College of Nursing: Pharmacological Management
College of Nursing: Pharmacological Management
Uploaded by
JOHN PEARL FERNANDEZCopyright:
Available Formats
College of Nursing: Pharmacological Management
College of Nursing: Pharmacological Management
Uploaded by
JOHN PEARL FERNANDEZOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
College of Nursing: Pharmacological Management
College of Nursing: Pharmacological Management
Uploaded by
JOHN PEARL FERNANDEZCopyright:
Available Formats
Mindanao State University – Iligan Institute of Technology Student: JOHN PEARL A.
FERNANDEZ Block: CCC
COLLEGE OF NURSING MARIA ANTOINETTE SICLOT
PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
DRUG STUDY
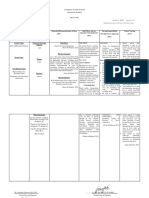
Brand Name: DUPHALAC Generic Name: LACTULOSE Drug Classification: OSMOLAR LAXARTIVES
Dosage, Route & Frequency Drug-Drug & Drug- Side Effects Adverse Reactions
Drug Action Indications Contraindications
Recommended Prescribed Food Interactions (By System) (By System)
PO 30–60 mL/d 20cc now then Increases water content and Anti-infectives: Treatment for Patients on low- GI: nausea, vomiting, EENT: tinnitus
prn BID softens the stool. Lowers the pH decreased lactulose constipation galactose diets. diarrhea, intestinal
of the colon, which inhibits the efficacy cramps, abdominal GI: fecal impaction
diffusion of ammonia from the Hypersensitivity to distention, flatulence
Other laxatives: lactulose Other: salicylate
colon into the blood, thereby
interference with toxicity
reducing blood ammonia levels.
response to lactulose
Absorption:Less than 3%
absorbed after oral
administration.
Distribution: Unknown.
Metabolism and Excretion:
Absorbed lactulose is excreted
unchanged in the urine.
Unabsorbed lactulose is
metabolized by colonic bacteria
to lactic, acetic, and formic
acids.
Half-life: Unknown
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 1
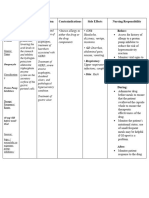
Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE) Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE)
A: Assess patient for abdominal distention, presence of bowel sounds, and normal pattern of I: Monitor fluid intake and output. Note signs and symptoms of fluid and electrolyte imbalances
bowel function. Assess color, consistency, and amount of stool produced. PSE: Assess mental that may result from watery stools. Habitual use of laxatives can cause fluid volume deficit,
status (orientation, level of consciousness) before and periodically throughout course of therapy. electrolyte losses, and loss of urge to defecate. Encourage patient to increase water intake (if
Monitor serum electrolytes periodically when used chronically. May cause diarrhea with resulting not contraindicated), which will decrease hard, dry stools. Teach patient not to chew tablets but
hypokalemia and hypernatremia to swallow them whole. Encourage patient to time administration of drug so as not to interfere
with activities or sleep.
D: Constipation related to ignoring urge to defecate
E: Determine effectiveness of nonpharmacologic methods for alleviating constipation. Evaluate
P: Patient will have a normal bowel elimination pattern. Patient will exercise, eat foods high in patient’s use of laxatives in managing constipation. Identify laxative abuse.
fiber, and have adequate fluid intake to avoid constipation.
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 2
You might also like
- Drug Study TableDocument4 pagesDrug Study TableSheena Friales Dorin100% (2)
- Drug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)AgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: West Visayas State UniversityDocument2 pagesDrug Study: West Visayas State UniversityDivine Mercy De JulianNo ratings yet
- Campillo-Drug-Study M1Document4 pagesCampillo-Drug-Study M1NICOLE CAMPILLONo ratings yet
- Lactulose Drug StudyDocument1 pageLactulose Drug StudyJhanine ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LactuloseDocument2 pagesDrug Study - LactuloseCath Bril100% (1)
- Drugs Affecting The 3Document20 pagesDrugs Affecting The 3beatrixjohannahNo ratings yet
- SUMAOANG - Maalox Drug StudyDocument4 pagesSUMAOANG - Maalox Drug StudyMina SumaoangNo ratings yet
- LACTULOSE Drug StudyDocument6 pagesLACTULOSE Drug StudyJay Ann Joy PerudaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyfaula rocamoraNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument1 pageDrug Name1E SENSANO LEAHNo ratings yet
- PHRM 465Document56 pagesPHRM 465api-649060644No ratings yet
- DRUG LactuloseDocument1 pageDRUG LactuloseJona Phie Domingo MonteroNo ratings yet
- Cabasis1 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCabasis1 Drug StudyNick James CabasisNo ratings yet
- DS - Senokot ForteDocument1 pageDS - Senokot ForteMarjorie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- MaaloxDocument2 pagesMaaloxJulia HermoginoNo ratings yet
- PURGATIVES AND LAXATIVES JM'sDocument8 pagesPURGATIVES AND LAXATIVES JM'sProvidence UzomaNo ratings yet
- Constipation & Diarrhoea PowerpointDocument7 pagesConstipation & Diarrhoea PowerpointsamritiNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On GIT Laxatives & Purgatives: Dr. Syed Muneeb Anjum (PH.D.) Ips, UvasDocument13 pagesDrugs Acting On GIT Laxatives & Purgatives: Dr. Syed Muneeb Anjum (PH.D.) Ips, UvasSultan Abdul Hamid IINo ratings yet
- Lida AjocDocument10 pagesLida AjocEzra Knight Llesis AcebedoNo ratings yet
- 2 LaxativesDocument17 pages2 Laxativesمشتاقة للجنةNo ratings yet
- Lactulose DrugDocument3 pagesLactulose Drugjangzie100% (1)
- Drugstudy Ms. IbaleDocument23 pagesDrugstudy Ms. IbaleNabor, MelagroseNo ratings yet
- Lactomed and MethergineDocument2 pagesLactomed and MethergineLeah Mae LiragNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Body System and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesDrugs Affecting The Body System and Nursing ConsiderationsLOVELLE GRACE DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiespircanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing Drug Study Age: 69 Ward/Bed Number:MMSW-2 Impression/Diagnosis: HAP, COPD Acute ExacerbationDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing Drug Study Age: 69 Ward/Bed Number:MMSW-2 Impression/Diagnosis: HAP, COPD Acute ExacerbationSian AsadaNo ratings yet
- Tugas DulcolaxDocument2 pagesTugas DulcolaxPriska Nagh Gas-oneNo ratings yet
- Management of ConstipationDocument3 pagesManagement of ConstipationFarah Balqis BaragbahNo ratings yet
- X. Medical ManagementDocument12 pagesX. Medical ManagementXy-Za Roy MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Mode of Action Indicati On Contra Indicati On Adverse Reaction Nursing ReponsibilityDocument10 pagesDrug Classification Mode of Action Indicati On Contra Indicati On Adverse Reaction Nursing ReponsibilitymegNo ratings yet
- Laxatives PpsDocument22 pagesLaxatives Ppschan_dar100% (1)
- Constipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BDocument2 pagesConstipation: Patient Name: Shehzad Age: 45 Ward: Emergency BShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Classification Generic Name Brand NameDocument42 pagesClassification Generic Name Brand NameMARIA ROWENA VIA J. LUCENANo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY GROUP 4Document62 pagesPHARMACOLOGY GROUP 4cutty.santillanNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDYDocument6 pagesDRUGSTUDYMauriceNo ratings yet
- CaCO3 Drug StudDocument2 pagesCaCO3 Drug StudAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis Group 3 NCM 116Document21 pagesPancreatitis Group 3 NCM 116Diana Jane LauretaNo ratings yet
- Viii. Pharmacologic Intervention (Drug Study)Document10 pagesViii. Pharmacologic Intervention (Drug Study)Cyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Constipation and DiarrheaDocument40 pagesDrugs For Constipation and Diarrheagirgray100% (1)
- Osmotic LaxativesDocument2 pagesOsmotic LaxativesACanNo ratings yet
- LaxativesDocument9 pagesLaxativesomar khanNo ratings yet
- DulcolaxDocument1 pageDulcolaxKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyKaty PerchieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Med Ward Duty)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Med Ward Duty)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Treatment of ConstipationDocument34 pagesTreatment of ConstipationDr. Lokeshwar ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting GitDocument8 pagesDrugs Affecting GitReysel MonteroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HepatitisDocument7 pagesDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Gastro New NotesDocument12 pagesPart 2 Gastro New NotesanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (V.luna)Document4 pagesDrug Study (V.luna)carizzajoyNo ratings yet
- PHCP Lec Topic 4 To 10Document19 pagesPHCP Lec Topic 4 To 10armand bayoranNo ratings yet
- Drug Ana LaraDocument2 pagesDrug Ana LaralarapaulineNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyHanna La MadridNo ratings yet
- PHRM TemplateDocument4 pagesPHRM TemplateRichard SakyiamahNo ratings yet
- Cana LafutidineDocument3 pagesCana LafutidineJacob Clint LipuraNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studyzhapper2002No ratings yet
- GIT AgentsDocument51 pagesGIT AgentsEimhie Lee CasiNo ratings yet
- Bile Reflux: Navigating the Complexities of Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term WellnessFrom EverandBile Reflux: Navigating the Complexities of Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term WellnessNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Ii Gordon's Assessment: Maternal and Child NursingDocument3 pagesNursing Assessment Ii Gordon's Assessment: Maternal and Child NursingJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- 14 Landmark Medico Legal Philippine Jurisprudence 1946 To 2021 and Theory U Bunjing Transes in ProgressDocument6 pages14 Landmark Medico Legal Philippine Jurisprudence 1946 To 2021 and Theory U Bunjing Transes in ProgressJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Concept Map RubricDocument3 pagesConcept Map RubricJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- NSG 129.3 CASE 1 Discharge PlanDocument1 pageNSG 129.3 CASE 1 Discharge PlanJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: General ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesChapter 1: General ConsiderationsJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- NSG 129: Nursing Leadership and ManagementDocument13 pagesNSG 129: Nursing Leadership and ManagementJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZ100% (1)
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Medico-Legal Case Involving Bell's PalsyDocument18 pagesMedico-Legal Case Involving Bell's PalsyJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- The Histopathological Pattern of Skin Cancers in IraqDocument4 pagesThe Histopathological Pattern of Skin Cancers in IraqAamir Jalal Al-MosawiNo ratings yet
- Mednet RI FormDocument2 pagesMednet RI FormhhmoudNo ratings yet
- HIRAID - An Evidence-Informed Emergency Nursing Assessment FrameworkDocument15 pagesHIRAID - An Evidence-Informed Emergency Nursing Assessment FrameworkHNdbzek Y;daeNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Care For Woman in Labor: Angeles University Foundation College of Nursing S.Y. 2010-2011Document5 pagesAssessment and Care For Woman in Labor: Angeles University Foundation College of Nursing S.Y. 2010-2011Patricia Alissa Mariz ManalangNo ratings yet
- Sindrome AMSDocument4 pagesSindrome AMSCons TanzaNo ratings yet
- Surat Pesanan APL Okt 18Document234 pagesSurat Pesanan APL Okt 18Eko EdgarNo ratings yet
- Prelim: (Exam Schedule:)Document4 pagesPrelim: (Exam Schedule:)Nestor BalboaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Asphyxia (PPTminimizer)Document281 pages12 - Asphyxia (PPTminimizer)Husam ShawagfehNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene Tool As Per WHODocument4 pagesHand Hygiene Tool As Per WHOPayal ThakkerNo ratings yet
- BioquimicaDocument2,040 pagesBioquimicaJoao Manoel100% (2)
- Assessment of PWD Checklist Rev 7-19-17Document2 pagesAssessment of PWD Checklist Rev 7-19-17riddhiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Shock Sepsis and Organ Failure PDFDocument1,179 pagesPathophysiology of Shock Sepsis and Organ Failure PDFNotInterested100% (1)
- Asccp Updated Guidelines - 3.21.13Document27 pagesAsccp Updated Guidelines - 3.21.13Luis Enrique Moscoso OrtizNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Pylorospasm in Infants 1922Document2 pagesTreatment of Pylorospasm in Infants 1922muradchy321No ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument24 pagesNephrotic SyndromeSamah KhanNo ratings yet
- Sib Abdomen HermanDocument62 pagesSib Abdomen Hermanapi-396702708No ratings yet
- Chimaphila Pipsissewa Materia Medica HerbsDocument3 pagesChimaphila Pipsissewa Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra Guerrero100% (1)
- Clinical Definition of Heart FailureDocument12 pagesClinical Definition of Heart FailureFreddy PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- 2007 PFTs The Forced Oscillation TechniqueDocument50 pages2007 PFTs The Forced Oscillation TechniqueServiço de Imunoalergologia - H.S. João100% (1)
- HOSPITALFORMULARYDocument32 pagesHOSPITALFORMULARYRana EhtishamNo ratings yet
- cliexa-RA Implementation in Colorado Arthritis Center: A Case Study of Quadruple Aim ImpactsDocument3 pagescliexa-RA Implementation in Colorado Arthritis Center: A Case Study of Quadruple Aim ImpactsPR.comNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Aural Hematoma in Dog: December 2017Document5 pagesSurgical Management of Aural Hematoma in Dog: December 2017Satria Adi MarhendraNo ratings yet
- The Health Care Delivery SystemDocument14 pagesThe Health Care Delivery SystemDolma Tamang100% (1)
- Lucy Mayienga CV RecentDocument3 pagesLucy Mayienga CV Recentlucy.mayiengaNo ratings yet
- Rencana Kebutuhan Obat JiwaDocument1 pageRencana Kebutuhan Obat JiwadiapalupiNo ratings yet
- ECG QuizDocument6 pagesECG QuizIsland Rae100% (1)
- Mechanism of InjuryDocument3 pagesMechanism of InjuryJohn BrittoNo ratings yet
- Naso Orogastric Tube Management Guidelines For The Newborn V2.0 Sept 16 PDFDocument20 pagesNaso Orogastric Tube Management Guidelines For The Newborn V2.0 Sept 16 PDFWilda Awlia100% (1)
- 2030 - The Future of Medicine: Avoiding A Medical Meltdown. ISBN 019960066X, 978-0199600663Document23 pages2030 - The Future of Medicine: Avoiding A Medical Meltdown. ISBN 019960066X, 978-0199600663anettemaurillak100% (13)
- Antonio Daniele Pinna, Giorgio Ercolani (Eds.) - Abdominal Solid Organ Transplantation - Immunology, Indications, Techniques, and Early Complications-Springer International Publishing (2015)Document443 pagesAntonio Daniele Pinna, Giorgio Ercolani (Eds.) - Abdominal Solid Organ Transplantation - Immunology, Indications, Techniques, and Early Complications-Springer International Publishing (2015)blooom_00No ratings yet