0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 viewsInferior Good. 1 (Positive), It Is A Luxury Good or A Superior Good
Inferior Good. 1 (Positive), It Is A Luxury Good or A Superior Good
Uploaded by
Sakshi AgarwalIncome elasticity of demand is the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in income. It is measured as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income. Goods with income elasticity less than 1 are necessities or inferior goods, while goods with income elasticity greater than 1 are luxuries or superior goods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Inferior Good. 1 (Positive), It Is A Luxury Good or A Superior Good
Inferior Good. 1 (Positive), It Is A Luxury Good or A Superior Good
Uploaded by
Sakshi Agarwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views14 pagesIncome elasticity of demand is the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in income. It is measured as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income. Goods with income elasticity less than 1 are necessities or inferior goods, while goods with income elasticity greater than 1 are luxuries or superior goods.
Original Title
Qs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Income elasticity of demand is the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in income. It is measured as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income. Goods with income elasticity less than 1 are necessities or inferior goods, while goods with income elasticity greater than 1 are luxuries or superior goods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views14 pagesInferior Good. 1 (Positive), It Is A Luxury Good or A Superior Good
Inferior Good. 1 (Positive), It Is A Luxury Good or A Superior Good
Uploaded by
Sakshi AgarwalIncome elasticity of demand is the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in income. It is measured as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income. Goods with income elasticity less than 1 are necessities or inferior goods, while goods with income elasticity greater than 1 are luxuries or superior goods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
1-If income elasticity of demand of a commodity is
less than 1(negative), it is a necessity good or an
inferior good.
If the elasticity of demand is greater than
1(positive), it is a luxury good or a superior
good.
Income elasticity of demand
Description
In economics, the income elasticity of demand is
the responsiveness of the quantity demanded for a
good to a change in consumer income. It is
measured as the ratio of the percentage change in
quantity demanded to the percentage change in
income.
2-. Adam Smith is known as father of economics
& “An Enquiry into the Nature and Cause of Wealth
of Nation” was written by him.
3- What effect is working when the price of a good
falls and consumers tend to buy it instead of other
goods: Substitution Effect
4-Incremental Principle is closely related to the
marginal costs and marginal revenue of economic
theory32
5-If the income and substitution effect of a price
increase works in the same direction the good
whose price has changed is a normal goods.
6-An isoquant is a firm's counterpart of the
consumer's indifference curve. An isoquant is a
curve that shows all the combinations of inputs
that yield the same level of output. 'Iso' means
equal and 'quant' means quantity. Therefore, an
isoquant represents a constant quantity of
output.
7-In Linear homogeneous production
function ,the degree of homogeneity is always one.
The Linear Homogeneous Production Function
implies that with the proportionate change in all
the factors of production, the output also
increases in the same proportion. Such as, if the
input factors are doubled the output also gets
doubled. This is also known as constant returns to
a scale.
8-Short Run Law- Law of Diminishing Returns
9- Fixed cost per unit increases when volume of
production decreases.
10- Variable cost per unit varies with the volume of
production.
11-Firms in an oligopoly can each influence the
market price.
12-Product differentiation is an important feature of
monopolistic competition.
Selling Cost is the feature of monopolistic
competition.
The product under monopolistic competition is
differentiated with close substitute
A monopoly is the type of imperfect competition
where a seller or producer captures most of the
market share due to the lack of substitutes or
competitors. A monopolistic competition is a
type of imperfect competition where many
sellers try to capture the market share by
differentiating their products.
13-Supply refers to the quantity of a good or service
that producers are willing and able to sell during a
certain period under a given set of conditions.
14- Market supply function for a product is a
statement of the relation between the quantity supplied
and all factors affecting that quantity.
Cost of Production is the determinant of Supply.
15-Supply schedule a statement in the form of a table
that shows the different quantities of a commodity that
a firm or a producer offers for sale in the market at
different prices.
16- An input should be so allocated that the value
added by the last unit is the same in all cases : equi-
marginal principle
17-Managerial utility function is expressed as: u = f
(s, m, i)
18- Explicit cost ( out of pocket expenses)are
recorded in Books of Accounts.
Implicit cost - The value of an entrepreneur’s
resources (assets) that she uses in production.
The main difference between the two types of costs
is that implicit costs are opportunity costs, while
explicit costs are expenses paid with a company's
own tangible assets. This makes implicit costs
synonymous with imputed costs, while explicit
costs are considered out-of-pocket expenses.
19- Utility is want satisfying power of Commodity.
( How much useful the commodity is
The utility of a commodity is its relative scarcity.
20-Demand: Desire backed by purchasing power.
21-The demand has three essentials ‐ Desire, purchasing
power and willingness to pay.
“Demand means effective desire or want for a
commodity, which is backed by the ability (i.e.,
money or purchasing power) and willingness to
pay for it.
22- Law of demand shows the functional relationship
between Price and quantity demanded.
23- Higher the price of certain luxurious articles, higher
will be the demand, this concept is called Veblen Effect.
A Veblen good is a type of luxury good for which the
demand for a good increase as the price increases,
in apparent contradiction of the law of demand,
resulting in an upward-sloping demand curve.
24- Demand for milk, sugar, tea for making tea, is an
example of Joint Demand.
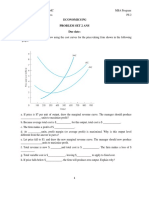
25-Perfect elasticity is known as Infinite Elastic.
Perfect elasticity, the demand curve is Horizontal.
The horizontal demand curve for a commodity
shows that its demand is Perfectly Elastic.
A demand curve which takes the form of horizontal
line parallel to quantity axis illustrates elasticity which is
less than one.
26- Perfect competition is characterized by
A. large number of buyers and sellers
B. homogeneous product
C. free entry and exit of firms
D. all the above
27-In economics equilibrium means ‘a state of rest ‘or
‘stability’.
28-Selling at a lower price in export market and at a
higher price at home market is called Dumping.
29-An exceptional demand curve is one that slopes
upward to the right.
30-A fall in the price of a commodity whose demand
curve is a rectangular hyperbola causes total
expenditure on the commodity to remain unchanged.
When the demand curve is a rectangular hyperbola, it
represents unitary elastic demand.
81. Consider a demand curve which takes the form of a
straight line cutting both axes.Elasticity at the mid-point
of the line would be:
A. zero
B. one infinite
C. infinite
D. cannot be calculated
Discussion
B. one infinite
82. The elasticity of demand for a product will be higher:
A. the more available are substitutes for that product
B. the more its buyers demand loyalty
C. the more the product is considered a necessity by its buyers
D. all of the above
Discussion
A. the more available are substitutes for that product
83. In case of Giffen goods, demand curve will slope:
A. vertical
B. horizontal
C. upward
D. downward
Discussion
C. upward
84. Cross elasticity of demand between tea and sugar is:
A. positive
B. zero
C. infinity
D. negative
Discussion
D. negative
85. If the percentage increase in quantity of a commodity
demanded is its price, thecoefficient of price elasticity of
demand is:
A. greater than 1
B. equal to 1
C. less than 1
D. zero
Discussion
C. less than 1
86. If the quantity of a commodity demanded remains
unchanged as its price changes, thecoefficient of price
elasticity of demand is
A. greater than 1
B. equal to 1
C. less than 1
D. zero
Discussion
D. zero
87. Unitary elasticity of demand is:
A. zero
B. equal to one
C. greater than 1
D. less than 1
Discussion
B. equal to one
88. The real business cycle theory is most closely related
to
A. keynesian theory
B. monetarist theory
C. the classical theory
D. the new keynesian theory
Discussion
C. the classical theory
89. In the real business cycle model, business cycles are
A. efficient and do not represent lost output
B. driven by technology shocks
C. occur when markets clear
D. all of the above
Discussion
D. all of the above
90. Real business cycle proponents argue that
A. recessions are caused by movements of output away from the natural rate
of output
B. prices and wages are sticky
C. macroeconomics should be based on the same assumptions as
microeconomics
D. monetary policy is important in determining recessions
Discussion
C. macroeconomics should be based on the same assumptions as microeconomics
91. Implicit costs are:
A. equal to total fixed costs.
B. comprised entirely of variable costs.
C. "payments" for self-employed resources.
D. always greater in the short run than in the long run.
Discussion
C. "payments" for self-employed resources.
92. The law of diminishing returns only applies in cases
where:
A. there is increasing scarcity of factors of production.
B. the price of extra units of a factor is increasing.
C. there is at least one fixed factor of production.
D. capital is a variable input.
Discussion
C. there is at least one fixed factor of production.
93. When the total product curve is falling, the:
A. marginal product of labour is zero.
B. marginal product of labour is negative.
C. average product of labour is increasing.
D. average product of labour must be negative.
Discussion
B. marginal product of labour is negative.
94. When marginal product reaches its maximum, what
can be said of total product?
A. total product must be at its maximum
B. total product starts to decline even if marginal product is positive
C. total product is increasing if marginal product is still positive
D. total product levels off
Discussion
C. total product is increasing if marginal product is still positive
95. Variable costs are:
A. sunk costs.
B. multiplied by fixed costs.
C. costs that change with the level of production.
D. defined as the change in total cost resulting from the production of an
additional
Discussion
C. costs that change with the level of production.
96. The reason the marginal cost curve eventually
increases as output increases for thetypical firm is
because:
A. of diseconomies of scale.
B. of minimum efficient scale.
C. of the law of diminishing returns.
D. normal profit exceeds economic profit.
Discussion
C. of the law of diminishing returns.
97. If the short-run average variable costs of production
for a firm are rising, then thisindicates that:
A. average total costs are at a maximum.
B. average fixed costs are constant.
C. marginal costs are above average variable costs.
D. average variable costs are below average fixed costs.
Discussion
C. marginal costs are above average variable costs.
98. If a more efficient technology was discovered by a
firm, there would be:
A. an upward shift in the avc curve.
B. an upward shift in the afc curve.
C. a downward shift in the afc curve.
D. a downward shift in the mc curve.
Discussion
D. a downward shift in the mc curve.
99. The firm's short-run marginal-cost curve is increasing
when:
A. marginal product is increasing.
B. marginal product is decreasing.
C. total fixed cost is increasing.
D. average fixed cost is decreasing.
Discussion
B. marginal product is decreasing.
100. A firm encountering economies of scale over some
range of output will have a:
A. rising long-run average cost curve.
B. falling long-run average cost curve.
C. constant long-run average cost curve.
D. rising, then falling, then rising long-run average cost curve.
Discussion
B. falling long-run average cost curve.
1. Which of the following is a variable cost?
The correct answer was: b. Raw materials costs.
2. Incorrect. You answered: a. The salary earned by a corporate executive.
Which of the following is an implicit cost?
The correct answer was: b. Depreciation in the value of a company-owned car as it
wears out.
3. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
If the output levels at which short-run marginal and average cost curves reach a
minimum are listed in order from smallest to greatest, then the order would be
The correct answer was: c. MC, AVC, ATC.
4. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
Learning curves represent the relationship between
The correct answer was: b. average variable cost and the cumulative number of
units produced..
5. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
If an input is owned and used by a firm, then its
The correct answer was: a. explicit cost is zero..
6. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
Short-run marginal cost is equal to
The correct answer was: d. all of the above..
7. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
Short-run average variable cost is equal to
The correct answer was: d. all of the above..
8. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
Which of the following short-run cost curves declines continuously?
The correct answer was: c. Average fixed cost.
9. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
The law of diminishing returns begins at the level of output where
The correct answer was: a. marginal cost is at a minimum..
10. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
The long-run average cost curve is at a minimum at a level of output where
The correct answer was: d. all of the above occur..
11. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
If a firm has a downward sloping long-run average cost curve, then
The correct answer was: c. it is a natural monopoly..
12. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
One reason that a firm may experience increasing returns to scale is that greater
levels of output make it possible for the firm to
The correct answer was: d. All of the above are correct..
13. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
One reason that a firm may experience decreasing returns to scale is that greater
levels of output can result in
The correct answer was: b. an increase in meetings and paperwork..
14. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
Economies of scope refers to the decrease in average total cost that can occur
when a firm
The correct answer was: a. produces more than one product..
15. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
Breakeven analysis identifies the
The correct answer was: b. level of output where economic profit is equal to zero..
16. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
Which of the following is an assumption of linear breakeven analysis?
The correct answer was: c. Average fixed cost is constant.
17. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
The responsiveness or sensitivity of a firm's profits to changes in output is
measured by a firm's
The correct answer was: c. degree of operating leverage..
18. Incorrect. You did not provide an answer.
Which of the following values cannot be calculated at the firm's breakeven level of
output?
The correct answer was: c. degree of operating leverage..
19-If a linear short-run variable cost function is estimated using cross-sectional
data, then the corresponding marginal cost function will be
The correct answer was: d. horizontal..
20-The survival technique
a. can be used to estimate short-run total variable cost functions.
b. is based on a technical knowledge of a firm's production function.
c. uses regression analysis in combination with time-series or cross-
sectional data.
d. None of the above is correct.
The correct answer was: d. None of the above is correct..
21-The process whereby firms reduce their production costs by taking
advantage of international differences in the prices of inputs and
international similarities in preferences is referred to as the
The correct answer was: b. new international economies of scale.
22-Which of the following would be referred to as "outsourcing?"
The correct answer was: c. Subcontracting production to firms in other countries.
23- When a firm designs a core product for the entire world that can be
adapted in a number of ways to accommodate different types of markets,
it is taking advantage of the
The correct answer was: b. new international economies of scale.
24-The Japanese cost-management system involves
The correct answer was: c. determining how much a product should cost and then
determining how it should be produced.
25-The contribution margin per unit is equal to the
The correct answer was: d. difference between price and average variable cost.
32-The law of demand implies that : Demand Curve
Slope Down.
33-AFC Curve is Convex & Downward Sloping,
Output increases – AFC starts falling. & AFC Curve
is never U shaped,
34-U-shaped average cost curve is based on:
Law of Variable Proportion
35- When shape of average cost curve is
upwards, marginal cost must be rising.
36- Economic cost excludes: Accounting cost +
explicit cost
37- Necessary condition for firm to be in Equilibrium
The necessary condition for equilibrium position of a firm is MC=MR. A firm is in
equilibrium when it has no tendency to change its level of output. It needs neither
expansion nor contraction. It wants to earn maximum profits in by equating its
marginal cost with its marginal revenue, i.e. MC = MR.
38- A factor of production, whose supply is fixed in the short run, may get
additional earnings. These earnings are generally referred to as Quasi-rent. The
earnings from machines and instruments are termed as quasi-rent. The quasi-rent
refers to the income produced when the demand for products increases suddenly.
39- In May 2013, firm was supplying 500kg of sugar at market price of Rs.30/- per
kg. During June 2013, firm's supply of sugar had decreased to 450kg at price of
Rs.20/- per kg. These changes show that supply of sugar is less elastic.
You might also like
- Multiple Choice 1Document5 pagesMultiple Choice 1віра сіркаNo ratings yet
- Economics for CFA 2024: level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4From EverandEconomics for CFA 2024: level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Econ SG Chap08Document20 pagesEcon SG Chap08CLNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1AkshitaNo ratings yet
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Chapter 11 The Marketing Plan: Marketing Defined, Explained, Applied, 2e (Levens)Document14 pagesChapter 11 The Marketing Plan: Marketing Defined, Explained, Applied, 2e (Levens)MeconNo ratings yet
- Appendix ADocument38 pagesAppendix ABammBamNo ratings yet
- Eco-401 Current Quiz SolvedDocument8 pagesEco-401 Current Quiz SolvedKashif Jemy50% (2)
- Introduction To EconomicsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To EconomicsNasty KidrevychNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter 8 SummaryDocument6 pagesEconomics Chapter 8 SummaryAlex HdzNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Managerial Economics List of ConceptsDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts in Managerial Economics List of Conceptsghosh7171No ratings yet
- NotesDocument26 pagesNotesEwa PateckaNo ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics IIDocument5 pagesBasic Microeconomics IIcamellNo ratings yet
- ME I - EA1-BFE - Topic 16 - Partial Competitive Equilibrium - 2023-2024Document34 pagesME I - EA1-BFE - Topic 16 - Partial Competitive Equilibrium - 2023-2024mfialka2016No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Answer All QuestionsDocument8 pagesManagerial Economics Answer All Questionsajeet gautam75% (4)
- WEEK 6 Supply and Demand Analysis ExpandedDocument2 pagesWEEK 6 Supply and Demand Analysis ExpandedAlipio Desuyo LaDjarNo ratings yet
- Eco QuestionsDocument18 pagesEco QuestionsShashankSinghNo ratings yet
- UD Econ Comps Study GuideDocument23 pagesUD Econ Comps Study GuideUDeconNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis For Business Decisions MCQ&A-1Document22 pagesEconomic Analysis For Business Decisions MCQ&A-1ravi kangneNo ratings yet
- Assignment ECON 260Document13 pagesAssignment ECON 260Mohammed AwadNo ratings yet
- C5 Micro EconomicsDocument31 pagesC5 Micro Economicshht2107No ratings yet
- In Class Checkpoint Quiz ManaeconDocument17 pagesIn Class Checkpoint Quiz ManaeconDũng HoàngNo ratings yet
- دارسات تجاريةDocument9 pagesدارسات تجاريةymhdz6hpj4No ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument53 pagesEconomicsNora SalemNo ratings yet
- ECO 100 Quiz 1 02 2020 Your Name Your Student NumberDocument12 pagesECO 100 Quiz 1 02 2020 Your Name Your Student NumberbalalaNo ratings yet
- Me Set I (Key)Document10 pagesMe Set I (Key)Vivek Tiwari100% (1)
- Assignment of EconomicDocument33 pagesAssignment of Economicহকের পথNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Reviewer - EconDocument3 pagesMidterm Exam Reviewer - EconHatdog KaNo ratings yet
- M.B.A. (First Semester) Examination, 2014-15 Managerial Economics Model Answer Section - ADocument28 pagesM.B.A. (First Semester) Examination, 2014-15 Managerial Economics Model Answer Section - AIjaz M.KNo ratings yet
- AC TC/Q, AFC FC/Q, AVC VC/Q: Between Pure Monopoly & Pure CompetitionDocument3 pagesAC TC/Q, AFC FC/Q, AVC VC/Q: Between Pure Monopoly & Pure CompetitionSadnima Binte Noman 2013796630No ratings yet
- Eco 111Document2 pagesEco 111nchau190104No ratings yet
- Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument5 pagesDemand and Supply AnalysisMelinda LeeNo ratings yet
- Final Exam (Answer) : ECO1132 (Fall-2020)Document13 pagesFinal Exam (Answer) : ECO1132 (Fall-2020)Nahid Mahmud ZayedNo ratings yet
- Ebenstein and Ebenstein Chapter 8Document4 pagesEbenstein and Ebenstein Chapter 8David Bryan Tan OngNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Topics in Demand and Supply Analysis - HandoutsDocument15 pagesModule 1 - Topics in Demand and Supply Analysis - HandoutsAyman Al HakimNo ratings yet
- Economics Practice Questions and Answers - Year 11 Preliminary (Likely Not 100% Accurate)Document6 pagesEconomics Practice Questions and Answers - Year 11 Preliminary (Likely Not 100% Accurate)Jack CarterNo ratings yet
- Chapter Twenty: Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument5 pagesChapter Twenty: Elasticity of Demand and SupplyMya BallinNo ratings yet
- Basics of MicroeconomicsDocument3 pagesBasics of MicroeconomicsfatsothepuppyNo ratings yet
- Half-Yearly Examination Paper 2014 Class Xii Subject: EconomicsDocument10 pagesHalf-Yearly Examination Paper 2014 Class Xii Subject: EconomicsNisha JainNo ratings yet
- ECO401 Short Notes Lectures 1 22 Objective Type By: What Is Economics?Document21 pagesECO401 Short Notes Lectures 1 22 Objective Type By: What Is Economics?Aanis NA100% (1)
- 1629204622-1. Basic of MicroeconomicDocument5 pages1629204622-1. Basic of MicroeconomicTigerNo ratings yet
- Answers of Econ Quiz Level-1Document6 pagesAnswers of Econ Quiz Level-1basitahmedNo ratings yet
- Merged PDF 20241119 12.07.02q - CompressDocument49 pagesMerged PDF 20241119 12.07.02q - Compressabinponnappan9No ratings yet
- Manecon ReviewerDocument6 pagesManecon ReviewershynrieljoycNo ratings yet
- Week 5-11Document15 pagesWeek 5-11imemunetuNo ratings yet
- thuật ngữ ktvmDocument3 pagesthuật ngữ ktvmHà Ly Đỗ NgọcNo ratings yet
- Theory of Consumer BehaviourDocument11 pagesTheory of Consumer BehaviourAli ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Mara Lavin - Topic 003 Tutorial Questions - Consumer DecisionDocument3 pagesMara Lavin - Topic 003 Tutorial Questions - Consumer DecisionLee XingNo ratings yet
- Micro Full HD 1Document24 pagesMicro Full HD 1ducd2415No ratings yet
- Eco401 Economics Solved Mcqs and Subjective Questions: SolutionDocument5 pagesEco401 Economics Solved Mcqs and Subjective Questions: SolutionSadiq OrakzaiNo ratings yet
- Economics AssigmentDocument5 pagesEconomics AssigmentAditya JoshiNo ratings yet
- Micro 2Document10 pagesMicro 2Hương GianggNo ratings yet
- SOV E05169BCOM PBD Answer SchemeDocument7 pagesSOV E05169BCOM PBD Answer SchemeNeeraj KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleFrom EverandSummary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Economics for Investment Decision Makers Workbook: Micro, Macro, and International EconomicsFrom EverandEconomics for Investment Decision Makers Workbook: Micro, Macro, and International EconomicsNo ratings yet
- Fashion Inn: Marketing PlanDocument22 pagesFashion Inn: Marketing Plansalman_80No ratings yet
- Quiz 6 - Accounting: Paid For The Publication in A Newspaper of The Consultancy Firm 'S Opening, P15,000Document3 pagesQuiz 6 - Accounting: Paid For The Publication in A Newspaper of The Consultancy Firm 'S Opening, P15,000Gavin Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Theory and PracticeDocument18 pagesMarketing Theory and PracticeRohit SahniNo ratings yet
- Penerapan Metode Just in Time Terhadap Efisiensi Biaya Bahan Baku PT Harmonize Invitation (Jira) KualiDocument19 pagesPenerapan Metode Just in Time Terhadap Efisiensi Biaya Bahan Baku PT Harmonize Invitation (Jira) KualiPrima MeilisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Excercise - Updated2Document2 pagesChapter 6 Excercise - Updated2Phương Thảo HoàngNo ratings yet
- 1 - Financial Report Analysis v.5Document55 pages1 - Financial Report Analysis v.5Joi Pia Sison SantosNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Chapter 07 SolutionsDocument13 pagesMicroeconomics Chapter 07 SolutionsRex CalibreNo ratings yet
- Summary Standard CostingDocument2 pagesSummary Standard CostingMaria Callista LovinaNo ratings yet
- T HAN H: Chapter 2. Trade and Technology: The Ricardian ModelDocument25 pagesT HAN H: Chapter 2. Trade and Technology: The Ricardian ModelHien PhanNo ratings yet
- Research Project Work BrajeshDocument97 pagesResearch Project Work BrajeshRajeew Ranjan0% (2)
- Chapter Six 6. Asset Valuation For Financial Reporting Contents of ChapterDocument6 pagesChapter Six 6. Asset Valuation For Financial Reporting Contents of Chaptergetahunb97No ratings yet
- Swot Analysis FeasibDocument2 pagesSwot Analysis FeasibIan Kirby AlegadoNo ratings yet
- SCM Group 3 Sec EDocument30 pagesSCM Group 3 Sec EpankajsyalNo ratings yet
- Negociación - Nota DidácticaDocument21 pagesNegociación - Nota DidácticaGregorio GarcésNo ratings yet
- Cost and Break Even Analysis SummaryDocument5 pagesCost and Break Even Analysis Summarypre.meh21No ratings yet
- Statement of Changes in Equity ReviewerDocument3 pagesStatement of Changes in Equity ReviewerSean Arvy Samson100% (1)
- T O S E E: ClearlyDocument308 pagesT O S E E: ClearlyAngel MaNo ratings yet
- Brand Management LirilDocument24 pagesBrand Management LirilArpan SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Poa T - 6Document2 pagesPoa T - 6SHEVENA A/P VIJIANNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Vs Management AccountingDocument2 pagesFinancial Accounting Vs Management AccountingMuhamamd Asfand YarNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship-1112 Q2 SLM WK4Document8 pagesEntrepreneurship-1112 Q2 SLM WK4mariceldaan2No ratings yet
- Your Content Marketing Success Metrics: Traffic by ChannelDocument2 pagesYour Content Marketing Success Metrics: Traffic by ChannelIbban JavidNo ratings yet
- MKTGDocument6 pagesMKTGshrutiu443No ratings yet
- Economics PG Problem Set 2 Ans Due DateDocument15 pagesEconomics PG Problem Set 2 Ans Due DateHuỳnh LinhNo ratings yet
- Charcoal Briquettes Production and Distribution Business PlanDocument14 pagesCharcoal Briquettes Production and Distribution Business PlanEmmanuel Bibandor100% (1)
- Pricing Strategies of Mercedez-BenzDocument9 pagesPricing Strategies of Mercedez-BenzKristi PodgoricaNo ratings yet
- Project Report of Share KhanDocument117 pagesProject Report of Share KhanbowsmikaNo ratings yet