THE CELL Concept Map
THE CELL Concept Map
Uploaded by
Dae PelayoCopyright:
Available Formats
THE CELL Concept Map
THE CELL Concept Map
Uploaded by
Dae PelayoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
THE CELL Concept Map
THE CELL Concept Map
Uploaded by
Dae PelayoCopyright:
Available Formats
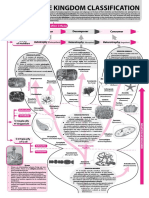
THE CELL
PELAYO, FRANCIS DAE A.
MD-1A
3 pages (Page 1 of 3)
(THE PLASMA MEMBRANE)
REFERENCE: Mescher, Junquiera’s Basic Histology and Atlas 14 th Edition
PLASMA MEMBRANE CYTOPLASMIC NUCLEUS CYTOSKELETON INCLUSIONS
ORGANELLES
composed of Vesicular transport
PHOSPHOLIPIDS PROTEINS CHOLESTEROL ENDOCYTOSIS EXOCYTOSIS
-amphipatic - macromolecules are
- restrict the - Movement of large
-two nonpolar (hydrophobilc) long chain fused and pinched off
movement and molecules from inside
fatty acids Types to a vesicle (vacuoles)
modulate the fluidity of to outside of cell
- polar (hydrophilic head)
all membrane
components
RECEPTOR
INTEGRAL PROTEINS PERIPHERAL PROTEINS TRANSMEMBRANE PROTEINS PHAGOCYTOSIS PINOCYTOSIS CONSTITUTIVE REGULATED
MEDIATED
- Bound to one of - Completely - ingestion of ENDOCYTOSIS - products that - occurs in a
- incorporated - Smaller
directly within the two span the bilayer particles such as invaginations are released response to
the lipid bilayer membranes bacteria and dead of the cell - Receptors attach as soon as stimulus/ signal
- extracted by - extracted by cell remnants membrane to a ligand to synthesis is coming to the
detergents salt Mechanisms of exchange - e.g. macrophage fuse and promote complete cells
between cell and environment and neutrophils entrap ECF - e.g. collagen - e.g. release of
endocytosis
- seen in LDL subunits of digestive
transport ECM enzyme from
AQUAPORINS CHANNELS CARRIERS pancreatic cells
ATP DEPENDENT
TRANSPORTERS
- proteins that allow - Multipass proteins - Bind small molecules
through which ions and translocate them - Requires ATP fot
water molecule to
(Na2+, K+, Ca2+) or across the membrane molecules to pass
cross the molecules pass via conformational
membrane selectively changes
REFERENCE: Mescher, Junquiera’s Basic Histology and Atlas 14th Edition
THE CELL
(THE CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES)
PLASMA MEMBRANE CYTOPLASMIC NUCLEUS CYTOSKELETON INCLUSIONS
ORGANELLES
RIBOSOMES PROTEOSOME PEROXISOMES SECRETORY
LYSOSOME MITOCHONDRIA ENDOPLASMIC GOLGI APPARATUS
S GRANULES
- macromolecules about 20-30 nm- Spherical, 0.05 to 0.5 um in diameter
RETICULUM - Degrade denatured or - Spherical organelles
- sites of intracellular digestion and
- Elongated structures with dm of 0.5-1 - Dynamic organelle nonfunctional polypeptides after enclosed by single - Found in cells that store a
- assemble polypeptides from amino um and lengths upto 10x greater - Completes posttranslational they are tagged with ubuquitin membrane and produce the-
acids molecules of tRNA in a turnover of cell components product until its release
Membrane-limited vesicles that contain- Membraned enclosed with arrays of modifications - Cylindrical structure made of 4 enzyme H2O2
sequence bound to the strand of- - Packages and addresses these by exocytosis is signaled
40 hydrolytic enzymes primarily, acid enzymes specialized for aerobic stacked rings, each composed- Enzymes produced
mRNA respiration and production of ATP proteins to their proper by a metabolic hormonal
hydrolyases Types of 7 proteins including inactivates various potentially
or neural message
- Abundant in macrophages and - Abundant in cardiac muscle and cells destination proteases toxic molecules
of kidney
neutrophils
ER BOUND POLYRIBOSOMES ROUGH ER SMOOTH ER CIS-GOLGI MEDIAL GOLGI TRANS GOLGI
FREE POLYRIBOSOMES
NETWORK
- synthesize cytosolic and - The proteins synthesized by - Prominent in cells specialized - Lack bound - Sialic acid is added as the
- Mannose-6- - New glycosylation of
cytoskeletal proteins and these ribosomes are for protein secretion e.g. ribosomes terminal sugar to certain
phosphate is added occurs on H groups
proteins for import into the segregated during Pancreatic acinar cells, - Tubular or sac-like oligosaccharides
to future lysosomal of some lipids and
nucleus, mitochondria, translation into the interior of fibroblast, and plasma cells cisternae - Sulfation of tyrosine
enzymes serine and threonine
and peroxisomes ER e b a e ci e ae - Sac-like or parallel stack - Functions: residues and some sugars
- N-linked residues (O-linked)
- Proteins synthesized are for flattened cisternae 1. Synthesis of - Specific vesicles with
oligosaccharides are - N-linked
import to Golgi apparatus, - Major function: production of phospholipids and different destinations are
trimmed and other oligosaccharides on
secretory vesicles, and membrane-associated steroids separated and sorted
sugars added proteins are modified
lysosomes proteins, proteins of many 2. Detoxification: c
further
organelles, and proteins to be P450
- Glycoproteins and
excreted by exocytosis 3. Sequestration and
glycolipids are
controlled release
sorted into specific
of Ca++
vesicles
THE CELL
(THE NUCLEUS, CYTOSKELETON, & INCLUSIONS)
PLASMA MEMBRANE CYTOPLASMIC NUCLEUS CYTOSKELETON INCLUSIONS
ORGANELLES
Types
LIPID DROPLETS LIPID DROPLETS
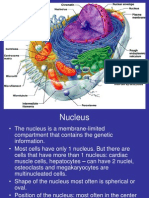
NUCLEAR CHROMATIN NUCLEOLUS MICROTUBULES MICROFILAMENTS INTERMEDIATE
ENVELOPE FILAMENTS
- Composed of actin
S - restrict the - Fine tubular structures PIGMENTED
- that confer significant subunits and allow
movement and motility and most DEPOSITS
modulate the fluidity of rigidity to maintain cell
shape contractile activity in With pathological
all membrane cells
components
importance - E.g. melanin, lipofuchsin, and hemosiderin
EUCHROMATIN HETEROCHROMATIN
CYTOKERATIN VIMENTIN NEUROFILAMENT LAMINS
- Finely, dispersed granular - Coarse, condensed
- Lightly stained basophilic - Intensely stained basophilic
- Rich with genes - More compact; little to no
- Predominates in active transcriptional activity
cells (e.g. neurons) - Predominate in cells with little
- Active transcription of synthetic activity (e.g.
DNA to mRNA circulating lymphocytes)
- Regulator of gene expression
REFERENCE: Mescher, Junquiera’s Basic Histology and Atlas 14 th Edition
You might also like
- Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Distance LearningDocument10 pagesProtein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Distance LearningjaneyzhouNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell BIOLOGYDocument43 pagesParts of A Cell BIOLOGYSam Ferbyn LomotanNo ratings yet
- 9 Dna Replication Scramble KeyDocument2 pages9 Dna Replication Scramble KeyJustin Luu67% (3)
- Use This Form BLANK Blood Monitoring Report From RVBSPDocument21 pagesUse This Form BLANK Blood Monitoring Report From RVBSPBadjoy Arcilla Dollente-ParialNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Mutation Concept MapDocument1 pageDNA Replication and Mutation Concept MapVibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- UST Bio Exam Part ReviewerDocument6 pagesUST Bio Exam Part ReviewerAmanda PoetirayNo ratings yet
- Meiosis ActivityDocument3 pagesMeiosis ActivityEileen Joy NocedaNo ratings yet
- Marshmalien LabDocument9 pagesMarshmalien LabShonnefarrow14No ratings yet
- Emotion Charade CardsDocument2 pagesEmotion Charade Cardsapi-375168721100% (1)
- Organelle Biogenesis ILOs and ReferencesDocument3 pagesOrganelle Biogenesis ILOs and ReferencesDarren MohNo ratings yet
- Biology - November 2017Document1 pageBiology - November 2017Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Online Study GuideDocument7 pagesCH 12 Online Study Guideюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Biology Dna Worksheet Answer KeyDocument4 pagesBiology Dna Worksheet Answer KeyElena abigail silva vallecilloNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument16 pagesFrom Gene To ProteinPatricia NerNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Photosynthesis AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 10. Photosynthesis Answerskarlitarmz100% (2)
- Cell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsDocument21 pagesCell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsCristina MariaNo ratings yet
- Transcription: RNA Polymerases and General Transcription FactorsDocument77 pagesTranscription: RNA Polymerases and General Transcription FactorsmluluNo ratings yet
- Activity1 ConceptMapDocument1 pageActivity1 ConceptMapRegina AroNo ratings yet
- Membrane TransportDocument24 pagesMembrane Transportolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Practice - DNA, RNA, Gene Expression (Solutions)Document4 pagesPractice - DNA, RNA, Gene Expression (Solutions)SophieNo ratings yet
- Punnett SquaresDocument17 pagesPunnett Squaresapi-451330223No ratings yet
- DNA - Student NotesDocument23 pagesDNA - Student NotesCola ChauNo ratings yet
- One Gene - One Enzyme Theory 2016 EHSSDocument21 pagesOne Gene - One Enzyme Theory 2016 EHSSAdi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- 4 Pedigree AnalysisDocument48 pages4 Pedigree AnalysisBiologistAhmedNo ratings yet
- Theories Of: EvolutionDocument13 pagesTheories Of: EvolutionLorenz Dadis AlonosNo ratings yet
- Pedigree AnalysisDocument37 pagesPedigree Analysisshelren onlagadaNo ratings yet
- Bio Lecture 2 Cell StructureDocument46 pagesBio Lecture 2 Cell StructureLương Bang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cell JunctionsDocument30 pagesCell JunctionsNavodit GoelNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument29 pagesCellular RespirationDominic MaderaNo ratings yet
- Biological+Macromolecules KalmaDocument40 pagesBiological+Macromolecules Kalmajudy andradeNo ratings yet
- Rna and TranscriptionDocument46 pagesRna and TranscriptionReyana BaderNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document3 pagesCH 1Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Chemistry in Biology QuestionsDocument102 pagesChapter 6 Chemistry in Biology QuestionsOlga OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument36 pagesDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlex LlanoNo ratings yet
- Dna ExtractionDocument2 pagesDna Extractionapi-358984084No ratings yet
- Completed Concept Map PDFDocument1 pageCompleted Concept Map PDFBombo MartinNo ratings yet
- Genetics Patterns of Genetic Inheritance Genetic TerminologyDocument12 pagesGenetics Patterns of Genetic Inheritance Genetic TerminologyJustin CatalanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 9 14 Answers PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz 9 14 Answers PDFюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- S-B-5-3 - From Gene To Protein KEYDocument5 pagesS-B-5-3 - From Gene To Protein KEYfirebot4100% (1)
- Chapter 9 The Immune System NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 9 The Immune System NotesFelix LeNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Dna ReplicationDocument55 pagesUnit 5 - Dna Replicationapi-262235970100% (1)
- 1.3 Membrane Structure - Questions and AnswersDocument5 pages1.3 Membrane Structure - Questions and AnswersBordersv PoppwNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document18 pagesUnit 3harshbharatdesai_783No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: DECEMBER 13, 2010 Cape Biology Unit 1 Mrs. HaughtonDocument45 pagesProtein Synthesis: DECEMBER 13, 2010 Cape Biology Unit 1 Mrs. HaughtonAshley MorganNo ratings yet
- Intro To EcologyDocument44 pagesIntro To EcologyJinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument72 pagesTranscriptionMurthy MandalikaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle CheckpointsDocument3 pagesCell Cycle CheckpointsKristine Grace VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Cross ProblemsDocument4 pagesGenetic Cross Problemsapi-32772460No ratings yet
- Factoring ChartDocument1 pageFactoring Chartmishi19No ratings yet
- 11.1 Genetic Variation Within A PopulationDocument2 pages11.1 Genetic Variation Within A PopulationOmar AlwaerNo ratings yet
- BIO01 CO3.1 Transport Mechanisms in CellsDocument19 pagesBIO01 CO3.1 Transport Mechanisms in CellsJustine MarillaNo ratings yet
- Genome Organization - 2020Document26 pagesGenome Organization - 2020Bagus Arya MahartaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: The Molecular and Biochemical Basis of An OrganismDocument13 pagesUnit 2: The Molecular and Biochemical Basis of An OrganismMeghaNo ratings yet
- Monster MashDocument5 pagesMonster Mashapi-507320580No ratings yet
- Cmb-Ppt-5-Endoplasmic Reticulum-Borja, Jayven CDocument11 pagesCmb-Ppt-5-Endoplasmic Reticulum-Borja, Jayven CJboar TbenecdiNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: Magdalena F. Natividad, PHD Dean, School of Medical Lab Science Feu-NrmfDocument24 pagesChromosomes: Magdalena F. Natividad, PHD Dean, School of Medical Lab Science Feu-NrmfCharm AngelesNo ratings yet
- Cilia and FlagellaDocument25 pagesCilia and FlagellaLia Savitri RomdaniNo ratings yet
- 2.2 WATER: Essential Idea: Water Is The Medium of LifeDocument5 pages2.2 WATER: Essential Idea: Water Is The Medium of LifeKarisna HNo ratings yet
- The Cell NucleusDocument3 pagesThe Cell NucleushutterincNo ratings yet
- H2 Biology - Notes On Nervous ControlDocument7 pagesH2 Biology - Notes On Nervous ControlSefLRhoNo ratings yet
- Osteotomy at Low-Speed Drilling Without Irrigation Versus High-Speed Drilling With Irrigation: An Experimental StudyDocument6 pagesOsteotomy at Low-Speed Drilling Without Irrigation Versus High-Speed Drilling With Irrigation: An Experimental Studyanilsamuel0077418No ratings yet
- Allium Cepa (Onion) Capsicum (Pepper) Hydrilla Sprig Solanum Lycopersicum (Tomato) Cucurbita (Squash) ShootDocument3 pagesAllium Cepa (Onion) Capsicum (Pepper) Hydrilla Sprig Solanum Lycopersicum (Tomato) Cucurbita (Squash) ShootMEDELYN KEITH ESTANISLAONo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learner'S Activity Sheet For Quarter 2, Week - 4Document8 pagesDepartment of Education: Learner'S Activity Sheet For Quarter 2, Week - 4RubenNo ratings yet
- Bi12 LG U02-KeyDocument6 pagesBi12 LG U02-KeyZahida SultanNo ratings yet
- The Pathology Lab: Blood ScienceDocument1 pageThe Pathology Lab: Blood SciencejeanbeanjellymanNo ratings yet
- Compact Bone and Spongy Bone: OsteocytesDocument27 pagesCompact Bone and Spongy Bone: OsteocytesMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1 and Answer SheetDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1 and Answer SheetBalram Harold100% (1)
- Mounting Media: An Overview: January 2014Document9 pagesMounting Media: An Overview: January 2014Niketa SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document46 pagesCH 07abdurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Histology 2024-01Document39 pagesIntroduction To Histology 2024-01jcrosa137No ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument3 pagesUntitled Presentationapi-495307928No ratings yet
- Cells JeopardyDocument55 pagesCells Jeopardyapi-308745623No ratings yet
- DR Mohamed Serar Yusuf MSC, BSC, Ascpi, UMST/SudanDocument32 pagesDR Mohamed Serar Yusuf MSC, BSC, Ascpi, UMST/SudanAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- What Are The Components of BloodDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Components of BloodHerrieGabicaNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument2 pagesCell Analogyludwig abaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Document8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life - Hand Written Notes - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Hand Written Notes - Adobe Scan 16-Jun-2021 (1) (1) - CompressedDocument19 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life - Hand Written Notes - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Hand Written Notes - Adobe Scan 16-Jun-2021 (1) (1) - CompressedNikhil Kumar NiralaNo ratings yet
- Fixation and Types of Fixative AgentsDocument14 pagesFixation and Types of Fixative AgentsHARIS KHANNo ratings yet
- Reverse Blood Grouping Procedure: A B Serum or Plasma A RBC Reagent A B RBC Reagent BDocument1 pageReverse Blood Grouping Procedure: A B Serum or Plasma A RBC Reagent A B RBC Reagent Bmichael mannNo ratings yet
- Report: Gram Staining of Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia ColiDocument4 pagesReport: Gram Staining of Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia ColiMuhammed ElRakabawi100% (2)
- Histo ManualDocument16 pagesHisto ManualFitz Gerald CastilloNo ratings yet
- 2018 Bookmatter PlantAnatomy PDFDocument15 pages2018 Bookmatter PlantAnatomy PDFmichaelaapilat026No ratings yet
- NucleusDocument58 pagesNucleusImperiall100% (1)
- Introduction of White Blood Cell CountDocument9 pagesIntroduction of White Blood Cell CountShanaz ShaxawanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Neutrophilic GranulocytesDocument1 pageClassification of Neutrophilic Granulocytesripanga100% (1)
- Plasmodesmata and VacuoleDocument27 pagesPlasmodesmata and VacuoleDeepak ThakurNo ratings yet
- Collagen ProteoglycansDocument2 pagesCollagen ProteoglycansAlliah CasingNo ratings yet
- 4+5 Tissue Types and Epithelial TissueDocument44 pages4+5 Tissue Types and Epithelial Tissueyasser100% (2)