F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center
F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center
Uploaded by
Ave de GuzmanCopyright:
Available Formats
F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center
F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center
Uploaded by
Ave de GuzmanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center
F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center
Uploaded by
Ave de GuzmanCopyright:
Available Formats
F.A.L.
CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER
2ND Floor, Cartimar Building, C.M. Recto Avenue, Quiapo, Manila
Contact Number/s: 0995-351-7556; 0945-734-3928
Handout Exam – STATICS 5. In the angular motion amplifier shown, the oscillatory motion
Prepared by: Engr. Francis Arjay Pastores Luz of AC is amplified by the oscillatory motion of BC. Neglecting
friction and the weights of the members, determine the output
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose the letter that corresponds to your torque C0, given that the input torque is 36 N.m.
answer. Write the letter of your answer on the answer sheet
provided.
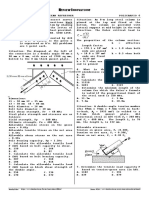
1. The three flat blocks are positioned on the 30° incline as
shown, and a force P parallel to the incline is applied to the
middle block. The upper block is prevented from moving by a
wire which attaches it to the fixed support. The coefficient of
static friction for each of the three pairs of mating surfaces is
shown. Determine the maximum value which P may have
before any slipping takes place. a. 24 N.m c. 28 N.m
b. 18 N.m d. 12 N.m
6. A vertical force P exerted on lever AB holds the weight 250 N
from falling, as shown. The coefficient of friction between the
lever and the 200-mm drum is 0.3. Determine the vertical force
P to hold the weight. Neglect the weight of the drum and the
lever.
a. 103.1 N c. 93.8 N
b. 112.6 N d. 121.7 N
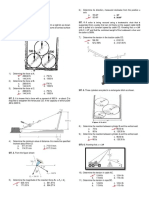
2. The 700-N force is applied to the 100-kg block, which is
stationary before the force is applied. Determine the magnitude a. 481.23 N c. 571.43 N
and direction of the friction force F exerted by the horizontal b. 208.45 N d. 681.74 N
surface on the block.
7. Determine the largest mass of cylinder A that can be
supported from the drum if a force P = 20 N is applied to the
handle of the lever. The coefficient of static friction between the
belt and the wheel is 0.3. The drum is pin supported at its center,
B.
a. 378.6 N c. 784.8 N
b. 588.6 N d. 504.8 N
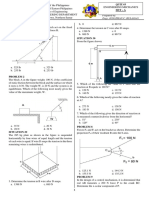
Situation. The light bar is used to support the 50-kg block in its
vertical guides. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.30 at the
upper end of the bar and 0.40 at the lower end of the bar, a. 1527.24 N c. 1341.56 N
b. 345.56 N d. 1236.47 N
8. From the given system of parallel forces, determine the
resultant and its location from the y-axis.
3. find the friction force acting at each end for x = 75 mm.
a. 133.1 N c. 126.6 N
b. 142.6 N d. 111.7 N a. 5.25 m c. 3.56 m
b. 6.23 m d. 4.27 m
4. find the maximum value of x for which the bar will not slip.
a. 86.2 mm c. 92.3 mm 9. From the truss shown. The value of P = 100 kN, determine the
b. 102.3 mm d. 113.4 mm forces on members AB and BC.
F.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER
2ND Floor, Cartimar Building, C.M. Recto Avenue, Quiapo, Manila
Contact Number/s: 0995-351-7556; 0945-734-3928
a. 75 kN c. 100 kN
b. 66.67 kN d. 50 kN
10. Two forces, 80N and 100N acting at an angle of 60° with each
other, pull on an object. What is the resultant force on an object?
a. 178.23 N c. 156.20 N 14. Determine the internal moment at B.
b. 123.45 N d. 141.81 N a. 3.12 kip.ft c. 4.26 kip.ft
b. 2.80 kip.ft d. 5.21 kip.ft
Situation. The section shown is used as a compression member
15. Determine the shear at B.
supported by a pin at both ends. If the length of the
a. 800 lb c. 960 lb
compression member is fy = 276 MPa:
b. 530 lb d. 720 lb
11. Determine the product of inertia of the section with respect
to its centroidal axes.
a. -1,619,504 𝑚𝑚4 c. -2,639,526 𝑚𝑚4
PART II – PROBLEM SOLVING
b. 3,629,541 𝑚𝑚4 d. 1,324,504 𝑚𝑚4
INSTRUCTIONS: Solve the following problems. Write your
12. Which of the following most nearly gives the maximum answers on the answer sheet provided.
moment of inertia of the section?
a. 5,279,464 𝑚𝑚4 c. -2,639,526 𝑚𝑚4 1. Find the tension on a wire weighing 0.15kg/m stretched
b. 3,629,541 𝑚𝑚4 d. 940,178 𝑚𝑚4 between supports 30m apart with a sag of 0.06m.
13. Which of the following most nearly gives the minimum 2. Determine the largest angle 𝜃, for which the homogeneous
moment of inertia of the section? block remains at rest.
a. 5,279,464 𝑚𝑚4 c. -2,639,526 𝑚𝑚4
b. 3,629,541 𝑚𝑚4 d. 940,178 𝑚𝑚4
3. Cable ABC of length 5m supports the force W = 100 kN at B.
Determine the angles 𝛽1 and 𝛽2 . Determine also the forces in
each cable segment.
Situation: The 800 lb load is being hoisted at a constant speed
using the motor M, which has a weight of 90 lb. Determine the
resultant internal loadings acting on the cross-section through
point B in the beam. The beam has a weight of 40lb/ft and is
fixed to the wall at A.
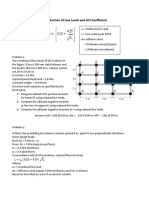
4. The water supply pipe shown is suspended from a cable
suspended from a cable using a series of closed and equally
spaced hangers. The length of the pipe supported by the cable
is 60m. The total weight of the pipe filled with water is 7KN/m.
F.A.L. CONDUCIVE ENGINEERING REVIEW CENTER
2ND Floor, Cartimar Building, C.M. Recto Avenue, Quiapo, Manila
Contact Number/s: 0995-351-7556; 0945-734-3928
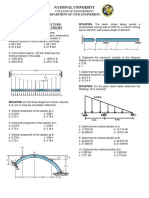
8. The tied three-hinged arch is subjected to the loading shown.
Determine the components of reaction at A and C and the
tension in the cable.
a. What is the maximum sag (m) at the lowest point of the cable
which occurs at the mid length of the allowable tensile load in
the cable is 3000KN.
b. The sag of the cable at mid length is 3m. Find the maximum
axial strength (MPa) if the cable diameter is 75mm. 9. MAY 2015 CE BOARD: Refer to the figure. Diagonals BG, CF,
c. The sag of the cable at mid length is 3m. If the allowable tensile CH, and DG are flexible cables.
load in the cable is 2000KN, how much additional load can the
cable carry?
5. (CE Board Dec. 2014)
In the Figure:
Force A = 6.0 kN
Force B = 2.4 kN
Angle β = 30 deg.
a. If the resultant of the three forces A, B, and C is 3.6 kN and it a. Determine the force on member AF.
acts along Y-axis, what is the angle θ in degrees? b. Determine the force on member FG.
b. If the resultant of the three forces A, B, and C is 5.4 kN and it
acts along Y-axis, what is the value of the force C (kN) and its 10. From the frame shown, the weight of pulley is 2 kN.
direction if angle θ is 45⁰?
Neglecting the weight of the bars.
c. If the angle θ = 60⁰ and the force C = 3kN, how much is the
resultant pulling force on the eyebolt?
6. Refer to Fig. EMS – 001. The mass of blocks A and B are 𝑚𝐴 =
30 𝑘𝑔 and 𝑚𝐵 = 50 𝑘𝑔, respectively.
a. Compute the reaction at D.
b. Determine the reaction at C.
c. Compute the angle that the reaction at A makes with the
horizontal.
a. Determine the smallest value of P to hold the blocks in
equilibrium.
b. Determine the smallest value of P to start block B to move up
the incline.
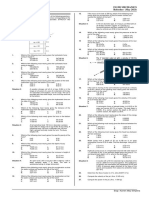
7. The uniform 50-kg plank in Fig. (a) is resting on friction
surfaces at A and B. The coefficients of static friction are shown
in the figure. If an 80-kg man starts walking from A towards B,
determine the distance x when the plank will start to slide.
You might also like
- Meralco Bill 325458600101 07272020 - 3 (3591)Document2 pagesMeralco Bill 325458600101 07272020 - 3 (3591)Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Document3 pagesCE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Meverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4Document3 pagesQuiz 4Nikki Marie G OclaritNo ratings yet
- Set ADocument12 pagesSet ADan Casurao0% (1)
- Practice Problems PDFDocument8 pagesPractice Problems PDFJea Clarie Mendioro EspinasNo ratings yet
- (Preboard Exam) : Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pages(Preboard Exam) : Multiple ChoiceNicole Rodil100% (1)
- OJT Endorsement LetterDocument1 pageOJT Endorsement LetterAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Construction of Blast FurnaceDocument90 pagesConstruction of Blast FurnacesuvraNo ratings yet
- SVC JIG Lists For Samsung Mobiles - Rev10Document37 pagesSVC JIG Lists For Samsung Mobiles - Rev10Ion PungaNo ratings yet
- Wendell Berry and The Christian Tradition: Environmental Ethics For A Postmodern AgeDocument133 pagesWendell Berry and The Christian Tradition: Environmental Ethics For A Postmodern Agerichard_klinedinst100% (2)
- Bottleneck AnalysisDocument19 pagesBottleneck AnalysisDivya S Nair100% (1)
- Sec - Forces and Principles of Equilibrium Module 00Document6 pagesSec - Forces and Principles of Equilibrium Module 00jovar jumao-asNo ratings yet
- MECHANICSDocument6 pagesMECHANICSNicole RodilNo ratings yet
- 5 Design Nov 2013 KeyDocument6 pages5 Design Nov 2013 KeyKenneth PadunanNo ratings yet
- Psad November 2022Document33 pagesPsad November 2022paisa baba100% (2)
- Policarpio 6 - Refresher SECDocument2 pagesPolicarpio 6 - Refresher SECJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 4: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Policarpio 4: Eview NnovationsKian Inductivo100% (1)
- Ce 603 Set CDocument12 pagesCe 603 Set CJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- Quiz #3 - Eng'g MechanicsDocument4 pagesQuiz #3 - Eng'g MechanicsAnthony Jay PoraqueNo ratings yet
- Tos 2Document4 pagesTos 2Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Beams Using Combined Load ApproachDocument48 pagesModule 2 Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Beams Using Combined Load ApproachVann AlfredNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 03 (M2) - Integral CalculusDocument1 pageRefresher Module 03 (M2) - Integral CalculusJessa Mae CabusNo ratings yet
- Structural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)Document4 pagesStructural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)ELMERNo ratings yet
- No Answer Eval Hydraulics Nov 2018 Set ADocument4 pagesNo Answer Eval Hydraulics Nov 2018 Set AAlthara BaldagoNo ratings yet
- Sec - PS1Document2 pagesSec - PS1Monica Amor AbengozaNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2022 - Construction PDFDocument2 pagesCE Board Nov 2022 - Construction PDFLouise CarleyNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Nov23 Hydraulics 01 06 Nov 2023Document16 pagesNov23 Hydraulics 01 06 Nov 2023Jayson Mari100% (1)
- Steel 3Document3 pagesSteel 3Mayya Bona100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines: Set - ADocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Set - AAnthony Jay PoraqueNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Design PreboardDocument9 pagesDesign PreboardReinyl Angelo Cruz100% (1)
- Mid Pre BoardDocument6 pagesMid Pre BoardJonathanNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1Document3 pagesAssignment - 1chritNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 SECDocument14 pagesPreboard 2 SECJae Han100% (1)
- Kippap-Handout-SEC (40 RCD - Footings)Document10 pagesKippap-Handout-SEC (40 RCD - Footings)top1echolocoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-Surveying-and-Transportation ProblemDocument9 pagesMathematics-Surveying-and-Transportation Problemarnie2295No ratings yet
- CE Review For April 2023 - Geotechnical Engineering 1Document4 pagesCE Review For April 2023 - Geotechnical Engineering 1Nica Sudama100% (1)
- Hge Mid PreboardDocument7 pagesHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Topics Problem Set 9 - Structural Theory (Final) 1ST Term 2020-2021Document1 pageTopics Problem Set 9 - Structural Theory (Final) 1ST Term 2020-2021Levi John Corpin AmadorNo ratings yet
- AsdfasdfasdfDocument8 pagesAsdfasdfasdfFleight Vandollin100% (1)
- EERC Fluid Mechanics Refresher May 2021Document2 pagesEERC Fluid Mechanics Refresher May 2021Chum ElbaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics EXAM ANSWEY KEYDocument3 pagesDynamics EXAM ANSWEY KEYlarry soiranoNo ratings yet
- StaticsDocument5 pagesStaticslakr lama100% (1)
- Steel Design 8 Nov 2020Document1 pageSteel Design 8 Nov 2020Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (4th Year)Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics (4th Year)Jaypee Calamba100% (1)
- RC 3Document4 pagesRC 3Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Review Module 41 RCD 1Document2 pagesReview Module 41 RCD 1Yang RhiaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 1 PDFDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials 1 PDFMaxNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Live Loads and ACI Coefficient: Structural TheoryDocument6 pagesReduction of Live Loads and ACI Coefficient: Structural TheoryAllan Añavisa Ostique Jr.No ratings yet
- Quiz No 2 - Set ADocument2 pagesQuiz No 2 - Set AMayoune Nasinopa Galvez100% (1)
- Preboard Examination 1 - Structural Engineering (Set A) : Situation 6Document4 pagesPreboard Examination 1 - Structural Engineering (Set A) : Situation 6Jaycee UyNo ratings yet
- Stdl02e Final ExamDocument6 pagesStdl02e Final ExamPaulo ValderamaNo ratings yet
- CE Board Problems in Steel DesignDocument10 pagesCE Board Problems in Steel DesignVaughn Carlisle BacayonNo ratings yet
- 2010 November CE Board ExamDocument15 pages2010 November CE Board ExamKai de LeonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledRojane FloraNo ratings yet
- RCD Reinforced Concrete Design Feu 2019Document4 pagesRCD Reinforced Concrete Design Feu 2019Josephbraken Balderama Labacanacruz100% (1)
- At 14 2Document7 pagesAt 14 2Icz Fuentes100% (1)
- Part 1 - Trigonometry and Surveying: Excel - Ri Ce Review Specialist, IncDocument4 pagesPart 1 - Trigonometry and Surveying: Excel - Ri Ce Review Specialist, IncKurapika Freccs ZoldyickNo ratings yet
- Set BDocument12 pagesSet BDan Casurao100% (1)
- Local Media3116916508017834053 2Document7 pagesLocal Media3116916508017834053 2Ben BenbenNo ratings yet
- PSAD 1 May 2 2023Document21 pagesPSAD 1 May 2 2023Renne Jude RollorataNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory Refresher SetDocument6 pagesStructural Theory Refresher SetLa BeamNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4 PSADDocument1 pageProblem Set 4 PSADJerona AyongNo ratings yet
- PSAD 4 May 5 2023Document19 pagesPSAD 4 May 5 2023Renne Jude Rollorata100% (1)
- First Assessment Exam - Correlation Ii: AB Is 2400 NDocument45 pagesFirst Assessment Exam - Correlation Ii: AB Is 2400 NAlyssa Marie AsuncionNo ratings yet
- CPM Case StudyDocument5 pagesCPM Case StudyAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- DIAGRAMDocument3 pagesDIAGRAMAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Name: Ave de Guzman Codename: PeriwinkleDocument1 pageName: Ave de Guzman Codename: PeriwinkleAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical Trigonometry (Part 1 & 2) Problem 1Document12 pagesPlane and Spherical Trigonometry (Part 1 & 2) Problem 1Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical TrigoDocument12 pagesPlane and Spherical TrigoAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical Trigonometry (Part 1 & 2) Problem 1Document12 pagesPlane and Spherical Trigonometry (Part 1 & 2) Problem 1Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures 1 (Part 1 & 2) Problem 1Document4 pagesTheory of Structures 1 (Part 1 & 2) Problem 1Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Quezon City: Document: 513-21920-P1 Rev. 1.0 Page 1 of 2 Effective: 1/23/2020Document2 pagesQuezon City: Document: 513-21920-P1 Rev. 1.0 Page 1 of 2 Effective: 1/23/2020Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Soa 0020230786687 (3525)Document1 pageSoa 0020230786687 (3525)Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cash Initialization Admin Perform Z-Read (Includes Cash Declaration) Perform Cash Initialization 2Document1 pageCash Initialization Admin Perform Z-Read (Includes Cash Declaration) Perform Cash Initialization 2Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ave de Guzman: Address: Block 21 Lot 33 Phase E-1 Francisco Homes Brgy. Mulawin City of San Jose DelDocument2 pagesAve de Guzman: Address: Block 21 Lot 33 Phase E-1 Francisco Homes Brgy. Mulawin City of San Jose DelAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACTDocument15 pagesABSTRACTAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- PCD Notes SirDocument29 pagesPCD Notes SirAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesTechnological Institute of The PhilippinesAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Extra chp1Document6 pagesExtra chp1Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines 938 Aurora BLVD., Cubao, Quezon CityDocument3 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines 938 Aurora BLVD., Cubao, Quezon CityAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Table 4.19: RC Column 1Document4 pagesTable 4.19: RC Column 1Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Company Visit ReportDocument1 pageCompany Visit ReportAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ave de Guzman ResumeDocument3 pagesAve de Guzman ResumeAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Types of SpecsDocument1 pageTypes of SpecsAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Using Ordinary Method of Slices Using Simplified Bishop's MethodDocument2 pagesUsing Ordinary Method of Slices Using Simplified Bishop's MethodAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Rotomac Industries PVT LimitedDocument3 pagesRotomac Industries PVT Limitedcia sin kwangNo ratings yet
- Invoice OD116706386055987000Document1 pageInvoice OD116706386055987000Chirag Gupta100% (1)
- Questioned Documents & Handwriting ExaminationDocument6 pagesQuestioned Documents & Handwriting ExaminationMayank MauryaNo ratings yet
- MC1 ANT-ASI4517R3v18-2496-003 Datasheet (Nueva Version Antena MC1)Document2 pagesMC1 ANT-ASI4517R3v18-2496-003 Datasheet (Nueva Version Antena MC1)Jhon Edisson90% (10)
- GE Amendment FormDocument1 pageGE Amendment FormFelix GanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9-Mysql Functions - 231006 - 173703Document3 pagesWorksheet 9-Mysql Functions - 231006 - 173703tinurafiya2006No ratings yet
- Aptitude Test - 4th August 2021 (30 Points)Document11 pagesAptitude Test - 4th August 2021 (30 Points)namNo ratings yet
- GE73 Raider RGB 8RF (20190701)Document3 pagesGE73 Raider RGB 8RF (20190701)Zul FahmiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Liquefaction of Natural Gas (CH16184)Document11 pagesPresentation On Liquefaction of Natural Gas (CH16184)vidit SinghNo ratings yet
- Working With PerspexDocument7 pagesWorking With PerspexNemanja DizdarevicNo ratings yet
- Table 2 WGBTDocument3 pagesTable 2 WGBTFrancis Enriquez TanNo ratings yet
- POSTSTRUCTURALISM. It Could Be Argued That Essentialism Results in StereotypesDocument1 pagePOSTSTRUCTURALISM. It Could Be Argued That Essentialism Results in StereotypesFrancis B. TatelNo ratings yet
- Strategic Development in Hospitality: Lesson 1Document26 pagesStrategic Development in Hospitality: Lesson 1Yeunna LaurenNo ratings yet
- 2018 Introduction To PbaDocument57 pages2018 Introduction To PbaWaqas ZafarNo ratings yet
- Synopsis PSPpumpsDocument12 pagesSynopsis PSPpumpsGaurav RaneNo ratings yet
- Particular Specification For StormDocument11 pagesParticular Specification For StormManju NaikNo ratings yet
- Student Centered Unit of LearningDocument5 pagesStudent Centered Unit of Learningapi-656805640No ratings yet
- Relational Identity and IdentificationDocument25 pagesRelational Identity and Identificationgabay123No ratings yet
- Synopsis Customer Satisfaction in Retail BankingDocument9 pagesSynopsis Customer Satisfaction in Retail BankingRuchi KashyapNo ratings yet
- Boyce ODEch 7 S 3 P 22Document4 pagesBoyce ODEch 7 S 3 P 22Severus SnapeNo ratings yet
- SkyscrapersDocument60 pagesSkyscrapersAnishNo ratings yet
- Nug 26Document103 pagesNug 26Dominic GiambraNo ratings yet
- DMC-LS80P Dmc-Ls80Pc Dmc-Ls80Pl DMC-LS80E Dmc-Ls80Eb Dmc-Ls80Ee Dmc-Ls80Ef Dmc-Ls80Eg Dmc-Ls80Gc Dmc-Ls80Gk Dmc-Ls80GnDocument41 pagesDMC-LS80P Dmc-Ls80Pc Dmc-Ls80Pl DMC-LS80E Dmc-Ls80Eb Dmc-Ls80Ee Dmc-Ls80Ef Dmc-Ls80Eg Dmc-Ls80Gc Dmc-Ls80Gk Dmc-Ls80GnRonal Gutierrez100% (1)
- Sample 3482Document16 pagesSample 3482erwin einsteinNo ratings yet
- Transformer Auxiliary Protection DevicesDocument34 pagesTransformer Auxiliary Protection Devicesyalewlet tarekeggnNo ratings yet
- Physics Project FinalDocument20 pagesPhysics Project FinalSIVAPRIYA .SNo ratings yet