Certify Baby'S Birth: Body Temperature
Certify Baby'S Birth: Body Temperature
Uploaded by
Jobelle AcenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Certify Baby'S Birth: Body Temperature
Certify Baby'S Birth: Body Temperature
Uploaded by
Jobelle AcenaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Certify Baby'S Birth: Body Temperature
Certify Baby'S Birth: Body Temperature
Uploaded by
Jobelle AcenaCopyright:
Available Formats
PEDIA Part 1 Put under the FLOOR LAMP, drop light or radiant
warmer
NORMAL Avoid putting crib near the cold wall (Radiation)
Avoid cold draft: aircon, fan, open window or
IMMEDIATE DELIVERY ROOM CARE door (Convection)
essential intrapartum NB care POSTPONE THE BATH until temperature is stable
In support of the MDG #4 (6hours)
to reduce childhood mortality
A- irway
B- reathing
CERTIFY BABY’s BIRTH
Plastic Bracelet (ankle) and crib card
C- ertify the Birth
D- etermine Adaptation to Extrauterine Life: APGAR Foot Prints- no longer recommended
Score Most Ideal: DNA
REGISTER
AIRWAY Local Civil Registrar then PSA (Philippine
the Band/Bound Intervention Statistics Authority/ NSO) for Birth Certificate
to prevent asphyxiation
to prevent aspiration
*accounts for 31% of NB death DETERMINE
WHAT CAUSES ASPHYXIATION? ADAPTATION TO
umbilical cord clamped
No more O2 from placenta
EXTRAUTERINE LIFE
*a crying baby is a breathing baby
HYPOXIA *the louder the cry- good expansion of lungs
Hypercapnia/ Hypercarbia CRITERIA ASSESS 0 1 2
PULSE Cardiac Absent 100 100
Acidosis
Rate
CNS Depression RESPIRATION Cry Absent Weak, slow, Strong
irregular regula
AIRWAY r
neonates must breath after birth If not:
Asphyxiation may result ACTIVITY Muscle Limp, Some Well
neonates breath after birth by CRYING so Tone Floppy flexion, Little flexed,
stimulate NB to cry effectively after birth to prevent tone movement active
asphyxiation
GRIMACE Reflex No Grimace Cry,
Suction with bulb syringe PRN if (w/ nasal
obstruction/ meconium stain amniotic fluid) to Irritabilit respons gag
prevent aspiration y e cough,
pulls
Encourage to cry effectively to maximize lung away
expansion
APPEARANCE Color Pale/ Acrocyanosi PINK/
BODY TEMPERATURE Blue all
over
s
(hands+feet
RED
all
Time Band/Time Bound Intervention are blue) over
PHYSIOLOGIC HEAT LOSS AFTER BIRTH
37.2 °C down to 35.5 to 36.5°C *You expect a pink/red baby depends on what continent
EXTREME HYPOTHERMIA can cause Cold you work
Stress causing ACIDOSIS
*prone to cold stress due to extreme hypothermia Expect a score of 8/9 at 1st minute
EXTREME HYPOTHERMIA SCORE INTERPRETATION & MGT
non shivering Burns brown fats SCORE OF 0 to 3
thermogenesis for heat POOR CONDITION
Resuscitation Needed/ NICU
O2 consumption Ketones/ fatty acids
SCORE of 4 to 6
O2, CO2 ACIDOSIS FAIR CONDITION but guarded
Closer Monitoring (baby goes to NICU)
Acidosis
Score of 7 to 10
MANAGEMENT GOOD CONDITION
DRY baby immediately after birth (heat loss by allowed to do “Unang Yakap”
Evaporation) ROOMING-IN
Put on TOP of MOTHER’s BODY: Skin to Skin
Contact (Conduction) “Unang Yakap” 1. NON TIME BAND/ BOUND INTERVENTION
Breastfeeding must be done atleast 8x/day on
DEMAND & EXCLUSIVE (no other milk)
2. EYE CARE (Crede’s Prophylaxis) Antibody: IgA: PASSIVE NATURAL IMMUNITY
Prevents OPHTHALMIA NEONATORUM d/t IgG- placenta
maternal gonorrhea/chlamydia
done to ALL babies delivered either CS/NSD after RA 9288 – NB Screening Act of 2004
initial bonding/ complete breastfeeding done to diagnose inborn errors of metabolism
Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Betadine Eyedrops Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
on the lower conjunctival sac Galactosemia
PKU
*don’t wash hands of the NB, let them smell the amniotic G6PD
fluid on their fingers/ hand, because the nipple of the Cretinism
mother has the smell of amniotic fluid. that may cause DEATH/ MENTAL
RETARDATION
3. CORD CARE
Done by HEEL PRICK when baby is atleast 24h
Clamp when NO LONGER PULSATING, at 2cm old/ not more than 72 hours (Best time: 48 hours)
& 5cm from the base.
DON’T MILK *reached 38-42 w- TERM Delivery
42 & above- POST TERM
Count no. of blood vessels
2 arteries & 1 vein (AVA)- rule out THE RISK NEONATES
Kidney Agenesis- absence of 1 kidney the premature infant is defined as baby born
Cardiac Defect before 37 weeks of pregnancy
Problems of Prematures= d/t IMMATURE
NEPHRITIS- most common cause of renal failure in ORGANS
children
*surfactant-allows lung to expand
PREVENT INFECTION Immature alveoli w/ less amount of surfactants
clean with soap and water if soiled
Keep umbilical cord clean and free of infection PROBLEMS: Atelectasis, prolong apnea (more than
to prevent sepsis neonatorum 20s), cyanosis, asphyxia
PROMOTE DRYING *Normal apnea- <20s
Expose to AIR
Do not use abdominal binders MANAGEMENT:
Should fall-off between 7-10 days MD inserts ET
Purpose: Artificial Surfactant given via ET
*In putting diaper, fold down waist band to expose cord CPAP via mechanical ventilation/ AmbuBag
4. VITAMIN K Administration *premature skin is gelatinous
to promote synthesis of prothrombin
Neonates cannot synthesize Vit K because of REGULATION OF BODY TEMPERATURE
absent intestinal bacterial flora (GI is sterile) Problem:
1 mg IM (in mL it’s 0.1) in the thigh muscle immature hypothalamus/ poikilothermia
(VASTUS LATERALIS) –biggest muscle mass & (temperature tends to go extreme depends on
most highly developed environment)
Avoid using the gluteal muscles (buttocks) less amount of subcutaneous tissues
because of the danger of sciatic nerve trauma
causing paralysis MANAGEMENT
put in an incubator for maintenance of NEUTRAL
*Allowed to be injected in buttocks: ask mother when did temperature setting
the baby started to walk. If walking already for just a month KANGAROO CARE
it gluteal muscles is not developed yet, wait for 1 year *KFC- Kangaroo father care, father helps in doing
*Baby should be walking for at least a year for gluteal M Kangaroo Care
to be developed. *temp goes down- shiver
*temp goes up- sweat
5. INJECT HEPATITIS B & BCG
Right Deltoid Muscle NUTRITIONAL DIFFICULTIES
prone to aspiration/ gastric distention and
6. INITIAL BATH hypoglycemia
done best when VS especially temperature is
stable/ 6hours after birth *You cannot BREATHE & SWALLOW at the same time-
DO NOT remove vernix caseosa epiglottis is closed when swallowing so that the food you
Vernix has antibodies that protects baby’s skin ate won’t go to lungs
from infection and prevents evaporation of heat.
MANAGEMENT:
7. ROOMING IN (Bonding & Feeding) Gavage (OGT) feeding
Provide Optimum Nutrition: small frequent feeding
RA 7600 / Rooming In/ Breastfeeding Act of
1992
EO 51- Milk Code of the Philippines HEMATOLOGIC DIFFICULTIES
immature liver function
*When Bilirubin goes very very high- Hyperbilirubinemia *Adult: 70-110 (Ph)
80-120 mg/dl (international)
can go to BRAIN Babies: divide by 2
If lower than normal: 40-60 mg/dl or mg% give
BRAIN DAMAGE glucose (D50W) as ordered
KERNICTERUS IV, umbilical cut down/ UV line (umbilical
Management: vein)
PHOTOTHERAPY/ BILI LIGHT *pusod
Cover eyes and genitals
Turn frequently NEONATES WITH CONGENITAL DEFECTS
GROWTH- is an increase in the no & size of cells
LOW RESISTANCE TO INFECTION Measured in terms of QUANTITY
Causes: Immature Immune System
DEVELOPMENT- is capacity of the individual to perform a
Problem: SEPSIS NEONATORUM task
MANAGEMENT: PREVENTION Measured in terms of QUALITY
strict compliance with nursery aseptic protocol
Antibiotic as ordered PRINCIPLES OF GROWTH & DEVELOPMENT
1. Unique- individualized
The POST MATURE INFANT 2. Continuous Process- begins at conception &
Born more than 42 w in gestation ends at death
3. PLAY is essential in a child
*nagdddry out na
Problem: PLACENTAL DEGENERATION INFANT 1mo-1yr
causing decreased utero placental perfusion Plays alone- SOLITARY GAMES
Long but thin, DRY CRACKING SKIN, No Vernix plays with their BODY & SENSES
& Lanugo, long hair & nails, alert look, possible TOYS- mobiles, rattles, teething, rings, music
IUFD (stillbirth/ intrauterine fetal death) boxes, squeeze toys
ASSOCIATED PROBLEMS *Ego- selfish, narcissitic
1. Hypoxia d/t placental insufficiency *pleasure principle
2. Hypoglycemia d/t decreased glycogen
3. Fetal Distress- Early Sign: restlessness (keeps TODDLERS 1-3 yrs
moving) very possessive/ cannot share
4. Seizure Disorders- hypoxia in brain loves to play BESIDE another child but must have
5. Meconium Aspiration- infection & respiratory each a toy- PARALLEL GAMES
distress *sticky meconium TOYS- promote skills of walking- push & pull toys
and talking- toy telephone, coordination-blocks.
PREVENT: Regular Prenatal Check Ups (because EDC is *reality principle
given)
*Accurate way to know EDC: UTZ by ultrasonographist PRESCHOOL 3-6 yrs
loves to share & imitate adults in their role play
BABY OF DIABETIC MOTHER
COOPERATIVE/ ASSOCIATIVE GAMES
TOYS- role playing games- play school, play
HPL (secreted by placenta) --- enemy of insulin --- GDM
house, doctor-nurse kit, etc
Glucose (food of cell)- cell opened by insulin (key)
*Stereotyping- outcasting, may gustong laruan
if glucose doesn’t enter cell- it starves- resulting to
polyphagia
SCHOOLER 6-12
glucose then goes to blood—hyperglycemia
must have a winner at the end of the game-
COMPETITIVE GAMES
*The blood that goes to uterus is high in sugar which the
TOYS- card games, scrabble, hopscotch (piko),
baby receivers and compensates by producing more
insulin (the baby is not diabetic, it’s the mother who’s skipping rope, etc.
diabetic and lacks insulin)
*The baby absorbs ALL GLUCOSE coming from mother 4. Rate of Growth varies:
resulting to a MACROSOMIC Baby Rapid Stages (growth spurts)
infancy & adolescent
EFFECT on BABY Slow Periods (growth gaps)
Toddler, preschooler, schooler
INTRAUTERINE more glucose absorption,
HYPERINSULINISM Macrosomia (large fetus) 5. Directional
Growth- horizontal & vertical
Macrosomia- Preterm Delivery
DEVELOPMENT- Cephalocaudal (Gross Motor)
AFTER BIRTH: HYPOGLYCEMIA Proximodistal (Fine Motor)
(possible death d/t Metabolic Acidosis) *near- far
MANAGEMENT: ASSESSMENT OF GROWTH
Monitor s/sx of Hypoglycemia- tremors, 1. Physiologic loss of weight days after birth- 5-10%
irritability, RESTLESSNESS of birth weight
Monitor blood glucose level 2. Most rapid during Infancy
Doubles at 6 mos, Triples at 1 year &
Adolescent Stages
ASSESSMENT OF DEVELOPMENT
DDST- Denver Developmental Screen Test
MMDST- Metro Manila Developmental Screen Test
AREAS ASSESSED
Gross Motor- skills done by the LARGE
muscles *Baby cried using mouth--- ORAL
Cephalocaudal Mistrust: drinking, drug addiction
Fine Motor- skills done by SMALL muscles Oral fixation/ residuals: foul mouth
Proximodistal *Phallic fixated- penis exhibitionist
Interpersonal- social
Language
DEVELOPMENTAL
MILESTONES (every 2 mos, pababa)
*Head Lag- No Head Control- CRADLE HOLD
FINE MOTOR SKILLS (every 3
mos, palayo)
NEONATE- STRONG GRASP REFLEX, hands fisted
3 mos- Grasp Reflex is gone/ hands are held open
6 mos- PALMAR GRASP; holds feeding bottle with
2 hands- BIG OBJECTS
9 mos- PINCER GRASP (thumb to finger to hold
SMALL OBJECTS)
12 mos- can hold BIG & SMALL Objects, throws
objects
DEVELOPMENTAL THEORIES
Erikson
PSYCHOSOCIAL
*son is a relationship- social
PERSONALITY
Developmental Task
Freud’s
PsychoSEXual
U
C Body Part (most important)
K
Genital Stage- Puberty, organs develop
Phallus- means penis
Genital- Latency- Latent means calm
TRUST 1st- to develop before LOVE
*You can never love w/o TRUST TODDLER
FREUD’S ANAL
ERIKSON’S AUTONOMY VS. SHAME & DOUBT ACHIEVEMENT ORIENTED YEARS
Pleasure in controlling his eliminatory function ADOLESCENT
TOILET TRAINING begins FREUD’S GENITAL
ERIKSON’S IDENTITY VS. ROLE CONFUSION
Important facts about TOILET TRAINING
Recommended to be started @ 18mos with Resurgence of sexual drives *di na homosexual
BOWEL 1st. Develops relationships w/ members of the
MOST IMPORTANT FACTOR is: READINESS OF OPPOSITE sex
THE CHILD (physical & psychological) completed Identity develops when there is a feeling of
by 4 years old. belongingness and acceptance by others.
*FEELING OF INDEPENDENCE Physical changes in the FEMALE in order of
appearance:
BEHAVIORS TO OBSERVE:
development of breast buds (THELARCHE)
growth of pubic (PUBARCHE) & axillary hair
Negativism “NO” stage
(ADRENARCHE)
Management: Offer acceptable choices
Menstruation (MENARCHE) *average 11-13
TEMPER TANTRUMS
Management: Physical changes in the MALE in order of
IGNORE THE BEHAVIOR/ Time Out appearance:
Place baby in a corner (safe place) for 1 minute for increase in the size of genitalia (SCROTUM)
each year of his life (toddler to preschool) 2 to 6 growth of pubic, axillary, facial & leg hair
voice changes
PRESCHOOLERS (3 to 6) Production of spermatozoa (NOCTURNAL
FREUD’S GENITAL (PHALLIC) EMISSIONS/ Wet dreams) *Average 14-16
ERIKSON’S INITIATIVE VS GUILT
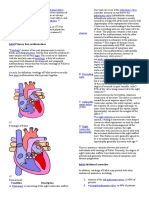
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES
OEDIPAL/ELECTRA PHASE- Child turns
toward the parent of opposite sex ACYANOTIC LEFT TO RIGHT Shunt
Initiative develops if the child is allowed freedom Aorta DOES NOT get unoxygenated
to initiate small activities & is appreciated for it. blood
Stage of “KUSA”
CYANOTIC RIGHT TO LEFT Shunt
*unresolved Oedipal gay Aorta GETS unoxygenated blood.
straight but finds a girl matured/ ACYANOTIC CYANOTIC
older than her
VSD TRANSPOSITION OF
THE GREAT VESSELS
*unresolved Electra male much older than her to ASD TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
satisfy PDA
mother & father role COARCTATION OF THE
AORTA
doesn’t want a man who isn’t Complication: Complication:
married.
CHF CEREBRAL
MISTRESS Complex (kabet)
THROMBOSIS
Commitment shallow, finds sugar
ASD- Atrial Septal Defect
daddy.
compensates by BEATING FAST
BEHAVIORS TO OBSERVE:
volume = workload
Very CURIOUS: “WHY” stage
gets bigger (hypertrophy)
Curious about gender differences reaches point of exhaustion
TOUCHES/ EXPLORES their body VSD
PDA- Ao & Pa connected
Exhibits FEAR & BODILY Injury Coarctation – DESCENDING AORTA STENOSIS
changes in pulse rate & BP
“CASTRATION Complex”
*In any surgery don’t use words “cut, remove / fix” PR & BP in arms
instead gagamutin/ tatanggalin yung sakit sa ex: tonsil”
ACYANOTIC CONGESTION OF CARDIAC
Very IMAGINATIVE- engages in fantasy play
CARDIAC SPHINCTER
CONDITIONS
SCHOOLER COMPENSATES BY RATE
FREUD’S LATENCY OF CONTRACTION
ERIKSON’S INDUSTRY VS. INFERIORITY Pul. Congestion LSHF (lungs)
CHF
The sexual drive (libido) is controlled & repressed. Systemic Congestion RSHF (systemic)
interest on the same sex only (normal
HOMOSEXUALS)
Chief Complaint: EARLY
Industry develops if the child is permitted to do
things by himself and praised for the results.
Pulmonary sx: dyspnea, fast breathing, moist ` R- VH
cough, rales, crackles O- pening in Septum
P- ulmonary Artery Stenosis
Dx:
1. CXR (Pulmonary Edema & Cardiomegaly) Sx: usually seen when child is more active because of
*athletes and older person- Normal cardiomegaly increased O2 demand.
2. ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY/ MRI- identifies type & size of EXERTIONAL DYSPNEA w/ Cyanosis (Central)
defect Activity Induced “TET SPELLS” relieved by
not invasive SQUATTING
3. CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION- identifies pressure
inside the heart (CHF) *Squatting venous return
CORRECTIVE SURGERY pressure in R side of
1. if in FAILURE & DEFECT is large (no
possibility of spontaneous closure KNEE-CHEST position if small baby
“BOOT-SHAPED” heart
OPEN - defect is inside the (ASD, VSD) CLUBBING OF FINGERS d/t Peripheral hypoxia
CLOSED - defect is outside the (PDA, Coarctation
of Aorta) additional capillaries are
formed
MEDICAL / NURSING MANAGEMENT: (collateral circulation is
made)
Objective 1: PREVENT CHF
SCHAMROTH SIGN- looking for diamond space in fingers
1. IMPROVE CARDIAC OUTPUT
Cardiac Glycoside- DIGOXIN POLYCYTHEMIA d/t CHRONIC HYPOXIA
(increase strength of contraction) -kidneys compensate by producing more
check for apical pulse/ cardiac rate erythropoeitin
don’t give if <60bpm if consistency is viscous blood flow slows down
(sluggish)
2. PREVENT Na RETENTION & PROMOTE
ELIMINATION OF EXCESS FLUIDS CLOT FORMATION
Diuretics- FUROSEMIDE
fast/rapid- 30 mins Intervention: SURGERY (Priority)
*1g= cc Palliative Close surgery then corrective Open
3. LOW Na INTAKE Medical/ Nursing Management:
Low Sodium Formula 1. Decrease O2 demand
Clarification on SOLIDS Allowed. *bawal maasin*
2. Monitor Hgb & Hct count- detects early
Not only the salty foods are rich in sodium
POLYCYTHEMIA
Objective 2: DECREASE O2 DEMAND 3. Assist in PHLEBOTOMY as needed to be done
cluster nursing care (organized) removal of blood
Quiet play activity (blocks, story book, puzzle) replacing amount removed w/ plasma
4. Increase Fluids/ Maintain IVF line as necessary
Decrease stress & anxiety level
5. POSITIONING during Attacks
*observe distance to child (Stranger Anxiety)
allow to SQUAT/ KNEE CHEST, give O2
Small frequent feeding
Objective 3: PREVENT RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS
GIT PROBLEM
Lung congestion prone to PNEUMONIA CLEFT LIP & PALATE
Vitamin C CLEFT LIP
Promote IMMUNIZATION Management: CHEILOPLASTY/ Z-PLASTY
The CYANOTIC CONDITIONS Post Operative:
Position: NEVER ON PRONE (no head control)
TRANSPOSITION OF GREAT VESSELS Prevent tension on suture lines
Ao & Pa switched Anticipate needs to lessen crying
Aorta receives pure unoxygenated blood use of ARM RESTRAINT- doctor’s order
Clean suture lines after feeding
sx: PERSISTENT CYANOSIS inspite of VIGOROUS
CRYING CLEFT PALATE
*less symptomatic if with Septal Opening Management: URANOPLASTY/ PALATOPLASTY
Management: Post Operative:
PALLIATIVE: Position: SHOULD BE ON PRONE (to promote
Emergency BALLOON ATRIAL natural drainage of secretions
SEPTOSTOMY- To open hole in the atrial *any surgery VASCULAR Prevent
septum that involves (lots of blood swallowing/
CORRECTIVE OPEN SURGERY mouth/oral vessels) ASPIRATION
of blood.
TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
D- isplaced Aorta (overriding) Feeding Device Post Operative:
DRINK FROM CUPS
NEVER USE STRAW adhesion obstruction distention
prevent NEGATIVE PRESSURE
*sipsip BILE STAINED VOMITUS
EFFECT: BLEEDING
ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA
TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL FISTULA
Problems: ASPIRATION/NUTRITION
Sx:
Mom w/ POLYHYDRAMNIOS
BABY is DROOLING/ very MUCOUSY
3C’s DURING FEEDING
BLOOD VESSEL Blood Supply
C caught between
layers NECROSIS
Dx: X-ray
Mgt: SURGERY (ASAP) PAIN/ BLEEDS
PreOp Care: CURRANT JELLY STOOLS
PREVENT ASPIRATION
Suction PRN
Strict NPO DANGER: PERFORATION bcausing PERITONITIS
PROMOTE NUTRITION Sx:
Gastrostomy Feeding spasmodic abdominal pain
TPN as ordered (check blood sugar) blood w/ mucus in the stool- Currant Jelly Stool
Vomiting of Bile-stained Vomitus
PYLORIC STRENOSIS SAUSAGE SHAPED MASS
cardiac sphincter –prob:GERD Management:
2 sphincter (open) IMMEDIATE SURGERY to prevent perforation that
can lead to peritonitis (Bowel Resection)
pyloric sphincter
HIRSCHSPRUNG’s DISEASE
(close)
Congenital Aganglionic Megacolon
*pyloric sphincter- holds stomach content until it is
nerve supply
mechanically digested
of LI
*sphincter is a circular M --- when pressure build up
inside HYPERTROPHY ---- small exit
absence of parasympathetic nerve supply
Sx: (ganglion cells) in LI
ABDOMINAL DISTENTION AFTER FEEDING or RECTOSIGMOID AREA
(+) peristaltic wave
Sx: Early: in the nursery – DELAYED MECONIUM
PROJECTILE VOMITING- pressure builds up
Later sx:
inside; Metabolic Alkalosis
Constipation
loss K
Frequency: stool <3x/wk Characteristic: HARD
Dehydration
Hypokalemia Pellet like stool/ RIBBON LIKE STOOLS
Weight loss Abdominal distention w/ possible fecaloid vomitus
Weight loss- don’t absorb nutrients the right way
PALPABLE OLIVE SHAPED mass in RUQ
Dx:
*palpation not a reliable technique
Dx: X-ray- BARIUM RECTAL BIOPSY
Management: PYLOROMYOTOMY (opening muscle) w/ BARIUM ENEMA- to determine EXTENT
PYLOROPLASTY (repair)
Management:
PreOp
INTUSSUSCEPTION
FACILITATE ELIMINATION
small intestines TELESCOPES into the lumen of
regular caloric irrigation
another
Palliative Colostomy- TEMPORARY
prevent COUGHING causing laryngospasm &
CORRECTIVE SURGERY respiratory distress
ERPT- Endorectal Pull Through
1. AVOID RESPIRATORY IRRITANTS & sudden
IMPERFORATE ANUS temperature changes
pollen, dust, dander, smoke, baby powder
Sx: Absence of Meconium 2. FEED & HYDRATE w/ ASPIRATION Precaution
Unable to Insert 3. Decrease O2 demand
4. Administer high humidity w/ MIST THERAPY
Management: during attacks
STEP 1: COLOSTOMY in the nursery (Palliative) cool mist vaporizer in the hospital- only water
no perfume
STEP 2: Before 1y/o (10 mos): liquefies secretions
CORRECTIVE SURGERY: steaming bathroom at home
ANOPLASTY- opening anus “tuob/ suob”
pull through procedure
*Kasi pag toddler na, dapat toilet training na BRONCHIAL ASTHMA
Avoid high sugar, high fibrous Pedia- Acute and involves only the MAINSTEM
BRONCHI; Prognosis: CURE
PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY CONDITIONS Adult- bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
Throat Problems: PHARYNGITIS/TONSILLITIS EXTRINSIC- Allergens Induced (GIT/RT)
caused by GABHS INTRINSIC- Idiopathic/ innert on the patient
if 10yr/more- Tonsillectomy (stress/anxiety)
Management: HISTAMINE
If (+) GABHS- Antibiotic
Erythromycin than PCN, for it’s the Mechanisms responsible for sx:
hypoallergenic form 1. Bronchospasm
Antipyretic PRN (NO ASA) 2. Inflammation & Edema of Airways
Paracetamol/ Acetaminophen 3. Accumulation of Tenacious Secretions
*reye’s syndrome- go to seizure MANAGEMENT
ALLERGEN CONTROL
TONSILLECTOMY if: recurrent, w/ peritonsillar SKIN TESTING followed by
abscess, w/ massive hypertrophy causing dyspnea HYPOSENSITIZATION (for 3 years)
CI: <6y/o
Management during EXACERBATION:
PreOp: 1. Administer BRONCHODILATORS/AEROSOL
Check dental (LOOSE TEETH-pedia, FALSE 2. IVF Drugs (Aminophylline, Steroids)
TEETH-adult) & bleeding status (bleeding DO) 3. Position: “ORTHOPNEIC”
4. Promote Oral fluids w/ ASPIRATION
Post Op: PRECAUTION
1. Position: while Asleep- PRONE/LATERAL
Limit MILK (thickens secretions) / AVOID VIT C
position to promote natural drainage of secretion
(high doses is an Allergen)
2. Observe for BLEEDING (FREQUENT
5. Promote breathing exercise- PURSE LIP
SWALLOWING & RESTLESSNESS) BREATHING
3. Prevent Bleeding
ice collar- potential for numbing to decrease
TOYS: flute, whistle, bubble blowing, pin wheel
pain sensation & vasoconstriction
SPORT: swimming
Avoid suctioning, throat clearing
Avoid Valsalva maneuver
4. Diet resume ONCE FULLY AWAKE & CAN RHEUMATIC FEVER
SWALLOW complication of STREPTO INFECTION
No ice cream- not advisable
COLD, CLEAR, NON IRRITATING FLUIDS
cool water, ice cold apple juice, frozen gelatin, JONES CRITERIA OF ASSESSMENT
suck on frozen popsicle, sherbet MAJOR SYMPTOMS
then SOFT DIET then DAT- (progressive diet)
Migratory POLYARTHRITIS- joint pains
SPASMODIC CROUP (LTB) CHOREA (St. Vitus Dance)- involuntary jerks
Laryngotracheobronchitis
Erythema Marginatum- rashes on the trunk
Subcutaneous nodules
Sx:
CARDITIS- Endocardium (3 layers epi, myo, endo)
hoarseness (BRASSY SPASMODIC “SEAL-
LiKE” COUGH)
inspiratory stridor MITRAL VALVE STENOSIS RHD
Fever
Possible distress d/t LARYNGOSPASM Diagnosis:
JONES CRITERIA + ASO titer= Rheumatic
Management: SUPPORTIVE CARE Fever
Normal Value ASO titer: 0-200 ‘iu’
PRICES TECHNIQUE (instead of RICE)
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY- if with valve damage
P- rotect (protective devices)
MITRAL VALVE= Stenosis/ Insufficiency RHD
R- est (immobilize)
I- ce (vasoconstriction)
Management:
C- ompression (apply pressure)
OBJECTIVE 1: Decrease Demand from the Weakened
E- levate (above the heart)
Heart
S- upport (parents, MDs, nurses, dentist, PT,
CBR/ Modify Lifestyle after discharge nutritionists)
Cluster care
LEUKEMIA
OBJECTIVE 2: Prevent further Cardiac Damage (RHD)
most common form of childhood cancer
Meds: PCN IM once a month x 3-5yrs/ ASA/ IMMATURE WBC’s (lymphoblast) *not
Steroids lymphocytes; not capable of phagocytosis is
formed
OBJECTIVE 3: Safety Precaution for CHOREA
Early Symptom: PRONE TO INFECTION
HEMATOLOGIC DISORDERS
Forms:
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA LYMPHOCYTIC- good prognosis
more common to 6mos & older children- Fe MYELOCYTIC- poor prognosis
from mother has been used up & d/t
3 MAIN CONSEQUENCES
OVERFEEDING of MILK INFECTION
ANEMIA
*occupational anemia- x-ray department
*pernicious anemia- Bariatric surgery (obese people) BLEEDING TENDENCIES
Management: *Prognosis is GOOD- if early detection and treatment
Introduction of COMPLEMENTARY
Dx: BONE MARROW BIOPSY
FEEDINGS after 6 mos of exclusive breastfeeding
ONE AT A TIME ONLY- to rule out allergy Management
1. REMISSION INDUCTION
IRON RICH FOODS
IV (systemic chemotherapy)
cereals
2. CNS PROPHYLACTIC THERAPY
egg yolk not egg white (allergenic part of egg)
dark green leafy vegetables- SPINACH (very rich Intrathecal Chemotherapy
in iron) 3. INTENSIFICATION/ CONSOLIDATION THERAPY
dark meat (organ meat)- liver of Cow regular systemic & intrathecal chemo
4. MAINTENANCE THERAPY
Supplemental Fe Preparation (FeSO 4) w/
Vitamin C (enhance absorption) Most Ideal: BONE MARROW TRANSPLANT
CHILD’s CONCEPT OF DEATH
HEMOPHILIA Below 5 y/o- form of a SLEEP/ REVERSIBLE
Deficiency in Factor VIII (anti-hemophilic factor) 6-9 y/o- person- Grim Reaper, Bogeyman, Devil,
transmitted as X-LINKED from carrier MOM Monster/ “KAMATAYAN”, REVERSIBLE
to AFFECTED SON (symptomatic) Above 9y/o- END OF LIFE on EARTH/
daughter gets it as a TRAIT from carrier MOM IRREVERSIBLE
(asymptomatic)
EARLY Sx in the NURSERY
PROLONG BLEEDING FROM THE UMBILICAL CORD
LATER SX:
EASY BRUISING (hematomas)
EASY EPISTAXIS & GUM BLEEDING
*epistaxis- balinguyngoy
HEMARTHROSIS- bleeding in between the ball joints (pain
& swelling)
*bone absorbs blood in synovial fluid
DEATH d/t INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE
Management:
MEDICAL: Transfusion of Factor 8,
cryoprecipitate, platelet concentrate
Prevent BLEEDING (AVOID TRAUMA)
soft bristled toothbrush, electric razor, no
tattoo, no contact sport
You might also like
- Step2Ck Nbme 8 QuestionsDocument166 pagesStep2Ck Nbme 8 Questionstaha albarghathy100% (1)
- Basic Science For The MRCS: A Revision Guide For Surgical Trainees (MRCS Study Guides) - ISBN 0702044830, 978-0702044830Document23 pagesBasic Science For The MRCS: A Revision Guide For Surgical Trainees (MRCS Study Guides) - ISBN 0702044830, 978-0702044830berenicerugenx100% (16)
- ER Protocols in The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesER Protocols in The PhilippinesJobelle Acena100% (3)
- Case Study (Lung Cancer)Document17 pagesCase Study (Lung Cancer)Jobelle Acena67% (3)
- Pediatric NursingDocument22 pagesPediatric NursingDarren Mae Mosada100% (1)
- Nursing Updates On AntidotesDocument1 pageNursing Updates On Antidotesseigelystic100% (15)
- Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MAN: Maternal and Child Nursing BulletsDocument10 pagesMark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MAN: Maternal and Child Nursing BulletsMark DaenosNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Case StudyDocument15 pagesGeriatric Case StudyJobelle Acena100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle Acena100% (2)
- Psychiatric Nursing Michael Jimenez, PENTAGON Slovin'S Formula: N 1 + NeDocument10 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Michael Jimenez, PENTAGON Slovin'S Formula: N 1 + NeJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Prelims Pedia 102Document10 pagesPrelims Pedia 102quidditch07No ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot Lesson PlanDocument25 pagesTetralogy of Fallot Lesson PlanUday Kumar100% (1)
- Answering NCLEX QuestionsDocument19 pagesAnswering NCLEX QuestionsNorma Zamudio92% (25)
- Pediatric NursingDocument6 pagesPediatric NursingViktoria Leeahna LehNo ratings yet
- Handouts Ob AbnormalDocument16 pagesHandouts Ob AbnormalShenn ChavezNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Nursing NCLEX Bullets Part 1Document166 pagesPEDIA Nursing NCLEX Bullets Part 1Russel Myron Adriano AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing ReviewerDocument66 pagesPediatric Nursing ReviewerLouis GaneNo ratings yet
- Pedia-Reviewer CompleteDocument36 pagesPedia-Reviewer CompletePotato BroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Respiratory DisordersDocument7 pagesLecture 6 - Respiratory DisordersMaikaylaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Sir CanlasDocument73 pagesPedia Sir CanlasFev BanataoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Medical - Surgical NursingDocument4 pagesModule 6 - Medical - Surgical NursingJohiarra TabigneNo ratings yet
- Immunology Intensive ReviewerDocument21 pagesImmunology Intensive ReviewerAllysa PrestonNo ratings yet
- Nle Notes PediaDocument53 pagesNle Notes PediaJonathan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Notes - CDDocument4 pagesNotes - CDYuxin LiuNo ratings yet
- 10 Medical Surgical Nursing Intensive Review PDFDocument68 pages10 Medical Surgical Nursing Intensive Review PDFShanine Alexia CordovezNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NotesDocument14 pagesPerioperative NotesGil GanibanNo ratings yet
- Pharma Gapuz IntroDocument40 pagesPharma Gapuz IntroHayes CloverNo ratings yet
- Nursing MnemonicsDocument2 pagesNursing MnemonicsJamie ElizabethNo ratings yet
- MS - NeuroDocument10 pagesMS - Neuroknowamai567No ratings yet
- CHN GapuzDocument23 pagesCHN GapuzMabes100% (1)
- Answer and Rationale FundamentalsDocument20 pagesAnswer and Rationale FundamentalsCharles Gerard B. BeluanNo ratings yet
- 17 2024 NLE Respi HandoutsDocument66 pages17 2024 NLE Respi HandoutsBasa, Rica Mae P.No ratings yet
- Anti Psychotic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti Psychotic DrugscalfornianursingacadNo ratings yet
- Disaster Triage NursingDocument2 pagesDisaster Triage NursingJohiarra TabigneNo ratings yet
- PEDIADocument56 pagesPEDIAstuffednurse100% (3)
- CD HandoutsDocument27 pagesCD HandoutsricogonzzzNo ratings yet
- NP2 Recalls5Document10 pagesNP2 Recalls5AhrisJeannine EscuadroNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIATRICDocument8 pagesPSYCHIATRICSusan Loida SorianoNo ratings yet
- CHN TopicsDocument19 pagesCHN TopicsKristine AnaenNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing DrillsDocument8 pagesPediatric Nursing DrillsClarence AnescoNo ratings yet
- CDC Immunization 0-6 YrsDocument2 pagesCDC Immunization 0-6 Yrsxoxo318100% (1)
- PRE MS N2016 Ans KeyDocument33 pagesPRE MS N2016 Ans Keyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 2Document2 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 2yunjung0518100% (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing By: Joshua James L. Diao, BSN-RN, BSMT, AMT, ASCPT, MAN (On-Going)Document22 pagesPsychiatric Nursing By: Joshua James L. Diao, BSN-RN, BSMT, AMT, ASCPT, MAN (On-Going)Joshua DiaoNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NotesDocument18 pagesMedical Surgical NotesshalomNo ratings yet
- Nle Pentagon Reviewer For Nclex Answer QuestionsDocument30 pagesNle Pentagon Reviewer For Nclex Answer QuestionsSpoonNo ratings yet
- What Are The Main Symptoms of AsthmaDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Main Symptoms of AsthmaJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeleteal ReviewerDocument24 pagesMusculoskeleteal ReviewerRobert BoongalingNo ratings yet
- MnemonicsDocument10 pagesMnemonicsRichard GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice II 2010Document16 pagesNursing Practice II 2010Anonymous NnC87DtzQNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On DigoxinDocument8 pagesDrug Study On DigoxinDonald BidenNo ratings yet
- Ob Penta NotesDocument56 pagesOb Penta Notesstuffednurse100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing TionkoDocument40 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing TionkojeshemaNo ratings yet
- All Absolute Statements With Words Like and Is Considered A and Is ThereforeDocument20 pagesAll Absolute Statements With Words Like and Is Considered A and Is ThereforeJohnmer AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Medical Cartoon and The AwesomeDocument2 pagesMedical Cartoon and The Awesomekrrishshrish140% (1)
- CHN Finals-ReviewerDocument14 pagesCHN Finals-ReviewerKayobi BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing Human Sexuality SexualityDocument30 pagesObstetric Nursing Human Sexuality SexualityKim RamosNo ratings yet
- Gapuz Communicable Disease NursingDocument46 pagesGapuz Communicable Disease NursingBJ DUQUESANo ratings yet
- Ina Pedia1Document14 pagesIna Pedia1Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing 2Document18 pagesPediatric Nursing 2Benedict Mendiola TibeNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing PDFDocument15 pagesPediatric Nursing PDFAte Icé100% (4)
- Essential Immediate Newborn CareDocument33 pagesEssential Immediate Newborn CareShenaNo ratings yet
- MCN 2Document13 pagesMCN 2Peter Angelo GeleraNo ratings yet
- Vital-Signs 042951Document37 pagesVital-Signs 042951alyssaburgos02No ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument21 pagesCerebral Palsysuryakoduri93% (14)
- Care of The Newborn: By: Myra DG. Angeles, RN, MANDocument44 pagesCare of The Newborn: By: Myra DG. Angeles, RN, MANMyra De Guzman AngelesNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn Care: Fluid (Green Amniotic Fluid) ) To Prevent AspirationDocument17 pagesEssential Newborn Care: Fluid (Green Amniotic Fluid) ) To Prevent AspirationthadzamingNo ratings yet
- Apgar Scoring Description: 2 Points 1 Point 0 Points Point/SDocument6 pagesApgar Scoring Description: 2 Points 1 Point 0 Points Point/SksjsellsNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NursingDocument18 pagesPediatric NursingEinjel Pearl100% (1)
- 04 Pediatric Basic Life SupportDocument2 pages04 Pediatric Basic Life Supportbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Bec Quick CardsDocument14 pagesBec Quick CardsUmidagha BaghirzadaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Case StudyDocument21 pagesPediatric Case StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Date/Schedule Activities Expected Output Verified/Checked by Area in ChargeDocument2 pagesDate/Schedule Activities Expected Output Verified/Checked by Area in ChargeJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Leadership and Management RLEDocument4 pagesNCM 107 Leadership and Management RLEJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- GC ncp1 and 2Document4 pagesGC ncp1 and 2Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Union Christian College School of Health and Sciences City of San Fernando La UnionDocument11 pagesUnion Christian College School of Health and Sciences City of San Fernando La UnionJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument11 pagesNCPsJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Lung Cancer)Document10 pagesDRUG STUDY (Lung Cancer)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Online LectureDocument9 pagesOnline LectureJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Ventilation AssistanceDocument3 pagesSubjective: Ventilation AssistanceJobelle Acena100% (2)
- Nursing: Core Values of NursingDocument14 pagesNursing: Core Values of NursingJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Er Drugs StudyDocument80 pagesEr Drugs StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Pulmonary EmbolismDocument12 pagesCase Study On Pulmonary EmbolismJobelle Acena100% (3)
- Case Study (Preeclampsia)Document6 pagesCase Study (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- PHARMAfdDocument7 pagesPHARMAfdJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- EsrdcasestudyDocument43 pagesEsrdcasestudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Obstetrics: Normal Labor (Theories of Labor Onset)Document22 pagesNotes On Obstetrics: Normal Labor (Theories of Labor Onset)Jobelle Acena100% (1)
- Diabetes Type 2Document45 pagesDiabetes Type 2Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Appendicitis)Document14 pagesDRUG STUDY (Appendicitis)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Pe)Document15 pagesDrug Study (Pe)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Third Year Child Health Nursing 02-17Document16 pagesThird Year Child Health Nursing 02-17Nosy ParkerNo ratings yet
- Role of Transesophageal Echocardiography (Tee) in Cardiac SurgeryDocument35 pagesRole of Transesophageal Echocardiography (Tee) in Cardiac SurgeryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Syndromic Tetralogy of Fallot - A Case ReportDocument1 pageSyndromic Tetralogy of Fallot - A Case ReportArisyi Sunu PradonoNo ratings yet
- MCCQE PediatricsDocument80 pagesMCCQE PediatricsDrSheika Bawazir100% (2)
- Singkatan Diagnosa A-ZDocument23 pagesSingkatan Diagnosa A-ZElisabeth AnitaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DisordersDocument182 pagesPediatric DisordersErnesto Trinidad Jr RN83% (6)
- MDS-6-Mock-exam-QAE - Unlocked FINALDocument70 pagesMDS-6-Mock-exam-QAE - Unlocked FINALSubhashNo ratings yet
- Surgery Unas N We Red Without GapsDocument64 pagesSurgery Unas N We Red Without GapsSnkita RahaNo ratings yet
- DR - Azad A Haleem AL - Brefkani: University of Duhok Faculty of Medical Science School of Medicine Pediatrics DepartmentDocument58 pagesDR - Azad A Haleem AL - Brefkani: University of Duhok Faculty of Medical Science School of Medicine Pediatrics DepartmentGomathi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing 4Document106 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing 4Vin Santos33% (3)
- Anesthesia For Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument59 pagesAnesthesia For Congenital Heart DiseaseAndika Ahadyat Lukman Wiriaatmaja100% (1)
- Tetralogy of Fallot.......Document7 pagesTetralogy of Fallot.......Sam AlipioNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Residen CardioDocument13 pagesContoh Soal Residen CardioLusyAlwiNo ratings yet
- Kothari 1992Document5 pagesKothari 1992Intan Robi'ahNo ratings yet
- High Risk NewbornDocument8 pagesHigh Risk NewbornAngela Del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Tof Care PlanDocument4 pagesTof Care Plankayal67% (12)
- MCN 2Document106 pagesMCN 2Nicole Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiac Disorders 2018 StudentDocument47 pagesPediatric Cardiac Disorders 2018 Studentddowdy6737No ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument26 pagesTetralogy of FallotGI SanadaNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesTetralogy of Fallottinsilog100% (1)
- Pbl3b End of Year SolvedDocument63 pagesPbl3b End of Year Solvedmedaaaf1No ratings yet
- (UpToDate) Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis of Tetralogy of FallotDocument27 pages(UpToDate) Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis of Tetralogy of FallotNhựt Ý Nguyễn PhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cath NotesDocument21 pagesCardiac Cath NotesNaseeb UllahNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument9 pagesQuestionsDennis Dane AngelesNo ratings yet