Chapter 12: HEART
Chapter 12: HEART
Uploaded by
Precious Faith RodriguezCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 12: HEART
Chapter 12: HEART
Uploaded by
Precious Faith RodriguezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 12: HEART
Chapter 12: HEART
Uploaded by
Precious Faith RodriguezCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 12: HEART
Chapter 12: HEART Heart Chambers
Four Chambers:
The Cardiovascular System Left Atrium (LA)
the heart is a muscular organ that is essential for life because Right Atrium (RA)
it pumps blood through the body. Left Ventricle (LV)
the heart is a member organ of the cardiovascular system, Right Ventricle (RV)
which consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
the heart of a healthy adult, at rest, pumps approximately 5 Coronary sulcus:
liters (L) of blood per minute. separates atria from ventricles
Functions of the Heart It contains:
the right coronary artery
generates blood pressure
the small cardiac vein
routes blood
the coronary sinus
ensures one-way blood flow
the circumflex artery
regulates blood supply
Pericardia
Heart Characteristics
Pericardium
double-layered sac that anchors and protects
heart
Parietal pericardium
membrane around heart’s cavity
Visceral pericardium
membrane on heart’s surface
Pericardial cavity
space around heart
Size
size of a fist and weighs less than 1 lb.
Location
between lungs in thoracic cavity
Orientation Blood Flow Through Heart
apex (bottom) towards left side
Ventricles
inferior chambers
pumping chambers
thick, strong walled
contract forcefully to propel blood out of heart
Interventricular septum
separates right and left ventricles.
The Atria
superior chambers
holding chambers 1. Right Atrium 5. Pulmonary 9. Left Atrium 13. Aorta
small, thin walled trunk
2. Tricuspid valve 6. Pulmonary 10. Bicuspid 14. Body
contrast minimally to push blood into ventricles
arteries valve
3. Right Ventricle 7. Lungs 11. Left Ventricle
Interatrial septum
separates right and left atria 4. Pulmonary 8. Pulmonary 12. Aortic
semilunar valve veins semilunar valve
Precious Faith Rodriguez
CHAPTER 12: HEART
Semilunar Heart Valves Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
the semilunar valves have three half-moon shaped cusps, and record of electrical events in heart
are valves between the pulmonary trunk and aorta. diagnoses cardiac abnormalities
uses electrodes
Pulmonary valve contains P wave, QRS complex, T wave
between RV and pulmonary trunk
Aortic valve Components of ECG/EKG
between LV and aorta P wave
depolarization of atria
Atrioventricular Heart Valves
valves between the atria and ventricles QRS complex
depolarization of ventricles
Tricuspid valve contains Q, R, S waves
AV valve between RA and RV
3 cusps T wave
repolarization of ventricles
Bicuspid valve
AV valve between LA and LV
2 cusps Heart Sounds
heart sounds are produced due to the closure of heart
Heart Wall valves
a stethoscope is used to hear heart sounds
the first heart sound makes a ‘lubb’ sound
the second heart sound makes a ‘dupp’ sound
the first heart sound is due to the closure of the
atrioventricular valves
the second heart sound is due to the closure of the
semilunar valves
Heart Disease
Coronary Artery Disease
due to decrease blood supply to the heart
Epicardium coronary arteries are narrowed for some reason
surface of heart (outside)
Myocardial Infarction (heart attack)
Myocardium due to closure of one or more coronary arteries
thick, middle layer composed of cardiac muscle area(s) of cardiac muscle lacking adequate blood
supply die, and scars (infarct)
Endocardium
smooth, inner surface Heart Procedures
Angioplasty
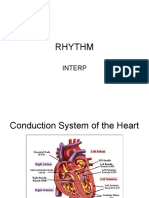
Action Potential Path through Heart procedure opens blocked blood vessels
1. SA node
2. AV node (atrioventricular) Stent
3. AV bundle structures inserted to keep vessels open
4. Right and Left Bundle branches
5. Purkinje fibers Bypass
procedure reroutes blood away from blocked
Conduction System of the Heart
arteries
Cardiac Cycle
Atrial systole
contraction of atria
Ventricular systole
contraction of ventricles
Atrial diastole
relaxation of atria
Ventricular diastole
relaxation of ventricles
Precious Faith Rodriguez
You might also like
- NurseBossStore Nursing NotesDocument17 pagesNurseBossStore Nursing NotesMary Kimberly S. CaberteNo ratings yet
- UGANDA Voter Count by Polling Stations 2021Document1,446 pagesUGANDA Voter Count by Polling Stations 2021jadwongscribdNo ratings yet
- Case #44 Hershey'sDocument6 pagesCase #44 Hershey'sSantos DegolladoNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Mock Test - Vskills Practice TestsDocument15 pagesDigital Marketing Mock Test - Vskills Practice Testsjayant bansal100% (1)
- DYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDocument3 pagesDYSRHYTHMIAS (A.k.a. Arrhythmias) Disorders in TheDarell M. Book100% (1)
- ASEAN SCOUT ON REGIONAL COOPERATION-ASARC DocNo.4a ConstitutionDocument10 pagesASEAN SCOUT ON REGIONAL COOPERATION-ASARC DocNo.4a ConstitutionAri Wijanarko Adipratomo, A.A.No ratings yet
- Anaphy CardioDocument6 pagesAnaphy CardioDianne DimaanoNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsDocument7 pagesPRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 8.cardiovascular SystemDocument13 pages8.cardiovascular Systempodki gurungNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medicines List For TheDocument9 pagesEmergency Medicines List For TheBisakha DeyNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- IV Solutions (Hyper, Hypo, Isotonic)Document1 pageIV Solutions (Hyper, Hypo, Isotonic)Paola OrtizNo ratings yet
- Sirs & ModsDocument5 pagesSirs & Modsmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- My Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMy Cheat SheetTenzin KyizomNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Medications by at A GlanceDocument4 pagesCardiac Medications by at A GlanceZhukma BogeeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory MedicationsDocument14 pagesRespiratory MedicationsissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionDocument6 pagesElectrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionmkninnyNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesLiel TorresNo ratings yet
- ECG Dysrhthmias IIIDocument31 pagesECG Dysrhthmias IIIAmani Kayed100% (1)
- Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument5 pagesCondition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsCasey Fioravante100% (1)
- Study Guide Med Surg #1Document22 pagesStudy Guide Med Surg #1cfunk929No ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms (2011)Document6 pagesACLS Algorithms (2011)senbonsakuraNo ratings yet
- MEDSURG 1 NotesDocument43 pagesMEDSURG 1 NotesNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- Cardio TransDocument7 pagesCardio TransweissNo ratings yet
- MSN NotesDocument23 pagesMSN NotesPauline JyNo ratings yet
- The Easy R's EKG Interpretation FinalDocument9 pagesThe Easy R's EKG Interpretation FinalMatar PaneerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology LectureDocument18 pagesPharmacology LectureChloe MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Lab Values - Chart by PriorityDocument2 pagesLab Values - Chart by Priorityashley100% (1)
- Assessment of The Chest and LungsDocument46 pagesAssessment of The Chest and LungsSumathi GopinathNo ratings yet
- Pharm SummaryDocument3 pagesPharm Summaryastorm0872No ratings yet
- Dosage CalculationsDocument39 pagesDosage Calculationssalak9462900% (1)
- Dysrhythmia Instructor 2018 2 PDFDocument105 pagesDysrhythmia Instructor 2018 2 PDFtvrossyNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument86 pagesCongestive Heart FailureNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- Cardio - ECGDocument13 pagesCardio - ECGSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocument69 pagesEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraNo ratings yet
- MNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryDocument38 pagesMNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryJosephine A. Bertulfo100% (1)
- Assessment of Kidney and Urinary FunctionDocument72 pagesAssessment of Kidney and Urinary Functionmoncalshareen3100% (2)
- Drug Compatibility in Intravenous Y-Site AdministrationDocument4 pagesDrug Compatibility in Intravenous Y-Site Administrationtuti haryatiNo ratings yet
- Nursing School EKGDocument43 pagesNursing School EKGRob Dickerson100% (2)
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument9 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PDFSheryl Ann Mae BombalesNo ratings yet
- ABGs Respiratory/MetabolicDocument3 pagesABGs Respiratory/MetabolicJoe B100% (1)
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument58 pagesCardiovascular Disordersehjing100% (3)
- EndocrineDocument23 pagesEndocrinensvickneswaran100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System Acronyms and MnemonicsDocument18 pagesCardiovascular System Acronyms and Mnemonicsdecsag06No ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument3 pagesECG InterpretationBIANCA ROMELLE STEPHANIE PAYOTNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsDocument29 pagesManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsYlanni Coritana100% (2)
- ACLS ChartDocument1 pageACLS ChartJev DespiNo ratings yet
- PVD-PAD Simple NursingDocument3 pagesPVD-PAD Simple NursingJerica Mae VenoyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac NotesDocument24 pagesCardiac NotesYary MayorNo ratings yet
- Arteries and Veins Mind MapDocument7 pagesArteries and Veins Mind MapNo Name100% (1)
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument69 pagesCardiovascular NotesAnnissaLarnardNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - Part 2 4-8-14 For BBDocument23 pagesCirculatory System - Part 2 4-8-14 For BBroman7dbNo ratings yet
- 60 Most Common DrugsDocument1 page60 Most Common DrugsNikkaLim100% (1)
- Fluid Overload Student PagesDocument4 pagesFluid Overload Student PagesJess OswaldNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument11 pagesCardiac Study Guidesurviving nursing school100% (2)
- How To Read An ECGDocument21 pagesHow To Read An ECGSlychenko100% (2)
- Assessment of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument48 pagesAssessment of The Cardiovascular Systemkimberlyrwarren8817No ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Cardiovascular DisorderDocument16 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Cardiovascular DisorderLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Review For MedicalDocument15 pagesThe Ultimate Review For MedicalJap Avila BernasNo ratings yet
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Strategies for ManagementFrom EverandCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia: Strategies for ManagementAntoni TorresRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument37 pagesCardiovascular System - The HeartCecil AlbaNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Heart PDFDocument5 pagesMammalian Heart PDFKhaled TurkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid Balance: TH RDDocument3 pagesChapter 18: Urinary System and Fluid Balance: TH RDPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- O CO O CO O CO: Chapter 15: Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesO CO O CO O CO: Chapter 15: Respiratory SystemPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Nervous System: With Opposite Effects, One Inhibits The Other Stimulates)Document6 pagesChapter 8: Nervous System: With Opposite Effects, One Inhibits The Other Stimulates)Precious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Endocrine System: To Body Fluids, Including BloodDocument4 pagesChapter 10: Endocrine System: To Body Fluids, Including BloodPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgmentsDocument3 pagesAcknowledgmentstealicelandyesNo ratings yet
- Journal Pone 0265501Document17 pagesJournal Pone 0265501Belayneh ChekleNo ratings yet
- Place Order Before February To Get 50% DiscountDocument32 pagesPlace Order Before February To Get 50% DiscountJony Saiful100% (2)
- Credit Risk Management-634Document96 pagesCredit Risk Management-634Ranjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Eriugena, in Martianum, Ed. LutzDocument274 pagesEriugena, in Martianum, Ed. Lutzdrugformind100% (1)
- (1983) Narration As Non-Communication. On Ann Banfield's ''Unspeakable Sentences''Document20 pages(1983) Narration As Non-Communication. On Ann Banfield's ''Unspeakable Sentences''Macedoniano100% (1)
- module-4-PE-Health 3rdyearDocument10 pagesmodule-4-PE-Health 3rdyearAngelica SaczNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500Document2 pagesPathophysiology: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500Ladybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- THE DARK SIDE OF Dialectics - Files PDFDocument32 pagesTHE DARK SIDE OF Dialectics - Files PDFJohn LiNo ratings yet
- 9324-Qr001 - En-P Studio 5000 Logix Designer Ordering GuideDocument4 pages9324-Qr001 - En-P Studio 5000 Logix Designer Ordering Guidesmith_raNo ratings yet
- Study Text: Business CommunicationDocument270 pagesStudy Text: Business CommunicationTeacher HaqqiNo ratings yet
- Research Defense - GROUP 1Document15 pagesResearch Defense - GROUP 1Juan Luis Dasas GantinaoNo ratings yet
- The Professional BartenderDocument84 pagesThe Professional BartenderJay-are Bayaua100% (1)
- Importance of Art in EducationDocument6 pagesImportance of Art in EducationMarilia GomesNo ratings yet
- O The Teacher Will AskDocument2 pagesO The Teacher Will AskJasellay Camomot100% (1)
- Poetry Prose DramaDocument28 pagesPoetry Prose DramaAliana CruzNo ratings yet
- Apical Pulse WSDocument2 pagesApical Pulse WSAlisa ChisholmNo ratings yet
- RubricsDocument4 pagesRubricsapi-307769664No ratings yet
- Report On Industrial Visit: Visited Professor Visited StudentsDocument10 pagesReport On Industrial Visit: Visited Professor Visited StudentsRishabh MishraNo ratings yet
- King ApplicationDocument75 pagesKing ApplicationJenniferNo ratings yet
- SDCA PortalDocument22 pagesSDCA Portalanon_393736085No ratings yet
- FCM1 - S01-T01-Introduction To FCM and The Five Star Doctor PDFDocument6 pagesFCM1 - S01-T01-Introduction To FCM and The Five Star Doctor PDFGianne OgacoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5 Week 4-Quarter 4 LASDocument5 pagesSCIENCE 5 Week 4-Quarter 4 LASArVin SantosNo ratings yet
- Script DocumentaryDocument3 pagesScript DocumentaryUsran Ali BubinNo ratings yet
- RJ14EA4072 NYSA - ICICI LombardDocument3 pagesRJ14EA4072 NYSA - ICICI Lombardaakashgupta viaanshNo ratings yet
- Ipl - The New Marketing Cocktail: Submitted by - Sugandha Sharma Mba Ii SemDocument11 pagesIpl - The New Marketing Cocktail: Submitted by - Sugandha Sharma Mba Ii SemSugandha SharmaNo ratings yet