Mokasa Physics pp1
Uploaded by
Benjamin mwanikiMokasa Physics pp1
Uploaded by
Benjamin mwanikiNAME: …………………………………………………… ADM. No…………CLASS:……….
DATE………….…… SIGN ……………
232/1
Physics
Paper 1
DECEMBER 2021
MOKASA II JOINT EXAMINATION
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (KCSE)
Instructions to candidates
• This paper consists of two sections A and B.
• Answer all the questions in the two sections in the spaces provided after each question
• All working must be clearly shown.
• Electronic calculators and Mathematical tables may be used.
• All numerical answers should be expressed in the decimal notations.
• Take g = 10m/s²
For Examiner use only
SECTION QUESTION MAX MARKS CANDIDATE’S
SCORE
A 1 – 12 25
13 10
14 11
B 15 12
16 11
17 11
TOTAL 80
This paper consists of 11 printed pages. Candidates should check to ascertain that all pages are
printed as indicated and that no questions are missing.
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 1
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
1. The reading of volume of a liquid in a burette is 37.5cm³. What is the new volume
when 10 ml of the same liquid is added? (1 mk)
2. A block of dimension 0.2m by 0.1m by 5cm has a mass of 500g and rests on a flat
surface. Determine the least pressure that can be exerted by the block on the surface.
(2mks)
3. The mass of a body is constant but its weight on earth is not. Explain. (2 mks)
4. i) Two samples of bromine vapour are allowed to diffuse separately under different
conditions: one a vacuum and the other in air. State with reason the condition in which
the bromine vapour will diffuse faster. (2 mks)
ii) What precautions should be taken when performing the experiment above
(1 mk)
5. What do you understand by the term carbon dating (1 mk)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 2
6. State and explain two factors which affect surface tension of a liquid. (2 mks)
7. The uniform rod of length one metre shown in figure below is in equilibrium.
Find the value of x if the weight of the rod is 40N. (3mks)
8. The figure below shows the displacement – time graph for a certain body
80
Displacement, s(m)
60
A
B
40
20
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Time (s)
a) Describe the motion of the body between A and B (1 mk)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 3
b) Determine the velocity between OA (2 mks)
9.a) A body of mass 20kg hangs 4m and swings through a vertical height of 0.9m as
shown in the figure below.
Determine;
i) The potential energy at its highest position. (1 mk)
ii) The speed of the body when passing through the lowest point.
(2 mks)
10. A crane lifts a load of 2000N through a vertical distance of 3.0m in 6 seconds.
Determine the power developed by the crane. (2 mks)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 4
11. A gun of mass 10kg fires a bullet of mass 30g at a speed of 500m/s. what is the recoil
velocity of the gun? (1 mk)
12. The mass of an empty density bottle is x g. when full of water its mass is 70g and
when full of liquid Y whose density is 0.96g/cm³ its mass is 68.4g. Determine the value of
x. (density of water is 1g/cm³) (2 mks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
13.a) i) Define absolute zero temperature (1 mk)
ii) When marking the fixed points of a thermometer, it was observed that at 0°C the
mercury thread was 2cm long and at 100°C the thread was 8 cm long. Determine the
length that would correspond to a temperature of 24°C.
(2 mks)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 5
b) Why is steam preferred when determining the upper fixed point of a thermometer
(1 mk)
c) State the purpose of a constriction in a clinical thermometer (1 mk)
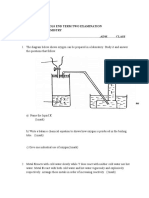
d) The figure below shows a solar water system
a) State the following in regard to the solar water system
i) Why the pipes are made of copper (1 mk)
ii) Why the pipe is coiled several times (1 mk)
iii) Why the panel front is covered with glass (1 mk)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 6
iv) Why the copper pipes are blackened (1 mk)
b) What can be done to minimize heat losses as the water moves through the hot
water pipe (1 mk)
14. a) A particle moving along a circular path of radius 10cm describes an arc of 5cm
every second. Determine
i) The angular velocity (2 mks)
ii) Its periodic time (1 mk)
b) The figure below shows a graph of tension T exerted by a stone whirled in a
circle in a vertical plane using an inextensible string and moving at an increasing
velocity against its angular velocity ( ⍵²) at its lowest point of rotation.
T(N)
40
30
20
10
0 2
5 10 15 20 25 ⍵²(𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑠−1 )
i) Explain what caused the increase in tension (2 mks)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 7
ii) Write an expression governing the graph (1 mk)
c) Use the graph to determine:
i) The mass of the stone (2 mks)
ii) The radius r of rotation of the stone (3 mks)
15.a) State Boyle’s law of gases (1 mk)
b) The diagram below shows an experiment set up to investigate Boyle’s law
i) State the measurements that were taken in order to verify the law
(2 mks)
ii) Explain how the measurements can be used to verify the law
(3 mks)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 8
c) A column of air 14 cm long is trapped by mercury thread 5cm long as shown in
the figure below. When the tube is vertically inverted the air column now becomes
16cm long.
Air
16cm
5cm
Mercury
14cm 5cm
Air
Determine the value of the atmospheric pressure in mmHg (2 mks)
d) In an experiment to determine the specific heat capacity of a 2.0 kg aluminium
block, a potential difference of 12V is used to supply a constant current of 2A
through a heater coil for 5 minutes. The block is well lagged and its temperature
rises from 21°C to 37.1°C within this period. Using the values given, determine:
i) The total electrical energy supplied by the heater (2 mks)
ii) The specific heat capacity of aluminium (2 mks)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 9
16. a) A garden sprinkler of x holes each of cross-sectional area 3.0x10-6m² and is
connected to a horse-pipe of cross-sectional area of 2x10-4m². If the speed of the water
in the horse pipe is 1.35 m/s, calculate;
i) The mass flow rate of water in kg/s (3 mks)
ii) The number of holes, x if the speed of water as it emerges from the holes is
3m/s. (3 mks)
b) The figure below shows air flowing through a pipe of different cross sectional areas.
The two pipes A and B are dipped into water.
Air
B Water
A
i) Indicate on the figure the levels of water A and B (1 mk)
ii) Explain the cause of the difference in the levels of water in the pipes A and B
(2 mks)
iii) Explain why a lorry loaded with bags of maize packed high up is likely to topple
when negotiating a sharp bend (2 mks)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 10
17. a) State Archimedes’s principle (1 mk)
b) You are provided with the following apparatus to carry out an experiment to verify
Archimedes’s principle: a spring balance, a eureka can, a beaker, a weighing balance,
water in a container and a 50g metal block
i) Draw a set up showing how the apparatus are used in the experiment (2 mks)
ii) List down the measurements taken (3 mks)
(c) Figure below shows a buoy of capacity 4.0x104cm³ and mass 10kg. It is held in
position in sea water of density 1.04g/cm³ by a light cable fixed to the bottom so that
¾ of its volume is below the water surface.
Buoy
Water
Cable
Sea bed
i) Indicate on the diagram the forces acting on the buoy (2mks)
ii) Determine the tension in the cable. (3 mks)
MOKASA 2 PHYSICS PAPER 1 2021 Page 11
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life4/5 (6392)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You Are4/5 (1173)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On It4.5/5 (983)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy Answers4.5/5 (361)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space Race4/5 (1008)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New America4.5/5 (278)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first Century3.5/5 (2283)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True Story3.5/5 (233)
- 2021-2022 Maranda Mock 121 MATHEMATICS P1 QSNo ratings yet2021-2022 Maranda Mock 121 MATHEMATICS P1 QS16 pages
- NAME .ADM CLASS : 2022 Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exam - (April 2022)No ratings yetNAME .ADM CLASS : 2022 Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exam - (April 2022)6 pages
- Opener Exam Year 2021 Term 2: NAME ADM ..CLASS Physics Form 2 70MKSNo ratings yetOpener Exam Year 2021 Term 2: NAME ADM ..CLASS Physics Form 2 70MKS5 pages
- This Document Has Been Prepared by Sunder Kidambi With The Blessings ofNo ratings yetThis Document Has Been Prepared by Sunder Kidambi With The Blessings of8 pages
- Enphase - Conformiteitscertificaten en 6ma VerklaringNo ratings yetEnphase - Conformiteitscertificaten en 6ma Verklaring3 pages
- Daily Material Receipt Details: May'2022: Voltas Limited Upbg PantnagarNo ratings yetDaily Material Receipt Details: May'2022: Voltas Limited Upbg Pantnagar17 pages
- Materials: Optimization of The Iron Ore Direct Reduction Process Through Multiscale Process ModelingNo ratings yetMaterials: Optimization of The Iron Ore Direct Reduction Process Through Multiscale Process Modeling18 pages
- EE 8602 - Protection and Switchgear Unit I - MCQ BankNo ratings yetEE 8602 - Protection and Switchgear Unit I - MCQ Bank11 pages
- Entrepreneurship Opportunities in EV IndustryNo ratings yetEntrepreneurship Opportunities in EV Industry14 pages
- Datasheet BlueSolar Charge Controller MPPT 250 70, 150 100 & 250 100 VE - Can ENNo ratings yetDatasheet BlueSolar Charge Controller MPPT 250 70, 150 100 & 250 100 VE - Can EN2 pages
- Rapida 105 - Innovative Rapida 106 Technology InsideNo ratings yetRapida 105 - Innovative Rapida 106 Technology Inside32 pages