0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 viewsPlug-Flow Digesters: Technical Details
Plug-Flow Digesters: Technical Details
Uploaded by
Ahmed MedhatA plug-flow digester is used to digest manure from ruminant animals like dairy cows. It consists of a mix tank, heated in-ground digester tank, biogas recovery system, effluent storage, and a biogas utilization system. Manure is mixed in the tank to 11-14% solids and fed into the rectangular digester daily. Proper operation requires daily mixing and heating to maintain the mesophilic temperature range, along with regular inspection and maintenance of components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Plug-Flow Digesters: Technical Details
Plug-Flow Digesters: Technical Details
Uploaded by
Ahmed Medhat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesA plug-flow digester is used to digest manure from ruminant animals like dairy cows. It consists of a mix tank, heated in-ground digester tank, biogas recovery system, effluent storage, and a biogas utilization system. Manure is mixed in the tank to 11-14% solids and fed into the rectangular digester daily. Proper operation requires daily mixing and heating to maintain the mesophilic temperature range, along with regular inspection and maintenance of components.
Original Title
RCM-Plug-Flow-Technical-Details-RCM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
A plug-flow digester is used to digest manure from ruminant animals like dairy cows. It consists of a mix tank, heated in-ground digester tank, biogas recovery system, effluent storage, and a biogas utilization system. Manure is mixed in the tank to 11-14% solids and fed into the rectangular digester daily. Proper operation requires daily mixing and heating to maintain the mesophilic temperature range, along with regular inspection and maintenance of components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesPlug-Flow Digesters: Technical Details
Plug-Flow Digesters: Technical Details
Uploaded by
Ahmed MedhatA plug-flow digester is used to digest manure from ruminant animals like dairy cows. It consists of a mix tank, heated in-ground digester tank, biogas recovery system, effluent storage, and a biogas utilization system. Manure is mixed in the tank to 11-14% solids and fed into the rectangular digester daily. Proper operation requires daily mixing and heating to maintain the mesophilic temperature range, along with regular inspection and maintenance of components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Plug-Flow Digesters:
Technical Details
Information excerpted from: Biomethane from Dairy Waste: A Sourcebook
for the Production and Use of Renewable Natural Gas in California
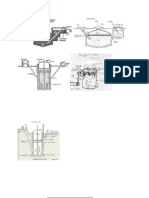
Description of Plug-Flow Digester
A plug-flow digester is used to digest manure from ruminant animals (dairy, beef, sheep) that
can be collected as a semisolid (10% to 60% solids) daily to weekly with minimal contamination
(dirt, gravel, stones, straw) and delivered to a collection point.
Plug-Flow Digester: How it Works
Components of Plug-Flow Digester
A plug-flow digester system generally includes a mix tank, a digester tank with heat exchanger
and biogas recovery system, an effluent storage structure, and a biogas utilization system. Post
digester solids separation is optional.
Collection/mix tank. A mix tank as described above for a complete digester is used to achieve a solids
concentration between 11% and 14% solids.
Plug-flow digester. A plug-flow digester is a heated, in-ground concrete, concrete block or lined
rectangular tank. The digester can be covered by a fixed rigid top, a flexible inflatable top or a floating
cover to collect and direct biogas to the gas utilization system.
Biogas utilization system. The recovered biogas can be used to produce space heat, hot water,
cooling, or electricity.
Solids separator (optional). A mechanical separator may be installed between the plug-flow digester
outflow and the effluent storage structure.
Methane recovery system. A plug-flow digester is covered by a gas tight fixed solid top, a flexible top,
or a floating cover to collect and direct biogas to the gas utilization system.
Solid cover. A solid cover is constructed to avoid cracking and leaks. Solid covers should resist
corrosion. A solid cover allows for minimal gas storage.
Inflatable Cover. A coated fabric is generally used for inflatable covers. An inflatable cover can be
designed for some gas storage. Wind protection may be necessary. The cover must have a gas tight
seal.
Floating cover. A floating cover is designed to lie flat on the digester surface.
Biogas Utilization with Plug Flow Digester
Design Criteria and Sizing the Plug-Flow Digester
Location. If a manure pump is installed to pump the 12% solids manure, the digester can be located
within a 300 ft radius of the mix tank at a convenient location with good access.
Mix tank. The mix tank can be round, square, or rectangular. A pump may be required to move
manure to the plug flow digester.
Hydraulic retention time and sizing of plug-flow digester. A plug-flow digester will function with an
HRT from 12 to 80 days. However, an HRT between 15 and 20 days is most commonly used to
economically produce 70% to 80% of the ultimate methane yield.
Dimensions. The depth of a plug-flow digester can be between 8 feet and 16 feet depending upon soil
conditions and the required tank volume. The width:depth ratio is usually greater than 1 and less than
2.5. The length:width ratio should be between 3.5 and 5.
Heat exchanger: An external heat exchanger or an internal heat exchanger is required to maintain the
digesting mixture at the design temperature. Hot water circulated through the heat exchanger is
heated using biogas as a fuel for a boiler or waste heat from a biogas fueled engine-generator.
Operating temperature. The daily temperature fluctuation should be less than 1o F. Most plug flow
digesters operate in mesophilic range between 95o to 105o F with an optimum of 100o F. It is
possible to operate in the thermophilic range between 135 to 145o F, but the digestion process is
subject to upset if not closely monitored.
Insulation. A plug flow digester surface may be insulated to control heat loss.
Construction materials. The digester can be constructed as a lined trench or as a reinforced concrete
or block tank.
Methane recovery system and covers. See discussion of methane recovery system above under
complete mix digesters.
P.O. Box 4716 PH: 510-834-4568 www.rcmdigesters.com
Berkeley, CA 94704 FAX: 510-834-4529 contact@rcmdigesters.com
Operation and Maintenance of Plug-Flow Digesters
Proper operation and maintenance of plug-flow digesters is necessary for successful operation.
Mix tank — operation. On a daily or every other day basis, collectible manure is pushed, dragged or
dumped into the mix tank. If necessary, dilution water or drier manure is added to the collected
manure and mixed to achieve the design total solids mixture. The mixed manure is released via
gravity gate or pumped into the digester.
Mix tank — maintenance. Mix tank maintenance consists of normal maintenance of pumps and
mixers per manufacturers recommendations. The mix tank will require occasional cleaning to remove
accumulated sand, gravel, steel and wood.
Plug-flow digester — operation. A plug-flow digester is fed from the mix tank daily or every other day.
The digester heating and mixing system should be checked daily to verify operation.
Plug-flow digester — maintenance. The digester temperature should be checked daily. The effluent
outlet and digester gas pressure relief should be checked weekly to be sure that they are operating
properly. The heat exchanger pump should be lubricated per the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Sludge accumulation may require sludge removal every 8 to 10 years.
Cover — maintenance. The cover should be visually inspected weekly for rainwater accumulation,
cracks, tearing, wear, and tensioning.
P.O. Box 4716 PH: 510-834-4568 www.rcmdigesters.com
Berkeley, CA 94704 FAX: 510-834-4529 contact@rcmdigesters.com
You might also like
- Fixed Film Anaerobic DigesterDocument3 pagesFixed Film Anaerobic DigesterTyan NufutomoNo ratings yet
- Brewing Technology From BriggsDocument14 pagesBrewing Technology From BriggsDuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Biogas Plant: Biogas Digester Design, Gas Production and PurificationFrom EverandBiogas Plant: Biogas Digester Design, Gas Production and PurificationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Agstar Technical Series:: Complete Mix DigestersDocument2 pagesAgstar Technical Series:: Complete Mix DigestersdeliomfNo ratings yet
- Biogas PowerplantDocument7 pagesBiogas PowerplantAndrei BarbazaNo ratings yet
- Sludge Treatment: Efficient Solutions For Wastewater Treatment PlantsDocument10 pagesSludge Treatment: Efficient Solutions For Wastewater Treatment PlantsLaurentiu ApostolNo ratings yet
- 55 Gal Drum Biogas Digester - Design and OperationDocument15 pages55 Gal Drum Biogas Digester - Design and OperationEd CasasNo ratings yet
- Review On Different Types of DigesterDocument10 pagesReview On Different Types of Digestercharmy rockzz100% (2)
- Biomass Pellet MillsDocument4 pagesBiomass Pellet MillsRadmila BlagojevicNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1 BiogasDocument27 pagesPresentation 1 BiogasGaurav SehrawatNo ratings yet
- Biogas Power Generation SystemDocument21 pagesBiogas Power Generation Systemfiraol temesgenNo ratings yet
- A Biogas Plant For The Digestion of Fresh Undiluted Cattle DungDocument3 pagesA Biogas Plant For The Digestion of Fresh Undiluted Cattle DungNilamdeen Mohamed ZamilNo ratings yet
- Biogas Systems: By: John Megryan B. SamartinoDocument15 pagesBiogas Systems: By: John Megryan B. SamartinoJohn MegryanNo ratings yet
- 2010 NRAES Paper - Klaesi DigesterDocument8 pages2010 NRAES Paper - Klaesi DigesterAleksandra Cvetković NedeljkovićNo ratings yet
- Biocomposting_SOP_for_distillery-Final_10.08.2018Document10 pagesBiocomposting_SOP_for_distillery-Final_10.08.2018Soundharya RNo ratings yet
- (SOP) For Composting Operation For Molasses Based DistilleriesDocument10 pages(SOP) For Composting Operation For Molasses Based Distilleriesmohsin husen BargirNo ratings yet
- 18.introduction To A Large-Scale Biogas Plant in A Dairy FarmDocument4 pages18.introduction To A Large-Scale Biogas Plant in A Dairy FarmAndre SitohangNo ratings yet
- Biogas: by Aditya KumarDocument30 pagesBiogas: by Aditya Kumaradam sgfNo ratings yet
- Biogas Plant Site Selection Criteria-UpdateDocument6 pagesBiogas Plant Site Selection Criteria-UpdateAbduletif HeboNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual of Bio-Gas ReactorDocument23 pagesOperation Manual of Bio-Gas ReactormaheshggargNo ratings yet
- Sludge TreatmentDocument8 pagesSludge TreatmentHausland Const. Corp.No ratings yet
- Fertilizer Industry Tcm11-16156 Rotary DryerDocument4 pagesFertilizer Industry Tcm11-16156 Rotary DryerwenigmaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase StudyMec InovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1shahidlatif_mughalNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic-Digest DesignsDocument7 pagesAnaerobic-Digest DesignsJaydev ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Technical Characteristics - Apollo PlantDocument15 pagesTechnical Characteristics - Apollo PlantNidDouNo ratings yet
- Bio Gas Plant From Kitchen WasteDocument5 pagesBio Gas Plant From Kitchen WasteArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Info-Tech SawdustDocument16 pagesInfo-Tech SawdustAnna SuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Fermenter Types and Microbial Gowth Kinetics 1 1459529119 1489994861Document36 pagesLecture 5 Fermenter Types and Microbial Gowth Kinetics 1 1459529119 1489994861jeevalakshmanan29No ratings yet
- Construction Manual Modified GGC Model Biogas Plant For Pakistan 2009Document25 pagesConstruction Manual Modified GGC Model Biogas Plant For Pakistan 2009Shaukat KhanNo ratings yet
- Proces Equipment Design Guide For FermenDocument23 pagesProces Equipment Design Guide For FermenTheodoros AtheridisNo ratings yet
- Flottweg DecandersDocument12 pagesFlottweg DecandersRagha Rag100% (1)
- Size and Site Selection For Biogas Plant: Lecture-14Document3 pagesSize and Site Selection For Biogas Plant: Lecture-14Sachin PetleNo ratings yet
- TET 412 Lecture 5Document7 pagesTET 412 Lecture 5Monterez SalvanoNo ratings yet
- BIOREACTORDocument38 pagesBIOREACTORijat_No ratings yet
- Bio Gas Plant PDFDocument7 pagesBio Gas Plant PDFrajasekaran2323No ratings yet
- Biogas PlantDocument38 pagesBiogas PlantcamillenericNo ratings yet
- مشروع المعالجة البيولوجية للصرف الصحىDocument10 pagesمشروع المعالجة البيولوجية للصرف الصحىalaaam352No ratings yet
- Biogas Plant ConstructionDocument27 pagesBiogas Plant ConstructionAnkit Anurag NaikNo ratings yet
- Biogas PlantDocument42 pagesBiogas PlantPradeepLokhande100% (1)
- BIOGASDocument9 pagesBIOGASmitianrocksNo ratings yet
- Solid-Waste Treatment and Disposal: IncinerationDocument7 pagesSolid-Waste Treatment and Disposal: IncinerationCourage ChigerweNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of A Rotary D R U M Drier Processing Pre-Dried Chicken ManureDocument21 pagesEvaluation of A Rotary D R U M Drier Processing Pre-Dried Chicken ManureDiego Manuel Fuentes mejiaNo ratings yet
- Power NotesDocument20 pagesPower NotesCristy JeanNo ratings yet
- Fermenter DesignDocument59 pagesFermenter DesignPratishtha RawatNo ratings yet
- Application Guide Sludge Mixers en Rev 1Document8 pagesApplication Guide Sludge Mixers en Rev 1gazwang478No ratings yet
- Fermentor Design and BioreactorDocument40 pagesFermentor Design and BioreactorVivek Dhiman0% (1)
- 10.1351 Pac197229010173Document17 pages10.1351 Pac197229010173isidora.valdivia.pNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Food Processing Plant Layout and DesignDocument9 pagesAssignment of Food Processing Plant Layout and DesignSadasis SinghNo ratings yet
- TDB& C Training ManualDocument54 pagesTDB& C Training ManualArthurNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor DesignDocument18 pagesBioreactor DesignAmrie IamNo ratings yet
- Broiler & ManagmentDocument8 pagesBroiler & ManagmentrajeevknpNo ratings yet
- Turning Food and Animal Waste To EnergyDocument23 pagesTurning Food and Animal Waste To Energylpulian100% (2)
- Prefabricated Biogas SystemsDocument8 pagesPrefabricated Biogas Systemsahtisham shahNo ratings yet
- The Dranco Technology: A Unique Digestion Technology For Solid Organic WasteDocument7 pagesThe Dranco Technology: A Unique Digestion Technology For Solid Organic Wastemime840% (1)
- Anaerobic DigestionDocument8 pagesAnaerobic DigestionEbsiba Beaula JNo ratings yet
- Cip in Dairy Plant, Composting of Biological Waste & EffliuDocument48 pagesCip in Dairy Plant, Composting of Biological Waste & EffliualanpaulparakkalNo ratings yet
- The Machinery of Hay Harvesting - With Information on the Equipment and Methods Mowing, Raking and BailingFrom EverandThe Machinery of Hay Harvesting - With Information on the Equipment and Methods Mowing, Raking and BailingNo ratings yet
- The Machinery of Dairy Farming - With Information on Milking, Separating, Sterilizing and Other Mechanical Aspects of Dairy ProductionFrom EverandThe Machinery of Dairy Farming - With Information on Milking, Separating, Sterilizing and Other Mechanical Aspects of Dairy ProductionNo ratings yet
- PIKEMDocument2 pagesPIKEMDream CakeNo ratings yet
- 02 P ConstantheadpermeabilitytestnewDocument8 pages02 P ConstantheadpermeabilitytestnewAfiq AimanNo ratings yet
- Boiler RoomDocument1 pageBoiler RoomtylerstearnsNo ratings yet
- Self-Study On MESC SPE 77.300 - TAT ValvesDocument34 pagesSelf-Study On MESC SPE 77.300 - TAT Valvesrosli2503No ratings yet
- Well AS - 107 Well AS - 106 Well AS-110: 301 EBLA Gas Porject)Document1 pageWell AS - 107 Well AS - 106 Well AS-110: 301 EBLA Gas Porject)Ali YousefNo ratings yet
- Flow of Fluids: 6.1. Properties and UnitsDocument19 pagesFlow of Fluids: 6.1. Properties and UnitsKevin Alberto Tejera PereiraNo ratings yet
- Sci8 Q3 Module2Document15 pagesSci8 Q3 Module2Angelie Astorga TambilawanNo ratings yet
- ECE 309 Tutorial # 4 First Law of Thermodynamics: Control VolumesDocument6 pagesECE 309 Tutorial # 4 First Law of Thermodynamics: Control VolumesSaran JiNo ratings yet
- Writing and Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument4 pagesWriting and Balancing Chemical EquationsEmmarie MercadoNo ratings yet
- Pulsator - P ER 003 EN 1603 - v2 PDFDocument2 pagesPulsator - P ER 003 EN 1603 - v2 PDFVictor Abraham Lim Su KangNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Compressed Air Validation 1657011960Document6 pagesPharmaceutical Compressed Air Validation 1657011960Huỳnh Ngọc Sáng100% (1)
- 3rd - Sem-Ct-23-Chemical EngineeringDocument3 pages3rd - Sem-Ct-23-Chemical EngineeringJay RanjanNo ratings yet
- Glass Fibre Filters - AxivaDocument4 pagesGlass Fibre Filters - AxivaKapil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aa10vg Rexroth PDFDocument44 pagesAa10vg Rexroth PDFJonathan GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Bioheat Equations: Heat Transfer in Blood Vessels and TissuesDocument36 pagesBioheat Equations: Heat Transfer in Blood Vessels and TissuesalirezamdfNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Report 5Document8 pagesPhysics Practical Report 5NatashaAnneNo ratings yet
- Sphera H2 PDFDocument2 pagesSphera H2 PDFHabli MawardiNo ratings yet
- FiltrationDocument19 pagesFiltrationSalman CnNo ratings yet
- The Advantages of Mazda Genuine Super CoolantDocument2 pagesThe Advantages of Mazda Genuine Super CoolantOrshanetzNo ratings yet
- John Thompson Enviropac Boiler BrochureDocument2 pagesJohn Thompson Enviropac Boiler BrochureInnocent LavoeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27-Cell Growth in Continuous CultureDocument19 pagesLecture 27-Cell Growth in Continuous CultureHemanth Peddavenkatappa GariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid PowerDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Fluid PowerRahmad SudirmanNo ratings yet
- Evaluation & Redesign of University of Guyana Sanitary Sewer SystemDocument32 pagesEvaluation & Redesign of University of Guyana Sanitary Sewer SystemPeter NobregaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Conventional Wastewater Treatment Plant Design CDocument24 pagesChapter 5 Conventional Wastewater Treatment Plant Design Ctony13touchNo ratings yet
- Equipment For CrystallizationDocument6 pagesEquipment For CrystallizationOmkar MudkannaNo ratings yet
- Fractal Impeller Amol KulkarniDocument10 pagesFractal Impeller Amol KulkarniTej ChoksiNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger BasicsDocument59 pagesHeat Exchanger BasicsPassionNo ratings yet
- Selection of A Suction Line Accumulator - Carly - The International Expert in Refrigeration ComponentsDocument3 pagesSelection of A Suction Line Accumulator - Carly - The International Expert in Refrigeration ComponentsbarnNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Analysis of Growth of Boundary Layer Thickness Over A Flat PlateDocument15 pagesPresentation On Analysis of Growth of Boundary Layer Thickness Over A Flat PlateSurajit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Prova 5Document3 pagesProva 5LorenzoNo ratings yet