Research Methodology: 571216 Business Research Methods Unit - I
Research Methodology: 571216 Business Research Methods Unit - I
Uploaded by
Deepa DilCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Methodology: 571216 Business Research Methods Unit - I
Research Methodology: 571216 Business Research Methods Unit - I
Uploaded by
Deepa DilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Research Methodology: 571216 Business Research Methods Unit - I
Research Methodology: 571216 Business Research Methods Unit - I
Uploaded by
Deepa DilCopyright:
Available Formats
571216
BUSINESS RESEARCH METHODS UNIT I
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Research means a search for knowledge. It refers to a scientific and systematic search for pertinent information on a specific topic. The term research refers to the systematic method consisting of enunciating the problem, formulating a hypothesis, collection the facts or data , analyzing the facts and reaching certain conclusions. Research is thus an original contribution to the existing stock of knowledge making for its advancement. OBJECTIVES
To explore a phenomenon or to achieve new insights into it. To discover the characteristic of a particular individual, situation or a group. To examine the frequency with which something occurs or with which it is associated with something else. To test a hypothesis of a casual relationship between variables.
RESEARCH TYPES BASIC VS APPLIED Basic means the investigation of problems to further and develop existing knowledge. It is mainly concerned with generalization and formulation of theories. Gathering knowledge for knowledges sake is termed basic research. E.g. Physics, astronomy. Similarly, studying the behavior of individual to make some generalization about their social learning, memory pattern, and intelligence level are also examples of fundamental research. DESCRIPTIVE VS ANALYTICAL RESEARCH Descriptive research describes the present state of affairs as it exists without having any control over variables. The researcher can only report what has happened or what is happening. In analytical research on the other hand the researcher has to use facts or information already available and analyze these to make a critical evaluation of the material. QUANTITATIVE VS QUALITATIVE RESEARCH Quantitative research is based on the measurement of quantity or amount. It is applicable to phenomenon that can be expressed in terms of quantity. Qualitative research is concerned with qualitative phenomenon. Qualitative research is especially important in the behavioral sciences where the aim is to discover the underlying motives , interest , personality and attitudes of human beings.
CONCEPTUAL VS EMPIRICAL RESEARCH Conceptual research is related to some abstract ideas or theory. Philosophers and thinkers generally use it to develop new concepts or to interpret existing ones. Empirical research is data based coming up with conclusions that are capable of being verified, by observation or by experiment. Empirical research is appropriate when proof that certain variables affect other variables in some way is sought. It is considered that evidence gathered through experiments or empirical studies provides the most powerful support for a given hypothesis LABORATORY RESEARCH The emphasis in laboratory research is on controlling certain variables in such as to observe the relationship between two or three other variables. CLINICAL OR DIAGNOSTIC RESEARCH This type of research follows case study methods or in-depth approaches to reach the basic causal relationship. This research takes only a few samples and studies the phenomenon in depth and observes the effects. EXPLORATORY RESEARCH The objective of exploratory research is the development of hypothesis rather than their testing. The major emphasis is on the discovery of ideas and insights. It is more flexible and highly informal. HISTORICAL RESEARCH This type of research utilizes historical sources like documents, literature, leaflets etc PANEL RESEARCH Panel methods are broader than descriptive than descriptive research. These methods are normally used in sales forecasting by measuring consumer preferences for various products measuring audience size and character for media programmes, testing new products and product concepts and testing any variable in a firms marketing mix. Generally the survey is valid for one time period, which is known as study period and they do not reflect changes occurring over time. EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH A process where events occur in a setting at the discretion of the experimenter and control are used to identify the sources of variation in subjects response. The investigator or experimenter systematically manipulates some factor to elicit a response from the subjects. Experimentation is considered to be process of manipulating one variable constant in order to establish a casual relationship.
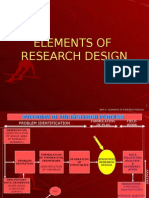
RESEARCH PROCESS
Define research Problem
Review Of Literature
Developing Hypothesis Research Design Sample Design
Data Collection
Analysis Of Data
Hypothesis Testing Interpretation
Report Preparation
DEFINING THE RESEARCH PROBLEM: Defining the basic problem, constitute the first step in a scientific enquiry. While formulating the research problem there are two main issues.
Review of Literature
It is a stage in which the researcher makes himself familiar with all the previous studies and their findings relevant to his field of work. He learns the methodology and approach developed by these past studies. He evaluates the conclusion of the previous studies in the light of the data he has collected. He questions these conclusions and tries to develop the alternative, possible better conclusions.
Developing the hypothesis: Hypothesis is a statement developed on the basis of suspected or anticipated relationship among various factors studied. Normally at the beginning of the research, the scholar would formulate a working hypothesis. It enables him to avoid collecting irrelevant data and facts. It helps him in focusing his attention on a particular aspect thereby eliminating wastage of time and resources.
Research Design Research design is a description of conceptual structure within which the research will be conducted. Here the researcher indicates the method of data collection the skills at the command of the researcher, the execution plan collection of data, the time and other resources available the financial implication etc,
Sample Design The researcher has to make a careful selection of a few elements from the population and then study them intensely and reach conclusion, which can be safely applied to the population. The selection of sample is a very important task. The researcher should determine the size of sample, the method of sampling, the test of sample etc.
Collecting Data The researcher at this stage should clearly spell out the sources of data for his work. He could use both primary as well as secondary data. While the former refers to the data collected for the first time by the researcher himself from the informants or the sample respondents specifically for his work. The latter means the data already, published or unpublished & available for use. The quality of data collected will ultimately decide the findings of the research work and so the researcher should arrange for surprise checks and controls over the collection of field data.
Analysis Of data:
Once the data are collected they should be classified and tabulated. Then the analysis of the data should be undertaken. At this stage, the researcher should select the tools of analysis, which are consistent with the objectives of the study. The tendency to carry out irrelevant analysis should be avoided. He should be strong in reasoning, drawing inferences and reaching conclusions. Testing Hypothesis: After analyzing the data as stated above the researcher is in a position to test the hypothesis, if any he had formulated earlier. Statistician has developed various tests such as chisquare test, t-test, F- test for the purpose. The hypothesis may be tested through the use of one or more of such tests, depending upon the nature and object of research inquiry. The test result may result in either accepting the hypothesis to start with , generalization established on the basis of data may be stated as hypothesis to be tested by subsequent researches in time to come. Generalization & interpretation: If a hypothesis is tested and upheld several times it may be possible for the researcher to arrive at generalization, The real value of the researcher lies in its ability to arrive at certain generalizations. If the researcher had no hypothesis to start with he might seek to explain his findings on the basis of some theory. it is called as interpretation. The process of interpretation may quite often trigger off new questions that in turn may lead to further researchers. Report Preparation: Finally the researcher has to prepare the report of what has been done by him. Writing of report must be done with great care. The report should clearly indicate the justification of the study, period of study, sample size, sources of data, tools of analysis, bibliography, review of past studies etc. It should also have a separate chapter on results and discussions where the researcher would report all his findings and give his interpretations. Care should be taken to incorporate relevant tables, diagrammed etc at the appropriate places.
CRITERIA OF GOOD RESEARCH
The purpose of the research should be clearly defined and common concepts be used. The research procedure used should be described in sufficient detail to permit another researcher to repeat the research for further advancement, keeping the continuity of what has already been attained. The procedural design of the research should be carefully planned to yield results that are as objective as possible. The researcher should report with complete frankness, flaws in procedural design and estimate their effects upon the findings. The analysis of data should be sufficiently adequate to reveal its significance and the methods of analysis used should be appropriate. Conclusion should be confined to those justified by the data of the research and limited to those for which the data provide an adequate basis. Greater confidence in research is warranted if the researcher is experienced has a good reputation in research and is a person of integrity.
QUALITIES OF GOOD RESEARCH Good research is systematic: It means that research is structured with specified steps to be taken in a specified sequence in accordance with the well-defined set of rules. Systematic characteristics of the research do not rule out creative thinking but it certainly does reject the use of guessing and intuition in arriving at conclusions. Good research is logical: This implies that research is guide by the rules of logical reasoning and the logical process of induction and deduction are of great value in carrying out research. Good Research is empirical: It implies that research is related basically to one or more aspects of a real situation and deals with concrete data that provides a basis for external validity to research results. Good Research is Replicable: This allows research to be verified by replicating the study and thereby building a sound basis for decisions.
Problems Encountered by researcher in India:
The lack of a scientific training in the methodology of research Insufficient interaction between the university research departments on the side and business establishments, governments department, and research institution on the other side. The business unit do not have confidence that the information supplied by them to researchers will be misused and so such they are often reluctant in supplying the needed information to researchers. Research studies overlapping one another are undertaken quite often for want of adequate information. There does not exist a code of conduct for researcher The difficult of adequate and timely secretarial assistance. Library management and functioning is not satisfactory at many place. There is also the problem that many of our libraries are not able to get copies of old and new Acts/ rules, reports and other government publications in time. There is also the difficulty of timely availability of published data. There may at times take place the problem of conceptualization.
HYPOTHESIS It is a tentative generalization, the validity of which remains to be tested. At the elementary level it may be mere hunch, guess, and imaginative data, which becomes the basis for action or investigation. Lundberg Hypothesis is a proposition, which can be put to test to determine validity. Goode & Hatt. A tentative solution posed on a cursory observation of known and available data and adopted provisionally to explain certain events and to guide in the investigation of others. It is in fact, a possible solution to a problem.
Characteristic Of Hypothesis Clarity:
The hypothesis must be conceptually clear. When the researcher attempts to establish relationship among various facts and translates these relationships into concepts he succeeds in formulating the hypothesis. Hence when a hypothesis is conceptually clear it provides a clear direction to the researcher. Scope For Verification: Hypothesis should be amenable for verification and empirical analysis. Though hypothesis can be verified in terms of moral judgments yet such verifications process will be questionable. Specific: The hypothesis should be very specific and not a general statement. It should not be ambiguous and it should be clearly stated. It is wiser to construct a hypothesis in simple language than resorting to flowery and confusing terminology. Testable: It should be testable with the available technique of analysis. Even while formulating a researcher should ascertain the relevant techniques with which it could be tested. Linked To Theory Hypothesis should facilitate establishing relationship with a body of theory. Therefore when the hypothesis is formulated the researcher should confirm whether it is related to any existing theory or not. Consistent It should be consistent with a most known facts ie it must be consistent with a substantial body of established facts. It should be one which judges accept as being the most likely.
TYPES OF HYPOTHESIS: Crude Hypothesis:
A crude hypothesis is formed to initiate the process of research. When the researcher is commencing his research work he needs some guidelines or focus. For this purpose he might develop a hypothesis based on the available evidence or data. Refined hypothesis: Hypothesis that state the existence of empirical uniformities, hypothesis that are concerned with complex ideal types and hypothesis that are concerned with complex ideal types and hypothesis that are concerned with the relation of analytical variables. Working hypothesis It is formed in the process of verifying the relationship among various variables included in research. It provides useful guideline to the researcher in determining the nature of data to be collected, volume of data required, the sample technique to be used analytical tools to be selected etc. Statistical hypothesis Statistical hypothesis are those, which are formulated based on the sample data or facts. They serve the usual purpose of testing any expected relationship among variables. Once these hypotheses are tested or verified the conclusion about the population is drawn. Null hypothesis It is formulated only to test whether there is any relationship between variables related to the problem being studied. Usually the null hypothesis is formed as a negative statement. Alternative hypothesis It is a statement, which is accepted after the null hypothesis is rejected based on the test results. Procedure for Hypothesis Testing: It refers to all those steps that we undertake for making a choice between the two actions i.e. Rejection and acceptance of a null hypothesis. The various steps involved in hypothesis testing are stated below; Making a formal statement: The step consists in making a formal statement of the null hypothesis and also of the alternative hypothesis.
Selecting a significance level: The hypothesis is tested on a pre- determined level of significance and as such the same should be specified. Generally 5% or 1% is adopted for the purpose. The factors that
affect the level of significance are; a) the magnitude of the difference between sample means. b) Whether the hypothesis is directional or non directional. c) The variability of measurements within samples d) whether the hypothesis is directional or non directional. Deciding the distribution to use: After deciding the level of significance the next step in hypothesis testing is to determine the appropriate sampling distribution. The choice generally remains between normal distribution and the t-distribution. Selecting a random sample and computing an appropriate value: The next step is to select a random sample and compute an appropriate value from the sample data concerning the test statistic utilizing the relevant distribution. Calculation of the probability: Then calculate the probability that the sample result would diverge as widely as it has from expectations, if the null hypothesis were in fact true. Comparing the probability: In this step compare the probability thus calculated with the specified value for the significance level. If the calculated probability is equal to or smaller than the value in case of one tailed test , then reject the null hypothesis but if the calculated probability is greater then accept the null hypothesis. Sources Of hypothesis Theory: This is one of the main sources. It gives direction to research by stating what is known. Logical deduction from theory leads to new hypothesis. E.g. The rate of return on capital employed is an index of business success. Observation: Hypothesis can be derived from observation . from observing price behavior in a market a hypothesis can be formulated on the relationship between price & demand for an article.
Analogies: Julian Huxley pointed out that casual observation in nature or in the framework of another science may be fertile source of hypothesis. The hypothesis that similar human
types or activities may be found in similar geophysical regions came from studying plant ecology. Intuition & personal experience: Personal life and experience of persons determine their perception. These may in turn direct a person to certain hypothesis more quickly. Eg Newton & falling of apple. Findings Of studies: Hypothesis may be developed from the findings of other studies in order to replicate and test. State Of Knowledge: An important source of hypothesis is the state of knowledge in any particular science. Where formal theories exist , hypothesis can be deduced from them. If the hypothesis were rejected theories would be modified. Where formal theories are scarce, hypothesis are generated from conceptual frameworks. Culture: Another source of hypothesis is the culture in which the researcher has been nurtured. In India in socio economic and leadership studies, hypothesis based on caste- ridden, hierarchical and segmental and the Indian economic system riddled with inequalities and privileges. Continuity Of research: The continuity of research in a field itself constitute an important source of hypothesis leads to the formulation of new ones capable of explaining dependent variables in a subsequent researchers on the same subject.
CHARACTERISTIC OF A GOOD HYPOTHESIS: Conceptual Clarity:
It should be conceptually clear. It should consist of clearly defined and understandable concepts. Clarity is obtained by defining operationally the concepts in the hypothesis. Specificity: A hypothesis should be specific and explain the expected relations between variables and the conditions under which these relations will hold. Testability : A hypothesis should be testable and should not be a moral judgement. It should be possible to collect empirical evidence to test the hypothesis. Eg Bad partners produce bad children. Availability Of technique: Hypothesis should be related to available techniques. Otherwise they will not be researchable. Therefore the research must make sure that methods for testing his proposed hypothesis are available. Theoretical relevance: It should be related to a body of theory. A science can be cumulative only building on an existing body by building on an existing body of facts and theory. When research is systematically based upon a body of existing theory , a genuine contribution to knowledge is more likely to result. Therefore a hypothesis should posses theoretical relevance. Consistency: Hypothesis should be logically consistent. Two or more propositions logically derived from the same theory must not be mutually contradictory. Objectivity: Scientific hypothesis should be free from value judgments. However as social phenomenon are affected by the milieu in which they take place, the researcher must be aware of his values and state them explicitly. Simplicity : A hypothesis should be a simple one requiring fewer conditions or assumptions. It demands insight. The more the insight the researcher has into a problem, the simple will be his hypothesis about it.
Rules in Hypothesis Development:
Search for variable measurements with the most quantitative characteristic.
Make the variable like properties explicit by stating all of the variables mutually exclusive and totally inclusive categories by degree. Describe the means used to sort observation into your variable categories insufficient detail so that methods may be evaluated and replicated by others . Always consider alternative operations that might be more appropriate for a given variable. Analyze variable through their relationship. Link two or more formal propositions through a shared independent or dependent variable where possible.
You might also like
- What Is The Relationship Between The Number of Punches A Fighter Lands in A Fight and If The Fight Ended in A KO or NotDocument16 pagesWhat Is The Relationship Between The Number of Punches A Fighter Lands in A Fight and If The Fight Ended in A KO or NotAnthocityNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Nature and Scope of Educational Psychology: John ParankimalilDocument6 pagesMeaning, Nature and Scope of Educational Psychology: John Parankimaliltemesgen biftuNo ratings yet
- Mid TermDocument7 pagesMid Termapi-547386122No ratings yet
- Business Research Methods NotesDocument106 pagesBusiness Research Methods NotesAce Emil100% (2)
- Case Study Research.: Design and MethodsDocument9 pagesCase Study Research.: Design and MethodsAkshu GillNo ratings yet
- 02 Bed15202 Guidance and CounsellingDocument161 pages02 Bed15202 Guidance and CounsellingVaishali ChellappaNo ratings yet
- The Validity of Surveys Online and OfflineDocument13 pagesThe Validity of Surveys Online and OfflineBuburuz CarmenNo ratings yet
- Extraneous VariablesDocument3 pagesExtraneous VariablesAmna MazharNo ratings yet
- Experimenta L Method: Eunice Dimple B. CaliwagDocument5 pagesExperimenta L Method: Eunice Dimple B. CaliwagEunice Dimple Caliwag100% (1)
- HypothesisDocument22 pagesHypothesisAnonymous kTVBUxr100% (1)
- Features of Choice Based Credit SystemDocument2 pagesFeatures of Choice Based Credit SystemFaizargarNo ratings yet
- Purpose of ResearchDocument3 pagesPurpose of ResearchPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Research Design Elements and TypesDocument9 pagesResearch Design Elements and TypesSMiley XeroxNo ratings yet
- FORMAT FOR RESEARCH PROPOSAL AND REPORT WRITING Dec. 2010 (1) Dr. KidomboDocument10 pagesFORMAT FOR RESEARCH PROPOSAL AND REPORT WRITING Dec. 2010 (1) Dr. KidomboMartin Mutua100% (2)
- Research Methodology and Publication Ethics NotesDocument134 pagesResearch Methodology and Publication Ethics NotesBhagya S GNo ratings yet
- Psychology and Common Sense ArticleDocument12 pagesPsychology and Common Sense ArticleAdarsha DhakalNo ratings yet
- Assumptions Limitations de Limitations XDocument3 pagesAssumptions Limitations de Limitations XAmir AlazhariyNo ratings yet
- Mb0034 Research Methodology Set 1Document15 pagesMb0034 Research Methodology Set 1image_2010No ratings yet
- Role of Hypothesis in ResearchDocument12 pagesRole of Hypothesis in ResearchOm Prakash Choudhary100% (2)
- Research MethodologyDocument5 pagesResearch Methodologymoulya100% (1)
- Primary Vs Secondary Sources of Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesPrimary Vs Secondary Sources of Literature ReviewSabarishNo ratings yet
- Reporting and Thesis WritingDocument13 pagesReporting and Thesis WritingABHIRAM100% (1)
- Group 2 - QUANTITATIVE RESEARCHDocument12 pagesGroup 2 - QUANTITATIVE RESEARCHTanaka Majoboro100% (1)
- Population and SampleDocument5 pagesPopulation and SampleDesi PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Scientific Misconduct: Fabrication, Falsification and Sanctity of DataDocument24 pagesScientific Misconduct: Fabrication, Falsification and Sanctity of DataPrabhu Prasad Dev0% (1)
- Participant Observation: History and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesParticipant Observation: History and DevelopmentAmadaLibertadNo ratings yet
- RFP - MRF-108 - VHC Evaluation Study - MeghalayaDocument8 pagesRFP - MRF-108 - VHC Evaluation Study - MeghalayaplantsakhiNo ratings yet
- Question 1:-What Do You Mean by Research? Explain Its Significance in Social and Business Sciences. AnswerDocument32 pagesQuestion 1:-What Do You Mean by Research? Explain Its Significance in Social and Business Sciences. Answersaurabh_rtlNo ratings yet
- Educational PsychologyDocument28 pagesEducational PsychologysyedmirsyedNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Selecting A TopicDocument5 pages1.1 Selecting A TopicAthamiz SelvanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Cognitive PsychologyDocument2 pagesImportance of Cognitive PsychologyHazel Vakharia100% (1)
- Most Important Online Tools For ResearchersDocument7 pagesMost Important Online Tools For ResearchersAna Mae CatubesNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Disadvantages of The Use of The Scientific Method in PsychologyDocument3 pagesDiscuss The Disadvantages of The Use of The Scientific Method in PsychologyAmy Clark100% (2)
- Primary Data Collection MethodsDocument2 pagesPrimary Data Collection MethodsPoonal AsasNo ratings yet
- Methods and Tools Fo Data CollectionDocument12 pagesMethods and Tools Fo Data CollectionJananee RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- Tools of Data Collection (Sadia)Document11 pagesTools of Data Collection (Sadia)Ayesha AasshNo ratings yet
- Data Collection ToolsDocument19 pagesData Collection ToolsMahmudulHasanHirokNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 DoptDocument33 pagesUnit 2 Doptpreetcharan001No ratings yet
- Q2 L3 HypothesisDocument16 pagesQ2 L3 HypothesisKd VonnNo ratings yet
- Threats To Validity of Research DesignDocument10 pagesThreats To Validity of Research DesignSamir AlamNo ratings yet
- Methods in PsychologyDocument4 pagesMethods in PsychologyIhtisham Ul haqNo ratings yet
- Steps Involved in Research Process - AbridgedDocument11 pagesSteps Involved in Research Process - AbridgedAnjie NathaniNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Is A Tentative Explanation That Accounts For A Set of Facts and Can Be Tested by Further InvestigationDocument9 pagesHypothesis Is A Tentative Explanation That Accounts For A Set of Facts and Can Be Tested by Further InvestigationScreaMonster PicNo ratings yet
- Experimental Method of ResearchDocument21 pagesExperimental Method of ResearchCiashell LayeseNo ratings yet
- Personality: Freud Psychoanalytic Theory: Defense MechanismsDocument10 pagesPersonality: Freud Psychoanalytic Theory: Defense MechanismsAadil JuttNo ratings yet
- Logic Chapter 1Document22 pagesLogic Chapter 1studentdu15No ratings yet
- Self Presentation and Impression ManagementDocument22 pagesSelf Presentation and Impression ManagementAbdul SamiNo ratings yet
- Lesson No 5 Elements of Research DesignDocument26 pagesLesson No 5 Elements of Research DesignJosephine Lourdes Valan0% (1)
- GROUNDING HYPOTHESES PRESENTATION - (English)Document17 pagesGROUNDING HYPOTHESES PRESENTATION - (English)Andres AngaritaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Unit 1 Ph.D. Course WorkDocument15 pagesResearch Methodology Unit 1 Ph.D. Course WorkMOHAMMAD WASEEMNo ratings yet
- UNIT TWO - Types of Research, Quantitative ResearchDocument22 pagesUNIT TWO - Types of Research, Quantitative ResearchSerawit DejeneNo ratings yet
- So What Is The Difference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchDocument2 pagesSo What Is The Difference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchAbdishakur Dahir MuseNo ratings yet
- Tools For Data CollectionDocument22 pagesTools For Data CollectionVarun KumarNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document86 pagesCH 01VVaasseem KhhaanNo ratings yet
- Reasearch SampleDocument13 pagesReasearch SampleRezpect QueenNo ratings yet
- Critical Theory: From Michael Apple's Perspective (Review)Document5 pagesCritical Theory: From Michael Apple's Perspective (Review)Johan Fernando Aza Rojas100% (1)
- Introduction To Research MethodsDocument66 pagesIntroduction To Research MethodsHayelom Tadesse GebreNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Social ScienceDocument7 pagesResearch Methods in Social ScienceNicholas SiochaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology AND Review of Literature: Chapter-3Document28 pagesResearch Methodology AND Review of Literature: Chapter-3Marco RegunayanNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods (KMB 203) Unit 1Document27 pagesBusiness Research Methods (KMB 203) Unit 1Archi VarshneyNo ratings yet
- High PE Vs Low PEDocument11 pagesHigh PE Vs Low PEHema KhatwaniNo ratings yet
- Module 16Document14 pagesModule 16Sarah VillaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 The Plausibility of µ as a Value for a Normal Population Mean μDocument23 pages4.1 The Plausibility of µ as a Value for a Normal Population Mean μTolesa F BegnaNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Architectural Design of The Kindergarten Space On The Children's Intelligence and CreativityDocument15 pagesThe Effects of Architectural Design of The Kindergarten Space On The Children's Intelligence and CreativityexeNo ratings yet
- Example of Article ReviewDocument8 pagesExample of Article ReviewNurun Nadia MasromNo ratings yet
- Psychological Statistics - 2nd SemDocument5 pagesPsychological Statistics - 2nd SemLykaNo ratings yet
- Two-Variable Regression-Interval 123estimation & Hypothesis TestingDocument31 pagesTwo-Variable Regression-Interval 123estimation & Hypothesis Testingkrish.dpatel14No ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belagavi: VTU-ETR Seat No.: ADocument48 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University, Belagavi: VTU-ETR Seat No.: Avaruna KNo ratings yet
- School As Learning Organisation: The Role of Principal's Transformational Leadership in Promoting Teacher EngagementDocument6 pagesSchool As Learning Organisation: The Role of Principal's Transformational Leadership in Promoting Teacher EngagementHafeez UllahNo ratings yet
- Stat ZttestsExer Two SampleTests ExSW StudDocument3 pagesStat ZttestsExer Two SampleTests ExSW StudpazicolilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Research MethodologyDocument15 pagesChapter 4 Research Methodologyffll18No ratings yet
- Math204 NonParOneTwoDocument4 pagesMath204 NonParOneTwoNeeti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Development MakalahDocument6 pagesHypothesis Development MakalahSamsi DewiNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Learning Module (3rd Quarter)Document95 pagesStatistics and Probability Learning Module (3rd Quarter)Moises John SangalangNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Research Methodology PDFDocument25 pagesBasic Concepts of Research Methodology PDFRKJhalendraNo ratings yet
- Old Syllabus Psychology 1Document60 pagesOld Syllabus Psychology 1Forough AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Anova-Ppt For Sonia Kalra Ma'AmDocument31 pagesAnova-Ppt For Sonia Kalra Ma'Amaakash rayNo ratings yet
- SEM Boot Camp Day 1 Morning: Basics & Data Screening: James Gaskin James - Gaskin@byu - EduDocument38 pagesSEM Boot Camp Day 1 Morning: Basics & Data Screening: James Gaskin James - Gaskin@byu - EduTram AnhNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear AggressionDocument46 pagesSimple Linear Aggressionshadowhunter200No ratings yet
- Econometrics Lecture Notes BookletDocument81 pagesEconometrics Lecture Notes BookletilmaNo ratings yet
- EPI 1.05 Basic BiostatisticsDocument7 pagesEPI 1.05 Basic BiostatisticsJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Statistical Significance and MeaningfulnessDocument3 pagesStatistical Significance and MeaningfulnessBeverly WangareNo ratings yet
- All About Statistical Significance and TestingDocument15 pagesAll About Statistical Significance and TestingSherwan R ShalNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS FOR BUSINESS - CHAP07 - Hypothesis Testing PDFDocument13 pagesSTATISTICS FOR BUSINESS - CHAP07 - Hypothesis Testing PDFHoang NguyenNo ratings yet
- ACJC - H1 - MATH - Prelim QP (2012)Document6 pagesACJC - H1 - MATH - Prelim QP (2012)Qinwei ZhangNo ratings yet
- Statistics With R Fall 20180912 PDFDocument101 pagesStatistics With R Fall 20180912 PDFPedro PereiraNo ratings yet
- Discussion-2: Example: 11-3Document4 pagesDiscussion-2: Example: 11-3Abdullah Al MuhitNo ratings yet
- Business Statistic Chapter 11Document11 pagesBusiness Statistic Chapter 11Noor Ainaa AzyanNo ratings yet
- Ijimsep M 2 2018Document13 pagesIjimsep M 2 2018JosephNathanMarquezNo ratings yet