PneumoniaSystem Disorder
PneumoniaSystem Disorder
Uploaded by
AA DDCopyright:
Available Formats
PneumoniaSystem Disorder
PneumoniaSystem Disorder
Uploaded by
AA DDOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
PneumoniaSystem Disorder
PneumoniaSystem Disorder
Uploaded by
AA DDCopyright:
Available Formats
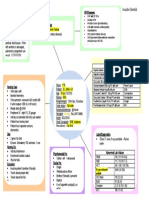
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System Disorder
STUDENT NAME______________________________________
acute respiratory disorder
DISORDER/DISEASE PROCESS___________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER____________
Alterations in Pathophysiology Related Health Promotion and
Health (Diagnosis) to Client Problem Disease Prevention
an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs.
Pneumonia with copd The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus , causing cough with wash hands, eat right, get adequate
phlegm or pus, fever, chills, & difficulty breathing. A variety amount of sleep, exercise, stay from
of organisms, including bacteria, viruses & fungi, can sick people, quit smoking/2nd hand
cause pneumonia
smoke
ASSESSMENT SAFETY
CONSIDERATIONS
Risk Factors Expected Findings -droplet isolation
-Having a weakened immune system anxiety, fatigue, weakness, chest for patient
-Being hospitalized or being on a ventilator discomfort due to coughing, confusion -position of bed for
-Having a chronic condition including asthma, from hypoxia is the most common
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, manifestation of this disease in older
maximum
structural lung disease and heart disease.
adults ventilation
-Smoking or 2nd hand smoking -regularly check
O2 to make sure
pt can breathe
Laboratory Tests Diagnostic Procedures adequately
-Sputum culture -chest xray: will show density of -risk for aspiration
-CBC:elevated wbc count(infection)
-ABGs:hypoxemia lung tissue
-Blood culture: to rule out organisms in the blood -Pulse Ox: pt will usually have less
electrolytes: to identify manifestations of dehydration
than expected range of 95-100%
PATIENT-CENTERED CARE Complications
Nursing Care Medications Client Education -Atelectasis:
continue meds for treatment of
airway
-position pt for max vantilation -Antibiotics: given
(high-Fowlers), encourage coughing to destroy the disease, rest as needed, maintain inflammation &
admin breathing treatments & hand hygiene, avoid crowded areas edema can lead to
medications, admin O2 & assess skin infectious for risk of infection, discontinue use of
breakdown from method, promote pathogens tobacco, obtain vaccinations for alveolar collapse
nutrition & fluid intake, rest periods -Bronchodilators: influenza & pneumonia, drink fluids to & increase risk of
thin the mucus
given to reduce hypoxemia
bronchospasms &
reduce irritation
-Bacteremia
(sepsis): occurs if
Therapeutic Procedures -Anti-inflammatorie Interprofessional Care
s: decrease airway pathogens enter
-medications (antibiotics, inflammation -respiratory services: for inhalers, the bloodstream
-Antipyretic: breathing treatments, suctioning
cough medicine, inhaler, -nutrition: consulted for weight loss from the infection
reduces fever
antipyretic) -rehab: consulted if pt has in the lungs
-position in bed prolonged weakness & needs -Acute respiratory
assistance with increase of ADL
-breathing treatment distress syndrome
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
You might also like
- Community Health Nursing Examination Part IDocument17 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Examination Part Iɹǝʍdןnos97% (65)
- Keith RN Asthma Case StudyDocument16 pagesKeith RN Asthma Case StudyCHARLES MAINANo ratings yet
- System Do CopdDocument1 pageSystem Do CopdMarissa Hamby100% (2)
- Small Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderDocument1 pageSmall Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderMarina Wasem Netzlaff0% (1)
- System Disorder - Cystic FibrosisDocument1 pageSystem Disorder - Cystic Fibrosisjorge herreraNo ratings yet
- Concept Map HypertensionDocument1 pageConcept Map Hypertensiongeorge pearson0% (1)
- System Disorder: Renal CalculiDocument1 pageSystem Disorder: Renal CalculiHolly DeckelmanNo ratings yet
- System Disorder CP CLDocument1 pageSystem Disorder CP CLSariahNo ratings yet
- Acute PainDocument1 pageAcute Painnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- History and Physical Report SampleDocument2 pagesHistory and Physical Report SampleloisebadNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesPneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaGayle MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug Card TemplateDocument1 pageDrug Card TemplatePcc100No ratings yet
- Nurses Note DONEDocument1 pageNurses Note DONEjhenssineNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Drug CardsDocument5 pagesWeek 13 Drug CardsPRECIOUS wardNo ratings yet
- Template For NURSING NotesDocument2 pagesTemplate For NURSING Notesbngraham4No ratings yet
- Patient Assessment Marking SheetDocument2 pagesPatient Assessment Marking SheetJim Courtney100% (4)
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument1 pagePeptic Ulcer DiseaseEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Soap TemplateDocument3 pagesSoap TemplaterohitNo ratings yet
- Common Asthma MedicationsDocument1 pageCommon Asthma MedicationsHeart of the Valley, Pediatric CardiologyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Meds To MemorizeDocument4 pagesCardiac Meds To MemorizekellyaeNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors Pathophysiology Concept Potential ComplicationsDocument1 pageRisk Factors Pathophysiology Concept Potential ComplicationsiamdarnNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument44 pagesFundamentals of NursingAilene Ponce Fillon100% (1)
- Coumadin Dosing GuideDocument3 pagesCoumadin Dosing Guidemorale28No ratings yet
- Concept Map Et Al 11-04-15Document7 pagesConcept Map Et Al 11-04-15api-353656227No ratings yet
- Refrigerate: Hives, RashDocument5 pagesRefrigerate: Hives, RashstarobinNo ratings yet
- Waiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFTommieNo ratings yet
- PEEP Positive End Expiratory Pressure and Its ConsequencesDocument2 pagesPEEP Positive End Expiratory Pressure and Its ConsequencesSadiq ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Notes Full Document 2Document433 pagesPathophysiology Notes Full Document 2Feven Abraham100% (1)
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument3 pagesHead To Toe Assessmentsandaman2225No ratings yet
- 6 Nursing Assessment MnemonicsDocument4 pages6 Nursing Assessment MnemonicsEunice Angela FulguerasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNursing Cheat Sheetramesh kumarNo ratings yet
- 8.cardiovascular SystemDocument13 pages8.cardiovascular Systempodki gurungNo ratings yet
- CHF Concept MapDocument1 pageCHF Concept MapChristy Wegner Cooper100% (4)
- Drug CardDocument2 pagesDrug CardHannahNo ratings yet
- NUR 317L Head-to-Toe Assessment 8 NUR 317L Head-to-Toe Assessment 8Document4 pagesNUR 317L Head-to-Toe Assessment 8 NUR 317L Head-to-Toe Assessment 8Mary LowryNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Nursing Clinical-Concept Map-2Document3 pagesMedSurg Nursing Clinical-Concept Map-2adaezeNo ratings yet
- ABG Compensation InterpretationDocument2 pagesABG Compensation InterpretationLauren MarieNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisAkasha FrostmourneNo ratings yet
- Normal Breath SoundsDocument1 pageNormal Breath Soundsyanks1120No ratings yet
- 0 - Cece's Study Guides Part 2Document25 pages0 - Cece's Study Guides Part 2SoruyorNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideDocument15 pagesNursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nursing PharmacologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Nursing PharmacologyJon Adam Bermudez SamatraNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors 6Document10 pagesAce Inhibitors 6api-316574434No ratings yet
- Assessment Info NotesDocument3 pagesAssessment Info NotesDiana Decker100% (1)
- Patient Medication Reconciliation Form SampleDocument1 pagePatient Medication Reconciliation Form SampleMohammed HaiderNo ratings yet
- Clinical Replacement Student Packet-2Document12 pagesClinical Replacement Student Packet-2ida50% (2)
- Critical Thinking Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCritical Thinking Cheat SheetRebecca PughNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument96 pagesDrug StudyirismirzigNo ratings yet
- TMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Document5 pagesTMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Theresa Fernandez Mendoza0% (1)
- Physical Examinations Respiratory System: InspectionDocument5 pagesPhysical Examinations Respiratory System: InspectionAzizan HannyNo ratings yet
- Student Name:: Clinical Week #: Clinical InstructorDocument5 pagesStudent Name:: Clinical Week #: Clinical InstructorSusan BensonNo ratings yet
- Drug Card Week 2Document4 pagesDrug Card Week 2stacylynnschmidt8No ratings yet
- Sepsis Pathophysiology Cheat Sheet 2 September 13 2018 Fall 2018 PDFDocument2 pagesSepsis Pathophysiology Cheat Sheet 2 September 13 2018 Fall 2018 PDFsophia onuNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe Physical AssessmentDocument6 pagesHead To Toe Physical AssessmentGarrett BatangNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Hesi Pharmacology Test Bank 2018 RN V2 14 Total QuestionsDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Hesi Pharmacology Test Bank 2018 RN V2 14 Total QuestionsCrystal B Costa78No ratings yet
- Patho PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPatho PhysiologyMarion Liana DayritNo ratings yet
- Fluids Electrolytes Visual NotesDocument8 pagesFluids Electrolytes Visual NotesVin Lorenzo CampbellNo ratings yet
- MEDSURG 1 NotesDocument43 pagesMEDSURG 1 NotesNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- How to Succeed New Graduate Nursing Job Interview & Bachelor of Nursing Clinical Placement?From EverandHow to Succeed New Graduate Nursing Job Interview & Bachelor of Nursing Clinical Placement?No ratings yet
- Complicated Community Acquired Pneumonia Clinical PathwayDocument14 pagesComplicated Community Acquired Pneumonia Clinical PathwayFaisalMuhamadNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin 2010 11 45 PdARDocument29 pagesClarithromycin 2010 11 45 PdARswabrijNo ratings yet
- Science Unit 1 7TH JDocument2 pagesScience Unit 1 7TH JHafiz Danish Rehman RanaNo ratings yet
- Final Death Note - Compre NotesDocument1,550 pagesFinal Death Note - Compre NotesSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- ParamyxoviridaeDocument27 pagesParamyxoviridaeFarrah BenoitNo ratings yet
- July 2011 Nurse Licensure Examination Result July 2011 Nurse Board Exam ResultDocument28 pagesJuly 2011 Nurse Licensure Examination Result July 2011 Nurse Board Exam ResultDarren FloresNo ratings yet
- Lung Disease: PneumoniaDocument2 pagesLung Disease: Pneumoniacayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- #2. Respiratory SymptomsDocument43 pages#2. Respiratory SymptomsDr-i Barre100% (1)
- Pneumonia Detection Using Deep LearningDocument6 pagesPneumonia Detection Using Deep Learningmainproject967No ratings yet
- Meningitis and Encephalitis: PGI Roddame Angelo ErispeDocument100 pagesMeningitis and Encephalitis: PGI Roddame Angelo ErispeAngelo ErispeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsDr-Sanjay Singhania100% (7)
- Pharmacology Notes 201Document49 pagesPharmacology Notes 201Glaren HamiliNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Healthcare c19 GuidanceDocument54 pagesAshrae Healthcare c19 GuidanceKazuto KawakitaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis SepticemiaDocument13 pagesSepsis Septicemiamardsz100% (11)
- Slow Contact Tracing' Blamed For Spread of New CoronavirusDocument6 pagesSlow Contact Tracing' Blamed For Spread of New CoronavirusProdigal RanNo ratings yet
- 个人陈述:我的生物医学工程之旅Document7 pages个人陈述:我的生物医学工程之旅v1f1bosah1k2No ratings yet
- Pyothorax / Purulent Pleuritis / Empyema Thoracis: Prepared By: Sharmin SusiwalaDocument22 pagesPyothorax / Purulent Pleuritis / Empyema Thoracis: Prepared By: Sharmin SusiwalaAnkan Dey100% (2)
- Agas - Case No4 - Sec18Document2 pagesAgas - Case No4 - Sec18Maxine AgasNo ratings yet
- Candidates Mcqs Pathology Week 11: 1 JF A BDocument3 pagesCandidates Mcqs Pathology Week 11: 1 JF A Bمجتبى علي0% (1)
- Infections Diseases MRCP Crib Sheet by Law and MedicineDocument33 pagesInfections Diseases MRCP Crib Sheet by Law and MedicineMatin Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- CHN ExamDocument35 pagesCHN ExamYessamin Paith RoderosNo ratings yet
- Peri-Operative QuestionsDocument8 pagesPeri-Operative QuestionsHersheys AbellaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Clinical Features of Pulmonary Histoplasmosis - UpToDateDocument25 pagesPathogenesis and Clinical Features of Pulmonary Histoplasmosis - UpToDatemihaela popescuNo ratings yet
- EXAM 3 20210405 C11 NUR310G.C Health Assessment PDFDocument37 pagesEXAM 3 20210405 C11 NUR310G.C Health Assessment PDFCeciliaNo ratings yet
- IMCI Flip ChartDocument30 pagesIMCI Flip ChartChrizelle Esperanzate Florentino50% (2)
- Management of AIDS-Related Opportunistic Infections IDocument53 pagesManagement of AIDS-Related Opportunistic Infections IRaniNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy and Diagnostic ToxicologyDocument83 pagesChemotherapy and Diagnostic ToxicologySunilNo ratings yet
- 2005 Idsa Ats Hospital Acquired Pneumonia GuidelinesDocument8 pages2005 Idsa Ats Hospital Acquired Pneumonia GuidelinesAlejandro CasillasNo ratings yet