Assignment Notes
Uploaded by
Natasha TegelaarAssignment Notes
Uploaded by
Natasha Tegelaar1.
Discuss your assessments on this patient, identify signs of deterioration and clearly state if the
patient requires a clinical review or rapid response as per Between the Flags (BTF). Justify your
decision with data from the case and relevant support.
Objective & subjective data
Decreased mobility
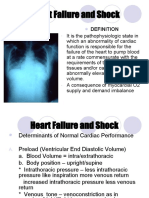
Heart failure
Swelling on knees – few days
SOB
Speak in short sentences
Increase work of breathing
intercostal recession and crackles at the lung bases (reasoning and justify back to the HF)
Warm to touch, diaphoretic
Pink
Capaillary refill – less then 2 seconds
passed urine in shower
BGL 6.4 MMOL
History: Acute kidney failure due to heart failure
Findings
Pt is in respiratory failure.
breathlessness resting and active ( Tachypnea - High respiration rate) Normal respiration 12-20 over
a minute. In conjunction with other evidence such (shortness of breath - dyspnea, speaking in short
sentences, exhaustion / fatigue, diaphoretic, increase in accessory muscles). = Acute respiratory failure
(link evidence back to heart failure) = damaged heart cannot pump blood as effectively from
your lungs out to your body. Blood backs up, raising pressure in the veins inside your lungs. This
pushes fluid into your air sacs. As liquid builds up, it gets harder to breathe. Pt could also be anemia or
developing chest infection or possible pneumonia
BP: 182/102 – Hypertensive ( a systolic BP of 130mmHh or higher, or dialostic pressure of 80mmHg
or higher is considered as hypertension. It is increasing the workload on the heart inducing structural
and functional changes in myocardium progressing to heart failure. Acute Kidney failure could be
having an impact on the BP as it changes the way the kidneys handle salt resulting in hypertension.
Low oxygen sats 88% is considered Hypoxic. With HF, the heart muscle might be weaker and not
pump blood the way is normally would resulting in the body not receiving the oxygen it requires.
Supplemental Oxygen therefore should be commenced.
If the heartbeat is very fast, known as tachycardia, there is less time for the heart chamber to fill with
blood between beats.
swelling of the knees (Peripheral oedema) – heart is not pumping efficiently, which can lead to a
build up of fluid. Oedema is one of the fundamental features of heart failure.
You might also like
- Natasha Tegelaar 220197803 HSNS246 Assignment1No ratings yetNatasha Tegelaar 220197803 HSNS246 Assignment17 pages
- HSNS273 Integrated Nursing Practice - LRNo ratings yetHSNS273 Integrated Nursing Practice - LR14 pages
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manualpdf download100% (1)Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manualpdf download32 pages
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual pdf download100% (3)Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual pdf download46 pages
- Get Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual free all chapters100% (32)Get Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual free all chapters38 pages
- Access Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual All Chapters Immediate PDF Download100% (4)Access Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual All Chapters Immediate PDF Download43 pages
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual - Download Today For Unlimited ReadingNo ratings yetMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual - Download Today For Unlimited Reading36 pages
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual instant download100% (2)Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual instant download47 pages
- Case Presentation On "Congestive Heart Failure" General ObjectiveNo ratings yetCase Presentation On "Congestive Heart Failure" General Objective7 pages
- Cardio Lecture Notes: Congestive Heart Failure100% (5)Cardio Lecture Notes: Congestive Heart Failure7 pages
- Subjective: Fully Met If:: Short Term ObjectiveNo ratings yetSubjective: Fully Met If:: Short Term Objective4 pages
- Heart Failure and Rheumatic Heart DieaseNo ratings yetHeart Failure and Rheumatic Heart Diease28 pages
- 0 No Musc. Contrac'n, 1-Visible Musc. Con W/no or Trace Movement, 2-Limb Movmnt But Not AgaistNo ratings yet0 No Musc. Contrac'n, 1-Visible Musc. Con W/no or Trace Movement, 2-Limb Movmnt But Not Agaist7 pages
- Nursing Care of CHF (Congestive Heart Failure)100% (2)Nursing Care of CHF (Congestive Heart Failure)25 pages