0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
106 viewsVancomycin DRUGSTUDY
Vancomycin DRUGSTUDY
Uploaded by
Emagra AzilThis document provides information about the drug Vancomycin Hydrochloride including its dosage, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, and nursing considerations. Vancomycin is an antibiotic that works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It is indicated to treat serious infections caused by gram-positive bacteria including MRSA and CDAD. Common adverse effects include fever, headache, ototoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of the "red man syndrome" if administered intravenously too quickly and assess renal function during treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Vancomycin DRUGSTUDY
Vancomycin DRUGSTUDY
Uploaded by
Emagra Azil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
106 views3 pagesThis document provides information about the drug Vancomycin Hydrochloride including its dosage, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, and nursing considerations. Vancomycin is an antibiotic that works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It is indicated to treat serious infections caused by gram-positive bacteria including MRSA and CDAD. Common adverse effects include fever, headache, ototoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of the "red man syndrome" if administered intravenously too quickly and assess renal function during treatment.
Original Description:
Vancomycin DRUGSTUDY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document provides information about the drug Vancomycin Hydrochloride including its dosage, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, and nursing considerations. Vancomycin is an antibiotic that works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It is indicated to treat serious infections caused by gram-positive bacteria including MRSA and CDAD. Common adverse effects include fever, headache, ototoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of the "red man syndrome" if administered intravenously too quickly and assess renal function during treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
106 views3 pagesVancomycin DRUGSTUDY
Vancomycin DRUGSTUDY
Uploaded by
Emagra AzilThis document provides information about the drug Vancomycin Hydrochloride including its dosage, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, and nursing considerations. Vancomycin is an antibiotic that works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It is indicated to treat serious infections caused by gram-positive bacteria including MRSA and CDAD. Common adverse effects include fever, headache, ototoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of the "red man syndrome" if administered intravenously too quickly and assess renal function during treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
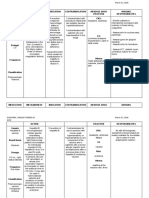
DRUG NAME DOSAGE MECHANISM INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING
OF ACTION EFFECT CONSIDERATIONS
Generic Availability: Hinders Indicated • Contraindicated in CNS: fever, pain, • Obtain hearing
Name: Capsules: 125 mg, bacterial cell- treatmeant for: patients hypersensitive to headache, fatigue. evaluation before and
Vancomycin 250 mg wall synthesis, Renal drug or its components. during prolonged
Hydrochloride Powder for damaging the insufficiency, CV: hypotension, therapy.
(van-koh-MYE- injection: 500-mg bacterial plasma Serious or severe • Use cautiously in thrombophlebitis at
sin) vials, 750-mg vials, membrane and infections when patients receiving other injection site. • Monitor patient's
1-g vials Powder making the cell other antibiotics neurotoxic, nephrotoxic, fluid balance and
Brand Name: for oral solution: more vulnerable are ineffective or or ototoxic drugs; in EENT: ototoxicity, watch for
Cytovan 25 mg/mL, 50 to osmotic contraindicated, patients older than age tinnitus. oliguria and cloudy
Forstaf mg/mL pressure. Also including those 60; and in those with urine
Vanco – Cp Premixed for interferes with caused by impaired hepatic or renal GI: .
Vancocin Cp injection: 500 RNA synthesis MRSA, function, hearing loss, or pseudomembranous • Monitor patient
Vancogen mg/100 mL, 750 Staphylococcus allergies to other colitis, nausea, carefully for red-man
Vancogram – mg/150 mL, 1 epidermidis, or antibiotics. abdominal pain, syndrome, which can
500 g/200 mL diphtheroid vomiting, diarrhea, occur if drug is infused
Vancorin organisms • It isn't known if drug flatulence. too rapidly. Signs and
Vancotech Cp CDAD CDAD causes fetal harm. Use symptoms include
Vanlid Adults: 125 mg PO during pregnancy only if GU: maculopapular rash on
Staphylococcal nephrotoxicity.
Vanmycos – Cp every 6 hours for 10 enterocolitis clearly needed. face, neck, trunk, and
Vansafe – Cp days. Children: 40 • Drug appears in human limbs and pruritus and
milk. Patient should Hematologic:
Vantox Cp mg/kg/day PO in leukopenia, hypotension caused by
three or four discontinue breastfeeding histamine release. If
Classification: divided doses for 7 or discontinue drug. neutropenia,
eosinophilia. wheezing, urticaria, or
Anti- bacterial to 10 days. pain and muscle spasm
agent. Belongs Maximum daily Metabolic: of the chest and back
to dose is 2 g hypokalemia (PO). occur, stop infusion
aminoglycoside Staphylococcal and notify prescriber.
antibiotics enterocolitis
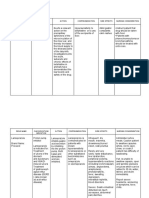
Adults: 500 mg to 2 Respiratory: • Don't give drug IM.
g PO in three or dyspnea, wheezing.
Route: four divided doses Skin: red-man
PO syndrome (with • Assess renal function
daily for 7 to 10
IV rapid IV infusion). (BUN, creatinine level
days. Children: 40
Other: anaphylaxis, and CrCl, urinalysis,
mg/kg/day PO in
Forms: chills, and urine output)
three or four
Capsule before and during
divided doses for 7
Powder for oral therapy.
to 10 days.
solution
Maximum daily • Carefully monitor
Powder for
dose is 2 g serum concentrations
Injection
Pharmacokinetics of vancomycin to
Absorption: adjust IV dosage
GI tract: Poorly requirements.
absorbed
Systemic • Monitor patient for
absorption(60%) signs and symptoms of
Peak: superinfection. CDAD
IV: Immediate can occur up to 2
Distribution: months after therapy
Distributed into ends.
milk
Metabolism: Not
metabolized in the
body
Elimination: Urine
and fecal
elimination
Half Life:
4-6hr
You might also like
- Unit-3 - Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics (BP604T)Document34 pagesUnit-3 - Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics (BP604T)Vìćķý PŕãbhâNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 RLE Case 2Document8 pagesNCM 105 RLE Case 2Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- HSN CodesDocument50 pagesHSN CodesManoj T PNo ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument1 pageVancomycinJUSTINE ALLYSA MAY CASTILLONo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Case StudyDocument7 pagesDrugstudy Case StudyHerwincayeNo ratings yet
- Doxorubicin: Mechanism of ActionDocument3 pagesDoxorubicin: Mechanism of ActionGeorge FogNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole 2018: Newborn Use OnlyDocument5 pagesOmeprazole 2018: Newborn Use OnlyHengky AntonNo ratings yet
- Case Study Medical WardDocument14 pagesCase Study Medical WardJoshNo ratings yet
- Stress TabsDocument2 pagesStress TabsPamela Joy PacanaNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting Nausea and VomitingDocument6 pagesNausea and Vomiting Nausea and VomitingTHERESA CLAIRE ENCINARESNo ratings yet
- Insulin As PartDocument3 pagesInsulin As PartRezaNo ratings yet
- Hyoscine-N-butylbromide (HNBB)Document1 pageHyoscine-N-butylbromide (HNBB)Kyle DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Fluphenazine Hydrochloride Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFluphenazine Hydrochloride Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJenny YenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Form TJDocument4 pagesDrug Study Form TJJasmin Santiago CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaDocument1 pageAripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaRHUBY ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaDocument5 pagesDrug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaMarie PotayreNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsDocument4 pagesConcept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsWendy Escalante0% (1)
- Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameDocument3 pagesDrug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIAdrugstudyDocument5 pagesPSYCHIAdrugstudyJss Rosete-De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- MultivitaminDocument1 pageMultivitaminAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studypopoyoio100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryKyla ToledoNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 (DUTY) - Risperidone Drug StudyDocument1 pageNCM 104 (DUTY) - Risperidone Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GlyburideDocument5 pagesDrug Study GlyburideSchyna Marielle VitaleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study.Document9 pagesDrug Study.Chelsea Therese GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- LidocaineDocument1 pageLidocaineRich LewisNo ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument2 pagesVancomycingchojn7338100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMelody Forca FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Apixaban 5 PDFDocument2 pagesApixaban 5 PDFWanie Al-basriNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Grand Case PresDocument8 pagesDrug Study-Grand Case PresLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument2 pagesOmeprazoleKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument1 pageAzithromycinGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolDocument3 pagesPedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolKuro HanabusaNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid Drug StudyDocument1 pageFolic Acid Drug Studysha rcNo ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone Inj. (IV)Document2 pagesHydrocortisone Inj. (IV)zepoli_zepoly6232No ratings yet
- Name of Drug: Ceftazidime Therapeutic Class: Pharmacologic Class: CephalosporinsDocument20 pagesName of Drug: Ceftazidime Therapeutic Class: Pharmacologic Class: CephalosporinsianNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Tablets (Chewable) : Tablets (Extended-Release)Document1 pageTablets: Tablets (Chewable) : Tablets (Extended-Release)Melissa Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- نسخة 264889196 Tramadol Drug StudyDocument1 pageنسخة 264889196 Tramadol Drug StudyMeteab AlzhiryNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageCeftriaxone Sodium Drug StudyMelissa Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- FDAR - Shortness of BreathDocument2 pagesFDAR - Shortness of BreathPRINCESS KOBAYASHINo ratings yet
- Myonal, LevoprontDocument1 pageMyonal, LevoprontMarieCrisNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyshiela marie cortezNo ratings yet
- Drug MetronidazoleDocument1 pageDrug MetronidazoleSrkocherNo ratings yet
- DS BiperidenDocument3 pagesDS BiperidenbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Ceftriaxone ClindamycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Ceftriaxone ClindamycinDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesLevofloxacinEliza Rahardja100% (1)
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetronidazole Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HeparinDocument2 pagesDrug Study HeparinJasmin T. RegaspiNo ratings yet
- GAT NCP Surgery WardDocument4 pagesGAT NCP Surgery WardDon Richard0% (1)
- Blood TransfucionDocument2 pagesBlood TransfucionShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Document2 pagesLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)ENo ratings yet
- Bearse Tablet InsertDocument2 pagesBearse Tablet InsertLeonard Byun100% (1)
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- LevofloxacinDocument3 pagesLevofloxacinLIEZEL GRACE VELAYO100% (1)
- Drug Study: Adult: Induction: 40 MGDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Adult: Induction: 40 MGpretty_mary100% (4)
- MEFENAMIC ACID (Edited)Document2 pagesMEFENAMIC ACID (Edited)Emagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Macrolide Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMacrolide Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Tetracycline Drug StudyDocument5 pagesTetracycline Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Tinidazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTinidazole Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Fluoroquinolone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFluoroquinolone Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Penicillin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPenicillin Drug StudyEmagra Azil100% (1)
- Pharmacology LogbookDocument4 pagesPharmacology LogbookMahmudul Hasan SazibNo ratings yet
- Formularium Rs Meta IndustriDocument36 pagesFormularium Rs Meta Industritiara dinantiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - CANCER FinalDocument18 pagesPharmacology - CANCER FinalCarol NavidadNo ratings yet
- Routes of Administration of Drugs: by Dr.P.Surekha Assistant Professor PharmacologyDocument40 pagesRoutes of Administration of Drugs: by Dr.P.Surekha Assistant Professor PharmacologyManglarapu SuryaNo ratings yet
- Cor-Aco-345 Adjuvant - Chemotherapy Order Form PDFDocument1 pageCor-Aco-345 Adjuvant - Chemotherapy Order Form PDFHosam MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy PracticeDocument4 pagesPharmacy PracticePrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- SERCDocument5 pagesSERCdipenhydramineNo ratings yet
- MD Anesthesiology - Plan of Thesis (Year 2016)Document5 pagesMD Anesthesiology - Plan of Thesis (Year 2016)Alan MendozaNo ratings yet
- E. Rodriguez Vocational High School: Department of Education Nagtahan, Sampaloc, ManilaDocument7 pagesE. Rodriguez Vocational High School: Department of Education Nagtahan, Sampaloc, ManilaJonar AbañoNo ratings yet
- CEP Health SectorDocument94 pagesCEP Health SectorJamila KapasiNo ratings yet
- Post Herpetic NeuralgiaDocument2 pagesPost Herpetic NeuralgiaTeuku ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- Acute Stress Disorder in Adults: Treatment Overview - UpToDateDocument14 pagesAcute Stress Disorder in Adults: Treatment Overview - UpToDateJoão VictorNo ratings yet
- Pain Control in The Critically Ill Adult PatientDocument72 pagesPain Control in The Critically Ill Adult PatientWalaa YousefNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HeparinDocument1 pageDrug Study HeparinAkiraMamoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Care: Qais AlefanDocument18 pagesPharmaceutical Care: Qais AlefanSaddamix AL OmariNo ratings yet
- Rumus & Dosis Obat AnakDocument1 pageRumus & Dosis Obat AnakMeky SuhendraNo ratings yet
- Formularium FinisingDocument7 pagesFormularium FinisingutamiNo ratings yet
- Vpap-IV Quick-Setup-Guide Row EngDocument2 pagesVpap-IV Quick-Setup-Guide Row EngHamada ElmahyNo ratings yet
- UltraMIST PatientBrochureDocument4 pagesUltraMIST PatientBrochureMarin ChianuNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy Versus Medication For Depression Challenging The Conventional Wisdom With DataDocument30 pagesPsychotherapy Versus Medication For Depression Challenging The Conventional Wisdom With DataMira BurovaNo ratings yet
- Indicatii Tot 3Document1 pageIndicatii Tot 3Andreea VrabieNo ratings yet
- TDM Pharmacy Practice ProjectDocument21 pagesTDM Pharmacy Practice ProjectTejpal singh100% (1)
- TDM Practical Guide Part1Document7 pagesTDM Practical Guide Part1Ahmedshaker21100% (1)
- Generic & Trade Name of Drug: Novolog Insulin, Novolog: Adult: SC 0.25-0.7 Units/kg/d Injected 5-10 Min Before Each MealDocument2 pagesGeneric & Trade Name of Drug: Novolog Insulin, Novolog: Adult: SC 0.25-0.7 Units/kg/d Injected 5-10 Min Before Each Mealjshcfdhsgfveugwd8iuNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumeSheng EsquilloNo ratings yet
- To Whome Soever It May ConcerDocument25 pagesTo Whome Soever It May ConcerRam MohanNo ratings yet
- Demonstration of Child HealthDocument5 pagesDemonstration of Child HealthAmy Lalringhluani100% (1)
- Amended Intravenous Unfractionated Heparin Recommended StandardDocument4 pagesAmended Intravenous Unfractionated Heparin Recommended StandardTOJO JOSEPH TOMNo ratings yet