0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 viewsHACVD Patho
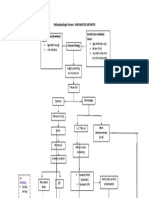
The document summarizes the pathophysiology of heart and cardiovascular disease. It describes how LDL and triglycerides damage endothelial cells, leading platelets and monocytes to adhere and abnormal proliferation of smooth muscles. This causes inflammation and narrowing of blood vessels from atherosclerotic plaque formation. Over time, plaque rupture can decrease blood flow and increase vascular resistance, raising afterload and preload on the heart. As a compensatory mechanism, the heart undergoes hypertrophy but eventually fails in oxygen compensation, leading to tissue ischemia, injury, and infarction which decreases cardiac output and causes systemic hypoxia and multiorgan failure and death.
Uploaded by
Angel FiloteoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 viewsHACVD Patho
The document summarizes the pathophysiology of heart and cardiovascular disease. It describes how LDL and triglycerides damage endothelial cells, leading platelets and monocytes to adhere and abnormal proliferation of smooth muscles. This causes inflammation and narrowing of blood vessels from atherosclerotic plaque formation. Over time, plaque rupture can decrease blood flow and increase vascular resistance, raising afterload and preload on the heart. As a compensatory mechanism, the heart undergoes hypertrophy but eventually fails in oxygen compensation, leading to tissue ischemia, injury, and infarction which decreases cardiac output and causes systemic hypoxia and multiorgan failure and death.
Uploaded by
Angel FiloteoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 1
Pathophysiology HACVD LDL and Tryglycerides
Damage to intimal endothelial cells
Platelets and Monocytes adhere to injured site
Abnormal proliferation of smooth muscles and connective tissue
Inflammation of blood vessels
Migration of monocytes beneath the endothelium and become macrophage
Permeability of endothelium
Formation of Atherosclerotic plaque (CXR: Atherosclerosis of thoracic aorta)
Narrowing of the blood vessel lumen
Blood flow Plaque hemmorrhage/rupture Vascular resistance
Afterload
Preload
Compensatory Mechanism: Myocardial Hypertrophy
Cardiomegaly
Increased O2 demands
Failure of O2 compensation
Cardiac Tissue Ischema
Cardiac Tissue Injury
Cardiac tissue Infarction
Decreased functioning contractile tissue
Cardiac output
Perfusion/Hypoperfusion
Systemic Hypoxia
Multiorgan Failure
Death
You might also like
- Pathology - Lab: Pathology of The Blood VesselsNo ratings yetPathology - Lab: Pathology of The Blood Vessels5 pages
- CABAGNOT, Karl Jasper Atherosclerosis Case StudyNo ratings yetCABAGNOT, Karl Jasper Atherosclerosis Case Study2 pages
- Cardiovascular Pathology: (Modification of Dr. Veinot's Presentation)No ratings yetCardiovascular Pathology: (Modification of Dr. Veinot's Presentation)99 pages
- 1. concept of cardiovascular disease as non communicable disease.No ratings yet1. concept of cardiovascular disease as non communicable disease.53 pages
- Cagayan State University College of Medicine and Surgery SY: 2009-2010No ratings yetCagayan State University College of Medicine and Surgery SY: 2009-201041 pages
- Pathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsNo ratings yetPathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors3 pages
- Medical Nutrition Therapy in Cardiovascular DiseaseNo ratings yetMedical Nutrition Therapy in Cardiovascular Disease93 pages
- Pathophysiology of Pathophysiology of Ischemic Heart Ischemic Heart Disease DiseaseNo ratings yetPathophysiology of Pathophysiology of Ischemic Heart Ischemic Heart Disease Disease6 pages
- Congestive Heart Failure Secondary To Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyNo ratings yetCongestive Heart Failure Secondary To Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology5 pages
- Hypertension: Synthesis of The Disease For Coronary Artery Disease (Book-Based) b.1. Definition of The DiseaseNo ratings yetHypertension: Synthesis of The Disease For Coronary Artery Disease (Book-Based) b.1. Definition of The Disease9 pages
- Pathophysiology and Risk Factors of Coronary Artery DiseaseNo ratings yetPathophysiology and Risk Factors of Coronary Artery Disease55 pages
- The Biology of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseNo ratings yetThe Biology of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease62 pages
- Pathogenesis of Ischemic Heart Disease: Diploma ThesisNo ratings yetPathogenesis of Ischemic Heart Disease: Diploma Thesis24 pages
- Pathology of the cardiovascular system and typeNo ratings yetPathology of the cardiovascular system and type47 pages
- HNI 310 - Cardiovascular System BB 2015No ratings yetHNI 310 - Cardiovascular System BB 201559 pages
- Increased Serum Glucose Level (Hyperglycemia) 278.14 MG/DL (Normal: 70-100 MG/DL)No ratings yetIncreased Serum Glucose Level (Hyperglycemia) 278.14 MG/DL (Normal: 70-100 MG/DL)3 pages
- Key Issues Desired Outcome Independent Intervention Actual Outcome March 5, 2015No ratings yetKey Issues Desired Outcome Independent Intervention Actual Outcome March 5, 20154 pages
- Filoteo, Angel Hannah A. BSN 3B: Pathophysiologic Process - RHEUMATOID ARTHRITISNo ratings yetFiloteo, Angel Hannah A. BSN 3B: Pathophysiologic Process - RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS1 page
- Name: Filoteo, Angel Hannah A. Date: Sept. 7,2020No ratings yetName: Filoteo, Angel Hannah A. Date: Sept. 7,20203 pages
- Neurological Function: Mark Ebony SumalinogNo ratings yetNeurological Function: Mark Ebony Sumalinog51 pages
- Rest and Sleep: Week 4 Mr. Mark Ebony C. Sumalinog, RN MSN100% (1)Rest and Sleep: Week 4 Mr. Mark Ebony C. Sumalinog, RN MSN80 pages
- Musculoskeletal System/ Movement: Mark Ebony C. Sumalinog, RN MSNNo ratings yetMusculoskeletal System/ Movement: Mark Ebony C. Sumalinog, RN MSN85 pages
- Chapter 28: Virology: Poxvirus Herpes Virus Adenovirus Papovavirus Hepatitis BNo ratings yetChapter 28: Virology: Poxvirus Herpes Virus Adenovirus Papovavirus Hepatitis B2 pages
- Velez College College of Nursing F. Ramos St. Cebu CityNo ratings yetVelez College College of Nursing F. Ramos St. Cebu City3 pages
- Death Can Occur From The Misuse of Cough and Cold Medicines in Very Young ChildrenNo ratings yetDeath Can Occur From The Misuse of Cough and Cold Medicines in Very Young Children4 pages
- Key Issues Desired Outcomes Interventions Actual OutcomesNo ratings yetKey Issues Desired Outcomes Interventions Actual Outcomes4 pages
- Sodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)No ratings yetSodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)17 pages