1.2 The Heart (Notes)
1.2 The Heart (Notes)
Uploaded by
Stella StaryCopyright:
Available Formats
1.2 The Heart (Notes)
1.2 The Heart (Notes)
Uploaded by
Stella StaryOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
1.2 The Heart (Notes)
1.2 The Heart (Notes)
Uploaded by
Stella StaryCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
2 The Heart
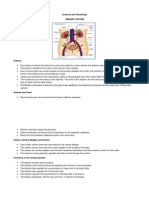
The circulatory system
The main function is to transport substances such as oxygen,
food and wastes.
The circulatory system in humans consists of three main
parts: (1) a fluid (blood) that transports substances in the
body; (2) blood vessels that carry the blood; and (3) a heart
that pumps the blood round the body.
The heart pumps blood around the body through the blood
vessels. There are three types of blood vessels: arteries,
capillaries and veins.
Arteries pump blood away from the heart to the rest of the
body. (A good way of remembering this is that both arteries
and away start with the letter ‘a’.)
Arteries have a thick muscular wall which contracts and
forces the blood along. This can be felt as a pulse. They carry
oxygenated blood, except for the pulmonary artery.
Capillaries are a network of tiny blood vessels that connect
the arteries and veins. The capillaries release substances
such as oxygen and digested food molecules into the cells
and carry away waste substances such as carbon dioxide
from cells. They have thin walls.
Veins carry blood to the heart. Some veins have one-way
valves to stop blood from flowing backwards. Veins are wider
than arteries and have thinner walls. They carry de-
oxygenated blood, except for the pulmonary veins.
The heart and double circulation
The heart is really two separate pumps joined together.
One pump pushes the blood into the lungs. In the lungs,
oxygen diffuses into the blood through the thin capillary walls
and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood.
The oxygenated blood is pumped from the lungs to the left
side of the heart.
The other pump takes the oxygenated blood and pumps it,
under pressure, to other parts of the body through the
arteries. (Note: all the arteries carry oxygenated blood to the
body organs except for the pulmonary artery. The pulmonary
artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
where the blood is oxygenated.)
The system of two pumps is called double circulation.
Deoxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart.
Oxygenated blood enters and leaves the left side of the heart.
In the rest of the body, cells absorb oxygen and food from the
blood and release carbon dioxide and other wastes into the
blood.
In the lungs, blood absorbs oxygen and carbon dioxide
diffuses out of the blood.
You might also like
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory Systemkashaf bhuttaNo ratings yet
- Topic:: The Circulatory System (Heart and Blood Vessels)Document3 pagesTopic:: The Circulatory System (Heart and Blood Vessels)Ck DhiyanNo ratings yet
- Types of Circulation of BloodDocument5 pagesTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNo ratings yet
- Types of Circulation of BloodDocument4 pagesTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNo ratings yet
- M10 Myself - JawapanDocument4 pagesM10 Myself - JawapanSteven OwenNo ratings yet
- Compare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCompare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular Systememanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- Topic 12. Circulatory System AutosavedDocument25 pagesTopic 12. Circulatory System AutosavedJanine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORYDocument3 pagesCIRCULATORYSumbul ShoaibNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystembluewindNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory SystemEzequiel ManluluNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemKrizza Dawn QueNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument17 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationRisavina Dorothy CondorNo ratings yet
- Branching Blood VesselsDocument2 pagesBranching Blood VesselsMarjia TulyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory 1Document2 pagesCirculatory 1Allana Louisse AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesCirculatory SystemKeyur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology-The HeartDocument7 pagesBiology-The Heart2k7wmbhxqfNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- I. Anatomy and Pathophysiology: Cardiovascular System Heart Blood VesselDocument5 pagesI. Anatomy and Pathophysiology: Cardiovascular System Heart Blood VesselDibb Fabiania Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Systemic Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesSystemic Circulatory SystemTinaRahmawatiKadabraNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculationDocument8 pagesBlood CirculationnorafidaishakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12, BioDocument26 pagesChapter 12, BioRylee LNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemDainara ReyesNo ratings yet
- Notes in Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Circulatory SystemVianney CamachoNo ratings yet
- What Is Circulatory System Best Definition?Document15 pagesWhat Is Circulatory System Best Definition?MAXAMEDDEEQOW CabdiNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument23 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportcikzafirahNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System 2024 1 20 22 51 0Document12 pagesThe Circulatory System 2024 1 20 22 51 0Andre GreenNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System) Pumps Blood From TheDocument6 pagesThe Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System) Pumps Blood From ThevanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Word OfficeDocument6 pagesCirculatory Word OfficeMaria Christina CaceresNo ratings yet
- CVS NotesDocument13 pagesCVS NotesMind PowerNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Nervous SystemsDocument15 pagesCirculatory Nervous SystemsVhonPeterNo ratings yet
- Minggu 13 Peredaran DarahDocument11 pagesMinggu 13 Peredaran Darahcuksam27No ratings yet
- GIDB4288666-Circulatory System NotesDocument6 pagesGIDB4288666-Circulatory System Notessky moonNo ratings yet
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDocument46 pagesTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasNo ratings yet
- Sistem Peredaran DarahDocument4 pagesSistem Peredaran DarahIndah SariNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in HumansDocument4 pagesCirculatory System in Humanspetra.t.ayalNo ratings yet
- Transport Systems in HumansDocument4 pagesTransport Systems in HumansLenon TemboNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System or Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System or Circulatory SystemAleeza gondalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasculr SYSTEMDocument3 pagesCardiovasculr SYSTEMCharisse Elica LucasNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory Systems HandoutsDocument1 pageThe Circulatory Systems HandoutsTeacher MelNo ratings yet
- Cardiac SystemDocument18 pagesCardiac Systemviduship322No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesCirculatory SystemCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyClint-Marie LaxaNo ratings yet
- CVS IDocument7 pagesCVS Itemple samNo ratings yet
- Course of Circulation Through Human Heart: Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesCourse of Circulation Through Human Heart: Lymphatic Systemvishal pundirNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemMarnel DincolNo ratings yet
- The Casrdiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Casrdiovascular SystemGilberth MoreraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument33 pagesCirculatory SystemRhynette NaridoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemKyra Aliyah SambranoNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System IsDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System IsKieth ObaobNo ratings yet
- Angelo Jhuan ScienceDocument2 pagesAngelo Jhuan ScienceGoldenaholicNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Miss Javi ZúñigaDocument9 pagesCirculatory System: Miss Javi ZúñigaadisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1Document2 pagesLesson 3.1Evangelia GkNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyCherry Oña AntoninoNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Circulatory SystemLëz NérNo ratings yet
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Saturated & Unsaturated SolutionDocument12 pagesSaturated & Unsaturated SolutionStella StaryNo ratings yet
- Name The Separation Technique Shown in The Diagram.: A. Evaporation B. Distillation C. FiltrationDocument13 pagesName The Separation Technique Shown in The Diagram.: A. Evaporation B. Distillation C. FiltrationStella StaryNo ratings yet
- 1.7 What Does The Brain DoDocument3 pages1.7 What Does The Brain DoStella StaryNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Ppt2Document10 pagesDigestive System Ppt2Stella StaryNo ratings yet
- Jeopardy GameDocument17 pagesJeopardy GameStella StaryNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Circulatory System:movement of Blood Around Your BodyDocument17 pagesThe Circulatory System: Circulatory System:movement of Blood Around Your BodyStella StaryNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Ppt2Document10 pagesDigestive System Ppt2Stella StaryNo ratings yet