0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 viewsTask 1 - Introduction To Electromagnetic Waves
Task 1 - Introduction To Electromagnetic Waves
Uploaded by
andreajamaica oreo1. Electromagnetic waves are produced by accelerated charges, such as an oscillating electric charge which creates oscillating electric and magnetic fields that propagate as waves.
2. Electromagnetic waves, including light, travel at the fixed speed of about 300,000 km/s in a vacuum.
3. The different types of electromagnetic waves are radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays which have various applications like communication, heating, imaging, and medical use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Task 1 - Introduction To Electromagnetic Waves
Task 1 - Introduction To Electromagnetic Waves
Uploaded by
andreajamaica oreo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views1 page1. Electromagnetic waves are produced by accelerated charges, such as an oscillating electric charge which creates oscillating electric and magnetic fields that propagate as waves.
2. Electromagnetic waves, including light, travel at the fixed speed of about 300,000 km/s in a vacuum.
3. The different types of electromagnetic waves are radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays which have various applications like communication, heating, imaging, and medical use.
Original Title
Task 1_Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
1. Electromagnetic waves are produced by accelerated charges, such as an oscillating electric charge which creates oscillating electric and magnetic fields that propagate as waves.
2. Electromagnetic waves, including light, travel at the fixed speed of about 300,000 km/s in a vacuum.
3. The different types of electromagnetic waves are radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays which have various applications like communication, heating, imaging, and medical use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views1 pageTask 1 - Introduction To Electromagnetic Waves
Task 1 - Introduction To Electromagnetic Waves
Uploaded by
andreajamaica oreo1. Electromagnetic waves are produced by accelerated charges, such as an oscillating electric charge which creates oscillating electric and magnetic fields that propagate as waves.
2. Electromagnetic waves, including light, travel at the fixed speed of about 300,000 km/s in a vacuum.
3. The different types of electromagnetic waves are radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays which have various applications like communication, heating, imaging, and medical use.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
OREO, ANDREA JAMAICA D.
FEBUARY 10, 2022
SCIENCE
1. How are electromagnetic waves produced?
Accelerated charges radiate electromagnetic waves. An oscillating charge is an example of an
accelerating charge. For example, consider a charge oscillating with some frequency. This produces an
oscillating electric field in space, which creates an oscillating magnetic field, which in turn, is a source of
the oscillating electric field, and so on. The oscillating electric and magnetic fields thus revive each other
as the wave propagates through space. Usually, the frequency of the electromagnetic wave and the
frequency of oscillation of the charge are equal.
2. How fast does an electromagnetic wave travel? How does it travel?
Light is an electromagnetic wave, and its speed is the speed of all forms of electromagnetic radiation.
That speed is 186,282 miles (299,792 km) per second in vacuum, slightly less in any material medium. It
depends on how the motion got started and what forces are acting. but for electromagnetic radiation, it
only has one speed - the speed of light - no matter what frequency or wavelength or intensity of the
radiation. Sound waves travel through air at the speed of approximately 1,100 feet per second; light
waves travel through air and empty space at a speed of approximately 186,000 miles per second.
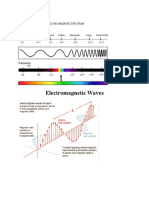
3. What are the different kinds of electromagnetic waves?
1. Radio waves: Communication
2. Microwaves: Heating and data transmission
3. Infrared waves: Used in remote control and imaging applications
4. Visible light: Help us see everything around us
5. Ultraviolet Waves: Useful in the study of galaxies
6. X-rays: Medical instruments to view bone structure
7. Gamma rays: Nuclear energy
4. Discuss the importance of frequency, wavelength, and energy in the study of electromagnetic waves?
Would this determine how safe are the electromagnetic waves? Explain.
The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is the range of all types of EM radiation. Radiation is energy that
travels and spreads out as it goes – the visible light that comes from a lamp in your house and the radio
waves that come from a radio station are two types of electromagnetic radiation. The other types of EM
radiation that make up the electromagnetic spectrum are microwaves, infrared light, ultraviolet light, X-
rays and gamma-rays.
You might also like
- Ss3 First Term Physics NoteDocument64 pagesSs3 First Term Physics NoteAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- Radio Communication Assignment 01Document79 pagesRadio Communication Assignment 01Amila Srimaal GamageNo ratings yet
- Investigation Project PhysicsDocument16 pagesInvestigation Project Physicskartikdutt.08No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic WavesHafid ZainulNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: Vina P. Hipolito Iv-Silvestre Assignment )Document7 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: Vina P. Hipolito Iv-Silvestre Assignment )VhinaP.HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: By: I Nyoman S. (X-8/09) Raka Pandam G. (X-8/21)Document11 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: By: I Nyoman S. (X-8/09) Raka Pandam G. (X-8/21)Nyoman SuryadinataNo ratings yet
- Christine Dianne C. Caisip Teacher IIIDocument82 pagesChristine Dianne C. Caisip Teacher IIIRyuji ReyesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic EnergyDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic EnergyJaisha NazNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electromagnetic WavesDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Electromagnetic WavesDharshana pjr100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument74 pagesElectromagnetic WavesJohnNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves Exploring The Invisible Spectrum 1Document10 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Exploring The Invisible Spectrum 1tsjeevanthanupillaiNo ratings yet
- Ec Seminar ReportDocument20 pagesEc Seminar ReportDevarajanRaghavan0% (1)
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumDenise Marie Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- C12-Electromagnetic WavesDocument74 pagesC12-Electromagnetic WavesGerald S. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Review!Document42 pagesReview!Marjorie Baya BidlanNo ratings yet
- Common Properties of Light Renzej - 20240309 - 201256 - 0000Document52 pagesCommon Properties of Light Renzej - 20240309 - 201256 - 0000Lidelyn Jane CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer QuizDocument4 pagesScience Reviewer Quiz28. Pinera, Yna Angela S.100% (1)
- History: Spectrum IsDocument23 pagesHistory: Spectrum IsMuhamad NurhudayahNo ratings yet
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDocument42 pagesSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- Review!Document42 pagesReview!Marjorie Baya BidlanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- ELECTROMAGNETICDocument48 pagesELECTROMAGNETICMichelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS 2 Lights and WavesDocument63 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 2 Lights and WavesalexandrearebucasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWShaku JoshiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAviation/Space History Library100% (4)
- Unidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)Document32 pagesUnidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)bemdasNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic WavesJahleel TroupeNo ratings yet
- GRADE10 - Electromagnetic - WavesDocument72 pagesGRADE10 - Electromagnetic - WavesyekcimhadjiamerNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves Regions of The EM WavesDocument73 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Regions of The EM WavesJR LubisNo ratings yet
- What Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarDocument18 pagesWhat Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarAndrei Cojanu100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument54 pagesElectromagnetic WavesPortia A. Egken100% (1)
- Grade 10 Reviewer ScienceDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Reviewer ScienceAntonette TabilNo ratings yet
- Homework Week 2bDocument6 pagesHomework Week 2bAlejandria SolisNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and OpticsDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Optics2244892No ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 2Document19 pagesGenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 2Jasmin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument2 pagesHeat TransferEmmanueNo ratings yet
- What Is The Electromagnetic Theor1Document10 pagesWhat Is The Electromagnetic Theor1gabezneNo ratings yet
- 1 - Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument5 pages1 - Electromagnetic Spectrumbinyang lalaNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1Document15 pagesScience Reviewer 1Symon MarianoNo ratings yet
- Waves Packet KEYDocument44 pagesWaves Packet KEYlauraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic WavesgnanaNo ratings yet
- AS Unit 2-Light and SoundDocument5 pagesAS Unit 2-Light and SoundAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument17 pages1.1 Electromagnetic SpectrumShreyas SvNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationEldsoky DabaNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument9 pagesScience ReviewerdomslangsakalamNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 2-Module 2 Electricity and MagnetismDocument81 pagesScience Quarter 2-Module 2 Electricity and MagnetismJazelle Kaye Azupardo100% (2)
- What Is Electromagnetic WaveDocument5 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetic WaveMico Angelo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves WSDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Waves WSSonny ArgolidaNo ratings yet
- Forms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumDocument6 pagesForms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumMicah TormonNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics2 Q2-Module-2 RemovedDocument17 pagesGenPhysics2 Q2-Module-2 RemovedJasmin SorianoNo ratings yet
- What Is Electro MegnaticDocument1 pageWhat Is Electro Megnaticzhungjian586No ratings yet
- Science Report Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument24 pagesScience Report Electromagnetic SpectrumJedí BelanoNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 1Document34 pagesQ2 Module 1renegadoaldronNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum - Sahana b1Document23 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum - Sahana b1Sarumathi ArunagiriNo ratings yet
- SS3 Ist Term PhysicsDocument52 pagesSS3 Ist Term Physicsojo ayodeji johnsonNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument50 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumMisty Vito100% (1)
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneFrom EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Electromagnetic Health: Making Sense of the Research and Practical Solutions for Electromagnetic Fields (EMF) and Radio Frequencies (RF)From EverandElectromagnetic Health: Making Sense of the Research and Practical Solutions for Electromagnetic Fields (EMF) and Radio Frequencies (RF)No ratings yet
- CL ThanksgivingDocument3 pagesCL Thanksgivingandreajamaica oreoNo ratings yet
- 2Q PoliticsAnddGovernanceAnswerDocument4 pages2Q PoliticsAnddGovernanceAnswerandreajamaica oreoNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Endocrine and Nervous SystemsDocument1 pageTask 3 - Endocrine and Nervous Systemsandreajamaica oreoNo ratings yet
- Synopsis ScriptDocument2 pagesSynopsis Scriptandreajamaica oreoNo ratings yet
- English ResearchDocument4 pagesEnglish Researchandreajamaica oreoNo ratings yet