The Human Cell
The Human Cell
Uploaded by
Aira Viloria OrbilloCopyright:
Available Formats
The Human Cell
The Human Cell
Uploaded by
Aira Viloria OrbilloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
The Human Cell
The Human Cell
Uploaded by
Aira Viloria OrbilloCopyright:
Available Formats
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
LABORATORY ACTIVTT 1
Name: Date:
Course:
Directions: Label the structures of the Human Cell, then below, list down the structures and
discuss its functions.
Nucleus – it controls cell activity, contains
Chromatin - its functions are to package DNA information that allows cells to reproduce, or
into a smaller volume to fit in the cell, strengthen make more cell.
the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis, and to
serve as a mechanism to control expression.
Nucleolus – serves as the Lysosomes - function as the digestive system of the
synthesis and assembly of cell, serving both to degrade material taken up from
ribosomes. outside the cell and to digest obsolete components of
the cell itself.
Centrioles - play a role in organizing
microtubules that serve as the cell's
skeletal system. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum – is
responsible for fat metabolism
Cytoskeleton - helps cells maintain
their shape and internal organization,
and it also provides mechanical
support that enables cells to carry out
essential functions like division and Golgi apparatus – a structure that
movement. stack of three to ten disc- shaped
envelopes bound by a membrane that
sort, processes, and packages
proteins and membranes.
Mitochondrion – it generates the cell’s
energy, the part of the cell where Ribosomes - serves as the
food and oxygen combine to make site for protein synthesis in
energy. the cell.
Cell membranes - are the outer layers that hold the cell
together, they let nutrients pass into the cell and waste Rough endoplasmic reticulum - hat plays a central role
products pass out. (not everything can pass through a cell in the synthesis of proteins.
membrane)
Cytoplasm – functions to support and
suspend organelles and cellular
molecules.
You might also like
- Organization of The Body: Lab Report 8Document5 pagesOrganization of The Body: Lab Report 8larry machonNo ratings yet
- Activity 3-1 StudentDocument4 pagesActivity 3-1 StudenttaviNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 CELLDocument101 pagesLesson 2 CELLJulius Memeg PanayoNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment ReflectionDocument2 pagesHealth Assessment Reflectionapi-582846016No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Functions TableDocument5 pagesCell Parts and Functions TableNyk Khow67% (3)
- Malnutrition BrochureDocument2 pagesMalnutrition Brochureapi-28482342150% (2)
- Transport Mechanism InfographicsDocument1 pageTransport Mechanism InfographicsLara Jade GomezNo ratings yet
- Stage Appropriate Teaching Strategies and Nursing InterventionsDocument5 pagesStage Appropriate Teaching Strategies and Nursing InterventionsMarie KitNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Term ReviewerDocument19 pagesAnaPhy Term ReviewerJoher Mendez100% (1)
- Travelbee, Joyce (Print)Document8 pagesTravelbee, Joyce (Print)Ahsia Lorraine100% (1)
- Activity 01 The Microscope and MicrosDocument3 pagesActivity 01 The Microscope and MicrosRacquel BanaoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System ReviewerDocument12 pagesIntegumentary System ReviewerLly Isidoro100% (4)
- 10 Herbal Plants Approve by DOHDocument3 pages10 Herbal Plants Approve by DOHIekzkad RealvillaNo ratings yet
- 2020-Biochem-Activity-17 - CLINICAL CHEMISTRYDocument42 pages2020-Biochem-Activity-17 - CLINICAL CHEMISTRYGabrielle John HernaezNo ratings yet
- B102 Animal Cell Flagged Color PDFDocument1 pageB102 Animal Cell Flagged Color PDFThomas HaleyNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and FunctionsKarren Ferrer-Mora Handayan100% (2)
- WEEK 6 LM#2 LymphaticsDocument5 pagesWEEK 6 LM#2 LymphaticsClyde Tan100% (1)
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ReviewerDocument11 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ReviewerMarmie Babaran GallibuNo ratings yet
- AkapulkoDocument5 pagesAkapulkoIanne Sandra SorrosaNo ratings yet
- IS Hay InfusionDocument3 pagesIS Hay InfusionRedstone SalazarNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument13 pagesCell TheoryDaryll BorjaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structure and TaxonomyEarl Nikko ChingNo ratings yet
- UTS Plato ReportDocument10 pagesUTS Plato ReportMaeq LolaNo ratings yet
- Phillipine Nurses Bill of RightsDocument2 pagesPhillipine Nurses Bill of RightsRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Origin and Development of Organ Systems NotesDocument4 pagesOrigin and Development of Organ Systems Notesimnas0% (1)
- Philippine Nursing Seminars and Training May 2011Document3 pagesPhilippine Nursing Seminars and Training May 2011PhilippineNursingDirectory.comNo ratings yet
- Resume Regie BautistabwnwDocument9 pagesResume Regie BautistabwnwGlobal medik indonesiaNo ratings yet
- Von Bertalanffy Presentation TFNDocument19 pagesVon Bertalanffy Presentation TFNWinter Sonata100% (2)
- Exercise 9Document9 pagesExercise 9Bishal KunworNo ratings yet
- Reflection Papers On Sense and PerceptionDocument2 pagesReflection Papers On Sense and PerceptionAgustin Barretto50% (4)
- A Stem Cell Story ReflectionDocument2 pagesA Stem Cell Story ReflectionCharlize Mae ArboladuraNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio W1Document8 pagesGen Bio W1Alyson EscuderoNo ratings yet
- New Technologies Related To Drug AdministrationDocument4 pagesNew Technologies Related To Drug AdministrationJastine Miguel EGUIANo ratings yet
- Module 1 - The Language of Anatomy and Physiology For StudentsDocument6 pagesModule 1 - The Language of Anatomy and Physiology For Studentsfirmo minoNo ratings yet
- Sas3 Bio024Document36 pagesSas3 Bio024Merlyn Limbaga CastroverdeNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TransesDocument3 pagesAnaphy TransesJoyce ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Resource Unit SampleDocument16 pagesResource Unit SampleShania CabucosNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document14 pagesLab Report 1Bella LopezNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 NotesDocument17 pagesGeneral Biology 2 NotesAlyssa Mae BinoNo ratings yet
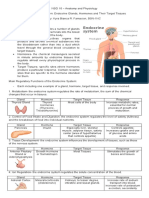
- The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Endocrine SystemKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of LeukemiaDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of LeukemiaJamaica Aurelio75% (4)
- Joyce TravelbeeDocument4 pagesJoyce TravelbeeElenor May Chantal Messakaraeng100% (2)
- Misericordia Activity Output OrtegaDocument4 pagesMisericordia Activity Output OrtegaKaye OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Culture Microorganism by Hay Infusion - forBSEd III-P PDFDocument2 pagesLab 1 Culture Microorganism by Hay Infusion - forBSEd III-P PDFKarl Francis Garcia100% (2)
- Funda Lab - Prelim ReviewerDocument16 pagesFunda Lab - Prelim ReviewerNikoruNo ratings yet
- TFN Chapter 1-3 YyyyDocument13 pagesTFN Chapter 1-3 YyyyIvana Yaga CantarNo ratings yet
- Casabar Crislyn Exercise 32 PDFDocument2 pagesCasabar Crislyn Exercise 32 PDFSEAN JODI M. COSEPENo ratings yet
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Science LT 10 - Reproductive SystemAlven Rey100% (2)
- Cell ModificationDocument1 pageCell ModificationAPZELIA ANGEL DURUIN100% (1)
- Traditional Teaching Strategies - LecturingDocument8 pagesTraditional Teaching Strategies - Lecturingsagami.g100% (2)
- Integumentary System 24Document10 pagesIntegumentary System 24Hampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Parts and FunctionsDocument6 pagesThe Digestive System Parts and FunctionsDixie MerinNo ratings yet
- Name of The Philosophers Brief History/Background Important ContributionsDocument4 pagesName of The Philosophers Brief History/Background Important ContributionsGladys Bacho Mujeres100% (1)
- Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesNarrative ReportRoxenette Gil Bernales PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Colorful Illustrative DNA Day Science Educational InfographicDocument1 pageColorful Illustrative DNA Day Science Educational InfographicKITIARA DIANELLA LEDESMANo ratings yet
- Nursing As Caring: A Model of Transforming PracticeDocument12 pagesNursing As Caring: A Model of Transforming Practicelalaine nadulpitNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper On The Story of Dolly PDFDocument1 pageReflection Paper On The Story of Dolly PDFKen Chinnie M. PresbiteroNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Format: Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors (Contributing) (Triggering)Document2 pagesPathophysiology Format: Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors (Contributing) (Triggering)AyaBasilio100% (1)
- Critique Movie - GhajiniDocument3 pagesCritique Movie - GhajiniLhaiela AmanollahNo ratings yet
- Malungay OintmentDocument6 pagesMalungay OintmentKc091150% (6)
- Assessment of The Heart and Neck Vessels ScriptDocument2 pagesAssessment of The Heart and Neck Vessels ScriptIvy Kaye TERRIBLENo ratings yet
- Pe 1Document1 pagePe 1Aries Buyacco100% (1)
- The Human CellDocument3 pagesThe Human CellA HNo ratings yet
- DAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 2: Cells and OrganellesDocument48 pagesDAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 2: Cells and OrganellesEmilyNo ratings yet
- 6th Science PDE Worksheet 2018 1 TermDocument5 pages6th Science PDE Worksheet 2018 1 TermJUAN CARLOS0% (1)
- Chapter 12 The Cell CycleDocument8 pagesChapter 12 The Cell CycleMicky Bandera100% (2)
- Exercise 4 Summary - KEY PDFDocument3 pagesExercise 4 Summary - KEY PDFFrida Olea100% (1)
- Cellbio 33Document2 pagesCellbio 33joker.fan245No ratings yet
- Module 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Document4 pagesModule 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Abegail ReluniaNo ratings yet
- Protein SortingDocument33 pagesProtein SortingFaddy Oraha100% (1)
- Bio 111 Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesBio 111 Lecture Notesflyerh65No ratings yet
- Mitosis ActivityDocument2 pagesMitosis Activityapi-433685905No ratings yet
- I Can : © Pearson Education LTD 2014. Copying Permitted ForDocument2 pagesI Can : © Pearson Education LTD 2014. Copying Permitted Forghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- 3D Cell Project and RubricDocument3 pages3D Cell Project and Rubricteresaeliezel.borja001No ratings yet
- Science 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - Week 1-Week 4 - SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesScience 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - Week 1-Week 4 - SY 2021-2022Lenette AlagonNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Organelles - Structure and FunctionKaryl Marie Rodas JaminNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PYQs Solution - 19189642 - 2023 - 06 - 05 - 12 - 38Document12 pagesCell Biology PYQs Solution - 19189642 - 2023 - 06 - 05 - 12 - 38Arsh DhawanNo ratings yet
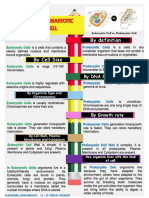
- Prokalytic Vs EurokalyticDocument1 pageProkalytic Vs EurokalyticJessielyn DangananNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure & Functiongundogan21100% (1)
- Mystery Cell ModelDocument5 pagesMystery Cell ModelMely VillacuraNo ratings yet
- Golgi Apparatus - WikipediaDocument17 pagesGolgi Apparatus - WikipediaPrakashananda ThakurNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of CellsDocument7 pagesParts and Functions of CellsKate Aireen JerezNo ratings yet
- Session No. 1.2. Cell Types and ModificationsDocument48 pagesSession No. 1.2. Cell Types and ModificationsShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- BIOL Molecular Basis of Life SlidesDocument422 pagesBIOL Molecular Basis of Life SlidesIsaac BateNo ratings yet
- Cellorganelles PPT 2Document20 pagesCellorganelles PPT 2Riyashika RNo ratings yet
- WS 1 - Cells (Answer Key) 2Document4 pagesWS 1 - Cells (Answer Key) 2Nandu SabkabanduNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: Structure Function The Nucleus Controls and Regulates The Activities of The CellDocument13 pagesNucleus: Structure Function The Nucleus Controls and Regulates The Activities of The CellAndres ValleNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument22 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsKurt DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Proteins Sorting Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument13 pagesProteins Sorting Mitochondria and ChloroplastAltaf khanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsDocument56 pagesTopic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsAhmed IqbalNo ratings yet