0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 viewsMacroeconomics Circular Flow
Macroeconomics Circular Flow
Uploaded by
Idha RahmaThis document contains information about Idha Rahma Iswianti, her student ID number, and her study of macroeconomics and the circular flow model. It describes the circular flow between households and firms, with households supplying factors of production to firms and purchasing goods and services, while firms pay for factors and supply goods. It also discusses how savings acts as a leakage from the circular flow, but investment injects savings back in and prevents a decrease in total spending.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Macroeconomics Circular Flow
Macroeconomics Circular Flow
Uploaded by
Idha Rahma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesThis document contains information about Idha Rahma Iswianti, her student ID number, and her study of macroeconomics and the circular flow model. It describes the circular flow between households and firms, with households supplying factors of production to firms and purchasing goods and services, while firms pay for factors and supply goods. It also discusses how savings acts as a leakage from the circular flow, but investment injects savings back in and prevents a decrease in total spending.
Original Title
CIRCULAR FLOW
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document contains information about Idha Rahma Iswianti, her student ID number, and her study of macroeconomics and the circular flow model. It describes the circular flow between households and firms, with households supplying factors of production to firms and purchasing goods and services, while firms pay for factors and supply goods. It also discusses how savings acts as a leakage from the circular flow, but investment injects savings back in and prevents a decrease in total spending.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesMacroeconomics Circular Flow
Macroeconomics Circular Flow
Uploaded by
Idha RahmaThis document contains information about Idha Rahma Iswianti, her student ID number, and her study of macroeconomics and the circular flow model. It describes the circular flow between households and firms, with households supplying factors of production to firms and purchasing goods and services, while firms pay for factors and supply goods. It also discusses how savings acts as a leakage from the circular flow, but investment injects savings back in and prevents a decrease in total spending.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Name : Idha Rahma Iswianti
NIM : 19080304009
Accounting Education 2019 I
Macroeconomics
Circular Flow
I. Circular flow of Income
The term circular flow of income or circular flow of economic activity refers to “a
simple economic model which describes the circulation/flow of income between
producers and consumers”.
In the circular flow model, producer and consumer are referred to as "firms" and
"households" respectively.
a. Firms
An organization that produces goods and services for sale. Main objective is
to maximize profit in the production process.
The two main functions are as follows:
Produce goods and services and supply them in the market.
Firms purchase inputs or raw materials from households to use them in the
production process.
b. Household
It is a person or a group of people that share their income. The members of
households have two functions:
They supply different factors of production
Members of household also work as consumers
II. Two Sector model :
a. The circular flow of income or circular flow is a model of the economy in which
the major exchanges are represented as flows of money, goods and services, etc.
between economic agents.
b. The flows of money and goods exchanges in a closed circuit and correspond in
value, but run in the opposite direction. The circular flow analysis is the basis of
national accounts and hence of macroeconomics.
III. Explanation of Figure
Name : Idha Rahma Iswianti
NIM : 19080304009
Accounting Education 2019 I
Firstly, the household sector supply their factors of production or factor services
(labor, land, capital...) to the business sector through the factor market.
Secondly the business sector pays the rewards to household sector for their
contribution to the production in kinds of rent for land, interest for capital, and
wages for laborers…
Thirdly business sector supply their outputs or goods and services in the goods or
product market.
Fourthly household sector pays their income for consumption expenditure.
Can we saw product market and factor market. Factor market refers to the market
for selling and purchasing or hiring of factors of production like labor, land …
Product market means the market in which the goods and services are supplying
and demanding.
IV. CFM with Saving & Investment
When household save, their expenditure on goods & services will decline to that
extent and as a result money flow to the business firms will contract.
With reduced money receipts, firm will hire fewer worker or reduce the factor
payments.
This will lead to the fall in total incomes of the households. Thus, saving reduces
the flow of money expenditure to the business firms and causes a fall in
economy’s total income.
Economists therefore call savings a leakage.
Business firms borrow from the financial market for investment in capital goods
such as machines, factories, tools & instruments etc.
Thus, saving again brought into the expenditures stream and as a result total flow
of spending does not decrease.
So, investment is called as injection to economy.
Name : Idha Rahma Iswianti
NIM : 19080304009
Accounting Education 2019 I
Questions and Answer
1. What happens if the household sector does a savings activity?
The expenditure on goods & services will decline to that extent and as a result
money flow to the business firms will contract. will lead to the fall in total incomes of
the households. Thus, saving reduces the flow of money expenditure to the business
firms and causes a fall in economy’s total income.
2. What is the purpose of saving back into the flow of expenditure?
Business firms borrow from the financial market for investment in capital goods such
as machines, factories, tools & instruments etc. As aresult total flow of spending does
not decrease.
3. What are the determinants of household consumption?
Disposable income
Wealth
Future income expectations
Interest rate
Inflation
Income distribution
Demographic factor
Taste and preferences
You might also like
- Detailed Lesson Plan On EconomicsDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan On EconomicsArchill Yapparcon92% (26)
- Pset 1Document5 pagesPset 1KennethFuNo ratings yet
- ACCCOB1 Chapter 5 Worktext Solution Exercise 5-1 and 5-2 Theory 5-3 To 5-5 PDFDocument4 pagesACCCOB1 Chapter 5 Worktext Solution Exercise 5-1 and 5-2 Theory 5-3 To 5-5 PDFJose GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Delhivery Project Report RahulDocument29 pagesDelhivery Project Report RahulEsha Gupta33% (3)
- VK FIN AnalysisDocument98 pagesVK FIN AnalysisVrajlal SapovadiaNo ratings yet
- 02 - Circular Flow of IncomeDocument12 pages02 - Circular Flow of Incomemahak20044No ratings yet
- Notes Concept of National Income and Related Aggregates Session 2024-25Document14 pagesNotes Concept of National Income and Related Aggregates Session 2024-25mtanisha801No ratings yet
- Ch. 1 - Macroeconomics Ni & Related Aggregates - NDocument26 pagesCh. 1 - Macroeconomics Ni & Related Aggregates - Nb.mariajo4No ratings yet
- National Income and AccountingDocument24 pagesNational Income and Accountingmouli poliparthiNo ratings yet
- 5th Semester Economics Seleted Questions PDFDocument24 pages5th Semester Economics Seleted Questions PDFAnil SonthaliaNo ratings yet
- Ppt4 Circular Flow Model of Output and IncomeDocument25 pagesPpt4 Circular Flow Model of Output and Incomejust myselfNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Basic MicroeconomicsDocument16 pagesLesson 1 Basic MicroeconomicsMickaela GulisNo ratings yet
- Social Studies 3rd GradingDocument14 pagesSocial Studies 3rd Gradingdana.andradeNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Mary Antonette LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow ModelDocument7 pagesCircular Flow ModelshaheenNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Income and Methods of Measuring National IncomeDocument4 pagesCircular Flow of Income and Methods of Measuring National IncomeshristysewaNo ratings yet
- Revised Supplementary Material Semester 2 2013Document98 pagesRevised Supplementary Material Semester 2 2013HeoHamHốNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Managerial Economicsmyra100% (1)
- Principle of Economics1 (Chapter2)Document7 pagesPrinciple of Economics1 (Chapter2)MA ValdezNo ratings yet
- Revision Circular FlowDocument18 pagesRevision Circular FlowenochscribdNo ratings yet
- Economics Fact Sheet - Notes MacroEconomicsDocument44 pagesEconomics Fact Sheet - Notes MacroEconomicsphemeloramaboa11No ratings yet
- Measuring The Lwvel of Econs ActivitiesDocument17 pagesMeasuring The Lwvel of Econs Activitiessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Unit 7A National Product and Its Measurement BitinfonepalDocument57 pagesUnit 7A National Product and Its Measurement BitinfonepalYogendra KshetriNo ratings yet
- JH EcampusUpload SubjectNote STD 12 ECONOMICS CHAPTER 18 NOTES 2023-24Document7 pagesJH EcampusUpload SubjectNote STD 12 ECONOMICS CHAPTER 18 NOTES 2023-24Zian HansotiaNo ratings yet
- Macro Environ-Circular Flow of IncomeDocument33 pagesMacro Environ-Circular Flow of Incomeamankamat2002No ratings yet
- Macro Economics-RokonDocument23 pagesMacro Economics-RokonImran HossainNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomesDocument9 pagesCircular Flow of IncomesMohammed NazeerNo ratings yet
- Ktu Studnts: Circular Flow of IncomeDocument12 pagesKtu Studnts: Circular Flow of IncomerichardhpdNo ratings yet
- National Income Lesson1Document8 pagesNational Income Lesson1Harsh MundhraNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument32 pagesCircular Flow of IncomeTarun SukhijaNo ratings yet
- The Model of Circular Flow of Income: Perspective in Bangladesh.Document22 pagesThe Model of Circular Flow of Income: Perspective in Bangladesh.Imran Hossain100% (1)
- Chapter 2 The Circular FlowDocument11 pagesChapter 2 The Circular FlowClaire Ann Salazar BorjaNo ratings yet
- Ciculer FlowDocument11 pagesCiculer FlowbadarNo ratings yet
- Include NCERT Notes in Your CBSE Class 12 Preparation - Chapter 2 of Marco EconomicsDocument14 pagesInclude NCERT Notes in Your CBSE Class 12 Preparation - Chapter 2 of Marco EconomicsAyush JainNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics-Unit 6-Lesson 1Document12 pagesApplied Economics-Unit 6-Lesson 1johnNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Funds: Through The EconomyDocument10 pagesCircular Flow of Funds: Through The EconomyHaji Saif UllahNo ratings yet
- Macro CH01 - Circular FlowDocument4 pagesMacro CH01 - Circular Flowvivaan6837No ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument193 pagesCircular Flow of Incomeallah dittaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Economics SLDocument3 pages8.1 Economics SLEman DhaifNo ratings yet
- Circular FlowDocument1 pageCircular FlowKimberly AvanzadoNo ratings yet
- Economy Part 1Document63 pagesEconomy Part 1Manoj ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Income - GeeksforGeeksDocument7 pagesCircular Flow of Income - GeeksforGeeksAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Economics Reviewer 2024 - Pages-1Document1 pageEconomics Reviewer 2024 - Pages-1Mary Aileen del FonsoNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics Cycle Contribute To The Growth BetweenDocument5 pagesMacro Economics Cycle Contribute To The Growth BetweenQNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Mr. AllicockDocument60 pagesLecture 2. Mr. AllicockPrecious MarksNo ratings yet
- Handout 2Document9 pagesHandout 2Satuti Seth 1545No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Business, Trade and Commerce: Economic and Non Economic ActivitiesDocument8 pagesChapter 1: Business, Trade and Commerce: Economic and Non Economic ActivitiesBhavya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Economy and The Financial SystemDocument30 pagesChapter 1: The Economy and The Financial SystemGwy RubisNo ratings yet
- Stock and Flow Concept: Macro Economic ConceptsDocument25 pagesStock and Flow Concept: Macro Economic ConceptsKeerthana BijuNo ratings yet
- Functions and Roles of The Financial System in The Global EconomyDocument10 pagesFunctions and Roles of The Financial System in The Global EconomyMH SahirNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument19 pagesCircular Flow of IncomePooja LakraNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of Income BmdsDocument38 pagesCircular Flow of Income BmdsBleh Bleh BlehNo ratings yet
- Chap. 7. Input Demand. The Capital Market and The Investment DecisionDocument43 pagesChap. 7. Input Demand. The Capital Market and The Investment DecisionPaul Jastine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Macroeconomics: After Reading This Section, You Should Be Able ToDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Macroeconomics: After Reading This Section, You Should Be Able ToKhaster NavarraNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Macroeconomics 1Document36 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Macroeconomics 1yuktabodeNo ratings yet
- CH 1 IntroductionDocument21 pagesCH 1 Introductionyosefaleme463No ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument5 pagesCircular Flow of IncomeRoshan Luke MathiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Managerial EconomicsNur DinieNo ratings yet
- Ekn 120 - Chapter 11Document9 pagesEkn 120 - Chapter 11u24669696No ratings yet
- MMPC 3 em 2024 25Document12 pagesMMPC 3 em 2024 25dimple agrawalNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow of EconomicsDocument7 pagesCircular Flow of EconomicsAmandeep sainiNo ratings yet
- Mgt028 Chapter 1 - Oct2023Document57 pagesMgt028 Chapter 1 - Oct2023lindahas271No ratings yet
- Debt or Equity-Which One Is Better For Your Business?: Name-Avani Shah Roll No-Pgdmrba019Document2 pagesDebt or Equity-Which One Is Better For Your Business?: Name-Avani Shah Roll No-Pgdmrba019avani shahNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument2 pagesCaseLester Sanchez100% (1)
- Sip Ab Sapne Such Karo-Ppt-RevisedDocument13 pagesSip Ab Sapne Such Karo-Ppt-RevisedMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Auditing 4 Chapter 1Document19 pagesAuditing 4 Chapter 1Mohamed Diab100% (1)
- Competitive InteligenceDocument15 pagesCompetitive InteligenceLarisa MarinNo ratings yet
- MMPL Annual Report 2016-17Document101 pagesMMPL Annual Report 2016-17xyzNo ratings yet
- The Digital FirmDocument4 pagesThe Digital FirmeldociNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard Notes by Anand R. BhangariyaDocument96 pagesAccounting Standard Notes by Anand R. BhangariyaSanjana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 2: Module - MBA 4643Document26 pagesAssignment No 2: Module - MBA 4643funksoul69No ratings yet
- First Exam 50 ItemsDocument3 pagesFirst Exam 50 ItemsEDLYN MABUTINo ratings yet
- Worldwide Paper Cworldwide Company FinalDocument4 pagesWorldwide Paper Cworldwide Company FinalNoor Ji100% (2)
- Set - A, BDD2813, MARKETING TESTDocument4 pagesSet - A, BDD2813, MARKETING TESTababsenNo ratings yet
- APPROACHES TO STRATEGY (CONTINUED) - Strategic ManagementDocument5 pagesAPPROACHES TO STRATEGY (CONTINUED) - Strategic Managementrohan_jangid8100% (4)
- Wealth Management AssignmentDocument2 pagesWealth Management AssignmentHimanshu BajajNo ratings yet
- Taxation Question 2017 SeptemberDocument16 pagesTaxation Question 2017 Septemberzezu zazaNo ratings yet
- BPM BrochureDocument5 pagesBPM Brochurenikki naiduNo ratings yet
- Bmc-section13-Group2 - Hangelica Harold SinpongDocument14 pagesBmc-section13-Group2 - Hangelica Harold SinpongMUHAMMAD ALIF AIMAN BIN AZLAN BA21110434No ratings yet
- Eight Areas of WasteDocument18 pagesEight Areas of WasteMelody Altubar-Beato100% (1)
- FAQ in KYC InterviewsDocument8 pagesFAQ in KYC InterviewsRuhan PrinceNo ratings yet
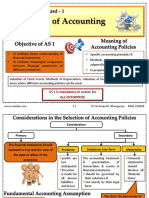
- AS14Document13 pagesAS14Browse PurposeNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Law 1Document162 pagesGlossary of Law 1rama12388100% (1)
- Presented By-:: Neelesh Shrivastava Nikhil Sood Nitin Malik Omansh Bhardwaj Mohd ArmanDocument30 pagesPresented By-:: Neelesh Shrivastava Nikhil Sood Nitin Malik Omansh Bhardwaj Mohd ArmanARMAN PILOTNo ratings yet
- Ba Invoice Month MarchDocument1 pageBa Invoice Month MarchSubash AryalNo ratings yet