Venn Diagram (MP)
Venn Diagram (MP)
Uploaded by
veralynnCopyright:
Available Formats
Venn Diagram (MP)
Venn Diagram (MP)
Uploaded by
veralynnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Venn Diagram (MP)
Venn Diagram (MP)
Uploaded by
veralynnCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME: VERALYNN J.
JACOSALEM BSN 2-PENDER B 09-03-21
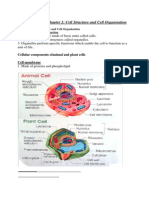
PROKARYOTES EUKARYOTES
• Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic • Has ordinarily larger
• Has (1-10um) cell size
cells bear a lipid bilayer.
(10-100um) cell size
• Unicellular
• Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells • Multicellular
• Have no nucleus
both use deoxyribonucleic acid as • Have true nucleus
• Prokaryotic DNA is circular basis for their genetic information.
bound
and is neither associated • Ribosomes aid in the translation of • Eukaryotic DNA is linear
with histones nor organized RNA and the production of protein, and complexed with
into chromosomes.
both of which are necessary for the packaging proteins.
• Do not contain membrane survival of eukaryotic and • Contain many
bound organelles.
prokaryotic cells.
membrane-enclosed
• Prokaryotic ribosomes are • The cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells large, complex
composed of only 3 kinds of includes everything between the organelles in the
rRNA and about fty kinds of plasma membrane and the nuclear cytoplasm
protein.
envelope, including organelles; the • Eukaryotic ribosomes
• In sexual reproduction nucleoplasm refers to the material show more complexity
prokaryotes reproduce within the nucleus. The cytoplasm, • Most eukaryotes
asexually.
which includes the cytoskeleton undergo sexual
• Prokaryotes undergo a and genetic material in reproduction.
simpler process of binary prokaryotes, encompasses • Eukaryotic cells undergo
ssion. everything within the plasma mitosis them
membrane.
cytokinesis.
• Both have cell membrane.
https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/Eukaryotic-and-Prokaryotic-Cells-Similarities-and-Di erences.aspx
fi
fi
ff
You might also like
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument28 pagesBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentAmarendra Shukla74% (247)
- A Level Biology For OCR A (Double Paged)Document360 pagesA Level Biology For OCR A (Double Paged)squishyboitae33% (3)
- Executive SummaryDocument5 pagesExecutive SummaryShayyNo ratings yet
- Metabolism, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity of Functional GroupsDocument545 pagesMetabolism, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity of Functional GroupsDenisa Nițu100% (2)
- Student Exploration: Disease SpreadDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Disease SpreadAndreNo ratings yet
- What Is Plasmodium Falciparum?: Protozoa MalariaDocument100 pagesWhat Is Plasmodium Falciparum?: Protozoa MalariaHasna Nur AiniNo ratings yet
- Kato Thick Smear Technique 0Document19 pagesKato Thick Smear Technique 0Abby Delos Santos ShinhyeNo ratings yet
- Sarcodina Amoebae (Amoebas) (False Feet)Document4 pagesSarcodina Amoebae (Amoebas) (False Feet)Lyka ReyesNo ratings yet
- Market Analysis On Oral Healthcare Products With Respected ToDocument78 pagesMarket Analysis On Oral Healthcare Products With Respected ToShailesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ancylostoma DuodenaleDocument2 pagesAncylostoma DuodenaleBlessy BreganzaNo ratings yet
- 16 Discourse Analysis and StylisticsDocument11 pages16 Discourse Analysis and StylisticsAwais TareqNo ratings yet
- Maley Ch1csDocument5 pagesMaley Ch1csRosten MusweuNo ratings yet
- Principles of SamplingDocument7 pagesPrinciples of SamplingShashank JainNo ratings yet
- Kato-Katz Technique: Gaviola. Gayamo. Guiyab. Herman. JaquiacaDocument13 pagesKato-Katz Technique: Gaviola. Gayamo. Guiyab. Herman. JaquiacaTrishia ClarisNo ratings yet
- Hand Washing1Document8 pagesHand Washing1Mohmad Ahasan HabibNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument8 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistrySudeshna KunduNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry and The Organization of Cells-Chap 1Document33 pagesBiochemistry and The Organization of Cells-Chap 1scribdusernumber210% (1)
- Parasitology 18 Lung FlukesDocument25 pagesParasitology 18 Lung FlukesJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Microscope and UsesDocument3 pagesDifferent Types of Microscope and UsesVienna TulauanNo ratings yet
- Special TopicsDocument8 pagesSpecial Topicskatherine ruizNo ratings yet
- Christian Morality Prelim ExamDocument2 pagesChristian Morality Prelim Examdan teNo ratings yet
- Bioethics HomosexualityDocument15 pagesBioethics HomosexualityJoen Alfuen CapiñaNo ratings yet
- 10 Chemical Tests Fecal Occult BloodDocument11 pages10 Chemical Tests Fecal Occult BloodAdarshBijapurNo ratings yet
- FixativesDocument10 pagesFixativesShirin Kay Oplenaria ButaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2: Venipuncture Using Vacuum Blood COLLECTION SYSTEM Skills 30 PointsDocument16 pagesExercise 2: Venipuncture Using Vacuum Blood COLLECTION SYSTEM Skills 30 PointsRue Wan UyNo ratings yet
- Tecniques of Immunohistochemistry:: Principles, Technique & Pitfalls Hena 4/7/13Document104 pagesTecniques of Immunohistochemistry:: Principles, Technique & Pitfalls Hena 4/7/13PerryNo ratings yet
- Histology: Microscopic Study of Biological Tissues ScientificDocument2 pagesHistology: Microscopic Study of Biological Tissues ScientificCaitlinNo ratings yet
- Poraginumus WestermaniDocument23 pagesPoraginumus WestermaniMika AndiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyrazikNo ratings yet
- Position Paper-UcoDocument4 pagesPosition Paper-Ucoapi-235712781No ratings yet
- Chapter 11: CarbohydratesDocument97 pagesChapter 11: CarbohydratesLeann Kate MartinezNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue NematodesDocument3 pagesBlood and Tissue Nematodesdotsdy100% (3)
- Impact of Globalization On TransportDocument12 pagesImpact of Globalization On Transportraavi0609100% (1)
- Parasitology PRKTKLDocument58 pagesParasitology PRKTKLmohamed100% (2)
- Cytology and Cytological TechniquesDocument29 pagesCytology and Cytological TechniquessafiNo ratings yet
- Histopathologic and Cytologic TechniquesDocument16 pagesHistopathologic and Cytologic TechniquesAngelica TabornalNo ratings yet
- Frozen SectionDocument3 pagesFrozen SectionMalf Vard100% (1)
- Parasitology (Laboratory) - NEMATODES - Enterobius VermicularisDocument3 pagesParasitology (Laboratory) - NEMATODES - Enterobius VermicularisJunno TurianoNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases in Everyday LifeDocument6 pagesAcids and Bases in Everyday LifeLothar GraudinsNo ratings yet
- Ra 8981Document2 pagesRa 8981Jaellah MatawaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument9 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyDr-Rmz RabadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EpidemiologyDocument15 pagesIntroduction To EpidemiologyNathnael Gebeyehu0% (1)
- Par201 S1lab4 Midterm Phamids Aphasmids PDFDocument27 pagesPar201 S1lab4 Midterm Phamids Aphasmids PDFHanna Alyssa Grace DimarananNo ratings yet
- Malaria ParasiteDocument22 pagesMalaria ParasiteAndy Putra HermawanNo ratings yet
- TroubleshootingDocument9 pagesTroubleshootingNaja Maziyatul INo ratings yet
- Cabbage As PH IndicatorDocument2 pagesCabbage As PH IndicatormorerupaliNo ratings yet
- Lung FlukesDocument23 pagesLung FlukesGelli LebinNo ratings yet
- Antigen and Its PropertiesDocument20 pagesAntigen and Its Propertiestusharpremin92% (12)
- Lec-3 FixativesDocument23 pagesLec-3 FixativesAbdul HafeezNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - General Pathology, Logic and Cytologic TechniquesDocument11 pagesGroup 4 - General Pathology, Logic and Cytologic Techniquesjulo_05No ratings yet
- Duaso QuizDocument20 pagesDuaso QuizCharchar HernandezNo ratings yet
- ANTIBODYDocument22 pagesANTIBODYapi-19916399100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFJulie Anne Soro ValdezNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1Document4 pagesLab Exercise 1Alessandra WyNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Lab Accidents and PrecautionsDocument6 pagesAssignment - Lab Accidents and PrecautionsAnchu AvinashNo ratings yet
- Journalism 9 Feature Writing For DisseminationDocument6 pagesJournalism 9 Feature Writing For DisseminationRainier LlorenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology PDFDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Immunology PDFanon_143800659100% (1)
- Reflection Paper Jackie Day Loras CollegeDocument7 pagesReflection Paper Jackie Day Loras Collegeapi-436866650No ratings yet
- 2 Hand HygieneDocument44 pages2 Hand Hygieneregisterpy0% (1)
- Notes On Antibodies PropertiesDocument3 pagesNotes On Antibodies PropertiesBidur Acharya100% (1)
- CarbohydratesDocument28 pagesCarbohydratesMae Codium GallentesNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 3. Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument25 pagesBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 3. Cell Structure and TaxonomyLindsay SwanepeolNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 3. Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument25 pagesBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 3. Cell Structure and TaxonomyLindsay SwanepeolNo ratings yet
- Modifikasi Formula Enteral Rumah Sakit Siap SeduhDocument8 pagesModifikasi Formula Enteral Rumah Sakit Siap SeduhAsfi Ni'amNo ratings yet
- Dna Mutations Practice Worksheet AnswersDocument3 pagesDna Mutations Practice Worksheet AnswersKiwi cute07No ratings yet
- Clinical Cytogenetics: The Chromosomal Basis of Human DiseaseDocument45 pagesClinical Cytogenetics: The Chromosomal Basis of Human DiseaseGia HoàngNo ratings yet
- Bio 6204 Quiz5,6&FinalsDocument12 pagesBio 6204 Quiz5,6&FinalsReynante RamosNo ratings yet
- CDMDL 22 025288Document2 pagesCDMDL 22 025288JOHN ROIENo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument1 pageBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsFathima VcNo ratings yet
- Essay LPDP English Study PlanDocument2 pagesEssay LPDP English Study PlanCindy BriaNo ratings yet
- BCG Hepatitisb Hexa1 Hexa2 Penta: Baby Immunization Schedule - QatarDocument3 pagesBCG Hepatitisb Hexa1 Hexa2 Penta: Baby Immunization Schedule - QatarKiran Kumar AkulaNo ratings yet
- BDS I Year Single Sheeter 2016 Jun 16 FinalDocument4 pagesBDS I Year Single Sheeter 2016 Jun 16 FinalNitish panghalNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument4 pagesBiology Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationSera ChanNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymesSarah Farhah2000100% (1)
- Station 1 MEIOSIS: Unit 4 Genetics Test ReviewDocument6 pagesStation 1 MEIOSIS: Unit 4 Genetics Test Reviewapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Green Book Chapter 11Document9 pagesGreen Book Chapter 11VergaaBellanyNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesGlaiza Dalayoan FloresNo ratings yet
- 2007 Cancer Stem Cells-Biol 610 No AnimDocument49 pages2007 Cancer Stem Cells-Biol 610 No Animapi-3746517No ratings yet
- Next Gen CARDocument11 pagesNext Gen CARJuhi VermaNo ratings yet
- Kajian Administratif Farmasetis Dan Klinis Resep oDocument7 pagesKajian Administratif Farmasetis Dan Klinis Resep omargaretaNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell MCQDocument5 pagesBiology Cell MCQminujeyapalNo ratings yet
- Test - IB Biology 7.1 - QuizletDocument5 pagesTest - IB Biology 7.1 - QuizletSumi VjNo ratings yet
- Production of Highly Active Extracellular Amylase and Cellulase From Bacillus Subtilis ZIM3 and A RecoDocument14 pagesProduction of Highly Active Extracellular Amylase and Cellulase From Bacillus Subtilis ZIM3 and A RecoMo RaflyNo ratings yet
- 8 Science Unit 2Document2 pages8 Science Unit 2usmanvirkmultanNo ratings yet
- Alpha InterferonDocument7 pagesAlpha InterferonLAURA MARCELA BARRENECHE CALLENo ratings yet
- BIOINFORMATICS - eNOTESDocument23 pagesBIOINFORMATICS - eNOTESRaja Durai RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 003 Geriatric Pharmacology: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument15 pagesChapter 003 Geriatric Pharmacology: Multiple Choice QuestionsgoldfishxNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Overview of BioinformaticsDocument1 pageIntroduction and Overview of Bioinformaticsfaraaaalya100% (1)
- Bio Physics: Prepared by Gayathry SatheesanDocument19 pagesBio Physics: Prepared by Gayathry SatheesanrehandeshmukhNo ratings yet