Biology
Biology
Uploaded by
dinnielCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology
Biology
Uploaded by
dinnielCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Biology
Biology
Uploaded by
dinnielCopyright:
Available Formats
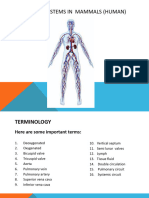
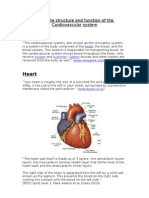
The heart is a hollow muscular organ located at the thoracic cavity.
This organ pumps blood
throughout the body.
Parts of the Heart
1. Right atrium- this chamber receives deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body.
2. Tricuspid valve- the valve that separates the right atrium from the right ventricle.
3. Right ventricle- this chamber pumps deoxygenated blood towards the pulmonary circuit.
4. Pulmonary semilunar valve- this valve opens to the pulmonary artery.
5. Pulmonary artery- carries deoygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
6. Pulmonary vein- returns oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
7. Left atrium- this chamber receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
8. Bicuspid valve- this valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle.
9. Left ventricle- this chamber pumps oxygenated blood towards the systemic circuit.
10. Aortic semilunar valve- this valve opens to the aorta.
11. Aorta-carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
12. Superior vena cava- returns deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body.
13. Inferior vena cava- returns deoxygenated blood from the lower part of the body.
14. Septum- this separates the left and right atria and the left and right ventricles.
15. Coronary artery- this supplies oxygenated blood to the heart muscle.
16. Coronary vein- this returns deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle to the right atrium.
17. Myocardium- this membrane surrounds the heart and protects it from outside pressure.
18. Sinoatrial node- this node is located in the right atrium and sets the pace of heart beat.
Blood flow through the heart
Blood from different parts of the body returns to the heart via the superior vena cava and
inferior vena cava. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps the blood
towards the right ventricle. The tricuspid valve prevents backflow towards the right atrium. The right
ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the pulmonary circuit. Blood passes through the pulmonary
semilunar valve to the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery delivers deoxygenated blood to the
lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs brings oxygen into the blood. This blood is then carried by the
pulmonary veins back to the heart. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and is
pumped into the left ventricle. The bicuspid valve prevents backflow into the left atrium. The left
ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the systemic circuit. Blood passes through the aortic semilunar
valve into the aorta. The aorta then delivers oxygenated blood to different parts of the body.
Arteries, veins and capillaries
Arteries deliver oxygen- rich blood from the heart to the body. Arteries branch out into smaller
arterioles and end up in the capillaries. It is in the capillaries where gas and nutrient exchange takes
place. Oxygen and nutrients from the blood diffuse through the capillary wall into surrounding tissue.
Waste products and carbon dioxide diffuse through the capillary wall into the blood in order to be
excreted. Blood from the capillaries exits through the venules, then, the venules merge into larger
veins. Veins carry oxygen- poor blood from the body and return the blood to the heart.]
Systolic pressure is the pressure in the arteries during ventricular systole; it is the highest
pressure in the arteries
Diastolic pressure is the pressure in the arteries during diastole; it is lower than systolic pressure
A pulse is the rhythmic bulging of artery walls with each heartbeat
Regulation of Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is determined by cardiac output and peripheral resistance due to constriction of
arterioles
Vasoconstriction is the contraction of smooth muscle in arteriole walls; it increases blood
pressure
Vasodilation is the relaxation of smooth muscles in the arterioles; it causes blood pressure to fall
Blood pressure is generally measured for an artery in the arm at the same height as the heart
Blood pressure for a healthy 20 year old at rest is 120 mm Hg at systole and 70/80 mm Hg at
diastole
You might also like
- Glossary of The Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesGlossary of The Circulatory SystemSandra GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardio Vascular SystemguptaasitNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Systemurooj100% (2)
- W.G. Igcse Transport in HumansDocument20 pagesW.G. Igcse Transport in Humansbloodshooter1996No ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument6 pagesCirculatory07mahmadkhan007No ratings yet
- Structure of Heart To SendDocument12 pagesStructure of Heart To SendlaibahundekarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryDocument73 pagesCardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryAparna RamachandranNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument11 pagesThe HeartElisa TapalesNo ratings yet
- Transport in HumanDocument12 pagesTransport in Humanahmedwessam66No ratings yet
- Cardiovascularsystem 090820055728 Phpapp02Document75 pagesCardiovascularsystem 090820055728 Phpapp02muhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- CNCQ Basic Reading Chapter 7Document10 pagesCNCQ Basic Reading Chapter 7Thiện NguyễnNo ratings yet
- BMICCT 102 Cardio Vascular System SUJOY TONTUBAYDocument11 pagesBMICCT 102 Cardio Vascular System SUJOY TONTUBAYSujoy TontubayNo ratings yet
- How The Normal Heart WorksDocument4 pagesHow The Normal Heart Worksnobhegrace.pinoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesDocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesELYANNo ratings yet
- Minggu 13 Peredaran DarahDocument11 pagesMinggu 13 Peredaran Darahcuksam27No ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesThe Circulatory SystemKami SookramNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System NotesDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System NotesMeleen ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- CirculatorySystem 3Document5 pagesCirculatorySystem 3Khoman SahuNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument6 pagesFetal Circulationkc-orense-1005100% (1)
- Group 6 "Circulatory System" Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesGroup 6 "Circulatory System" Circulatory SystemMitchelGramaticaNo ratings yet
- SystemDocument63 pagesSystemBeth Rubin RelatorNo ratings yet
- The Body and It's Systems - Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Body and It's Systems - Circulatory SystemosunfisanayomideNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Our Heart BeatsDocument7 pagesOur Heart BeatsferyNo ratings yet
- Topic 12. Circulatory System AutosavedDocument25 pagesTopic 12. Circulatory System AutosavedJanine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System P2Document17 pagesThe Circulatory System P2Kristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 2nd EditionDocument12 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 2nd EditionMoabi KeitirangNo ratings yet
- Heart and Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesHeart and Circulatory SystemJesson CabantogNo ratings yet
- Heart and Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesHeart and Circulatory SystemBryent GawNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemDaniel PancuNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Anatomy and Physiology of Heart: Submitted By: Submitted To: Jayita Gayen Madam S. PoddarDocument10 pagesAssignment On Anatomy and Physiology of Heart: Submitted By: Submitted To: Jayita Gayen Madam S. PoddarJayita Gayen DuttaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Recitation AnatomyDocument7 pagesRecitation AnatomyKent JuguilonNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System IsDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System IsKieth ObaobNo ratings yet
- GIDB4288666-Circulatory System NotesDocument6 pagesGIDB4288666-Circulatory System Notessky moonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology - Dra. ValerioDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Physiology - Dra. ValerioAlexandra Duque-David100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology ASCVDDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ASCVDAlvheen JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument32 pagesCardiovascular SystemAugustus Alejandro ZenitNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Blood and Cardiovascular System AwkaDocument80 pagesBlood and Cardiovascular System AwkaKcNo ratings yet
- Ch 11 Cardiovascular System 160217162530 (1)Document94 pagesCh 11 Cardiovascular System 160217162530 (1)raidoyel06No ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument15 pagesBiology ProjectNOT OPNo ratings yet
- Term 4Document40 pagesTerm 4thatolebelo9No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- Cardio-Respiratory System A&PDocument4 pagesCardio-Respiratory System A&Pbayoagunbiade0No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Cardiac SystemDocument18 pagesCardiac Systemviduship322No ratings yet
- HeartDocument9 pagesHeart..........No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Transport in Animals NotesDocument62 pagesIGCSE Biology Transport in Animals NotesSir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory System Systemleah rualesNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Agriscience 332 Animal Science #8646-A TEKS: (C) (2) (A) and (C) (2) (B)Document111 pagesThe Circulatory System: Agriscience 332 Animal Science #8646-A TEKS: (C) (2) (A) and (C) (2) (B)brdaisyNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument22 pagesCardio Vascular SystemdeborahNo ratings yet
- Heart and Circulatory System - Female VoiceDocument2 pagesHeart and Circulatory System - Female VoiceMeily ChandraNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesThe Circulatory SystemRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Reaction Paper On The Flight From ConversationDocument1 pageReaction Paper On The Flight From ConversationdinnielNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics: I. Identify The Following Wire Splices. (20 Points)Document3 pagesFundamentals of Electricity and Electronics: I. Identify The Following Wire Splices. (20 Points)dinniel100% (1)
- Scientific Name Common Name Order: (S) Local Name(s) DistributionDocument4 pagesScientific Name Common Name Order: (S) Local Name(s) DistributiondinnielNo ratings yet
- Summative CONTEMPORARY PHILIPPINE ARTS FROM THE REGIONSDocument2 pagesSummative CONTEMPORARY PHILIPPINE ARTS FROM THE REGIONSdinnielNo ratings yet
- Musical Play Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesMusical Play Reflection PaperdinnielNo ratings yet
- Solid Mens. InterviewDocument4 pagesSolid Mens. InterviewdinnielNo ratings yet
- Sandugo SculptureDocument2 pagesSandugo SculpturedinnielNo ratings yet
- Representational Art: Benjamin West, The Death of General WolfeDocument1 pageRepresentational Art: Benjamin West, The Death of General WolfedinnielNo ratings yet
- Lang Dulay: Textile WeaverDocument1 pageLang Dulay: Textile WeaverdinnielNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Essay of PlaceDocument2 pagesDescriptive Essay of PlacedinnielNo ratings yet
- Science and Technology Education CenterDocument1 pageScience and Technology Education CenterdinnielNo ratings yet
- Bio NoteDocument2 pagesBio NotedinnielNo ratings yet
- Misdiagnose of Acute Aortic Dissection: Case ReportDocument3 pagesMisdiagnose of Acute Aortic Dissection: Case ReportAnthony SetiawanNo ratings yet
- 44th Issue-Article 177Document2 pages44th Issue-Article 177Sohil ElfarNo ratings yet
- PlebitisDocument5 pagesPlebitisIndra PutraNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument53 pagesStrokeGhinaSofianaLestari100% (1)
- Heart: Know The Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesHeart: Know The Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular Systemnbeer93No ratings yet
- Cardiology Dissertation ExamplesDocument4 pagesCardiology Dissertation ExamplesThesisPaperHelpCanada100% (2)
- Myocardial Infarction With CABG Concept MapDocument1 pageMyocardial Infarction With CABG Concept MapMaria Therese100% (1)
- Vascular Diseases: Idar Mappangara Department of Cardiology Hasanuddin UniversityDocument31 pagesVascular Diseases: Idar Mappangara Department of Cardiology Hasanuddin Universitynurliah armandNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 (7) Origin and Conduction of Cardiac ImpulsesDocument31 pagesUnit 4 (7) Origin and Conduction of Cardiac ImpulsesDINAMANI 0inamNo ratings yet
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument2 pagesAortic RegurgitationJustine CastilloNo ratings yet
- MSN Exam For Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure RNpediaDocument21 pagesMSN Exam For Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure RNpedia20-08249No ratings yet
- 10 - Arterial Blood PressureDocument33 pages10 - Arterial Blood Pressurehizmaaeniy5No ratings yet
- 4 Mezil & Abed, 2021 Review - Complication of Diabetes MellitusDocument12 pages4 Mezil & Abed, 2021 Review - Complication of Diabetes Mellitusbangd1f4nNo ratings yet
- 2015 Akutni Koronarni SindromDocument98 pages2015 Akutni Koronarni SindromIvanMihailovicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 KeyDocument17 pagesChapter 9 KeySrinu WestNo ratings yet
- Small Animal Cardiology Auscultation - Vet VisionsDocument1 pageSmall Animal Cardiology Auscultation - Vet Visionsyuaifafa25No ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Osypka AesculonDocument2 pagesSpesifikasi Osypka AesculonAnonymous xF8fv4OYCgNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Document27 pagesCirculatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Pranati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument7 pagesAbdominal Aortic AneurysmShaastieNo ratings yet
- The Heart III - Chapter 19 Case StudyDocument5 pagesThe Heart III - Chapter 19 Case StudyBrad ConnersNo ratings yet
- Vascular Anatomy and Blood Supply To The Femoral Head: Marcin Zlotorowicz and Jaroslaw CzubakDocument8 pagesVascular Anatomy and Blood Supply To The Femoral Head: Marcin Zlotorowicz and Jaroslaw CzubakAzmi FarhadiNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Aspects of The Fontan PatientDocument69 pagesAnesthetic Aspects of The Fontan PatientdavidmontoyaNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Cardiac Cycle - Educational Game PDFDocument9 pages2018 - Cardiac Cycle - Educational Game PDFashraf alaqilyNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Sympo Edit1Document3 pagesJadwal Sympo Edit1reyNo ratings yet
- 214: Pharmacology and Venipuncture: Lesson 1Document24 pages214: Pharmacology and Venipuncture: Lesson 1Stephanie Marie Mendoza100% (1)
- Blood Pressure - WikipediaDocument3 pagesBlood Pressure - WikipediaGirish Chandra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure With Normal Ejection Fraction (HFNEF)Document64 pagesHeart Failure With Normal Ejection Fraction (HFNEF)medpedshospitalist100% (1)
- DR Mustika Mahbubi SPJP FIHA-How To Treat Acute Coronary Sydrome (STEMI Patient) in Pre and Post HospitalDocument59 pagesDR Mustika Mahbubi SPJP FIHA-How To Treat Acute Coronary Sydrome (STEMI Patient) in Pre and Post HospitalHiszom AsyhariNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Arterial Occlusive DiseaseDocument43 pagesPeripheral Arterial Occlusive DiseaseadystiNo ratings yet
- Basic EKG For DummiesDocument133 pagesBasic EKG For Dummieseduardocmoura88% (8)