0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 viewsMr. Sekar 1800032926 18025192:::::: Patient ID
Mr. Sekar 1800032926 18025192:::::: Patient ID
Uploaded by
lakshmisekar umapathyMr. SEKAR, age 60, had a fasting plasma glucose level of 194 mg/dL, above the normal range of 70-100 mg/dL and in the prediabetes range of 100-125 mg/dL. His HbA1c level was 8.5%, above the diabetic range of 6.5% or higher. His calculated mean blood glucose was 197 mg/dL. The test results indicate the patient has diabetes based on his HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose levels being above the cut-off points for diabetes. The report recommends HbA1c for monitoring diabetic control and discusses target HbA1c ranges for excellent, fair, unsatisfactory and poor control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Mr. Sekar 1800032926 18025192:::::: Patient ID
Mr. Sekar 1800032926 18025192:::::: Patient ID
Uploaded by
lakshmisekar umapathy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views1 pageMr. SEKAR, age 60, had a fasting plasma glucose level of 194 mg/dL, above the normal range of 70-100 mg/dL and in the prediabetes range of 100-125 mg/dL. His HbA1c level was 8.5%, above the diabetic range of 6.5% or higher. His calculated mean blood glucose was 197 mg/dL. The test results indicate the patient has diabetes based on his HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose levels being above the cut-off points for diabetes. The report recommends HbA1c for monitoring diabetic control and discusses target HbA1c ranges for excellent, fair, unsatisfactory and poor control.
Original Title
18025192-2022-12-10
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Mr. SEKAR, age 60, had a fasting plasma glucose level of 194 mg/dL, above the normal range of 70-100 mg/dL and in the prediabetes range of 100-125 mg/dL. His HbA1c level was 8.5%, above the diabetic range of 6.5% or higher. His calculated mean blood glucose was 197 mg/dL. The test results indicate the patient has diabetes based on his HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose levels being above the cut-off points for diabetes. The report recommends HbA1c for monitoring diabetic control and discusses target HbA1c ranges for excellent, fair, unsatisfactory and poor control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views1 pageMr. Sekar 1800032926 18025192:::::: Patient ID
Mr. Sekar 1800032926 18025192:::::: Patient ID
Uploaded by
lakshmisekar umapathyMr. SEKAR, age 60, had a fasting plasma glucose level of 194 mg/dL, above the normal range of 70-100 mg/dL and in the prediabetes range of 100-125 mg/dL. His HbA1c level was 8.5%, above the diabetic range of 6.5% or higher. His calculated mean blood glucose was 197 mg/dL. The test results indicate the patient has diabetes based on his HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose levels being above the cut-off points for diabetes. The report recommends HbA1c for monitoring diabetic control and discusses target HbA1c ranges for excellent, fair, unsatisfactory and poor control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
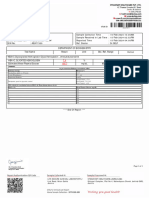
Patient : Mr.
SEKAR Patient ID : 1800032926
SID .No : 18025192 Age / Sex: 60 Y / Male
Referrer : Self
Reg Date/Time : 10/12/2022 07:29
Sample Collected Date/Time : 10/12/2022 08:26
Rpt Date/Time : 10/12/2022 11:37
Final Test Report Page # : 1 / 1
Parameter / Test Test Value / Report Biological Reference Interval
DEPARTMENT OF CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY
PLASMA GLUCOSE FASTING : 194 mg/dL Normal : 70- 100 mg/dl
( Method : Hexokinase) Impaired Fasting Glucose :100 mg/dl to 125
( Specimen: FLUORIDE PLASMA) mg/dl
Diabetes :126 mg/dl or higher
(American Diabetes Association Guidelines 2019)
HbA1C -Glycated Haemoglobin
HBA1C : 8.5 % Non-diabetic:<=5.6%
( Method :HPLC) Pre-diabetic:5.7-6.4%
( Specimen: EDTA BLOOD) Diabetic:>=6.5%
MEAN BLOOD GLUCOSE : 197 mg/dL
( Method :Calculated)
( Specimen: EDTA BLOOD)
Interpretation & Remark:
1. HbA1c is used for monitoring diabetic control. It reflects the Mean blood glucose .
2. HbA1c has been endorsed by clinical groups & ADA (American Diabetes Association) guidelines 2017, for diagnosis of diabetes using a cut-off point of 6.5%.
3. Interference of Haemoglobinopathies in HbA1c estimation.
A. For HbF > 25%, an alternate platform (Fructosamine) is recommended for testing of HbA1c.
B. Homozygous hemoglobinopathy is detected, fructosamine is recommended for monitoring diabetic status
C. Heterozygous state detected (D10/ turbo is corrected for HbS and HbC trait).
7. In known diabetic patients, following values can be considered as a tool for monitoring the glycemic control.
Excellent Control - 6 to 7 %, Fair to Good Control - 7 to 8 %, Unsatisfactory Control - 8 to 10 % and Poor Control - More than 10 % .
Discussed With
Dr. VINOD KUMAR PANICKER Dr.C.Vimala, M.D., (PATH)
M.D.,
Consultant Pathologist LAB DIRECTOR
End of Report
You might also like
- GNM Scientific ChartDocument172 pagesGNM Scientific Chartlisa90% (30)
- HBA1C Report - 25 Jan 23Document2 pagesHBA1C Report - 25 Jan 23Paranjoy DasNo ratings yet
- Neurology QuestionsDocument58 pagesNeurology QuestionsMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (2)
- Chanda Devi 48Document4 pagesChanda Devi 48molecularpathlab.raviNo ratings yet
- Chanda Devi-48 (1)Document2 pagesChanda Devi-48 (1)molecularpathlab.raviNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Komala Sukumaran 0800000333 08011267:::::: Patient IDDocument1 pageMrs. Komala Sukumaran 0800000333 08011267:::::: Patient IDFDHNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 120Document1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 120sanath kumarNo ratings yet
- Ms Rouza Bibi: InterpretationDocument11 pagesMs Rouza Bibi: InterpretationMrinal MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 000537582812Document6 pages000537582812Nevan SoNo ratings yet
- Mrs - Tayaba Farhat (48 Y/F) : Dilsukh NagarDocument2 pagesMrs - Tayaba Farhat (48 Y/F) : Dilsukh NagarMirza RehmanNo ratings yet
- 2020 01 10 PDFDocument2 pages2020 01 10 PDFMirza RehmanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 141Document6 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 141Ravichandran M.N.No ratings yet
- Efbu2630Document4 pagesEfbu2630Aniruddh NagaNo ratings yet
- Sathya VDocument2 pagesSathya VKrishna PrasathNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument2 pagesReportranjithento27No ratings yet
- Paresh CH Saha - HbA1cDocument2 pagesParesh CH Saha - HbA1cTanmoyNo ratings yet
- 592008000011: 59000720 03-Aug-20 08:49 AM: Mrs. Veena K Arora: 03-Aug-2020 08:49 AM: Dr. Self: 03-Aug-2020 12:47PM: 48 Y 06 M 12 D / F: 03-Aug-2020 01:12PMDocument2 pages592008000011: 59000720 03-Aug-20 08:49 AM: Mrs. Veena K Arora: 03-Aug-2020 08:49 AM: Dr. Self: 03-Aug-2020 12:47PM: 48 Y 06 M 12 D / F: 03-Aug-2020 01:12PMrajanarora72No ratings yet
- Fasting Blood GlucoseDocument7 pagesFasting Blood GlucosegoddeyNo ratings yet
- PDF TextDocument2 pagesPDF TextAmit PathakNo ratings yet
- Hba1 w Mrs.v.sita LakshmiDocument1 pageHba1 w Mrs.v.sita Lakshmidivya anithaNo ratings yet
- 1 Diabetes Screening PO4047576719 696Document4 pages1 Diabetes Screening PO4047576719 696rishiranjan04No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-06-08 at 12.08.40 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2022-06-08 at 12.08.40 PMashutosh ambeyNo ratings yet
- Gobardhan Banik-65Document1 pageGobardhan Banik-65Sanjoy DasNo ratings yet
- Raj RaniDocument12 pagesRaj RaniManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Mpix4185Document3 pagesMpix4185sairam4u99No ratings yet
- P.Ram Babu:::: Patient Age / Sex 41 Y / Male BranchDocument8 pagesP.Ram Babu:::: Patient Age / Sex 41 Y / Male BranchLoke RajpavanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 102Document3 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucose: 102Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Male 36 YearsDocument1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Male 36 YearsMeherNo ratings yet
- Yakkala Sandeep: 28 Y / Male: Dr. Doctor: Jayanagar - HubDocument5 pagesYakkala Sandeep: 28 Y / Male: Dr. Doctor: Jayanagar - HubY.v. SandeepNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: 19 Years / FemaleDocument3 pagesLaboratory Test Report: 19 Years / Femalesneha sahaNo ratings yet
- Karamjit KaurDocument12 pagesKaramjit KaurManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab Report NewDocument12 pagesLab Report NewpropertyyaarNo ratings yet
- LabReportNew - 2024-02-19T163907.126Document1 pageLabReportNew - 2024-02-19T163907.126anil KumarNo ratings yet
- PDF TextDocument12 pagesPDF TextPratham BhopatraoNo ratings yet
- VEENADocument4 pagesVEENAveenaraneeNo ratings yet
- R2286929 Shiva Kumar D K 080524135944Document10 pagesR2286929 Shiva Kumar D K 080524135944Yashaswini SNo ratings yet
- Mrs - Lalita SharmaDocument8 pagesMrs - Lalita SharmaManju JaswalNo ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269Document6 pages1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269KishoreNo ratings yet
- Blood TestDocument2 pagesBlood TestAll You NeedNo ratings yet
- Paresh Chandra SahaDocument14 pagesParesh Chandra SahaTanmoyNo ratings yet
- WVVP0662Document1 pageWVVP0662Khaleel ShaikNo ratings yet
- O P MalikDocument10 pagesO P MalikGarima MalikNo ratings yet
- Hba1C Study: 51 Years /femaleDocument4 pagesHba1C Study: 51 Years /femalesangani.gayatriNo ratings yet
- Hba1C %Document10 pagesHba1C %Jatinder Singh (Sugar sales/HO)No ratings yet
- Mr. Sanjay Sakolkar 19102024 052724 PMDocument11 pagesMr. Sanjay Sakolkar 19102024 052724 PMjagdishapsingekarNo ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Screening - PO3210290160-291Document4 pages1-Diabetes Screening - PO3210290160-291Jawed IqubalNo ratings yet
- Report of Mr. Amresh Kshirsagar PDFDocument4 pagesReport of Mr. Amresh Kshirsagar PDFSanket KathareNo ratings yet
- EGAC0401Document5 pagesEGAC0401bhanuprasadbkNo ratings yet
- Usjl2707Document2 pagesUsjl2707Ashvik AnumakondaNo ratings yet
- Shaharyar Ansari: Report Status: FinalDocument3 pagesShaharyar Ansari: Report Status: FinalAutonomous Alfa100% (1)
- Lipid Profile Oct 2019Document2 pagesLipid Profile Oct 2019PremNo ratings yet
- Mrs Neetu - ReportDocument14 pagesMrs Neetu - Reportyatan kapoorNo ratings yet
- PdfText (13)Document12 pagesPdfText (13)sandeepsambyal1239No ratings yet
- Annie George - 6773346119 - V2Document14 pagesAnnie George - 6773346119 - V2masterdoctor.clinicNo ratings yet
- Lab Report NeDocument4 pagesLab Report NePriyanka MahajanNo ratings yet
- Report GNDocument3 pagesReport GNPawan MadhesiyaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-09 at 5.41.51 PMDocument2 pagesScreenshot 2023-12-09 at 5.41.51 PManupkudubeyNo ratings yet
- Sakthirubni:::: Patient Age / Sex 35 Y / Female BranchDocument8 pagesSakthirubni:::: Patient Age / Sex 35 Y / Female BranchRaja DuraiNo ratings yet
- Anu Basodia ReportsDocument12 pagesAnu Basodia ReportsAkshat SachdevaNo ratings yet
- 102 MR Rajesh Kumar Nanavati: BiochemistryDocument2 pages102 MR Rajesh Kumar Nanavati: BiochemistryRajesh NanavatiNo ratings yet
- VijayDocument14 pagesVijayKumar VijayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 9Document34 pagesLesson 8 9genotaalliahloraine.mendelNo ratings yet
- Legal Module 1 AssignDocument4 pagesLegal Module 1 AssignSusan Loida SorianoNo ratings yet
- B Inggris Widya Tirta DewiDocument4 pagesB Inggris Widya Tirta Dewiwidya tirtaNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - NCM 108 - Activity - Report - Personalized SexualityDocument7 pagesWeek 13 - NCM 108 - Activity - Report - Personalized SexualityMaria Rhesilyn Kristhel MoranoNo ratings yet
- MAPEH-10 Q1 Summative Test2Document2 pagesMAPEH-10 Q1 Summative Test2Rhodora R. Del Rosario100% (2)
- DIC - Case Study (Blood 2)Document2 pagesDIC - Case Study (Blood 2)Aen BridgetteNo ratings yet
- CH 4-Strategy-and-Balanced-ScorecardDocument52 pagesCH 4-Strategy-and-Balanced-ScorecardCOVID RSHJNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Diabetes MelitusDocument7 pagesJurnal Diabetes MelitusNova RosalinaNo ratings yet
- Science Competencies For Grade 1Document5 pagesScience Competencies For Grade 1KAT DANTESNo ratings yet
- Ambient Air Quality and Lung Function of Children in DelhiDocument229 pagesAmbient Air Quality and Lung Function of Children in DelhiSachin WazalwarNo ratings yet
- Journal PediaDocument2 pagesJournal PediapeteiroNo ratings yet
- Ecfmg: Certification Fact SheetDocument4 pagesEcfmg: Certification Fact SheetJennifer NajemNo ratings yet
- Spikes PDFDocument11 pagesSpikes PDFMatsrialNo ratings yet
- Homework Should Not Banned DebateDocument8 pagesHomework Should Not Banned Debateafmroaceo100% (1)
- Peter Kathuki Concept PaperDocument10 pagesPeter Kathuki Concept PaperElias KumeloNo ratings yet
- Hygiene Exam Questions 2021-22Document32 pagesHygiene Exam Questions 2021-22Fatemeh Eshaghizadeh0% (2)
- Update: Diagnostic Statistical Manual Mental DisordersDocument30 pagesUpdate: Diagnostic Statistical Manual Mental DisordersFebelin Idjie ElsaMomNo ratings yet
- Practices During Labour and Delivery (Recommended & Not Recommended)Document4 pagesPractices During Labour and Delivery (Recommended & Not Recommended)Gwyneth Nicole Buday100% (1)
- Procedural Skills (Awasir)Document34 pagesProcedural Skills (Awasir)Yousef TaqatqehNo ratings yet
- JSSWH - Volume 53 - Issue 2 - Pages 295-334Document40 pagesJSSWH - Volume 53 - Issue 2 - Pages 295-334Ab AbdelmalikNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH-WPS Health-And-HospitalDocument9 pagesMAKALAH-WPS Health-And-HospitalM Rynaldy Al-HarpyNo ratings yet
- 6.4.2024 - Reading Passage 3Document4 pages6.4.2024 - Reading Passage 3thesolieltsNo ratings yet
- Cetamine G830 (GB-ENG)Document11 pagesCetamine G830 (GB-ENG)danielNo ratings yet
- MCN Drill 1Document23 pagesMCN Drill 1Cai Velasco DecenaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 6 - JimDocument1 pageCase Study 6 - Jimginabobina3337238No ratings yet
- HI 7th Ed V1.2 CombinedDocument342 pagesHI 7th Ed V1.2 CombinedXuaN XuanNo ratings yet
- 24qimkzbj - QUALITIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES-BIOETHICSDocument5 pages24qimkzbj - QUALITIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES-BIOETHICSEvelyn Medina0% (1)
- MDR ChecklistDocument6 pagesMDR ChecklistGretchen UptonNo ratings yet