Biological Organization
Biological Organization
Uploaded by
Shan Michael Sta. AnaCopyright:
Available Formats
Biological Organization
Biological Organization
Uploaded by
Shan Michael Sta. AnaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Biological Organization
Biological Organization
Uploaded by
Shan Michael Sta. AnaCopyright:
Available Formats
Shan Michael M. Sta. Ana STEM-J4 General Biology Ms.
Joice Barsaga
Biological Organization
Biological Organization is the hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems that define life using a
reductionistic approach. Organization is the arrangement of smaller components of nay structure, system or situation
into larger ones and larger ones into still larger ones in hierarchy, where components of each level coordinate with one
another towards a common goal. Organization is sort of hierarchy or pyramid of levels where each level is made of
components of lower level and itself becomes a component of higher level.
The basic unit or component of organization in both living and non-living object is an atom. An
atom is, of course further made of still smaller particles like electrons, protons and neutrons.
ATOM
Atoms combine with one another to form molecules.
Groups of atoms; smallest unit of most chemical compound.
MOLECULES Macromolecules are large, biologically important molecules inside cells.
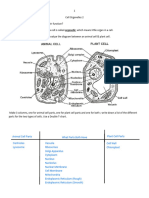
The subcellular components coordinate their activities to produce living cells. Living beings are
made of one cell (unicellular organisms) or numerous cells (multicellular organisms).
CELL
In multicellular organisms the cells may be similar (colonial organisms) or organized into distinct functional
units called tissue. A tissue is a group of cells with similar structure performing the same function
TISSUE
Two or more tissues are organized into distinct structures called organs . Organs are specialized for
performing one or more functions e.g. pumping by heart, photosynthesis by leaves.
ORGAN
Two or more organs coordinate their activities towards a common activity e.g. digestive system, respiratory
ORGAN system.
SYSTEM
Living beings are called organisms because they possess high level of organization. They are called
individuals as each organism has a distinct interact or individuality.
ORGANISM Individual living things.
All the individuals of a species found in an area where they can interact with one another is called
population.
POPULATION Group of organism of one type taht live in the same area.
The populations of different species found in an area also interact with one another . They constitute a
biotic community.
COMMUNITY Population that live togetherin a defined area.
The biotic community of an area and its abiotic environment together form an ecosystem.
Community and its nonliving surrounding.
ECOSYSTEM
All the ecosystems of the world interact further and form biosphere or livable space of the earth. An
organism is, therefore, not only an individual but also a part of population, community, ecosystem and
biosphere.
BIOSPHERE The part of earth that contains all ecosystems.
Reference: https://schooltutoring.com/help/biology-levels-of-organisation/
You might also like
- India Strategy - Modi 3.0 21may24 - BernsteinDocument21 pagesIndia Strategy - Modi 3.0 21may24 - BernsteinAbhinav BhattNo ratings yet
- Prison Break Season 1Document3 pagesPrison Break Season 1faith-sumagaysay-420440% (5)
- Triangle Agency - General Manager's ToolkitDocument27 pagesTriangle Agency - General Manager's ToolkitArthur De carvalho soares0% (1)
- Section 1.3 & 1.6 - Cell Structures and Functions QuizDocument1 pageSection 1.3 & 1.6 - Cell Structures and Functions QuizMay MontanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Document2 pagesCell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Kirsten Troupe100% (1)
- Geologic Time Web Quest - DBDocument4 pagesGeologic Time Web Quest - DBGab Reyes0% (1)
- Amoeba Sisters: Video Recap EnzymesDocument2 pagesAmoeba Sisters: Video Recap EnzymesYumalay MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cellgrow 10 AnsDocument6 pagesCellgrow 10 Ansprofesor_science100% (3)
- Cell Division ExerciseDocument3 pagesCell Division ExerciseFauziah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- ds74 Sol Review CellsDocument6 pagesds74 Sol Review Cellsapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Shark Dichotomous KeyDocument5 pagesShark Dichotomous KeyReviroda AnsayNo ratings yet
- As NZS 1841.1-2007 Portable Fire Extinguishers General RequirementsDocument9 pagesAs NZS 1841.1-2007 Portable Fire Extinguishers General RequirementsSAI Global - APAC0% (1)
- Comparacion Center Tap Vs DoublerDocument4 pagesComparacion Center Tap Vs DoublerGustavo MarquezNo ratings yet
- QCVN 03-2012BXD English PDFDocument20 pagesQCVN 03-2012BXD English PDFDinh Viet HaiNo ratings yet
- Biology CP Study Guide (Evolution & Classification)Document4 pagesBiology CP Study Guide (Evolution & Classification)misterbrownerNo ratings yet
- Intro To EcologyDocument44 pagesIntro To EcologyJinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Structurelingesh tamizhanNo ratings yet
- Allele Frequency LabDocument1 pageAllele Frequency Labjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- Cells & Cell Organelles: Doing Life's WorkDocument38 pagesCells & Cell Organelles: Doing Life's WorkLawrence RayappenNo ratings yet
- BIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and ObjectivesDocument24 pagesBIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and Objectivescheramae ancesNo ratings yet
- Histology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesHistology of Muscles: Learning ObjectivesLP BenozaNo ratings yet
- Science - Cell SpecializationDocument4 pagesScience - Cell SpecializationAvila VarshiniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To GeneticsDocument26 pagesLesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To Genetics宋臻若No ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetBianca BiancaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- SBI3U Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesSBI3U Digestive SystemMario AttallaNo ratings yet
- Rajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyDocument2 pagesRajeem Outlaw Wright - Mitosis Vs Meiosis BiologyRajeem Outlaw Wright100% (1)
- Bio - Cells - Amoeba Sisters Intro KEYDocument2 pagesBio - Cells - Amoeba Sisters Intro KEYMa.Janice GarciaNo ratings yet
- 63383-373662-Video Recap of Mitosis v. 2 by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pages63383-373662-Video Recap of Mitosis v. 2 by Amoeba SistersSean WongNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Chapter 36: Digestive Systems & NutritionDocument24 pagesAP Biology Chapter 36: Digestive Systems & Nutritionderekg608No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells PuzzleDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal Cells PuzzleLisa Ellis0% (1)
- 08 Lion Elephant Energy From MacromoleculesDocument8 pages08 Lion Elephant Energy From MacromoleculesJonghyun (Justin) YangNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Natural SelectionDocument22 pagesEvolution and Natural SelectionmalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Chemistry in Biology QuestionsDocument102 pagesChapter 6 Chemistry in Biology QuestionsOlga OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 Test Bank: The Human Body: A Nutrition PerspectiveDocument25 pagesChapter 03 Test Bank: The Human Body: A Nutrition Perspectivecynthiaaa sNo ratings yet
- Evolution Review Packet Key EditableDocument4 pagesEvolution Review Packet Key EditableMiljoy Delegado100% (1)
- Cell Organelles Worksheet KeyDocument7 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet KeyAngela Reyes100% (1)
- For SchoolDocument1 pageFor Schoolapi-252841138No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CAIE Biology IGCSEAiko KameishiNo ratings yet
- CH01 BiologyDocument36 pagesCH01 BiologysugisweNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument10 pagesCell CycleDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and OrgansDocument6 pagesCells, Tissues and OrgansatheelNo ratings yet
- In The WOMB-National Geographic ChannelDocument2 pagesIn The WOMB-National Geographic ChannelEmanuel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Biology Genetics TestDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Biology Genetics TestValerieNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life Long TestDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Life Long TestMichelle Ramirez Co-GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cladograms and Phylogenic TreesDocument5 pagesCladograms and Phylogenic TreesRachel WNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document3 pagesCH 1Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Organ Systems Cloze ReadDocument1 pageOrgan Systems Cloze Readapi-342334216No ratings yet
- AP Biology Parade Kingdoms KeyDocument21 pagesAP Biology Parade Kingdoms Keymoonbaby123No ratings yet
- Obtaining Energy and Removing WasteDocument14 pagesObtaining Energy and Removing WasteNeven FathyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Cell Division LabDocument3 pagesCell Division LabDoctorzo67% (6)
- Cie Igcse Bio Chapter01Document15 pagesCie Igcse Bio Chapter01Kulin Ranaweera100% (2)
- Human GeneticsDocument32 pagesHuman GeneticsLorenzo Maria CerviNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Digestion System (Kfogler)Document34 pagesAP Bio Digestion System (Kfogler)julie rainesNo ratings yet
- IB MYP U7 Peppered Moth Activity SolutionsDocument2 pagesIB MYP U7 Peppered Moth Activity SolutionsCoco LocoNo ratings yet
- Biology Life On Earth NotesDocument10 pagesBiology Life On Earth NotesEmmanuel Onyebuchi ObinwanorNo ratings yet
- Prokaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close ReadingDocument4 pagesProkaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close Readingapi-165869000No ratings yet
- AP Biology - Chapter 29 Discussion AnswersDocument3 pagesAP Biology - Chapter 29 Discussion Answersangel91me6371100% (1)
- Parts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryDocument3 pagesParts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryAnonymous giver100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LColeenNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet - WK7Document6 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet - WK7wobbleshopeNo ratings yet
- Cladogram WsDocument4 pagesCladogram Wsjeffery thomasNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2Document8 pagesKami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2bloomington369No ratings yet
- Body Systems Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesBody Systems Lesson PlanadelNo ratings yet
- Traditional vs. Modern Teaching Method: Effectiveness of The Methodologies On Education and Possible Resolution To Develop Better Students' OutcomeDocument57 pagesTraditional vs. Modern Teaching Method: Effectiveness of The Methodologies On Education and Possible Resolution To Develop Better Students' OutcomeShan Michael Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research FinalDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research FinalShan Michael Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 Personal RelationshipDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 10 Personal RelationshipShan Michael Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- STEM J4 - 1st Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument35 pagesSTEM J4 - 1st Laws of ThermodynamicsShan Michael Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- Yverdon de Pestallozi School, Inc.: IV. Data AnalysisDocument12 pagesYverdon de Pestallozi School, Inc.: IV. Data AnalysisShan Michael Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- The Seven Principal of Leave No TraceDocument22 pagesThe Seven Principal of Leave No TraceMadame UrsulaNo ratings yet
- Tabla Características CamesaDocument2 pagesTabla Características CamesaAntonio Del AngelNo ratings yet
- 5 StarDocument19 pages5 Starpagidimarrysaiakhil137No ratings yet
- List of Books by Author and TopicsDocument384 pagesList of Books by Author and TopicseternalhappinessNo ratings yet
- BV Module B H20R 07493 E0 ECDocument3 pagesBV Module B H20R 07493 E0 ECPhilSelborNo ratings yet
- NABH QuestionnairDocument3 pagesNABH QuestionnairRicha100% (4)
- GL Mathematics Paper 1 AnswersDocument5 pagesGL Mathematics Paper 1 AnswersBharath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Tunnelling-Induced Building DamageDocument10 pagesAssessment of Tunnelling-Induced Building DamageMarco NevesNo ratings yet
- Texas Rice Land Partners LTD v. Denbury Green Pipeline-Texas LLC, No 09-0901 (TX Apr 19 2011)Document16 pagesTexas Rice Land Partners LTD v. Denbury Green Pipeline-Texas LLC, No 09-0901 (TX Apr 19 2011)RHTNo ratings yet
- EE Lab 9Document6 pagesEE Lab 9Abdullah TahirNo ratings yet
- My CVDocument2 pagesMy CVGautam NaveenNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Orthodontic Relationships A Review of Integrated Treatment PlanningDocument18 pagesEndodontic Orthodontic Relationships A Review of Integrated Treatment PlanningAlfonso SernaNo ratings yet
- To Study The Digestion of Starch by Salivary AmylaseDocument20 pagesTo Study The Digestion of Starch by Salivary Amylasesureshk98438No ratings yet
- Specification 3528 STW9A12D-E2 2.1Document31 pagesSpecification 3528 STW9A12D-E2 2.1David CalabroNo ratings yet
- Haematology Basic Screening Package Complete Blood Count (CBC EXT)Document6 pagesHaematology Basic Screening Package Complete Blood Count (CBC EXT)Anil PeshinNo ratings yet
- Switch Below For Different ECU's: LegendDocument11 pagesSwitch Below For Different ECU's: LegendReza VaraminiNo ratings yet
- Trench AssaultDocument4 pagesTrench AssaultJim Wallman100% (1)
- Nonlinear Behavior and Design of Mid-To-Highrise Diagrid Structures in Seismic RegionsDocument41 pagesNonlinear Behavior and Design of Mid-To-Highrise Diagrid Structures in Seismic RegionsFATMAF HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- ETHICS 2022 Ethics Is The Branch of Philosophy That Studies Morality or The Rightness or Wrongness of HumanDocument20 pagesETHICS 2022 Ethics Is The Branch of Philosophy That Studies Morality or The Rightness or Wrongness of HumanJustin LapasandaNo ratings yet
- Peter Turner Volume 6 NumbersDocument61 pagesPeter Turner Volume 6 NumbersLorenzo TovagliaroNo ratings yet
- Application Information: ControlsDocument2 pagesApplication Information: ControlsIEQ DalvaNo ratings yet
- LAB - The Axial Skeleton: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLAB - The Axial Skeleton: ObjectivesSufiyaNo ratings yet
- Prepositions, A GuideDocument32 pagesPrepositions, A GuideGigliane SouzaNo ratings yet
- Techniques and Indices For Preventive Maintenance OptimizationDocument6 pagesTechniques and Indices For Preventive Maintenance OptimizationGopi SubramaniamNo ratings yet