings yet
- BIO100 Lecture 10Document17 pagesBIO100 Lecture 10Justus PfeifferNo ratings yet
- Diet and ExerciseDocument53 pagesDiet and ExerciseJessica SnowNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument24 pagesAminesRajdeep Singh RahiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Catabolism: N: Molecular Biochemistry IIDocument36 pagesAmino Acid Catabolism: N: Molecular Biochemistry IIbaderhistoNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument15 pagesResearch Articlekamransaeed668No ratings yet
- Chapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellDocument29 pagesChapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellSheila GarciaNo ratings yet
- 4 Aminokiseline. ProteiniDocument25 pages4 Aminokiseline. ProteiniКатарина БубањаNo ratings yet
- 1 Theory2Document16 pages1 Theory2Tushar RajNo ratings yet
- Incidence of Coxofemoral Joint Affections in Dogs - A Clinical Study of 575 PatientsDocument4 pagesIncidence of Coxofemoral Joint Affections in Dogs - A Clinical Study of 575 PatientsValentina CretuNo ratings yet
- Bandaging in Dogs and Cats: External Coaptation: Focal PointDocument8 pagesBandaging in Dogs and Cats: External Coaptation: Focal PointValentina CretuNo ratings yet
- Morchella. Crassipes The Irregular Pits andDocument6 pagesMorchella. Crassipes The Irregular Pits andValentina CretuNo ratings yet
- 1920 CPIV TransportDocument2 pages1920 CPIV TransportValentina CretuNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Laboratory 1º Veterinaria 18-19Document5 pagesBiochemistry - Laboratory 1º Veterinaria 18-19Valentina CretuNo ratings yet
- Classroom Practice III: Bioenergetics Bioenergetics ExercisesDocument4 pagesClassroom Practice III: Bioenergetics Bioenergetics ExercisesValentina CretuNo ratings yet
- CPII Enzymatic KineticsDocument13 pagesCPII Enzymatic KineticsValentina CretuNo ratings yet
- 9 - BICH 200-ProteinDocument21 pages9 - BICH 200-ProteinDR. ANUPAMA NAGARAJNo ratings yet
- Analisis ProteinDocument52 pagesAnalisis ProteinTabetaP.Rosemayanti100% (1)
- Essential Amino Acids Functions: Patricia Anne Nicole C. Mansat Bs Nursing BiochemDocument4 pagesEssential Amino Acids Functions: Patricia Anne Nicole C. Mansat Bs Nursing Biochembiology100% (2)
- Group 1 Peta 1 - DNA Fingerprinting PDFDocument9 pagesGroup 1 Peta 1 - DNA Fingerprinting PDFJohnrae mallaNo ratings yet
- Normal Reçete Ile Kontral Tabi ListeDocument4 pagesNormal Reçete Ile Kontral Tabi Listefurkan.aras000No ratings yet
- Metabolism of Essential and Non-Essential Amino AcidsDocument15 pagesMetabolism of Essential and Non-Essential Amino AcidsMrs SalimNo ratings yet
- Bull'S Eye Content Bull'S Eye Content: C H E M M I S T R YDocument5 pagesBull'S Eye Content Bull'S Eye Content: C H E M M I S T R YHitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Broiler and Breeder Nutrition. 2019 (JCALDAS)Document49 pagesBroiler and Breeder Nutrition. 2019 (JCALDAS)Paloma VivanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Pierce Amino Acid Standard H Using Vanquish FlexDocument1 pageAnalysis of Pierce Amino Acid Standard H Using Vanquish FlexAlexander Nieto VelaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids MCQ'sDocument4 pagesAmino Acids MCQ'sFari ZafarNo ratings yet
- Tabela BodyAction 06 - 2023Document32 pagesTabela BodyAction 06 - 2023pfvvsrhk2sNo ratings yet
- PROTEINS IntroductionDocument18 pagesPROTEINS IntroductionBrysin AENo ratings yet
- 3.#Amino#Acids# (Chapter#4) #: Proteins#And## Protein#Funclons#Document11 pages3.#Amino#Acids# (Chapter#4) #: Proteins#And## Protein#Funclons#Ferell GerryNo ratings yet
- Full Paper Gabriel MustățeaDocument7 pagesFull Paper Gabriel MustățealazersteveNo ratings yet
- Inventa RioDocument4 pagesInventa RioEsdras Amiud CarpioNo ratings yet
- ΔΤΦ 300413Document2,180 pagesΔΤΦ 300413farmakopoioiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid: Structure and ClassificationDocument7 pagesAmino Acid: Structure and Classificationsupremesiddharth0No ratings yet
- Amino Acids in VegetablesDocument12 pagesAmino Acids in Vegetablesdavid.fernando01No ratings yet
- SL & HL Questions On Proteins: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingDocument2 pagesSL & HL Questions On Proteins: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingOmar HijaziNo ratings yet
- J Institute Brewing - July August 1964 - Jones - Absorption of Amino Acids From Wort by YeastsDocument9 pagesJ Institute Brewing - July August 1964 - Jones - Absorption of Amino Acids From Wort by YeastsJean-Benoît OffieNo ratings yet
- Solutions Problems2Document4 pagesSolutions Problems2EfraínNo ratings yet
- Uncommon Amino Acid: Aileen C. Olantigue BSN - 1B 1:00pm - 7pmDocument3 pagesUncommon Amino Acid: Aileen C. Olantigue BSN - 1B 1:00pm - 7pmAshley Niño Jun AtuelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Amino Acids & Protein ChemistryDocument12 pagesLecture 2 - Amino Acids & Protein ChemistryAkram Khaled Ragab BayoumyNo ratings yet
- PricelistDocument12 pagesPricelisthananmasood7777No ratings yet
- BCHM 201 Amino Acid-1-1Document31 pagesBCHM 201 Amino Acid-1-1jemimahyusuf93No ratings yet
- BCAA-Do U Need Them - MNWDocument1 pageBCAA-Do U Need Them - MNWSita Ram ModiNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Amino Acid BiosynthesisDocument7 pagesMetabolism: Amino Acid BiosynthesisTamara Souza RossiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Interpretive GuideDocument6 pagesAmino Acids Interpretive GuideMetametrix100% (5)
- 7N Katalog ENGDocument38 pages7N Katalog ENGRafik BenyahiaNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument7 pagesBiochemistryAbdelwahab AliNo ratings yet