Final Dlp222
Final Dlp222
Uploaded by
Pauline Mae CañeteCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Dlp222
Final Dlp222
Uploaded by
Pauline Mae CañeteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Final Dlp222
Final Dlp222
Uploaded by
Pauline Mae CañeteCopyright:
Available Formats
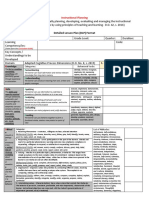
Instructional Planning
(The process of systematically planning, developing, evaluating and managing the instructional
process by using principles of teaching and learning - D.O. 42, s. 2016)
Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format
DLP No.: 1 Learning Area: CRMC Grade Level: 1 Quarter: 3 Duration: 60 mins
Learning Replicates the sounds heard from different sources Code: MU1TB-IIIb-3
Competency/ies: Uses voice and other sources of sound to produce a MU1TB-IIIb-4
(Taken from the Curriculum Guide) variety of timbres
Key Concepts /
Understandings to be Replicate and produce different sources and variety of timbre
Developed
Domain Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions (D.O. No. 8, s. 2015) 1. Objectives
Knowledge Categories: Behavioral Verbs:
The fact or condition
of knowing
Remembering identify, retrieve, recognize, Recognize and reproduce
The learner can recall information and retrieve relevant duplicate, list, memorize,
something with
knowledge from long-term memory repeat, describe, reproduce different sound heard from
familiarity gained
through experience
different sources.
or association Understanding interpret, exemplify, classify,
The learner can construct meaning from oral, written and summarize, infer, compare,
graphic messages explain, paraphrase, discuss
Skills Applying execute, implement, demonstrate,
The ability and The learner can use information to undertake a dramatize, interpret, solve, use,
capacity acquired procedure in familiar situations or in a new way illustrate, convert, discover
through deliberate, Analyzing differentiate, distinguish, compare,
systematic, and The learner can distinguish between parts and contrast, organize, outline, attribute,
sustained effort to determine how they relate to one another, and to the deconstruct
smoothly and overall structure and purpose
adaptively carryout
complex activities or Evaluating coordinate, measure, detect, defend,
the ability, coming The learner can make judgments and justify decisions judge, argue, debate, describe,
from one's critique, appraise, evaluate
knowledge, practice,
aptitude, etc., to do
Creating generate, hypothesize, plan, design, Produce a variety of timbres
The learner can put elements together to form a develop, produce, construct,
something functional whole, create a new product or point of formulate, assemble, devise using voice and other sources.
view
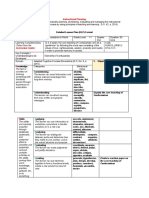
Attitude Categories: List of Attitudes:
Growth in 1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention Self-esteem, Self-confidence,
feelings Wellness, Respect, Honesty,
Show interest
Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, name,
or point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use Personal discipline, through
emotional Perseverance, Sincerity, identifying the
areas. Patience, Critical thinking,
A settled Open-mindedness, Interest, sounds we hear
way of Courteous, Obedience, Hope, in our
thinking Charity, Fortitude, Resiliency,
or feeling Positive vision, Acceptance, environment.
about 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends and Determined, Independent ,
someone reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance in Gratitude, Tolerant, Cautious,
or responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding (motivation). Decisive, Self-Control,
somethin Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label, Calmness, Responsibility,
g, perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write Accountability,
typically 3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from Industriousness, Industry,
one that simple acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the Cooperation, Optimism,
is internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these values are expressed in the Satisfaction, Persistent,
reflected learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable. Cheerful, Reliable, Gentle,
in a Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form, Appreciation of one’s culture,
person’s initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study Globalism, Compassion,
behavior 4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving Work Ethics, Creativity,
conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on Entrepreneurial Spirit,
comparing, relating, and synthesizing values. Financial Literacy, Global,
Solidarity, Making a stand for
Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, explain, the good, Voluntariness of
formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, relate,
human act, Appreciation of
synthesize
one’s rights, Inclusiveness,
5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their behavior. Thoughtful, Seriousness,
The behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly, characteristic of the Generous, Happiness,
learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's general patterns of Modest, Authority,
adjustment (personal, social, emotional). Hardworking, Realistic,
Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform, practice, Flexible, Considerate,
propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify Sympathetic, Frankness
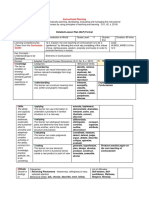
Values Categories: List of Values:
A 1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention 1. Maka-Diyos
learner's Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, name, Love of God, Faith, Trusting,
principles point to, reply, select, sit, Study, use Spirituality, Inner Peace, Love
or 2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends and of truth, Kindness, Humble
standards reacts to a particular phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance in
of responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in responding (motivation).
behavior; 2. Maka-tao
Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label,
one's Concern for Others, Respect
perform, practice, present, read, recite, report, select, tell, write
judgment for human rights, Gender
3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from simple
of what is equality, Family Solidarity,
acceptance to the more complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the internalization
important Generosity, Helping, Oneness
of a set of specified values, while clues to these values are expressed in the learner's overt
in life.
behavior and are often identifiable.
Go
beyond Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form, 3. Makakalikasan
learner’s initiate, invite, join, justify, propose, read, report, select, share, study Care of the environment, Show concern to
4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving Disaster Risk Management,
life on
conflicts between them, and creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on comparing, Protection of the the sounds we
earth,
include relating, and synthesizing values. Environment, Responsible hear in our
Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, explain, Consumerism, Cleanliness,
more
Orderliness, Saving the environment.
than formulate, generalize, identify, integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, relate,
wealth synthesize ecosystem, Environmental
and fame, 5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their behavior. sustainability
and The behavior is pervasive, consistent, predictable, and most importantly, characteristic of the 4. Makabansa
would learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with the student's general patterns of Peace and order, Heroism
affect the adjustment (personal, social, emotional). and Appreciation of Heroes,
eternal Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform, practice, National Unity, Civic
destiny of propose, qualify, question, revise, serve, solve, verify Consciousness, Social
millions. responsibility, Harmony,
Intention Patriotism,
ally Productivity
adding
value to
people
everyday.
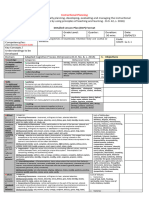
2. Content Quality of Sounds
3. Learning Resources
Visual Aids, Ppt presentation
4. Procedures:
4.1 Introductory Activity (7 minutes). This part introduces the lesson Curriculum
content. Although at times optional, it is usually included to serve as a warm- Contextualization
up activity to give the learners zest for the incoming lesson and an idea about
Activity: Copying the Different Sounds
Localization: Purpose: For them reproduce different
what it to follow. One principle in learning is that learning occurs when it is
Consider/include here the
conducted in a pleasurable and comfortable atmosphere.
appropriate Local sounds.
Heritage Themes: Procedure:
A. Annual Rites, Festivals,
and Rituals The teacher will show
(Historical/Religious different pictures and explain
Festivals, Local Cultural
Festivals, Local
what’s in the pictures
Delicacies/Products The teacher will play the
Festivals, Rituals,
sounds of the pictures
Wedding Ritual, Palihi
Ritual, Burial Ritual, The students will replicate
B Literary Anthologies the sound of each picture
Written In Local Language
(BALITAW, BALAK,
Sample Pictures:
Folktales/ Short Stories,
Local Heroes
C. Historical Events,
Enduring Values,
Indigenous Materials,
Indigenous Cultural
Communities/Indigenous
People, Indigenous
Games
D. Topography, Flora/
Fauna (Falls, Mountains,
River, Cave, Trees, Flower,
Fauna
E. Food & Local products
G. Role Model Family
Okey very good you all did a
good job
Now that you learn how to
produce and replicate sounds, I
will read you a story entitled
The Circus
4.2 Activity/Strategy (15 minutes). This is an interactive strategy to elicit
learner’s prior learning experience. It serves as a springboard for new
learning. It illustrates the principle that learning starts where the learners are.
Activity: Story Telling and Role
Carefully structured activities such as individual or group reflective exercises, Playing
group discussion, self-or group assessment, dyadic or triadic interactions, Purpose: After reading the story they
puzzles, simulations or role-play, cybernetics exercise, gallery walk and the like
may be created. Clear instructions should be considered in this part of the will have a role play.
lesson. Procedure:
The teacher will read a
story
The students will listen
After reading the story the
teacher will ask what are
the sounds they heard
from the story.
(Possible Answer): Roar
of a lion, Cheering crowd,
bark of a dog etc.
After reading the story it
will be use for a group
activity.
Sample Story:
The teacher will divide the
class into 6 groups
The teacher will provide a
raffle with their names,
and the group leaders will
pick one by one to
determine their one sound
character/object in the
story, and have them come
up with a sound
effect/accompanying
movement that would fit
their character/object.
Encourage the students to
make use of other sound
sources/materials they
have in the classroom to
make their sound more
interesting.
Give the groups 5-10
minutes to come up with
their sound effect and go
around to monitor/guide
the choices made by each
group.
When, everybody is done,
give the final instruction
that each group will only
perform the sound effect
when they see the picture
of their character/object. It
is important that the
teacher makes the
instructions understood
before starting the sound
story.
The students will be
graded based on the
rubrics given by the
teacher
Criteria
Collaboration 20%
Presentation 50%
Mastery 15%
Creativity 15%
TOTAL 100%
4.3 Analysis (5 minutes). Essential questions are included to serve as a The teacher will ask the students
guide for the teacher in clarifying key understandings about the topic at hand.
Critical points are organized to structure the discussions allowing the learners
to maximize interactions and sharing of ideas and opinions about expected 1. Did you enjoy the role playing?
issues. Affective questions are included to elicit the feelings of the learners A: Yes ma’am
about the activity or the topic. The last questions or points taken should lead
the learners to understand the new concepts or skills that are to be presented 2. What kind of sounds did you
in the next part of the lesson. produce?
A. Different sounds ma’am like
sound of the animals, people
things and many more.
3. What sources did you use to
produce sounds??
A. We use our voice, the table, our
hands etc.
4. What do you think will be our
topic for today?
A. Related to sounds ma’am,
sources of sounds.
5. Okey very good, all your
answers are correct.
4.4 Abstraction (15 minutes). This outlines the key concepts, important
skills that should be enhanced, and the proper attitude that should be
emphasized. This is organized as a lecturette that summarizes the learning
Activity: Discussion
emphasized from the activity, analysis and new inputs in this part of the Purpose: To summarize the learning
lesson. emphasized in the activities.
Procedure:
Last time we discussed about the
sources of sound right??
A. Yes ma’am
Who among you here can give me the
sources of sound that we discuss last
meeting?
A. People, animals, object and
nature
Okey very Good!!
Now!! Lets talk about Quality of
Sounds.
Different sounds are made and heard all
around us. Each sound produces a
unique or special quality.
The quality of sound in music is called
timbre or tone color. Timbre is what
differentiates a musical sound from
another even when they have the same
pitch and loudness.
Like what you said earlier we hear
sound from people like:
Talking
Shouting
Crying
Singing
Laughing
We also hear sounds from the animals
like :
Chirping bird
Buzzing bee
Barking dogs
Roar of lion
We also hear sound from nature like:
Raining
Wind
Thunder and lighting
We also hear sounds in objects like:
Radio
Television
Alarm clock
We also hear sounds from vehicle and
musical instruments like;
Motorcycle
Police car
Ambulance
Piano
Tambourine
Drum
Now let’s learn to replicate the sound
we hear from difference sources
Here are some examples of replicating
and producing sound heard from
different sources and how we can use
our voice and other source’s to produce
variety of timbre.
Clapping
Snapping
Drumming in a table
Whistling like a bird
Roar like a lion.
In clapping what source did we use??
A. Our hand
Very good!
How about in snapping what sources
did we use?
A. Hands
Excellent!
How about in drumming in the table
what sources did we use?
A. We use table.
Okey very good!
Okey now we’re done in our discussion
did you learn something class?
A. Yes ma’am
4.5 Application (10 minutes). This part is structured to ensure the
commitment of the learners to do something to apply their new learning in
their own environment. Now, to determine if you
understand our discussion for
today's lesson, I will divide you
into 6 groups.
I want you all to imagine your
one of the animals in the zoo.
(You pick your preferred
animal.)
After picking your preferred
animals, I want you to use their
sounds to replace the lyrics of
the song twinkle twinkle little
star.
You have 5 minutes to practice
before presenting your
performance.
You will be graded base on the
criteria given by the teacher.
Criteria:
Voice quality 25%
Creativity 25%
Confidence 25%
Performance 25%
TOTAL 100%
Example:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=O3AjVS9x2RY
Since we’re all done in your
presentation, I want you all to
get a piece of paper and answer
the following questions.
4.6 Assessment (6 minutes). For the Teacher to: a) Assess whether learning objectives have been met for a specified duration, b) Remediate and/or enrich with
appropriate strategies as needed, and c) Evaluate whether learning intentions and success criteria have been met. (Reminder: Formative Assessment may be given before,
during, or after the lesson). Choose any from the Assessment Methods below:
Assessment Method Possible Activities
a) Observation Investigation, Role Play,
(Formal and informal observations of learners’ performance or behaviors are Oral Presentation, Dance,
recorded, based on assessment criteria) Musical Performance,
Skill Demonstration,
Group Activity (e.g.
Choral Reading), Debate,
Motor & Psychomotor
Games, Simulation
Activities, Science
Experiment
b) Talking to Learners / Conferencing Hands-on Math Activities,
(Teachers talk to and question learners about their learning to gain insights on Written Work and Essay,
their understanding and to progress and clarify their thinking) Picture Analysis, Comic
Strip, Panel Discussion,
Interview, Think-Pair-
Share, Reading
c) Analysis of Learners’ Products Worksheets for all
(Teachers judge the quality of products produced by learners according to subjects, Essay, Concept
agreed criteria) Maps/Graphic Organizer,
Project, Model, Artwork,
Multi-media Presentation,
Product made in
technical-vocational
subjects
d) Tests Skill Performance Test,
(Teachers set tests or quizzes to determine learners’ ability to demonstrate Open-Ended Question,
Practicum, Pen and Paper
Identify the sources of sound. Write P
mastery of a skill or knowledge of content)
Test, Pre and Post Test, for people, A for Animals, N for nature,
Diagnostic Test, Oral
Test, Quiz
O for objects and MI for musical
instruments. Write your answer in your
notebook.
_____1. Washing machine
_____2. Water falls
_____3. Drum
_____4. Trumpet
_____5. Chicken
_____6. Singing
_____7. Radio
_____8. Dog
_____9. Thunder
_____10. Crying
4.7 Assignment (3 minutes). Fill-in below any of the four purposes:
Reinforcing / strengthening the day’s lesson List/Draw at least 3 object you have at
home/school and write down and
describe the sound they produce.
Enriching / inspiring the day’s lesson
Enhancing / improving the day’s lesson
Preparing for the new lesson
4.8 Concluding Activity (3 minutes).
This is usually a brief but affective closing activity such as a strong quotation, a short song, an anecdote,
parable or a letter that inspires the learners to do something to practice their new learning.
1. Remarks Indicate below special cases including but not limited to continuation of lesson plan to the following day in case of re-teaching or lack of time,
transfer of lesson to the following day, in cases of class suspension, etc.
3. Reflections Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your student’s progress this week. What works? What else needs to be
done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them
relevant questions. Indicate below whichever is/are appropriate.
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation.
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation.
C. Did the remedial
lessons work? No.
of learners who
have caught up
with the lesson.
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation.
E. Which of my
learning strategies
worked well? Why
did these work?
F. What difficulties
did I encounter
which my principal
or supervisor can
help me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials
did I use/discover
which I wish to
share with other
teachers?
Prepared by:
Name: Pauline Mae Canete School: Cebu Roosevelt Memorial Colleges
Position/Designation: Student Teacher Division: Bogo City
Contact Number: 09127088881 Email address: pauleenmae1030@gmail.com
References:
You might also like
- Erickson, M. H. (1944) - The Method Employed To Formulate A Complex Story For The Induction of An Experimental Neurosis in A Hypnotic Subject.Document20 pagesErickson, M. H. (1944) - The Method Employed To Formulate A Complex Story For The Induction of An Experimental Neurosis in A Hypnotic Subject.Franju SerraNo ratings yet
- Cot 3-Prepare AppetizersDocument5 pagesCot 3-Prepare AppetizersIvy Rosell Buayaban100% (3)
- IPlan DLP Format v.02Document5 pagesIPlan DLP Format v.02Alvin Cuandot100% (1)
- Organizes Dance Event For A Target Health Issue or Concern: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument4 pagesOrganizes Dance Event For A Target Health Issue or Concern: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatLuda Cababan SanesNo ratings yet
- C1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Document4 pagesC1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Jonathan Gabriel Nario Jr.No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning (Iplan)Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planning (Iplan)Nathalie Yvonne AliserNo ratings yet
- C1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Document5 pagesC1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3ludabelle19No ratings yet
- Final Curriculum Implementation Matrix Cim World ReligionDocument5 pagesFinal Curriculum Implementation Matrix Cim World ReligionBaby YanyanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Evaluates The Effectiveness of An Oral Communication Activity EN11/12OC-Ibe-14Document4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Evaluates The Effectiveness of An Oral Communication Activity EN11/12OC-Ibe-14Zeen DeeNo ratings yet
- DLP Format Blank SheetDocument25 pagesDLP Format Blank SheetRhea Rose PelaezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planningamy faith susonNo ratings yet
- OC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyDocument4 pagesOC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyZeen Dee100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJeanne AndradeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAhbby LaureaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAnonymous HJlXukJrNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- IPlan DLP Format v.02Document4 pagesIPlan DLP Format v.02Julie Anne MacuseNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning: Curriculum GuideDocument5 pagesInstructional Planning: Curriculum GuideBaby YanyanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- OC 11 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechDocument4 pagesOC 11 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningHelen LaurelNo ratings yet
- OC 12 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechDocument4 pagesOC 12 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PoetryDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Poetryjeremiejane.caraleNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm 1Document7 pagesOral Comm 1Theresa B.No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- IPlan DLP Format English-VersionDocument5 pagesIPlan DLP Format English-VersionDina ArcenalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- DLP-3 CS - RS11-IVd-f-3Document4 pagesDLP-3 CS - RS11-IVd-f-3aicavalerozoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 How World Religions BeganDocument5 pages2.1 How World Religions BeganRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- Iplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 1Document4 pagesIplan Philo LC 1.3 W1Day 1Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- OC 12.1 Comprehends Various Kinds of Oral TextsDocument4 pagesOC 12.1 Comprehends Various Kinds of Oral TextsZeen Dee100% (1)
- DLP Intro To World ReligionsDocument5 pagesDLP Intro To World ReligionssabellonanamariaNo ratings yet
- OC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesDocument4 pagesOC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesZeen Dee86% (7)
- 03 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionDocument15 pages03 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning (Iplan) : Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- IPLan TemplateDocument5 pagesIPLan TemplateSigrid Therese CañeteNo ratings yet
- Day 7Document4 pagesDay 7Jenn GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 How World Religions BeganDocument5 pages2.4 How World Religions BeganRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- DLP 3Document6 pagesDLP 3Baby YanyanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- 21st Century-LC-Q124Document5 pages21st Century-LC-Q124Shannen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- DRRR Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDRRR Lesson PlanJenn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: (With Inclusion of The Provisions of D.O. No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, S. 2016)Jhiamae PiqueroNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRendyNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAntonio CaballeroNo ratings yet
- IplanDocument4 pagesIplanJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionDocument5 pages3.2 Positive and Negative Effects of ReligionRay Hope P PuracanNo ratings yet
- OC 11.1 Ascertains The Verbal and Nonverbal Cues That Each Speaker Uses To Achieve His Her PurposeDocument4 pagesOC 11.1 Ascertains The Verbal and Nonverbal Cues That Each Speaker Uses To Achieve His Her PurposeZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Nail Care Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesNail Care Lesson PlanMa. Crissa Aboyme100% (1)
- DLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarDocument4 pagesDLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarRhona Liza CanobasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- DLP STEM BIO1112Ia-c-1Document10 pagesDLP STEM BIO1112Ia-c-1Jenn GarciaNo ratings yet
- DLP 2Document5 pagesDLP 2Raquel DomingoNo ratings yet
- DRRR Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDRRR Lesson PlanJenn GarciaNo ratings yet
- DLP Guide With DescriptionsDocument2 pagesDLP Guide With DescriptionsRovz GC Bin0% (1)
- DLP 51Document6 pagesDLP 51Maricris Galman SalamatNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Assignment! (New Teacher vs. Seasoned Teacher)Document1 pageAssignment! (New Teacher vs. Seasoned Teacher)Pauline Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- EJ772517Document13 pagesEJ772517Pauline Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Defining AssessmentDocument4 pagesDefining AssessmentPauline Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- g5 Science TM 02Document91 pagesg5 Science TM 02Pauline Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Activities and Games Animals HabitatsDocument26 pagesActivities and Games Animals HabitatsPauline Mae Cañete100% (1)
- GEC - Life and Works of Rizal Output No. 3Document1 pageGEC - Life and Works of Rizal Output No. 3Pauline Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Woldia University Faculty of Business and Economics Departement of ManagementDocument34 pagesWoldia University Faculty of Business and Economics Departement of ManagementFiteh KNo ratings yet
- L2 Demotivation Among Saudi Learners of English: The Role of The Language Learning MindsetsDocument267 pagesL2 Demotivation Among Saudi Learners of English: The Role of The Language Learning MindsetsQuân Võ MinhNo ratings yet
- Midterm 21.22Document4 pagesMidterm 21.22Hanh An Nguyen HoangNo ratings yet
- Long Answer Questions 40Document3 pagesLong Answer Questions 40Prabhdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Englih ProjectDocument8 pagesEnglih ProjectPrince Chouhan100% (1)
- Orca Share Media1677808465501 7037238758086591131Document44 pagesOrca Share Media1677808465501 7037238758086591131Clay HyeraiNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Professional EducationDocument8 pagesPart 3 Professional EducationMerry Cris Honculada Malalis100% (2)
- Elementary Logic PDFDocument59 pagesElementary Logic PDFJavier, Mavrin JadeNo ratings yet
- Literature Review and Theoretical FrameworkDocument14 pagesLiterature Review and Theoretical FrameworkDiksha KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Maslow Need Hierarchy and Herrzberg Two Factor TheoryDocument6 pagesComparison Between Maslow Need Hierarchy and Herrzberg Two Factor TheoryPrajna PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Why Traveling Is Important For Human LifeDocument2 pagesWhy Traveling Is Important For Human LifeHoonchyi KohNo ratings yet
- Public Communication-S2022Document41 pagesPublic Communication-S2022Aaila AkhterNo ratings yet
- RRL and RRSDocument11 pagesRRL and RRSKlain AzulNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Business EthicsDocument34 pagesPortfolio in Business EthicsMae Mendez TatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Moore'S On Refutation of IdealismDocument16 pagesUnit 5: Moore'S On Refutation of IdealismSajal MondalNo ratings yet
- Ethics 2Document3 pagesEthics 2OwenNo ratings yet
- Research 3RD Quarter Summative TestDocument3 pagesResearch 3RD Quarter Summative TestJazer LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Outline in Readings in Philippine History Part 1Document3 pagesOutline in Readings in Philippine History Part 1John Nicole QuinicoNo ratings yet
- Math and TOK: Exploring The Areas of KnowledgeDocument28 pagesMath and TOK: Exploring The Areas of KnowledgeIngrid DelangeNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Fidelity in TranslationDocument13 pagesConcepts of Fidelity in TranslationGabriel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- MMW-Chapter 3-1 Reasoning (New)Document35 pagesMMW-Chapter 3-1 Reasoning (New)Angelica Nicole Reyes MascariñasNo ratings yet
- Making Sense Out of Meaning - Discours, Figure TranslatedDocument5 pagesMaking Sense Out of Meaning - Discours, Figure TranslatedMcHackNo ratings yet
- ORAL-COMMUNICATION11 - Q1 - Module 1 - 08082020Document27 pagesORAL-COMMUNICATION11 - Q1 - Module 1 - 08082020Lily CruzNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyLearnJa Online SchoolNo ratings yet
- Bartlett 1932 Memory War of The GhostsDocument6 pagesBartlett 1932 Memory War of The GhostsJelena ZivkovicNo ratings yet
- The Phenomenon of Marriage Couples With Long-Distance RelationshipDocument9 pagesThe Phenomenon of Marriage Couples With Long-Distance RelationshipLaili Aulia RahmahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Science of PsychologyDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Science of PsychologyJasper Andal-CabanadoNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Your Cognitive Function Test ResultsDocument14 pagesInterpreting Your Cognitive Function Test ResultsThomas CruzNo ratings yet
- The Bystander EffectDocument9 pagesThe Bystander EffectSOPHIA ANGELA AÑOZANo ratings yet