Rohini 69771659590
Rohini 69771659590
Uploaded by
simman8371029Copyright:
Available Formats
Rohini 69771659590
Rohini 69771659590
Uploaded by
simman8371029Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Rohini 69771659590
Rohini 69771659590
Uploaded by
simman8371029Copyright:
Available Formats
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
1.2 ARCHITECTURE OF INTEL 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
Features of 8085
Intel 8085 is an 8-bit, NMOS microprocessor.
It is a 40 pin I.C. package fabricated on a single LSI chip.
The Intel 8085 uses a single +5Vd.c. supply for its operation
Its clock speed is about 3 MHz
The clock cycle is of 320 ns.
It has 80 basic instructions and 256 opcodes.
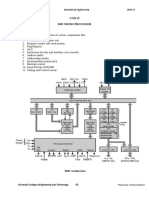
Figure 1.2.1 shows the functional block diagram of Intel 8085. It consists of three main
sections:
[1] Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
[2] Timing & Control Unit
[3] Set of registers.
Figure 1.2.1 Architecture 8085 processor
[Source: “Microprocessor Architecture Programming and Application” by R.S. Gaonkar, page-72]
EE8551 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
1. ALU (Arithmetic & Logic Unit):
As the name suggest, ALU i.e arithmetic & logic unit performs the following
arithmetic & logical opeartions:
i. Addition
ii. Subtraction
iii. Logical AND
iv. Logical OR
v. Logical EXCLUSIVE OR
vi. Complement (logical NOT)
vii. Increment (add 1)
viii. Decrement (Subtract 1)
ix. Left shift, Rotate left, Rorate Right
x. Cler, etc.
2. Timing & Control Unit:
It generates timing & control signals which are necessary for the execution of
instructions.
It controls data flow between CPU and peripherals including memory.
It provides status, control and timing signals which are required for the operation
of memory and I/O devices.
It controls entire operations of the microprocessor and peripherals connected to it.
Thus it is seen that the control unit of the CPU acts as the brain of the computer
system.
3. Set of Registers:
Fig 1.2.1 shows the various registers of Intel 8085 which are used by the
microprocessor for temporary storage and manipulation of data and intsructions.
Intel 8085 microprocessor has the following registers:
i. One 8-bit Accumulator (ACC) i.e register A
ii. Six 8-bit general purpose registers. These are B, C, D, E, H & L
iii. One 16-bit stack pointer, SP
iv. One 16-bit program Counter, PC
EE8551 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
v. Intruction register
vi. Temporary register
In addition to the above mentioned regiter the 8085 microprocessor contains a set
of five flipflops which serve as flag (or status flags). A flag is a flipflop which
indicates some condition which arises after execution of an arithmetic or logical
instruction.
Accumulator:
The accumulator (register A) is an 8-bit register associated with ALU.
It is used to hold one of the operands of an arithmetic or logical operation.
It serves as one input to the ALU. The other operand for an arithmetic or logical
opeartion may be stored either in the memroy or in one of the general purpose
registers.
Final result of an arithmetic or logical operation is placed in the accumulator.
General Purpose Registers
The 8085 microprocessor contains six 8-bit general purpose registers. They are B,
C, D, E, H and L.
To hold 16-bit data a combination of two 8-bit registers can be employed which
known as register pairs.
The valid register pairs in 8051 are B-C, D-E and H-L. the programmer cannot
form the register pair by selecting any two registers of his choice.
The H-L pair is used to act as memory pointer and for this purpose it holds the 16-
bit address of a memory location.
The general purpose registers and the accumulator are accessible to programmer.
He can store data in these registers during writing his program.
Program Counter (PC):
It is a 16-bit special purpose register used to hold the memory address of the next
instruction which is to be executed.
It keeps the track of memory addresses of the instructions in the program while
they are being executed.
EE8551 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
The microprocessor increments the content of the program counter during the
execution of an instruction so that it points to the address of the next instruction in
the program at the end of the execution of an instruction.
Stack Pointer (SP):
It is a 16-bit special purpose register.
“Stack is a sequence of memory location set aside by the programmer to
store/retrieve the content of accumulator, flags, program counter and general
purpose registers during the execution of a program.
Any portion of the memory can be used as stack. Since the stack works on LIFO
(last in first out) principle, its operation is faster compared normal store/ retrieve
of memory locations.
“The SP holds the address of the top element of data stored in the stack.
“The stack is defined and stack pointer is initialized by the programmer at the
beginning of a program which needs stack operation. Stack is also used by the
microprocessor. For example, it stores the contents of program counter when it
jumps to a subroutine using CALL instruction.
Instruction Register:
The instruction register holds the opcode (operation code or instruction code) of
the instruction which is being decoded and executed.
Temporary Register:
It is an 8-bit register associated with ALU. It holds data during an
arithmetic/logical operation.
It is used by microprocessor.
It is not accessible to programmer.
Flags (Program Status Word i.e. PSW):
The Intel 8085 microprocessor contains five flip-flops to serve as status flags.
The flip-flops are set or reset according to the conditions which arises during an
arithmetic or logical operation.
The five status flags of Intel 8085 are:
i. Carry flag (CS)
EE8551 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
ii. Parity Flag (P)
iii. Auxiliary Carry Flag (AC)
iv. Zero Flag (Z)
v. Sign Flag (S)
In fig 1.2.2, five bits indicates the five status flags and three bits are undefined.
“The combination of these 8-bits is called Program Status Word (PSW)”. PSW and
the accumulator are treated as a 16-bit unit for stack operation.
Figure 1.2.2 Flag Register
[Source: “Microprocessor Architecture Programming and Application” by R.S. Gaonkar, page-72]
Carry Flag (CS):
After execution of an arithmetic instruction if carry is produced, the carry flag CS
is set to 1. Otherwise it is 0.
The carry flag is set or reset in case of addition as well as subtraction.
After the addition of two 8-bit numbers, if the sum is larger than 8-bits, a carry is
produce; and the carry flag is set to 1.
In case of subtraction, if borrow occurs, the carry flag is set to 1.
The carry flag holds carry out of the most significant bit resulting from the
execution of an arithmetic operation.
Parity Flag (P):
The parity flag P is set to 1, if the result of an arithmetic or logical operation
contains even number of 1s.
It is reset i.e it is 0, if the result contains odd number of 1s.
EE8551 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Auxiliary Carry Flag (AC):
The auxiliary carry flag AC hold carry out of the bit number 3 to the bit number 4
resulting from the execution of an arithmetic operation.
The counting of bits starts from 0, and hence Bit No.3 is actually the fourth bit
from the least significant bit.
Zero Flag (Z):
The zero status flag Z is set to 1, if the result of an arithmetic or logical operation
is Zero otherwise it is set to 0.
Sign Flag (S):
The sign flag S is set to 1, if the result of an arithmetic or logical operation is
negative. If the result is positive, the sign flag is set to 0.
The sign flag has significance only when signed arithmetic operation is performed.
To represent a signed numbed the most significant bit is reserved by the
programmer to represent the sign of a number.
In other words, the MSB is used as a sign bit.
If the number is negative, the sign bit is 1. For positive, sign bit is 0.
In case of 8-bit sign operation, the remaining 7 bits are used to represent the
magnitude of a number.
Data and Address bus:
The Intel 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor. Its data bus is 8-bit wide and hence, 8bit
of data can be transmitted in parallel from or to the microprocessor.
The Intel 8085 requires a 16-bit wide address bus as the memory addresses are of
16 bits.
The 8 most significant bits of the address are transmitted by the address bus, a-bus
(pins A8 to A15).
The least significant bits of address are transmitted by address/ data bus, AD-bus
(pins AD0 to AD7).
The address/ data bus transmits data and address at different moments. At a
particular moment it transmits either data or address. Thus AD-bus operates in time
shared mode.
EE8551 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
This technique is known as multiplexing. First all 16-bit memory address is
transmitted by the microprocessor; the 8 MSBs of the address on A-bus and the 8
LSBs of the address on AD- bus. Thus effective width of address bus becomes 16
bit wide.
EE8551 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
You might also like
- Intel 8085 ArchitectureDocument8 pagesIntel 8085 ArchitectureAravind VJNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document12 pagesUnit 1Pallavi MNo ratings yet
- MP UNIT 1&2 - ClassDocument63 pagesMP UNIT 1&2 - Classaarav.a211123No ratings yet
- COA - Summer-2024 SolutionDocument26 pagesCOA - Summer-2024 Solutionzayoxop666No ratings yet
- W3 Microprocessor Architecture Module 3Document15 pagesW3 Microprocessor Architecture Module 3Aaron BasNo ratings yet
- Mpi Assignment Solution1Document15 pagesMpi Assignment Solution1alkesh.eng0% (1)
- 8085 Microprocessor - Block DiagramDocument5 pages8085 Microprocessor - Block DiagramShreyash ShindeNo ratings yet
- 1 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument7 pages1 8085 Microprocessor Architecturejosrichman75No ratings yet
- Sec 1323Document118 pagesSec 1323vkyashraj20No ratings yet
- Important Question Solutions of 8085 - ComputerSCDocument59 pagesImportant Question Solutions of 8085 - ComputerSCParamartha BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 8085 Important Short Questions (Part-1)Document11 pages8085 Important Short Questions (Part-1)Ln Amitav BiswasNo ratings yet
- CE 5 Sem QPDocument35 pagesCE 5 Sem QPJCT DesigningNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085Document58 pagesIntel 8085Ayoade Akintayo MichaelNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085 8-Bit MicroprocessorDocument58 pagesIntel 8085 8-Bit MicroprocessorMOHSIN BHATNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors Architecture NotesDocument18 pagesMicroprocessors Architecture Notesenockkibet800No ratings yet
- L-3 8 Bits MicroprocessorDocument12 pagesL-3 8 Bits Microprocessormuhamed.abdelhamid16No ratings yet
- Intel 8085Document6 pagesIntel 8085Prakhar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Mechatronics: Post Graduate CollegeDocument36 pagesMechatronics Mechatronics: Post Graduate CollegeAhmed Khalid MudawiNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085Document58 pagesIntel 8085michaeledem_royalNo ratings yet
- 8085Document47 pages8085Govind GuptaNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085 8-Bit MicroprocessorDocument8 pagesIntel 8085 8-Bit Microprocessordelkatty1No ratings yet
- Question: Describe The 8085 Programming Model in Detail. Answer: Following Is The Answer To The Above QuestionDocument9 pagesQuestion: Describe The 8085 Programming Model in Detail. Answer: Following Is The Answer To The Above QuestionSidh SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 ActivityDocument19 pagesUnit 2 ActivityRiza Pahama Mananaong100% (1)
- Architecture Diagram of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument4 pagesArchitecture Diagram of 8085 MicroprocessorbhatiaharryjassiNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument25 pages8085 Microprocessorprofessor2062No ratings yet
- FMM Unit-1Document28 pagesFMM Unit-1CS ENo ratings yet
- Unit - II Microprocessors-and-Microcontrollers - CompressedDocument22 pagesUnit - II Microprocessors-and-Microcontrollers - CompressedVishalNo ratings yet
- 8085 ArchitectureDocument30 pages8085 ArchitecturegokulchandruNo ratings yet
- Exp - 1Document7 pagesExp - 1rk5336222No ratings yet
- Ref Manual Microprocessor - Microcontroller by Krishna GaihreDocument91 pagesRef Manual Microprocessor - Microcontroller by Krishna GaihreEr SarbeshNo ratings yet
- MP & MC Micro Doc-20240520-Wa0000Document82 pagesMP & MC Micro Doc-20240520-Wa0000Deba Comedy ClubNo ratings yet
- MPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-3 13052022115048AMDocument15 pagesMPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-3 13052022115048AMmailsender787No ratings yet
- Eec Practical 8085 MicroprocessorDocument8 pagesEec Practical 8085 MicroprocessorinxludezNo ratings yet
- Unit I Microprocessor NotesDocument15 pagesUnit I Microprocessor NotesSaritha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers 1 37Document37 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers 1 37pothulanandini3No ratings yet
- FMPMC Unit 1Document48 pagesFMPMC Unit 1bhawanabaliwada2103No ratings yet
- MPMC - Unit 1 - 8085 ArchitectureDocument17 pagesMPMC - Unit 1 - 8085 ArchitectureWickNo ratings yet
- Ee6502 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument97 pagesEe6502 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersAnbalagan Guru0% (1)
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument10 pages8085 MicroprocessorgravitoniteNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorsDocument11 pagesMicroprocessors158 AshleshaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2Rajasekaran RNo ratings yet
- MechantronicsDocument11 pagesMechantronicsrajasree Marine Engg-Asst ProfNo ratings yet
- MCT Unit 2Document26 pagesMCT Unit 2Aravind RajNo ratings yet
- Micrprocessor Notes 2023Document18 pagesMicrprocessor Notes 2023GautamNo ratings yet
- MPMC Assignment-1Document7 pagesMPMC Assignment-113Panya CSE2No ratings yet
- Organization of 8085 (Part 1)Document7 pagesOrganization of 8085 (Part 1)Sarvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor June29Document9 pages8085 Microprocessor June29Mworozi DicksonNo ratings yet
- Registers of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument5 pagesRegisters of 8085 Microprocessorezekiel nyamuNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8085 ArchitectureDocument19 pagesMicroprocessor 8085 ArchitectureSindhujaSindhuNo ratings yet
- MAP Notes - CHapter 1Document5 pagesMAP Notes - CHapter 1Ubaid Saudagar100% (1)
- Computer Organization Architecture and Assembly Language File/8085 FileDocument32 pagesComputer Organization Architecture and Assembly Language File/8085 FileGarimaNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085Document80 pagesIntel 8085vsalaiselvamNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of 8085.Pptx1ENDDocument32 pagesBlock Diagram of 8085.Pptx1ENDAisha SarinNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085Document10 pagesIntel 8085venkatesh.mNo ratings yet
- EE6502 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers 16 MARK QA 1Document36 pagesEE6502 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers 16 MARK QA 1umramanNo ratings yet
- Blockdiagramof 8085Document40 pagesBlockdiagramof 8085Akhil NameirakpamNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument38 pages8085 Microprocessor Architectureashley panganNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor - 8085 ArchitectureAlok AnkitNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8085 Architecture - TutorialspointDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor - 8085 Architecture - TutorialspointProsenjit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- CAT-I Markstatement 2022-23 EVEN II EEEDocument2 pagesCAT-I Markstatement 2022-23 EVEN II EEEsimman8371029No ratings yet
- II Eee Name ListDocument2 pagesII Eee Name Listsimman8371029No ratings yet
- Cat-I QPDocument3 pagesCat-I QPsimman8371029No ratings yet
- Internal SeminarDocument2 pagesInternal Seminarsimman8371029No ratings yet
- Alteon TechSpec-v19Document3 pagesAlteon TechSpec-v19pabloNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ram Meghe Institute of Technology & Research, Badnera Amravati Department of Electronics & Telecommunication EnggDocument6 pagesProf. Ram Meghe Institute of Technology & Research, Badnera Amravati Department of Electronics & Telecommunication EnggvishalNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting I C Bus Protocol: Application ReportDocument10 pagesTroubleshooting I C Bus Protocol: Application ReportAbhishek BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Logic FamiliesDocument18 pagesLogic FamiliesHiiiNo ratings yet
- s7-200 SMART System Manual en-USDocument866 pagess7-200 SMART System Manual en-USvăn nguyễn100% (1)
- Kenwood DPX 5010Document37 pagesKenwood DPX 5010crishanNo ratings yet
- Number System and CodesDocument5 pagesNumber System and CodesPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Combinational Logic Circuits: Dr. C. Saritha Lecturer in Electronics SSBN Degree and PG College AnantapurDocument23 pagesCombinational Logic Circuits: Dr. C. Saritha Lecturer in Electronics SSBN Degree and PG College AnantapurerdvkNo ratings yet
- Rda5856te C95544Document17 pagesRda5856te C95544Monu DograNo ratings yet
- TMS320F2812-Flash ProgrammingDocument22 pagesTMS320F2812-Flash ProgrammingPantech ProLabs India Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- PIC10F320Document193 pagesPIC10F320Fernando Contreras AtuestaNo ratings yet
- Diocese of Baguio Schools High School Department Poblacion, La Trinidad, 2601 Benguet PhilippinesDocument6 pagesDiocese of Baguio Schools High School Department Poblacion, La Trinidad, 2601 Benguet PhilippinesSheiree CampanaNo ratings yet
- Frequently and Non Frequently Configurable Devices Applications of Reconfigurable DevicesDocument14 pagesFrequently and Non Frequently Configurable Devices Applications of Reconfigurable Devicesसुधांशु जनवाड़करNo ratings yet
- Control HazardsDocument19 pagesControl HazardsKRISHNA KUMAR MANCHALANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 4 PDFmitiku tolasaNo ratings yet
- Esamcb51 UmDocument28 pagesEsamcb51 Umtallurips91No ratings yet
- Micro MCQ Unit 4,5Document20 pagesMicro MCQ Unit 4,5Abhijit KumarNo ratings yet
- Dxdiag LumionDocument43 pagesDxdiag Lumionmegha guptaNo ratings yet
- 01introduction VLSI TechnologyDocument32 pages01introduction VLSI Technologyanand kumarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Automation - Prodotti & Configurazioni: Sistema Base Ht700-1Document2 pagesIndustrial Automation - Prodotti & Configurazioni: Sistema Base Ht700-1marcelloNo ratings yet
- Switch LevelDocument19 pagesSwitch LevelDayanand Gowda KrNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Anna University Important Questions 2 Marks and 16 Marks Questions - Repeated Questions in Anna University Question Papers From All 5 Units ...Document4 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers Anna University Important Questions 2 Marks and 16 Marks Questions - Repeated Questions in Anna University Question Papers From All 5 Units ...PrettyNo ratings yet
- 05 Engineering Electrical and Electronics January 2017Document100 pages05 Engineering Electrical and Electronics January 2017陳建亨100% (1)
- 239716035Document25 pages239716035sontuyet82No ratings yet
- Compiled Topical P-4Document470 pagesCompiled Topical P-4Muhammad Hamza ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Heidenhain Ik 121v ManualDocument116 pagesHeidenhain Ik 121v ManualmasinemaNo ratings yet
- Tanner IntroductionDocument15 pagesTanner IntroductionmohanrajNo ratings yet
- M48T02 150pciDocument15 pagesM48T02 150pciImran YaminNo ratings yet
- DE1-SoC User Manual v.1.2.2Document114 pagesDE1-SoC User Manual v.1.2.2wesley_azevedo_1No ratings yet