Practice Exam Question Practice Exam Question
Practice Exam Question Practice Exam Question
Uploaded by
Lily RobinsonCopyright:
Available Formats
Practice Exam Question Practice Exam Question
Practice Exam Question Practice Exam Question
Uploaded by
Lily RobinsonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Practice Exam Question Practice Exam Question
Practice Exam Question Practice Exam Question
Uploaded by
Lily RobinsonCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|8094069
Practice Exam Question
Introductory Biology: Life's Machinery (University of Melbourne)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Lily Robinson (angelwing2529811@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|8094069
BIO10008 PRACTICE EXAM
1. Phosphodiester bonds are important in the formation of polynucleotides. These bonds connect the
phosphate group of one nucleotide with the pentose sugar of a neighbouring nucleotide.
2. DNA replication is semiconservative because each new molecule incorporates half of the original
molecule. …in eukaryotes has multiple points of origin along the linear chromosome.
3. A large, charged molecules moving down its concentration gradient will most likely cross the cell
membrane via facilitated diffusion, proteins in the phospholipid bilayer.
A small, charged molecules moving againsts its concentration gradient will most likely cross the
cell membrane via active transport.
4. The main difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is eukaryotic cells have
membrane-bound subcellular compartments, called organelles, and prokaryotic cells do not.
5. The Golgi apparatus carries out sorting and packaging proteins.
6. During the process of translation, the anti-codon of a tRNA molecule binds to a complementary
mRNA codon to deliver a specific amino acid to the ribosome.
During the process of transcription, mRNA that is complementary to the DNA template is
synthesised by RNA polymerase.
7. The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
8. Enzymes as catalysts in cells do not alter the concentrations in the final equilibrium.
9. The Calvin Benson cycle occurs in the matrix of the chloroplast (stroma).
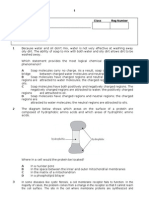
10.
‘A’ – Palisade Mesophyll: Responsible for the majority of
photosynthetic output.
‘B’ – Epidermis: Secrete waxy layer that helps prevent water
loss.
‘C’ – Spongy Mesophyll:
‘D’ – Vascular Tissue/ Bundle: Tissue responsible for the transport water, nutrients and sugars
around the plant. Tissue with intercellular spaces that facilitate gas exchange.
Downloaded by Lily Robinson (angelwing2529811@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|8094069
11. Transport of energy and carbon compounds around a plant take place mainly via sucrose in sieve
tubes.
12. The movement of water through plants is along a water potential gradient maintained in the xylem
by negative hydrostatic pressure.
13. A decrease in the pH of human blood caused by exercise would decrease the affinity of
haemoglobin for oxygen and shift curve to the right.
14. When the oxygen dissociation curve for haemoglobin shifts to the left, more oxygen remains
bound to the haemoglobin at low O2 partial pressures.
15. Countercurrent flow in gas exchange is more efficient mechanism than concurrent flow. It is
when water and circulatory fluid flow in opposite directions across the respiratory surface.
16. The control centre that regulates productive hormones in human female is the hypothalamus.
17. In vertebrate animals, transplanting cells from one part of the embryo to another part results in
abnormal development of the embryo.
18. In an animal with a closed circulatory system, pressure in the arteries is significantly higher than
in the veins. In an open circulatory system, circulating fluid mixes freely with extracellular fluid.
19. Animal were able to evolve to become larger because of the development of mechanisms for
efficient internal transport and gas exchange.
20. A non-sense mutation introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA.
21.
The DNA content of a cell at N is half that of cell at Q
22. A biochemical pathway determining flower colour is shown below.
White > Yellow > Green > Blue > Purple , where > represents Enzyme 1,2,3,4 respectively.
It can be concluded that Yy; gg; Bb; PP will produce yellow flowers.
Downloaded by Lily Robinson (angelwing2529811@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|8094069
23. “Secretors” (genotypes SeSe and Sese) secrete their ABO blood group antigens into their saliva
and other body fluids while “non secretors” (sese) do not. The secretor locus is on chromosome
17 in humans and the ABO locus on chromosome 9. From parents IBio; Sese and IAio; sese, the
chance of a child who secretes only antigen B in their saliva is 1/8.
24. An X linked recessive mutation in mice results in dwarfism. A second autosomal gene determines
coat colour. The two phenotypes for coat colour are yellow and agouti (wild type). Yellow coat is
the dominant phenotype but lethal when homozygous. If a yellow female, purebreeding for
normal height is crossed to a yellow, dwarf male. All of the female offspring that have yellow
coat and normal height are heterozygous at both loci.
25. Most fatal cancerous tumours are allowed to grow because the cells are not immunogenic as they
are recognised as self.
26. In photosynthesis by C4 plants, malate is transported into bundle sheath cells.
27. At a specific area of a chromosome, the sequence of nucleotides below is present where the DNA
opens to form a replication fork: 3’ C C T A G G C T G C A A T C C 5’. An RNA primer is
formed starting at the underlined T of this template strand. The primer sequence is 5’ A C G U U
A G G 3’.
28. Cyanobacteria are important in the evolution of life on earth because the chloroplasts in land
plants derived from cyanobacteria.
29. Structures enclosed by a single membrane: Vacuole, Lysosome, Golgi apparatus, ER
Double membrane: Mitochondria and Chloroplast
30. Glycolysis starts outside the outer mitochondrial membrane.
31. Enzymes are generally substrate specific.
32. Xylem cells in flowering plants include vessels and tracheids.
33. Luteinising Hormone in males stimulates Leydig cells and in females it triggers ovulation.
34. Follicle Stimulating Hormone in males stimulates Sertoli cells while in females it stimulates
follicles.
35. Guanine makes up 38% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an organism. The
approximate percentage of the nucleotides in this sample that will be thymine is 12
Downloaded by Lily Robinson (angelwing2529811@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|8094069
36. Two true-breeding stocks of pea plants are crossed. One parent had red, axillary flowers and the
other had white, terminal flowers; all F1 individuals have red, axillary flowers. The genes for
flower colour assort independently. If 1200 F2 offspring resulted from the cross, approximately
how many of them would you expect to have red, terminal flowers? 225
37. The dominant oncogene, ras is the gene for a protein which is part of a signal transduction
pathway.
38. CAM plants differ from C4 plants by having stomata open during the night. C4 have two kinds of
cell involved in photosynthesis.
39. The enzyme Rubisco can interact with O2 but has a greater affinity for CO2.
40. In animals, development involves differentiation, growth, morphogenesis, and determination.
41. Cells in a multicellular organism need to communicate because cells often need to coordinate
their activity.
42. Lipids and energy storage matches a macromolecule to an appropriate cellular component or
function.
43. Life is divided into three domains: Eukarya, Archaea and Bacteria. Eukarya are more closely
related to Archaea than they are to Bacteria.
44. All animal tissues are composed of specialized and differentiated cells that function in a
coordinated manner.
45. Sister chromatids are separated from each other during mitosis and meiosis II.
46. Cancer is not an inherited disease, but the predisposition to cancer is genetic. The majority of
cancers are sporadic (i.e. there is no family history).
47. A difference between plant cells and animal cells is that plants cells commonly have a large,
central vacuole.
48. Chloroplasts and mitochondria share the following feature. They both produce ATP.
Downloaded by Lily Robinson (angelwing2529811@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Biology HL - ANSWERS - Second Edition - Pearson 2014 PDFDocument73 pagesBiology HL - ANSWERS - Second Edition - Pearson 2014 PDFAngela LinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 PCR and Cloning of Alpha-Amylase Gene in E. ColiDocument12 pagesExperiment 4 PCR and Cloning of Alpha-Amylase Gene in E. ColiJiaying ChenNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument5 pagesThe CellAfida Razuna AveNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasmic InheritanceDocument26 pagesCytoplasmic Inheritancegoldyromaannie777No ratings yet
- Sample Questions BiologyDocument4 pagesSample Questions Biologybruhaan12No ratings yet
- Neet PT-8Document75 pagesNeet PT-8ViswaNo ratings yet
- 22100990cell and Molecular Biology-April 2022Document11 pages22100990cell and Molecular Biology-April 2022Sneha SonyNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes, Nucleic Acids & Other Genetic ElementsDocument22 pagesChromosomes, Nucleic Acids & Other Genetic ElementsRadius JuliusNo ratings yet
- Biology: Exclude: 19,20,25,55,56Document31 pagesBiology: Exclude: 19,20,25,55,56Venessa PerpetuaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Prelim Essays CompilationDocument79 pages2018 Prelim Essays CompilationpipelineNo ratings yet
- Polinar - Chapter 3Document10 pagesPolinar - Chapter 3Jayson PolinarNo ratings yet
- 113 Things You Should Know1Document4 pages113 Things You Should Know13tester1024No ratings yet
- Plant Cell Structure and Importance of Cell Organelles I Post Harvest PhysiologyDocument10 pagesPlant Cell Structure and Importance of Cell Organelles I Post Harvest Physiologychristom karungariNo ratings yet
- BLG1501 (Ass02) 599782 Student Number 57775222Document5 pagesBLG1501 (Ass02) 599782 Student Number 57775222Willenay JantjiesNo ratings yet
- Cels191 Things To RememberDocument9 pagesCels191 Things To RememberMimi BoisterNo ratings yet
- Microbial Genetics: Extra-Chromosomal InheritanceDocument24 pagesMicrobial Genetics: Extra-Chromosomal Inheritancearlene eranNo ratings yet
- Biology 115 Exam 2 Study Guide: Chapter 10: PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology 115 Exam 2 Study Guide: Chapter 10: PhotosynthesisTiffanyNo ratings yet
- 2324 S6 Summer Exam Final Concept ListDocument19 pages2324 S6 Summer Exam Final Concept Listbarborka.hruscovaNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem QuestionsDocument34 pages1st Sem Questionsazizirabia5No ratings yet
- Biology Quiz BeeDocument59 pagesBiology Quiz BeejmNo ratings yet
- Praxis Biology Content Knowledge (5236) Exam Review Qs&As 100% Pass!Document10 pagesPraxis Biology Content Knowledge (5236) Exam Review Qs&As 100% Pass!amocollie3No ratings yet
- t2 Bio Revision Ex 3Document11 pagest2 Bio Revision Ex 3Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologypardilloerica41No ratings yet
- EC13 Cell Ageing DNA TextDocument8 pagesEC13 Cell Ageing DNA TextSilvito94No ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 1: Cells and GenomesDocument17 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 1: Cells and GenomesIsmael Torres-PizarroNo ratings yet
- Shantonil Bal, XI Science - B, Roll No. 4Document8 pagesShantonil Bal, XI Science - B, Roll No. 4Shantonil BalNo ratings yet
- AAMC BioDocument8 pagesAAMC BiojyothsnaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Gradient. An Equilibrium Is Reached at Which CL - Influx and CL - Efflux Are EqualDocument4 pagesElectrical Gradient. An Equilibrium Is Reached at Which CL - Influx and CL - Efflux Are EqualMohib NirobNo ratings yet
- E Tate@imperial Ac UkDocument19 pagesE Tate@imperial Ac UkSoRina SabauNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Crop PhysiologyDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Crop PhysiologyRsNo ratings yet
- Polytene ChromosomesDocument6 pagesPolytene ChromosomesKhush BakhtNo ratings yet
- Bs Zoology All Questions Solved by Muhammad AnasDocument3 pagesBs Zoology All Questions Solved by Muhammad AnasdavidNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Exam 1Document4 pagesStudy Guide Exam 1NicolleNo ratings yet
- Organism Mitochondria: Shape Sand SizeDocument1 pageOrganism Mitochondria: Shape Sand SizeUtanka DeNo ratings yet
- Beckers World of The Cell Chapter-01 Test Bank Questions and AnswersDocument18 pagesBeckers World of The Cell Chapter-01 Test Bank Questions and AnswersiremsenakNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Quarter 3 Week 4Document5 pagesGrade 10 Quarter 3 Week 4James GalvezNo ratings yet
- BIL Exam 3 NotesDocument16 pagesBIL Exam 3 NotesCraig ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Molecular Bio PaperDocument7 pagesMolecular Bio Paperbenedict.callebautNo ratings yet
- Biology 9701 MJ23 P42Document15 pagesBiology 9701 MJ23 P422190ibrahimazeemNo ratings yet
- Notes About BiologyDocument81 pagesNotes About BiologyRichard Coffey100% (1)
- Ecology 1-3Document20 pagesEcology 1-3Nel PasaizNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Cells NotesDocument81 pagesBiomolecules and Cells NotesLily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Polytene and Lampbrush ChromosomesDocument3 pagesPolytene and Lampbrush Chromosomesneeru.bhagatNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper 2 Q As1ZaZDocument17 pagesModel Question Paper 2 Q As1ZaZPrithvi RajanNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Characteristics & Structure of GenesDocument64 pagesUnit-I: Characteristics & Structure of GenesMonika JosephNo ratings yet
- Much of what is known about prokaryoticDocument9 pagesMuch of what is known about prokaryotickinnerakakarla970No ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument1,942 pagesBiochemistryDiana Reyes100% (2)
- Science Half Yearly NotesDocument14 pagesScience Half Yearly NotesanonNo ratings yet
- Allot Mindorff Mitosis and MeiosisDocument11 pagesAllot Mindorff Mitosis and MeiosisElTrucoCeroNo ratings yet
- 2009 Midterm Introduction To Life Science I. Q&A (70%) : BMES - Chuang CYDocument8 pages2009 Midterm Introduction To Life Science I. Q&A (70%) : BMES - Chuang CYHsieh Chia YuNo ratings yet
- Bio 6204 Quiz1,2&PrelimsDocument4 pagesBio 6204 Quiz1,2&PrelimsReynante RamosNo ratings yet
- AC-HPAT Prep Questions 100% Answered CorrectlyDocument10 pagesAC-HPAT Prep Questions 100% Answered CorrectlywakwabubifelixNo ratings yet
- Workshop 2 BiologyDocument9 pagesWorkshop 2 BiologyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- BIO 310 Midterm 1 PackageDocument28 pagesBIO 310 Midterm 1 PackageNerdy Notes Inc.100% (1)
- 1 - Give An Illustrated Account of The Fine Staracture of A Plant Cell and Describe The Function of The Diffrent Cell OrgnagesDocument19 pages1 - Give An Illustrated Account of The Fine Staracture of A Plant Cell and Describe The Function of The Diffrent Cell OrgnagesMD shah KhanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Recombination Chapter Qxn'sDocument3 pagesGenetic Recombination Chapter Qxn'sjaelingabire05No ratings yet
- Key Points Biology-1Document29 pagesKey Points Biology-1Tanveer AliNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Cells Biol10002Document79 pagesBiomolecules and Cells Biol10002Lily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Biol10002 Notes PDFDocument60 pagesBiol10002 Notes PDFLily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Cells NotesDocument81 pagesBiomolecules and Cells NotesLily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- BIOL10002 2021 Lecture 12 1 Slide pp-1Document24 pagesBIOL10002 2021 Lecture 12 1 Slide pp-1Lily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- L1 - BIOM10001 - Welcome & Subject Intro - LMS - 1ppDocument28 pagesL1 - BIOM10001 - Welcome & Subject Intro - LMS - 1ppLily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- W1 - BIOM10001 - Workshop 1 - 1pp-1Document24 pagesW1 - BIOM10001 - Workshop 1 - 1pp-1Lily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- BIOL10002 Lecture1 1 SlideDocument45 pagesBIOL10002 Lecture1 1 SlideLily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- ARBC10006 Arabic 2 Semester Plan-2Document7 pagesARBC10006 Arabic 2 Semester Plan-2Lily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- ARBC10006 Arabic 2 Assignments, Practice and PreparationDocument16 pagesARBC10006 Arabic 2 Assignments, Practice and PreparationLily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Unit f215 Control Genomes and EnvironmentDocument24 pagesQuestion Paper Unit f215 Control Genomes and EnvironmentMohammed SaqlainNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Evolution Study GuideDocument4 pagesAP Biology Evolution Study Guidetanu96tpNo ratings yet
- SasangDocument11 pagesSasangVince Cinco ParconNo ratings yet
- Naas Score Of: (Effective From January 1, 2014)Document38 pagesNaas Score Of: (Effective From January 1, 2014)Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Guideline Human Cell Based Medicinal Products - enDocument25 pagesGuideline Human Cell Based Medicinal Products - enИринаNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorder Poster DirectionsDocument2 pagesGenetic Disorder Poster DirectionsMarkgil SabalzaNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesProtein-Synthesis WorksheetAme RealNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division High Yield MCQs For NEET 2022 RevisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division High Yield MCQs For NEET 2022 RevisionArushi & Ayushi Yadav XI - CNo ratings yet
- The Music of Life-Sourcebook PDFDocument98 pagesThe Music of Life-Sourcebook PDFAmal-krishnadas D'RiveroNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1Document4 pagesScience 9 q1cattleya abelloNo ratings yet
- Types of TransposonsDocument13 pagesTypes of Transposonsmozhi74826207No ratings yet
- Motamayor 2008Document8 pagesMotamayor 2008Luis PerniaNo ratings yet
- Functions of Nucleic Acids Are:: Nucleic Acids Consist of Either One or Two Long Chains of Two Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesFunctions of Nucleic Acids Are:: Nucleic Acids Consist of Either One or Two Long Chains of Two Types of Nucleic AcidsveloNo ratings yet
- Rise and SINEDocument12 pagesRise and SINEjsyou816No ratings yet
- A Nitric Oxide Burst at The Shoot Apex Triggers A Heat-Responsive Pathway in ArabidopsisDocument32 pagesA Nitric Oxide Burst at The Shoot Apex Triggers A Heat-Responsive Pathway in ArabidopsiseibadNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution Class 10 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 9 PDFDocument11 pagesHeredity and Evolution Class 10 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 9 PDFvanshNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mutation and DisorderDocument31 pagesGenetic Mutation and Disorderabrielle dytucoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 2421 Lecture Notes Microbial GeneticsDocument19 pagesMicrobiology 2421 Lecture Notes Microbial GeneticsFaye Coleen GozaNo ratings yet
- The Impossible Voyage of Noah's Ark - NCSE PDFDocument28 pagesThe Impossible Voyage of Noah's Ark - NCSE PDFtonymontana2009No ratings yet
- Edible Meiosis Model Performance TaskDocument2 pagesEdible Meiosis Model Performance TaskZyjan PerezNo ratings yet
- Small Animal Clinical NutritionDocument6 pagesSmall Animal Clinical NutritionJairo Pereira100% (1)
- Chromosomes WorksheetDocument6 pagesChromosomes WorksheetPaulína PalčinskáNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument20 pagesGeneticssirisha.moonsamyNo ratings yet
- CBCS BSC Zoology Sem III Sem IV 08192023161617Document11 pagesCBCS BSC Zoology Sem III Sem IV 08192023161617nadimshah890No ratings yet
- Focus On Colon CancerDocument4 pagesFocus On Colon CancerFlaKitaNo ratings yet
- BioNome Bioinformatics Training Programs-2021Document15 pagesBioNome Bioinformatics Training Programs-2021Arunangshu DevNo ratings yet
- Trichoepithelioma: A Comprehensive Review: Iman Karimzadeh, Amin KarimzadehDocument7 pagesTrichoepithelioma: A Comprehensive Review: Iman Karimzadeh, Amin KarimzadehrosaNo ratings yet
- Vector NTI® Express SoftwareDocument184 pagesVector NTI® Express SoftwareDrgemeNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lab Exercise 10 - The Tools of DNA TechnologyDocument7 pagesGenetics Lab Exercise 10 - The Tools of DNA Technologybry uyNo ratings yet