Chapter 1: Information Systems in Global Business Today
Chapter 1: Information Systems in Global Business Today
Uploaded by
Nam Phuong NguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1: Information Systems in Global Business Today
Chapter 1: Information Systems in Global Business Today
Uploaded by
Nam Phuong NguyenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1: Information Systems in Global Business Today
Chapter 1: Information Systems in Global Business Today
Uploaded by
Nam Phuong NguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION SYSTEMS
IN GLOBAL BUSINESS TODAY
Question 1: List and describe six reasons why information systems are so
important for business today.
Six reasons why information systems are so important for business today
include:
1) Operational excellence: businesses can constantly improve the efficiency
of their operations in order to achieve higher profitability. Managers of
businesses can accomplish these objectives by using information
systems and the latest technologies, particularly when combined with
changes in business practices and management behavior.
2) New Products, Services, and Business Models : information systems and
technologies play a major role for businesses in creating new products
and services. New business models can also be created and these can
describe how a company create, ship, and sell their products.
3) Customer and Supplier Intimacy: the better a company gets to know its
clients and provides excellent services, the more likely the customers
will come back and purchase more. Revenues and profits increase as a
result of this. Similarly, the more a company approaches its suppliers,
the better they are to provide critical inputs and to save costs. Figuring
out how to really understand millions of clients or suppliers is a major
challenge for businesses.
4) Improved Decision Making: many business managers depend on
forecases to make decisions instead of getting all of the necessary data
at the right time, which leads to the poor business performances.
Information systems make it possibly for managers to use real time data
to make better decisions and not have to waste time looking for
information.
5) Competitive Advantage: all the areas that information systems focus on
helps businesses create a competitive advanatge over their rivals, for
example, businesses might charge less for products or they might
respond to customers and suppliers under a faster time which increases
sales and profits.
6) Survival: information systems and technologies in a firm are necessary
and crucial to keep them catch up with industry-level changes.
Question 2: Define an information system and describe the activities it
performs.
Technically, an information system contains different interconnected
components that work together to collect, process, store, and distribute data
to support decision making and control in an organization. In addition,
information systems may also help managers and workers analyze problems,
visualize complex subjects, and create new products.
The three activities that information system controls in an organzition
are input, processing, and output. Each activity has its own function that it
serves in an organization. For example, input takes in all the information from
internal and external environments while processing converts that information
into something more meaningful. In the end, output takes care of distributing
the information to the right people for whom the information was intended
for.
Question 3: List and describe the organizational, management, and
technology dimensions of information systems.
Information systems assists firms in terms of the organization when it
serves the different levels that exists in the firm. The organization
dimension of information systems involves issues such as the
organization’s hierarchy, functional specialties, business processes,
culture, and political interest groups.
o In business hierachy, there are 3 principal levels:
+ Senior management: is responsible for the firm’s financial
results as well as making long-term strategic decisions on goods
and services.
+ Middle management: includes scientists and knowledge
workers. Middle management is in charge of carrying out senior
management’s programs and plans. Engineers, scientists, and
architects are knowledge workes who develop products or
services and generate new knowledge for the company, while
secretaries and clerks help with scheduling and communications
at all levels of the company.
+ Operational management: includes production and service
workers, data workers. Operational management is in charge of
overseeing the business’s daily operations. Production and
service workers are the ones who really make the product and
provide the service.
o Some experts are employed to manage some main business
functions such as sales and marketing, manufacturing and
production, finance and accounting, and human resources.
o An organization coordinates work through its hierarchy and
through its business processes. Business processes consists of
formal rules that have been built for guiding employees and
achieving daily tasks.
o Culture is also a big part of an organization as it is unique for each
organization. It is all the assumptions, values, and methods of
doing tasks that all employees must agree.
o Different levels have different points of view, which creates the
conflicts and these conflicts are basis for organizational politics.
Management: The role of management is to analyze of many situations
that companies face, make decisions, and develop action plans to
address organizational issues. Managers recognize business problems in
the surrounding environment and community, develop an organizational
plan to solve them, and assign human as well as financial capital to
organize work and achieve results. The management dimension of
information systems involves leadership, strategy, and management
behavior. Information systems supply tools and information needed by
managers to allocate, coordinate and monitor their work, make
decisions, create new products and services, make long-term strategic
decisions.
Information Technology: The technology dimensions consist of
computer hardware, software, data management technology, and
networking/telecomunications technology (including the Internet), the
WorldWideWeb. Management uses technology (hardware, software,
storage, telecommunications) to carry out their functions. It is one of the
methods used by managers to deal with transition.
o Computer hardware refers to the physical equipment that is used
for input, encoding, and output. Computers of different sizes and
shapes (including mobile handheld devices); various input, output,
and storage devices; and telecommunications devices that link
computers are all part of it.
o Computer software is known as the comprehensive,
preprogrammed instructions that guide and organize the
computer hardware components in an IS.
o Data management techonology refers to the program that
controls how data is organized on physical storage devices.
o Networking/telecomunications technology connects different
pieces of hardware and transfers data from one physical location
to another. It consists of both physical equipment and software.
o The WorldWideWeb is an Internet service that employs widely
agreed principles for storing, retrieving, formatting and displaying
information in a page formate. Web pages are connected to other
web pages which contain text, graphics, animations, music and
video.
Both of these systems, as well as the people who need to operate
and maintain them, are tools that can be spread around the
company and make up the information technology infrastructure.
The firm’s IT infrastructure serves as the base, or basis, on which
its unique information systems can be built.
Each business must carefully plan and manage its information
technology infrastructure to ensure that it has the technology
resources it requires to complete the work it intends to do with IS.
Question 4: Define complementary assets and describe their relationship
to information technology.
Complementary assets are those assets required to derive value from
a primary investment. In order to obtain meaningful value from
information systems, organization must support their technology
investments with appropriate complementary investments in
organization and management. These complementary assets include
new business models and business processes, supportive
organizational culture and management behavior, appropriate
technology standards, regulations and laws.
New information technology investments are unlikely to produce
high returns unless businesses make the appropriate managerial and
organizational changes to support technology. Firms must rely on
supportive values, structures, and behavior patterns to obtain a
greater value from their IT investments. Value must be added
through complementary assets such as new business processes,
management behavior, organizational culture and training.
Question 5: Describe the complementary social, managerial, and
organizational assets required to optimize returns from information
technology investments. (Table 1.2 page 27)
You might also like
- Questions Chapter 1 & 2Document11 pagesQuestions Chapter 1 & 2dhwani1621100% (20)
- Case Study 1Document3 pagesCase Study 1Nam Phuong Nguyen100% (2)
- Case Study 4Document4 pagesCase Study 4Nam Phuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3Document11 pagesCase Study 3Nam Phuong Nguyen100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Review Question and AnswerDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Review Question and AnswerAmy Aung100% (3)
- Information Management: By: Karl Steven A. Maddela InstructorDocument33 pagesInformation Management: By: Karl Steven A. Maddela InstructorKarl Steven Adalem Maddela100% (4)
- Bid Submission SheetDocument3 pagesBid Submission SheetARSE100% (1)
- Unit IDocument21 pagesUnit IRaghavkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Second LectureDocument44 pagesSecond LectureMahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Explain Why Information Systems Are So Essential in Business TodayDocument7 pagesExplain Why Information Systems Are So Essential in Business TodaySmitho UnpluggedNo ratings yet
- Project Management Information Systems: Nyambati N. RichardDocument29 pagesProject Management Information Systems: Nyambati N. RichardRichard NyasimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and Chapter 2 SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 1 and Chapter 2 SummaryGraciella AudreyNo ratings yet
- Mis Chap 1 NotesDocument5 pagesMis Chap 1 NotesShaheryar RashidNo ratings yet
- Mis CTDocument10 pagesMis CTJoy NathNo ratings yet
- MIS Chapter 1 - Information SystemsDocument4 pagesMIS Chapter 1 - Information Systemsstephenwainaina994No ratings yet
- Exam PreparationDocument5 pagesExam PreparationadsfNo ratings yet
- IT Supports Organizational Performance in Turbulent Business EnvironmentsDocument34 pagesIT Supports Organizational Performance in Turbulent Business EnvironmentsSakshi VermaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Semester Mis Notes 1Document56 pages3rd Semester Mis Notes 1Sanjay JaisiNo ratings yet
- Dis511 Jan-Apr 2020 Introduction To Information Systems - Lect 1Document11 pagesDis511 Jan-Apr 2020 Introduction To Information Systems - Lect 1Wycliff OtengNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Information SystemsDocument5 pagesApproaches To Information SystemsDenis GikenyeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management Information SystemsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Management Information SystemsYus MartianNo ratings yet
- Module 1.1Document25 pagesModule 1.1brantchikoyNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document6 pagesChap 1Sammy AcquahNo ratings yet
- MIS-Unit 1Document47 pagesMIS-Unit 1ghimirebob1998No ratings yet
- Mis NotesDocument64 pagesMis Notessucheta pandaNo ratings yet
- Mlo5s Is Elmnhg KoloDocument30 pagesMlo5s Is Elmnhg KoloRafeek makramNo ratings yet
- MIS Question Ans Answers ch1,2,3Document18 pagesMIS Question Ans Answers ch1,2,3Tamaada JbNo ratings yet
- MIS Research Ch1-4Document10 pagesMIS Research Ch1-4Louis Al BedouinNo ratings yet
- IS Summary ch.1,2,4Document22 pagesIS Summary ch.1,2,401157572404aNo ratings yet
- C1H021021 - Almas Delian - Resume MIS Bab 1Document2 pagesC1H021021 - Almas Delian - Resume MIS Bab 1Almas DelianNo ratings yet
- MIS-Unit 1Document61 pagesMIS-Unit 1BhagwatiNo ratings yet
- Managing The Digital Firm: This Chapter Will Help You UnderstandDocument33 pagesManaging The Digital Firm: This Chapter Will Help You UnderstandSuman BhandariNo ratings yet
- Whole Notes Combine Canvas PDFDocument17 pagesWhole Notes Combine Canvas PDFKhevana PurohitNo ratings yet
- Perspective of Information SystemDocument4 pagesPerspective of Information SystemTarek AsaduzzamanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Information Systems in Global Business TodayDocument48 pagesLecture 2 - Information Systems in Global Business TodayrachaelmercNo ratings yet
- Impact of IT On BusinessDocument33 pagesImpact of IT On BusinessSamiksha SainiNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual SimDocument6 pagesSolution Manual Simemail sekaliNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument78 pagesManagement Information SystemNORIZA BINTI CHE SOH STUDENTNo ratings yet
- MIS Module 1Document28 pagesMIS Module 1jsji14No ratings yet
- MIS Unit-1Document4 pagesMIS Unit-1Reeya JashuNo ratings yet
- ABI Summary LUsDocument35 pagesABI Summary LUsh9rkbdhx57No ratings yet
- Information System For Managers: Semesteri Cours E Code: S L I T 5 0 1 CR E Di T: 3Document42 pagesInformation System For Managers: Semesteri Cours E Code: S L I T 5 0 1 CR E Di T: 3varun kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6-10Document100 pagesUnit 6-10lucky dolphinNo ratings yet
- Information Systems - ReadingDocument23 pagesInformation Systems - ReadingAlejandro Rios MorenoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managing Information & TechnologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Managing Information & TechnologyABARRA, ZAIRAH L.No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Is Week 2Document19 pagesFundamentals of Is Week 2vmera23No ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument10 pagesChapter OneGetnetNo ratings yet
- Book Chapter 2 VivianDocument12 pagesBook Chapter 2 VivianThomasNo ratings yet
- Misreviewer 1Document13 pagesMisreviewer 1Reg El Ordeñiza OrtizNo ratings yet
- MIS Chapter 1Document22 pagesMIS Chapter 1Ropuk Paul 213-024No ratings yet
- Notes Management Information SystemDocument61 pagesNotes Management Information SystemMuneebAhmedNo ratings yet
- MIS Tutorial 1 AnswerDocument7 pagesMIS Tutorial 1 AnswerChia Kong Haw100% (1)
- Data and InformationDocument30 pagesData and InformationSyed SameerNo ratings yet
- BMA101B Tutor Slides 6-2020Document8 pagesBMA101B Tutor Slides 6-2020sicelo ncubeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Information SystemsDocument6 pagesUnit 6 - Information Systemslucky dolphinNo ratings yet
- ICT - PDF Version 1Document40 pagesICT - PDF Version 1Shah newaz ShawonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information SystemsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Information Systemshnyaga09100% (1)
- Organization StructuresDocument16 pagesOrganization Structuressami benamerNo ratings yet
- MIS Chapter 2Document18 pagesMIS Chapter 2Ropuk Paul 213-024No ratings yet
- Business Information Systems - NotesDocument6 pagesBusiness Information Systems - NotesLilian Njoki100% (1)
- Information Can Be Defined As Data That Have Been Converted Into ADocument10 pagesInformation Can Be Defined As Data That Have Been Converted Into AVishwanath HalemaniNo ratings yet
- IT Governance to Drive High Performance: Lessons from AccentureFrom EverandIT Governance to Drive High Performance: Lessons from AccentureNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document20 pagesCase Study 2Nam Phuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- JIT Issues and Implementation at Eicher TractorDocument20 pagesJIT Issues and Implementation at Eicher TractorPraveen Trivedi100% (2)
- Maruti 800 - PLCDocument13 pagesMaruti 800 - PLCAnkit Agrawal100% (1)
- How I Added $12,000 in Monthly Revenue in 3 Weeks of Working With My Client With Just 1700 Followers (And How You Can Too)Document22 pagesHow I Added $12,000 in Monthly Revenue in 3 Weeks of Working With My Client With Just 1700 Followers (And How You Can Too)CodeNo ratings yet
- Sales Ord 8074207Document1 pageSales Ord 8074207Magabata GoguNo ratings yet
- Kyc and Aml Guidelines-2020Document52 pagesKyc and Aml Guidelines-2020Nishesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Crăciun-SABĂU-Cristina-Mihaela-NAGY 2020Document18 pagesCrăciun-SABĂU-Cristina-Mihaela-NAGY 2020Cristina NagyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations and Supply Chain ManagementDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Operations and Supply Chain ManagementRahul JainNo ratings yet
- Class 3 - Chapter 3, and Google Analytics WalkthroughDocument28 pagesClass 3 - Chapter 3, and Google Analytics Walkthrough11803098danNo ratings yet
- NCCEdu L7DBM Unit Specification V1.5Document55 pagesNCCEdu L7DBM Unit Specification V1.5Abdallah HassanNo ratings yet
- Jio Fiber 1Document4 pagesJio Fiber 1Nayyar AlamNo ratings yet
- Assignment-7 Assignment-7 MB4706Document4 pagesAssignment-7 Assignment-7 MB4706efraimjeferson1010No ratings yet
- Problem Statements - Energy EfficiencyDocument2 pagesProblem Statements - Energy EfficiencyAkshay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Bunge Limited: Key FactsDocument3 pagesBunge Limited: Key FactsAnuj KrNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 15Document24 pagesIfrs 15Madhu Sudan DarjeeNo ratings yet
- Mojo-Jojos Ni Migs Business PaperDocument16 pagesMojo-Jojos Ni Migs Business PaperCaz AlmedaNo ratings yet
- Audit Under FiscalDocument108 pagesAudit Under FiscalAjay PanwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 15Document8 pagesChapter 14 15Yoda RindyNo ratings yet
- Marcom PlanningDocument3 pagesMarcom PlanningpranavNo ratings yet
- Fire Boltt WarrantyDocument2 pagesFire Boltt WarrantyVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Code of ConductDocument5 pagesCode of ConductAkhlesh ChoureNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Udyam RegistrationDocument10 pagesBenefits of Udyam Registrationudyam kumarNo ratings yet
- Project On Hawk Eye Securities Limited: BUS 620 (Marketing Management) - Section: 4Document34 pagesProject On Hawk Eye Securities Limited: BUS 620 (Marketing Management) - Section: 4Samia MahmudNo ratings yet
- CHP 20 Fin 13Document11 pagesCHP 20 Fin 13Player OneNo ratings yet
- Acc Excel BasicDocument5 pagesAcc Excel BasickokoNo ratings yet
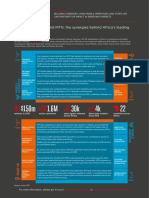
- $150m 1.6M 30k 4k 22: Case Study IDocument1 page$150m 1.6M 30k 4k 22: Case Study IMwaisa BangaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Partnership FormationDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Partnership FormationDante OrpianaNo ratings yet
- Informal Letter FormatDocument10 pagesInformal Letter Formatalexis cheongNo ratings yet
- Written SubmissionsDocument14 pagesWritten SubmissionsSahil ShrivastavNo ratings yet
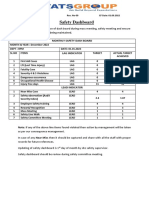
- 2.2 C New Safety Dashboard Dec2022Document1 page2.2 C New Safety Dashboard Dec2022subodh kumarNo ratings yet