Allergic Contact Dermatitis To Clostridiopeptidase A With A Nummular Eczema-Like Spread
Allergic Contact Dermatitis To Clostridiopeptidase A With A Nummular Eczema-Like Spread
Uploaded by
RickyCopyright:
Available Formats
Allergic Contact Dermatitis To Clostridiopeptidase A With A Nummular Eczema-Like Spread
Allergic Contact Dermatitis To Clostridiopeptidase A With A Nummular Eczema-Like Spread
Uploaded by
RickyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Allergic Contact Dermatitis To Clostridiopeptidase A With A Nummular Eczema-Like Spread
Allergic Contact Dermatitis To Clostridiopeptidase A With A Nummular Eczema-Like Spread
Uploaded by
RickyCopyright:
Available Formats
122 FOTI ET AL.
Allergic contact dermatitis to clostridiopeptidase A
with a nummular eczema-like spread
Caterina Foti | Gianluca Calianno | Silvia Mazzotta | Fabrizio Guarneri |
Paolo Romita
1
Department of Biomedical Science and Human Oncology, Dermatological Clinic, University of Bari, Bari, Italy
2
Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, University of Messina, Messina, Italy
Correspondence
Professor Caterina Foti, Unit of Dermatology, Department of Biomedical Science and Human Oncology, University of Bari, Policlinico, Piazza Giulio Cesare,
11 I-70124 Bari, Italy.
Email: caterina.foti@uniba.it
K E Y W O R D S : allergic contact dermatitis, case report, chloramphenicol, clostridiopeptidase A, collagenase I, leg ulcers, nummular eczema
Topical medications used for the treatment of venous leg ulcers are a
well-known cause of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).1 Among these, topi-
cal drugs containing proteolytic enzymes (used for wound debridement)
are rarely involved.2,3 We herein report a case of severe ACD caused by
clostridiopeptidase A, also known as collagenase I.
CASE REPORT
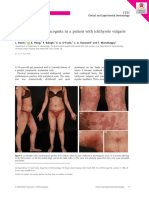
A nonatopic 64-year-old woman presented to our attention for the onset
of a diffuse crusted eczematous dermatitis with nummular aspects
(Figure 1). The patient reported that the eruption had started to appear
about 2 weeks after the application of a topical ointment containing chlor-
amphenicol 1% and clostridiopeptidase A 60 U.I. (Iruxol, Smith & Nephew
GmbH, Hamburg, Germany) under occlusion with a zinc oxide bandage,
prescribed by her physician to treat a venous ulcer on her left leg. The skin
lesions appeared around the leg ulcer and then spread within 3 weeks to
both lower limbs, the upper limbs, and trunk, with nummular eczema-like
aspects. Her physician already prescribed oral therapy with amoxicillin–
clavulanate (875 + 125 mg twice daily) for 6 days; however, there was no
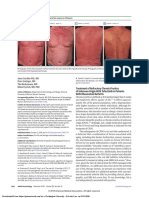
improvement of the skin lesions. Use of the topical ointment was immedi- F I G U R E 1 (A) Eczematous lesions around the leg ulcer and (B)
ately discontinued, and topical application of mometasone furoate once nummular eczema-like spreading; (C) positive patch test to Noruxol
“as is” on day 4
daily resulted in healing of the eczematous lesions in 2 weeks. Four weeks
after the resolution of the dermatitis, patch tests were performed with the paraffin, and white petrolatum; Smith & Nephew GmbH, Hamburg,
SIDAPA (Società Italiana di Dermatologia Allergologica Professionale e Germany), liquid paraffin, and white petrolatum, yielding positivity
Ambientale) baseline series (FIRMADiagent, Florence, Italy), a piece of the only to Noruxol (++; Figure 1). Based on these findings, we diag-
zinc oxide bandage, and the ointment used by the patient. Patch nosed ACD to clostridiopeptidase A. Ten healthy individuals were
tests were applied on the back and left under occlusion for 2 days patch tested with Iruxol and Noruxol with negative results.
with Haye's Test Chambers (Haye's Service B.V., Alphen aan den
Rijn, The Netherlands) on Soffix tape (Artsana, Grandate, Italy).
Readings were performed on day (D) 2 and D4 according to DI SCU SSION
guidelines,4 and showed a positive reaction to para-
phenylenediamine (++, past relevance) and Iruxol ointment (++). ACD caused by topical medications is a well-known, but probably
Subsequently, patch tests were performed with chloramphenicol underestimated and misdiagnosed complication.5 We herein reported
5% pet. and Noruxol (containing clostridiopeptidase A, liquid a case of severe ACD caused by clostridiopeptidase A, a proteolytic
FAYBUSOVICH ET AL. 123
enzyme widely used in wound and ulcer care. While chloramphenicol OR CID
is a well-known sensitizer,6 clostridiopeptidase A has rarely been Caterina Foti https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6196-9788
2,3
reported as the culprit of ACD. Nummular eczema is usually a mani- Fabrizio Guarneri https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0805-8496
festation of atopic dermatitis, but contact allergy has also been dem- Paolo Romita https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5559-9722
onstrated to be associated with nummular eczema-like aspects.7
To our knowledge, this is the first case of ACD to clostridiopeptidase RE FE RE NCE S
A with a nummular eczema-like spread. 1. Raudonis T, Vankeviciute RA, Lideikaite A, Grigaityte AG, Grigaitiene J.
We speculate that the application of the medication under occlusion Contact sensitization in patients with chronic leg ulcers: results of a 5-year
retrospective analysis. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2019;32(12):558-562.
could have favoured contact sensitization and lymphatic and/or hematoge-
2. Foti C, Conserva A, Casulli C, Scrimieri V, Pepe ML, Quaranta D. Con-
nous dissemination, which are proposed mechanisms for ACD spreading.8 tact dermatitis with clostridiopeptidase a contained in Noruxol oint-
Beyond the peculiar clinical manifestations, our case highlights that con- ment. Contact Dermatitis. 2007;56(6):361-362.
tact sensitization to topical medications containing clostridiopeptidase A, 3. Lisi P, Brunelli L. Extensive allergic contact dermatitis from a topical enzy-
matic preparation (Noruxol). Contact Dermatitis. 2001;45(3):186-187.
although rare, should be always borne in mind by physicians.
4. Stingeni L, Bianchi L, Hansel K, et al. Italian guidelines in patch testing -
adapted from the European Society of Contact Dermatitis (ESCD). G
ACKNOWLEDGEMEN TS Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2019;154(3):227-253.
Open Access Funding provided by Universita degli Studi di Bari Aldo Moro 5. Garval E, Plee J, Lesage C, Grange-Prunier A, Bernard P, Perceau G.
Frequency of contact sensitization to modern dressings used to treat
within the CRUI-CARE Agreement. [Correction added on 25 May 2022,
chronic leg ulcer. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2018;145(5):339-346.
after first online publication: CRUI funding statement has been added.]
6. Romita P, Stingeni L, Hansel K, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis caused
by chloramphenicol with prurigo nodularis-like spreading. Contact Der-
CONF LICT S OF INTE R ES T matitis. 2019;80(4):251-252.
All the authors have no conflict of interest to declare. 7. Bonamonte D, Foti C, Vestita M, Ranieri LD, Angelini G. Nummular eczema
and contact allergy: a retrospective study. Dermatitis. 2012;23(4):153-157.
8. Lachapelle JM. Allergic contact dermatitis: clinical aspects. Rev Environ
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Health. 2014;29(3):185-194.
Caterina Foti: Conceptualization (equal); data curation (equal); supervi-
sion (equal); writing – review and editing (equal). Gianluca Calianno: Con-
How to cite this article: Foti C, Calianno G, Mazzotta S,
ceptualization (equal); data curation (equal). Silvia Mazzotta: Data
Guarneri F, Romita P. Allergic contact dermatitis to
curation (equal); formal analysis (equal). Fabrizio Guarneri: Data curation
clostridiopeptidase A with a nummular eczema-like spread.
(equal); formal analysis (equal); supervision (equal). Paolo Romita: Con-
Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86(2):122-123. doi:
ceptualization (equal); data curation (equal); formal analysis (equal); super-
10.1111/cod.13982
vision (equal); validation (equal); writing – review and editing (equal).
Mepolizumab for treating systemic allergic dermatitis with
hypereosinophilia likely secondary to a nickel/
cobalt-containing coronary artery stent
Paul Faybusovich1 | Jordan Lim2 | Michael D. Ioffreda2 | Taha Al-Shaikhly1
1
Section of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, Department of Medicine, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania, USA
2
Department of Dermatology, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania, USA
Correspondence
Dr Paul Faybusovich, Penn State College of Medicine, 500 University Drive, PO Box 850, Hershey, PA 17033, USA.
Email: pfaybuso@nyit.edu
K E Y W O R D S : case report, cobalt, drug-eluting stent, hypereosinophilia, interleukin 5 (IL-5), medical device, mepolizumab, nickel, systemic
allergic dermatitis
Systemic allergic dermatitis (SAD) from endovascular devices is not secondary to an unretrievable nickel/cobalt-containing drug-eluting coro-
uncommon.1 We present a patient with SAD and hypereosinophilia likely nary artery stent, who responded to anti-interleukin (IL)-5 therapy.
You might also like
- Neuropsychology Study Guide & Board Review (2014)Document666 pagesNeuropsychology Study Guide & Board Review (2014)pachozal100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan On Creutzfeldt-Jakob DiseaseDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan On Creutzfeldt-Jakob DiseaseUjean Santos Sagaral100% (1)
- Jamadermatology Wang 2019 Lo 1900191 PDFDocument3 pagesJamadermatology Wang 2019 Lo 1900191 PDFvijaya abburamNo ratings yet
- Surgical Mask DermatitisDocument2 pagesSurgical Mask DermatitisChrisNo ratings yet
- Tinea CorporisDocument7 pagesTinea CorporisAziza Ulfie WijayaniNo ratings yet
- Iterleukin-4 and Interferon-Y in Allergic Contact Dermatitis With Atopic Background in Leather Tannery Factory WorkerDocument6 pagesIterleukin-4 and Interferon-Y in Allergic Contact Dermatitis With Atopic Background in Leather Tannery Factory WorkershaviraNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Tinea Incognita in A Patient With Ichthyosis Vulgaris and EczemaDocument3 pagesDisseminated Tinea Incognita in A Patient With Ichthyosis Vulgaris and EczemaNovia KurniantiNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Successful Treatment of Recalcitrant Condyloma With Topical CidofovirDocument2 pages(PDF) Successful Treatment of Recalcitrant Condyloma With Topical Cidofoviralihass88No ratings yet
- Urticarial Lesions If Not Urticaria WhatDocument29 pagesUrticarial Lesions If Not Urticaria WhatGabriella -No ratings yet
- Tinea CorporisDocument7 pagesTinea CorporisAziza Ulfie WijayaniNo ratings yet
- A Hands On Approach To Patch TestingDocument11 pagesA Hands On Approach To Patch TestingSundar RamanathanNo ratings yet
- 1952-Article Text-5752-1-10-20220823Document13 pages1952-Article Text-5752-1-10-20220823sidra shabbirNo ratings yet
- Hallopeau 10.1001@jamadermatol.2019.3515Document1 pageHallopeau 10.1001@jamadermatol.2019.3515Faten HayderNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Oral Albendazole As A Treatment For Pediculosis CapitisDocument6 pagesEffectiveness of Oral Albendazole As A Treatment For Pediculosis CapitisAlmuizzu NurjannahNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Moluskum KontangiosumDocument7 pagesJurnal Moluskum KontangiosumDila OktafianiNo ratings yet
- Treatment-Resistant Adult Atopic DermatitisDocument2 pagesTreatment-Resistant Adult Atopic DermatitisveehakNo ratings yet
- 25.anti ShanshalMDocument3 pages25.anti ShanshalMJUAN PABLONo ratings yet
- Hidraenitis 5Document1 pageHidraenitis 5Yudia MahardikaNo ratings yet
- Keratolyse Ponctuee Foot 1870519Document1 pageKeratolyse Ponctuee Foot 1870519redhaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Oral Albendazole As A Treatment For Pediculosis CapitisDocument8 pagesEffectiveness of Oral Albendazole As A Treatment For Pediculosis CapitisFlorensia WodaNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana HipersensitivitasDocument1 pageTatalaksana Hipersensitivitasapril babyNo ratings yet
- References: When A Gin and Tonic Can Mean Trouble: Fixed Drug Eruption Due To QuinineDocument3 pagesReferences: When A Gin and Tonic Can Mean Trouble: Fixed Drug Eruption Due To Quininechrislxt1No ratings yet
- PPE-25-Case Report of Aquagenic UrticariaDocument2 pagesPPE-25-Case Report of Aquagenic UrticariaSajin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Silverberg 2017Document1 pageSilverberg 2017Herdian KusumaNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 2352512622004027Document4 pagesPi Is 23525126220040277dsp7xvs8dNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Clausii As A Treatment of Small Intestinal Bacterial OvergrowthDocument2 pagesBacillus Clausii As A Treatment of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowthdrfaruqui2551No ratings yet
- (Maju) Molluscum ContagiosumDocument5 pages(Maju) Molluscum ContagiosumElliNo ratings yet
- Review: Tinea Corporis: An Updated ReviewDocument22 pagesReview: Tinea Corporis: An Updated ReviewMade SetiadjiNo ratings yet
- Alejandro 2014Document2 pagesAlejandro 2014Eki Yazid An NafiNo ratings yet
- Tozinameran Induced AGEP-DRESSDocument2 pagesTozinameran Induced AGEP-DRESSCHONG WEI SHENGNo ratings yet
- Acad Dermatol Venereol - 2019 - Nowak - Rosacea Fulminans Coincidence of The Disease With Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument2 pagesAcad Dermatol Venereol - 2019 - Nowak - Rosacea Fulminans Coincidence of The Disease With Inflammatory Bowel DiseasecamilabettiomatosNo ratings yet
- Acad Dermatol Venereol - 2020 - Misery - A Position Paper On The Management of Itch and Pain in Atopic Dermatitis From TheDocument10 pagesAcad Dermatol Venereol - 2020 - Misery - A Position Paper On The Management of Itch and Pain in Atopic Dermatitis From Themaituuyen1997No ratings yet
- Clinical and Instrumental Assessment of The Effects of A New ProductDocument5 pagesClinical and Instrumental Assessment of The Effects of A New ProductMyroslava KvitchukNo ratings yet
- A Distinctive Skin Rash LTEDocument2 pagesA Distinctive Skin Rash LTEeva yustianaNo ratings yet
- Hot Topics in Necrotising Skin and SoftDocument10 pagesHot Topics in Necrotising Skin and SoftPriyanshi PatelNo ratings yet
- Erythroderma Following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccination in A Patient With Atopic Dermatitis: A Case ReportDocument9 pagesErythroderma Following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccination in A Patient With Atopic Dermatitis: A Case Reportایران گرافیکNo ratings yet
- Therapy Selection For Tinea Corporis and Cruris With CommorbidityDocument9 pagesTherapy Selection For Tinea Corporis and Cruris With CommorbidityShimie Shimie KokobopNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0190962214011566Document2 pagesPi Is 0190962214011566LewishoppusNo ratings yet
- Herpes Zoster in COVID19Document2 pagesHerpes Zoster in COVID19Vienesha Aress ShaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Hotline: Tinea Profunda of The Genital Area. Successful Treatment of A Rare Skin DiseaseDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Hotline: Tinea Profunda of The Genital Area. Successful Treatment of A Rare Skin Diseasesoekarnohatta94No ratings yet
- 2021-Clinical and Pathologic Correlation of Cutaneous COVID-19 Vaccine Reactions Including V-REPP-A Registry-Based StudyDocument9 pages2021-Clinical and Pathologic Correlation of Cutaneous COVID-19 Vaccine Reactions Including V-REPP-A Registry-Based Studyseguridadyambiente641No ratings yet
- Lip Angioedema Swellimng and HSV Following HA InjDocument2 pagesLip Angioedema Swellimng and HSV Following HA InjOmar NagrashNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Patch Testing: Clinical CommentaryDocument7 pagesA Practical Guide To Patch Testing: Clinical CommentaryAlfita RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Interleukin-17 IL-17-mediated Immunity Controls SKDocument11 pagesInterleukin-17 IL-17-mediated Immunity Controls SKnadyasantikaNo ratings yet
- PPK Perdoski 2017 Skabies (English)Document3 pagesPPK Perdoski 2017 Skabies (English)yumizoneNo ratings yet
- Ccid 8 257 PDFDocument9 pagesCcid 8 257 PDFFahmil AgungNo ratings yet
- Kasus Ichthyosis Vulgaris IIDocument4 pagesKasus Ichthyosis Vulgaris IIfitriaNo ratings yet
- ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZDocument8 pagesZZZZZZZZZZZZZZchloramphenicolNo ratings yet
- Scabies and Pediculosis: Neglected Diseases To Highlight: Article Published Online: 1 February 2012Document2 pagesScabies and Pediculosis: Neglected Diseases To Highlight: Article Published Online: 1 February 2012Anonymous TVwR0FNo ratings yet
- Acquired Epidermolysis Bullosa Without Basement MeDocument2 pagesAcquired Epidermolysis Bullosa Without Basement MeAndrés WunderwaldNo ratings yet
- Chronic Inducible Urticaria: A Systematic Review of Treatment OptionsDocument10 pagesChronic Inducible Urticaria: A Systematic Review of Treatment OptionsAdventcia Tesha ParamithaNo ratings yet
- 13 DH-OrtizBDocument4 pages13 DH-OrtizBD U N I A A N I M ENo ratings yet
- 05 Palmieri-VadalaDocument7 pages05 Palmieri-VadalaSantosNo ratings yet
- Contact Dermatitis in The Patient With Atopic DermatitisDocument9 pagesContact Dermatitis in The Patient With Atopic Dermatitislina7soteroNo ratings yet
- An Interventional Skin CareDocument11 pagesAn Interventional Skin CareTatiana SiregarNo ratings yet
- 2017 Article 141 Part3Document5 pages2017 Article 141 Part3Karina MonasaNo ratings yet
- Allergic Contact Cheilitis Due To ShellaDocument18 pagesAllergic Contact Cheilitis Due To ShellaprimafilateliaNo ratings yet
- Intertrigo and Secondary Skin InfectionsDocument5 pagesIntertrigo and Secondary Skin Infectionskhalizamaulina100% (1)
- Itt 13 151Document22 pagesItt 13 151JUAN PABLONo ratings yet
- Development of Delayed Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Following The Second Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine - A Series of 37 CasesDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Delayed Dermal Hypersensitivity Reaction Following The Second Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine - A Series of 37 CasesAlpana MohtaNo ratings yet
- Childhood Erythrodermic Lichen Planus Pemphigoides After Nonavalent Human Papillomavirus VaccinationDocument3 pagesChildhood Erythrodermic Lichen Planus Pemphigoides After Nonavalent Human Papillomavirus Vaccinationnurul hidayatiNo ratings yet
- VitiligoFrom EverandVitiligoMauro PicardoNo ratings yet
- Manual Removal of The Placenta After Vaginal DeliveryDocument5 pagesManual Removal of The Placenta After Vaginal DeliveryDara Mayang SariNo ratings yet
- MLKLLKD 12 QweqzbnsqqazxsswqwerrtgfdsaDocument3 pagesMLKLLKD 12 QweqzbnsqqazxsswqwerrtgfdsalasovNo ratings yet
- Self-Monitoring and Automated Real-Time Trash Bin (SMART Bin) With Solar-Powered Integration For COVID-19 Infectious Waste PreventionDocument1 pageSelf-Monitoring and Automated Real-Time Trash Bin (SMART Bin) With Solar-Powered Integration For COVID-19 Infectious Waste PreventionjinotorrefielNo ratings yet
- Upper Intermediate: Level 2Document4 pagesUpper Intermediate: Level 2AngolTeadélutánAdrivalNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Follow-Up of Newborns at Neurological Risk: Research Open AccessDocument8 pagesLong-Term Follow-Up of Newborns at Neurological Risk: Research Open Accessleivaherre10No ratings yet
- Mekanisme Vitamin C Menurunkan Stres Oksidatif Setelah Aktivitas FisikDocument7 pagesMekanisme Vitamin C Menurunkan Stres Oksidatif Setelah Aktivitas Fisikpurity sabilaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Clinical PracticeDocument13 pagesNutrition in Clinical PracticeSCPNo ratings yet
- English Kumarbharati March 2020 STD 10th English Medium SSC Maharashtra State Board Question PaperDocument6 pagesEnglish Kumarbharati March 2020 STD 10th English Medium SSC Maharashtra State Board Question PaperJeetbahadur Tamang100% (5)
- Infographic 1 - Tendinopathy Management With Daniel SilvanDocument1 pageInfographic 1 - Tendinopathy Management With Daniel SilvanKeefe TanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Audit For PhysiciansDocument46 pagesClinical Audit For PhysiciansTatiana Araujo100% (2)
- CBT Mental Health Print NowDocument17 pagesCBT Mental Health Print Nowchristy INo ratings yet
- Alrouji 2018Document47 pagesAlrouji 2018farah maulida martaNo ratings yet
- MCN Test 1 Answer KeyDocument6 pagesMCN Test 1 Answer KeyJRMSU Learning HubNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Environmental Factor To The Microbial Growth"Document17 pagesThe Influence of Environmental Factor To The Microbial Growth"Mutmainna Ekawati Ewa50% (2)
- Health Insulrance Policy - Optima RestoreDocument2 pagesHealth Insulrance Policy - Optima RestoreSumit SinhaNo ratings yet
- CFS Fatigue Covid-19 Auto-Immune DysautonomiaDocument10 pagesCFS Fatigue Covid-19 Auto-Immune DysautonomiavalgurNo ratings yet
- Framingham Criteria For CHFDocument2 pagesFramingham Criteria For CHFFibrianti Ratna SariNo ratings yet
- Fibroid With PregnancyDocument5 pagesFibroid With PregnancyvaishaliNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia & MSCCDocument29 pagesHypercalcemia & MSCCSA NodeNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Cholestasis 2Document28 pagesNeonatal Cholestasis 2HafsaJabbarNo ratings yet
- Actcr 1 (3) 15Document11 pagesActcr 1 (3) 15Robinson Trujillo CabanillaNo ratings yet
- JZWM Jan 2010Document7 pagesJZWM Jan 2010llcoffeeNo ratings yet
- 308 TuberkulosisDocument14 pages308 TuberkulosisShinohara KawaiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Nebulization MedicationsDocument5 pagesDrug Study On Nebulization MedicationsDonald BidenNo ratings yet
- Cell Injury, Cell Death, and AdaptationsDocument81 pagesCell Injury, Cell Death, and AdaptationsDrSyeda RimaNo ratings yet
- A Designer Diet Layout For A Microbiome-Mediated ApproachDocument9 pagesA Designer Diet Layout For A Microbiome-Mediated ApproachahcyhahgaseNo ratings yet
- DY - DM&HO Daily Empty ReportDocument1 pageDY - DM&HO Daily Empty Reportphc kallumarriNo ratings yet
- Digital Transformation at Royal PhilipsDocument17 pagesDigital Transformation at Royal PhilipsSadasivuni007No ratings yet