0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 viewsAnaphy Lec Topic 5 - Cells
Anaphy Lec Topic 5 - Cells
Uploaded by
ydnic alykPCells are the basic units of life and come in two main types - eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles and are more complex, found in plants and animals, while prokaryotic cells do not have organelles and are unicellular. All cells contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. Organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and chloroplasts have specialized functions to keep the cell functioning. The nucleus contains DNA and controls the cell, mitochondria produce energy, and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus help synthesize and transport proteins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Anaphy Lec Topic 5 - Cells
Anaphy Lec Topic 5 - Cells
Uploaded by
ydnic alykP0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesCells are the basic units of life and come in two main types - eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles and are more complex, found in plants and animals, while prokaryotic cells do not have organelles and are unicellular. All cells contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. Organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and chloroplasts have specialized functions to keep the cell functioning. The nucleus contains DNA and controls the cell, mitochondria produce energy, and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus help synthesize and transport proteins.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Cells are the basic units of life and come in two main types - eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles and are more complex, found in plants and animals, while prokaryotic cells do not have organelles and are unicellular. All cells contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. Organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and chloroplasts have specialized functions to keep the cell functioning. The nucleus contains DNA and controls the cell, mitochondria produce energy, and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus help synthesize and transport proteins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesAnaphy Lec Topic 5 - Cells
Anaphy Lec Topic 5 - Cells
Uploaded by
ydnic alykPCells are the basic units of life and come in two main types - eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles and are more complex, found in plants and animals, while prokaryotic cells do not have organelles and are unicellular. All cells contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. Organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and chloroplasts have specialized functions to keep the cell functioning. The nucleus contains DNA and controls the cell, mitochondria produce energy, and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus help synthesize and transport proteins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Topic 5: Cells o Cytoplasm – substance where
ribosomes and rest of organelles
CELL STRUCTURE
float around
Cells – are the smallest living units of an o Endoplasmic Reticulum – aside
organism from cytoplasm, some ribosomes
float around here [ER]; enclosed
All cells have:
passageway for transportation of
Cell membrane – separates the materials (synthesized proteins)
inside from the environment 2 Types:
Cytoplasm – a jelly-like fluid a. Rough ER – has
DNA – cell’s genetic material ribosomes attached
to it
2 Categories of Cell
b. Smooth ER – no
1. Eukaryotic Cells – contain ribosomes are
organelles including nucleus and attached
other special parts; more o Small vesicles – where proteins
advanced complex cells found in and other materials emerge from
plants and animals ER
2. Prokaryotic Cells – do not contain o Golgi Apparatus (body) –
nucleus or membrane enclosed receives the protein and other
organelles, but have genetic materials where it is being
material; always once-celled customized in a form that cells
[unicellular organisms e.g. can use by folding into usable
bacteria] shapes or adding other materials
(carbohydrates, lipids)
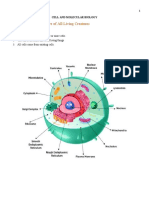
Organelles – “little organ” specialized
o Vacuoles – sac-like structure that
parts of a cell that have unique jobs to
store different materials [in plant
perform:
cell, it stores water]
o Nucleus – the control center of o Lysosome – take in damaged or
cell containing the DNA which worn out cell parts; filled with
tells the cell what to do and how enzymes that break down the
to do it cellular debris
o Chromatin – tangled, spread out o Mitochondrion – an organelle that
form of DNA found inside the is the powerhouse for both animal
nuclear membrane and plant cells
o Chromosomes – DNA condenses
Cellular Respiration -
into these structures when the
mitochondria make ATP
cell is ready to divide
molecules that provides energy
o Nucleolus – contained by nucleus
for all cell activities
where ribosomes are made
o Ribosomes – leaves the nucleus o Cytoskeleton – thread-like
to synthesize or make proteins microfilaments made of proteins
and microtubules that maintains
the shape of the cell
o Photoautotrophic [plants] –
capture sunlight for energy
o Chloroplast – where
photosynthesis happens
o Chlorophyll – green pigments
o Cell wall – found outside the cell
membrane that shapes, support,
and protect the plant cell; animal
cells don’t have cell walls
Other structures only some cell have:
o Cilia – found in respiratory tract;
microscopic hair-like projections
move in waves and can trap
inhaled particles in the air and
expels them when coughing
o Flagella – tail the helps cell move
or proper itself [sperm cell – only
human cell containing flagella]
You might also like
- Cell Structure and Function ReviewerDocument4 pagesCell Structure and Function ReviewerLeandre Jasmine Reyes100% (3)
- Chapter 4: Socializing The IndividualDocument24 pagesChapter 4: Socializing The IndividualSana ZahidNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- Cells StructuresDocument3 pagesCells StructuresPERJES, Sigrid Maial A.No ratings yet
- Biology Note About CellsDocument17 pagesBiology Note About CellsEK TubeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument5 pagesBiochemistry Reviewer202370092No ratings yet
- Gen Bio - First GradingDocument5 pagesGen Bio - First GradingCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- Bio Ncert GistDocument96 pagesBio Ncert GistrrphysicsinstituteNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- LESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypesDocument6 pagesLESSON 2.3 Basic Cell Typessandra100% (1)
- Gen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsDocument7 pagesGen Bio 1 Prelim HandoutsWinter ShiruzuNo ratings yet
- The Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument2 pagesThe Parts of The Cell and Their Functionsraphael100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - BiooDocument4 pagesLesson 2 - Bioohingingatensyonmo442No ratings yet
- Cell Theory ModifiedDocument33 pagesCell Theory ModifiedNazish Altaf100% (1)
- Topic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsDocument56 pagesTopic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsAhmed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyDocument6 pagesCells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSDocument38 pagesUNIT-2-SHORT NOTES Biology ALEVElSMohammed HasnatNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument28 pagesCell Structuresdnhira22No ratings yet
- Ch.4 Cell StructureDocument31 pagesCh.4 Cell StructureEmma WisemanNo ratings yet
- Biology Y10 Ch2Document7 pagesBiology Y10 Ch2zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Gen - Biology (REVIEWER)Document5 pagesGen - Biology (REVIEWER)Jainah Marie TambagoNo ratings yet
- Human and Social BiologyDocument21 pagesHuman and Social Biologybennettricardo024No ratings yet
- Biochem PrelimDocument42 pagesBiochem PrelimFaith RochaNo ratings yet
- Cellorganelles FNL 120130005530 Phpapp01Document18 pagesCellorganelles FNL 120130005530 Phpapp01Kairah MalikNo ratings yet
- 2 - Organisation of The OrganismDocument6 pages2 - Organisation of The OrganismAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- U1 Gen Bio Reviewer - VirusDocument4 pagesU1 Gen Bio Reviewer - Virusiron61883No ratings yet
- CELLDocument5 pagesCELLrazshellareignNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Organelles: Prepared By: SAPANA JHADocument14 pagesEukaryotic Cell Organelles: Prepared By: SAPANA JHAAppu JhaNo ratings yet
- ELS (2nd period)Document3 pagesELS (2nd period)wampiece18No ratings yet
- HANDOUTS-BioenergeticsDocument6 pagesHANDOUTS-BioenergeticsHenrick BajoNo ratings yet
- VIII Biology HO 3Document4 pagesVIII Biology HO 3aditiroy201208No ratings yet
- CellDocument11 pagesCelljhunard.asayas24No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesCell Parts and FunctionsMian Nakahara0% (1)
- Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiology ReviewerLycaNo ratings yet
- Major Components or Parts of The CellDocument2 pagesMajor Components or Parts of The CellArianeNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesWEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Sel PDFDocument32 pagesSel PDFJeje DengiNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument44 pagesCell TheoryAzalea SmithNo ratings yet
- 1 - CellDocument71 pages1 - CellEloiza Jamel Lanto100% (1)
- (M1) The CellDocument14 pages(M1) The CellBSN 1-1No ratings yet
- CELLSDocument7 pagesCELLSMaria Theresa BuscasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Cell: Cell-Is The Simplest Unit of Matter That Is AliveDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Cell: Cell-Is The Simplest Unit of Matter That Is AliveScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- biologyDocument2 pagesbiologygabrielakossi53No ratings yet
- biology-lecture (1)Document9 pagesbiology-lecture (1)masigansamanthaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- Gen Bio-1st Sem (Darlene Palanca 11sf-Stem)Document20 pagesGen Bio-1st Sem (Darlene Palanca 11sf-Stem)dcp.marie98No ratings yet
- HURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-2 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument20 pagesHURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-2 Cell Structure and OrganisationMahin IslamNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM-NOTES-BIODocument11 pagesMIDTERM-NOTES-BIOorxo80151No ratings yet
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCell OrganellesMark Kenneth CastilloNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Cell SGDocument6 pagesAP Biology Cell SGmatt69xNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument5 pagesCell Biologynaga.solitaryNo ratings yet
- Cell and its OrganellesDocument5 pagesCell and its OrganellesKarl BernardoNo ratings yet
- CELL ORGANIZATIONDocument6 pagesCELL ORGANIZATIONdiformeddinoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The CELLDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The CELLlorelie asisNo ratings yet
- Cellbio 1Document1 pageCellbio 1joker.fan245No ratings yet
- The Cell and Its OrganellesDocument7 pagesThe Cell and Its OrganellesJanine JoverNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Full Download Synthetic Biology Jeffrey Carl Braman PDFDocument52 pagesFull Download Synthetic Biology Jeffrey Carl Braman PDFeojmalaga100% (2)
- COVID Testing Labs 09112020Document132 pagesCOVID Testing Labs 09112020mommie magicNo ratings yet
- 1810222-Koldunism - Elemental Blood SorceryDocument21 pages1810222-Koldunism - Elemental Blood Sorcerysuperg96No ratings yet
- Guide For The Development of The Practical Component - Unit 2 - Phase 4 - Development of The Simulated Practical ComponentDocument15 pagesGuide For The Development of The Practical Component - Unit 2 - Phase 4 - Development of The Simulated Practical Componentfernando castroNo ratings yet
- LAL112 - Batch 1Document93 pagesLAL112 - Batch 1Kalumßa HillaryNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Comprehension - August 2021Document10 pagesIntermediate Comprehension - August 2021Ranuthi pereraNo ratings yet
- Abstract On 32nd West Bengal State Science CongressDocument1 pageAbstract On 32nd West Bengal State Science CongressAmisha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 ScriptDocument5 pagesBiology Form 4 ScriptsivanesshniNo ratings yet
- Álvarez Miguéns, Marta - Clark, Eugenie - Keating, Jess - Shark Lady - The True Story of How Eugenie Clark Became The Ocean's Most Fearless Scientist-Sourcebooks - Scholastic Inc (2018)Document37 pagesÁlvarez Miguéns, Marta - Clark, Eugenie - Keating, Jess - Shark Lady - The True Story of How Eugenie Clark Became The Ocean's Most Fearless Scientist-Sourcebooks - Scholastic Inc (2018)fatimazehranaqvi100% (1)
- Template in Monitoring and Evaluation On The Implementation of Science Curriculum (Regular Class)Document5 pagesTemplate in Monitoring and Evaluation On The Implementation of Science Curriculum (Regular Class)Archie PacaldoNo ratings yet
- Sarajevo School of Science and Technology: Questions 1-22, Circle The Correct AnswerDocument5 pagesSarajevo School of Science and Technology: Questions 1-22, Circle The Correct AnswerAmira SaidNo ratings yet
- Fungus God From OuterspaceDocument49 pagesFungus God From OuterspaceMaxime Khateeb100% (2)
- Key To Amphipoda: Paratanais Euelpis Barnard (Tanaidacea) - Arkiv. For Zool. 1: 357-360Document74 pagesKey To Amphipoda: Paratanais Euelpis Barnard (Tanaidacea) - Arkiv. For Zool. 1: 357-360OanaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Biology 0610/43 October/November 2021Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Biology 0610/43 October/November 2021pp baibeNo ratings yet
- 3 - ZOO - LIST OF Ph.D. REGISTRED STUDENTSDocument5 pages3 - ZOO - LIST OF Ph.D. REGISTRED STUDENTSRakesh PatleNo ratings yet
- STD 11 Bio Ch7 Neet-Jee Module With DPPDocument54 pagesSTD 11 Bio Ch7 Neet-Jee Module With DPPdmashrubkNo ratings yet
- Phrenology and PersonalityDocument3 pagesPhrenology and PersonalityParamesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Leroi-Gourhan: The Organised Inorganic' by Bernard Stiegler From Cahiers de Mediologie, No. 6, 2e Semestre, 1996Document8 pagesLeroi-Gourhan: The Organised Inorganic' by Bernard Stiegler From Cahiers de Mediologie, No. 6, 2e Semestre, 1996Charlie GereNo ratings yet
- Amphibians ReptilesDocument33 pagesAmphibians Reptileslau.wejarNo ratings yet
- Movement Leave and Head SunflowerDocument8 pagesMovement Leave and Head SunflowerRirin FardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Let's Talk About Newspapers:: Lesson 1: SpeakingDocument8 pagesLet's Talk About Newspapers:: Lesson 1: SpeakingNguyễn Hồng QuânNo ratings yet
- IFU NormaCont3+ EDocument1 pageIFU NormaCont3+ Ethuy dinhNo ratings yet
- Siklus Biogeokimia - Retensi NutrienDocument24 pagesSiklus Biogeokimia - Retensi NutrienPutri Nur Fadhilah YasharNo ratings yet
- Does Alternative Light Can Make The Okra SeedDocument8 pagesDoes Alternative Light Can Make The Okra SeedJuviel Ellah Mae VecinalNo ratings yet
- Salvador Edward Luria: Max DelrruckDocument4 pagesSalvador Edward Luria: Max DelrruckJaime Muñoz InsunzaNo ratings yet
- Lesson1Introduction To Social ScienceDocument59 pagesLesson1Introduction To Social ScienceShiarica Mae Neri100% (1)
- Brahmin DNA The Times of India - Upper Caste Indian Male More European, Says StudyDocument1 pageBrahmin DNA The Times of India - Upper Caste Indian Male More European, Says StudyRz RaselNo ratings yet
- 3a Faculty of Modern MedcineDocument32 pages3a Faculty of Modern MedcineKriti KumariNo ratings yet
- Afra Up CVDocument1 pageAfra Up CVapi-382711926No ratings yet