2015SepIJOCRNanodentistry PDF
2015SepIJOCRNanodentistry PDF
Uploaded by
Shivani DubeyCopyright:
Available Formats
2015SepIJOCRNanodentistry PDF
2015SepIJOCRNanodentistry PDF
Uploaded by
Shivani DubeyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
2015SepIJOCRNanodentistry PDF
2015SepIJOCRNanodentistry PDF
Uploaded by
Shivani DubeyCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/323800428
NANODENTISTRY – A DENTAL BOON
Article · March 2018
CITATIONS READS
0 2,047
1 author:
Umapathy Thimmegowda
RajaRajeshwari Dental College and Hospital
70 PUBLICATIONS 73 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
micronuclei View project
Genetics View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Umapathy Thimmegowda on 16 March 2018.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
Received : 21‑03‑15
Review completed : 10‑05‑15
Review Article Accepted : 23‑05‑15
NANODENTISTRY – A DENTAL BOON
Jaya AR, * Umapathy T, ** Nidhi K Nihal, *** Prasanna Kumar Bhat, †
Miloni S Vora, †† Ramya BJ †††
* Senior Lecturer, Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, Rajarajeswari Dental College & Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka,
India
** Reader, Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, Rajarajeswari Dental College & Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
*** MDS, Pediatric Dentist, Kolkatta, West Bengal, India
† Senior Lecturer, Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, Rajarajeswari Dental College & Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka,
India
†† MDS, Pediatric Dentist, Rajkot, India
††† Senior Lecturer, Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, R V Dental College & Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
_________________________________________________________________________
ABSTRACT science of manipulating matter measured in the
Nanotechnological advances should be viewed billionths of meters or manometer, roughly the
in the context of other expected developments size of 2 or 3 atoms.[1]
relevant to oral health in the coming decades. HISTORY
Biological approaches such as tissue and There is much controversy regarding the history
genetic engineering will yield new diagnostic of nanotechnology. Although some researchers
and therapeutic approaches much sooner than believe that it is a scientific evolutionary form
will nanotechnology. At the same time that did not develop until the late 1980s, evidence
continual refinement of traditional methods, of nanotechnology dates back to 1959. Others
development of advanced restorative material believe that humans have unwittingly employed
and new medications and pharmacological nanotechnological methods for thousands of
approaches will continue to improve dental years, perhaps even longer. One of the first
care. Trends in oral health and disease also mentions of the distinguishing concepts in
may change the focus on specific diagnostic nanotechnology (but predating the use of that
and treatment modalities. Deeper name) was in 1867. At that time, James Clerk
understanding of the causes and pathogenesis Maxwell proposed, as a thought experiment, a
of other disease processes such as periodontal tiny entity known as Maxwell’s Demon that was
disease, developmental craniofacial defects able to handle individual molecules.[2] The late
Nobel prize winning physicist Richard P.
malignant neoplasm should make prevention a
Feynman speculated the potential of nanosize
viable approach. The role of the dentist will
devices as early as 1959 and in his historic lecture
continue to evolve along the lines of currently
in 1959, he concluded saying, "this is a
visible trends. The best technical abilities,
development which I think cannot be avoided."
professional judgment and strong
Forty years ago, this talk was greeted with
interpersonal skills are the hallmark of the
astonishment and skepticism. However, since
contemporary dentist. Eventhough research
then, there has been a remarkable progress toward
work and clinical trials on nanorobots are in
realizing Feynman’s vision.[3] Nano in Greek
the early stage, researchers are quite
means “dwarf,” and the term “nanotechnology”
optimistic regarding the use these microrobots
was coined by a student at the Tokyo Science
in dentistry.
University in 1974.[4] Growing interest in the
KEYWORDS: Nanomedicine; nanodentistry;
future medical applications of nanotechnology is
nanotechnology; nanorobots leading to the emergence of a new field
called “Nanomedicine” , where it is defined as the
INTRODUCTION science and technology of diagnosing, treating,
Science is undergoing yet another change, in and preventing disease and traumatic injury,
helping mankind enter a new era, the era of relieving pain, and preserving and improving
nanotechnology. "Nano" is derived from the human health, with the help of nanotechnology.[5]
Greek word for 'dwarf. Nanotechnology is the
IJOCR July - Sep 2015; Volume 3 Issue 9 1
Nanodentistry Jaya AR, Umapathy T, Nihal NK, Bhat PK, Vora MS, Ramya BJ
Similarly, development of “nanodentistry” will or tissue samples and to make multiple analyses
make possible the maintenance of near-perfect at the subcellular level. From an in vivo
oral health through the use of nanomaterials,[6,7] perspective, nanodevices might be inserted into
biotechnology[7-11] including tissue engineering, the body to identify the early presence of a
and nanorobotics.[12,13] disease, or to identify and quantify toxic
APPLICATIONS OF NANOROBOTICS TO molecules, tumor cells, and so forth.[17,18]
DENTISTRY Diagnosis of oral cancer
Feynman has described how medical nanorobots Saliva is used as an inexpensive and
might use specific motility mechanisms to crawl noninvasively obtained diagnostic medium that
or swim through human tissues with navigational contains proteomic and genomic markers for
recession; acquired energy, and sense and molecular disease identification. Exosome, a
manipulate their surroundings; achieve safe membrane-bound secretory vesicle, is one such
cytopenetration (for example - pass through marker whose level is elevated in malignancy.
plasma membranes such as the odontoblastic This marker has been studied by using atomic
process without disrupting the cell, while force microscopy, which employs nanoparticles.
maintaining clinical biocompatibility) and use any The nano electromechanical system, oral fluid
of a multitude of techniques to monitor, interrupt nanosensor test, and optical nanobiosensor can
or alter nerve impulse traffic in individual nerve also be used for diagnosing oral cancer.[19,20]
cells.[14] Nanorobots in dentistry have a potential a) Nano Electromechanical Systems (NEMS)
to show its effectiveness in inducing oral Nanotechnology based NEMS biosensors that
analgesia, desensitizing tooth, and manipulating exhibit exquisite sensitivity and specificity for
the tissue to re-align and straighten irregular set detection of abnormal cells at molecular level are
of teeth and improving durability of teeth. being developed. They convert (bio) chemical to
However these devices are in the development electrical signal.[32]
phase and only hypothetical nanorobot has been b) Oral Fluid NanoSensor Test (OFNASET)
produced.[15] The Oral Fluid NanoSensor Test (OFNASET)
Mechanism of action of Nanorobots technology is used for multiplex detection of
The powering of nanorobots is expected to be salivary biomarkers for oral cancer.[33]
done by metabolism of local glucose, oxygen and c) Optical Nanobiosensor
externally supplied acoustic energy. Its functions The nanobiosensor is a unique fiberoptics-based
may be controlled by an on-board nanocomputer tool which allows the minimally invasive analysis
that executes preprogrammed instructions in of intracellular components (Cytochrome C).[19]
response to total local robots via acoustic signals NANOROBOTS IN CLINICAL DENTISTRY
(as are used in ultrasonography) or other means To Induce local anesthesia
similar to an admiral commanding a fleet and By applying a colloidal suspensions containing
Communication with the device can be obtained millions of active, analgesic, micron-sized dental
by acoustic signaling navigational network robots that respond to input supplied by the
installed in the body that would provide high dentist are applied on the crown or mucosa which
positional accuracy to all passing nanorobots and can reach the pulp via the gingival sulcus, lamina
help in keeping track of various devices in the propria, or dentinal tubules.This will result in the
body. When the task of the nanorobots is target tooth instantly becoming completely numb
completed, they can be retrieved by allowing by establishing control over nerve-impulse traffic.
them to effuse themselves via the usual human When treatment is over, a second signal causes all
excretory channels. These can also be removed by sensation to return to normal. providing the
active scavenger systems.[16] patient with anxiety-free and needleless comfort.
APPLICATION OF NANOTECHNOLOGY The advantages includes it is fast, reversible and
IN DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT not associated with any side effects or
Nanodiagnostics complications.[17,18]
Nanomedicine could increase the efficiency and Nonsurgical Devices and Nanoneedles
reliability of in vitro diagnostics, through the use A surgical knife has been designed from micro
of selective nanodevices to collect human fluids structured-silicon (non-magnetic and
IJOCR July - Sep 2015; Volume 3 Issue 9 2
Nanodentistry Jaya AR, Umapathy T, Nihal NK, Bhat PK, Vora MS, Ramya BJ
biocompatible) with a diamond-layered tip hybrid composites and composites containing a
(chemically rigid). Nanosized stainless-steel wider distribution of filler particles have come
crystals incorporated into suture needles have into use. Additionally, the even distribution of
been developed with an advantages of giving nanoparticles results in a smoother, creamier
sharper incisions and lower penetration pressure. consistency and improves flow characteristics.
Cell surgery may be possible in the near future Once the material is cured to its hardened state,
with nanotweezers, which are now under these properties contribute to the dentin-like
development.[21] cutability and polishability of the material.[26]
Nanorobotic Dentifrice [dentifrobots] Nanosolutions
Subocclusal dwelling nanorobotic dentifrice Because they produce unique and dispersible
delivered by mouthwash or toothpaste could nanoparticles, nanosolutions can be used as
patrol all supragingival and subgingival surfaces bonding agents. Homogeneity is ensured, because
atleast once a day, metabolising trapped organic the adhesive is mixed perfectly every time.
matter into harmless and odorless vapors and Nanoparticles have also been used as sterilizing
performing continuous calculus debridement. solutions in the form of nanosized emulsified oil
These invisibly small dentifrobots [1-10 micon], droplets that bombard pathogens.[17]
crawling at 1-10 microns/sec, would be Renaturalization Procedures
inexpensive, purely mechanical devices, that Dentition renaturalization procedures may
would safely deactivate themselves if swallowed become a popular addition to the typical dental
and would be programmed with strict occlusal practice providing perfect treatment methods for
avoidance protocol.[22] esthetic dentistry. There would be demand for
Dental Hypersensitivity full coronal renaturalization procedures with the
Dental hypersensitivity is another pathological affected teeth remanufactured to beome
phenomenon that may be amenable to nanodental indistinguishable from the original teeth.[5]
treatment. It may be caused by changes in Tooth repositioning
pressure transmitted hydrodynamically to the Orthodontic nanorobots could directly manipulate
pulp. This is based on the fact that hypersensitive the periodontal tissues including gingivae,
teeth have 8 times higher surface density of periodontal ligament, cementum and alveolar
dentinal tubules and tubules with diameters twice bone allowing rapid and painless tooth
as large than nonsensitive teeth. Dental straightening, rotating and vertical repositioning
nanorobots could selectively and precisely within minutes to hours. A new stainless-steel
occlude selected tubules in minutes, using native wire that uses nanotechnology is being studied
biological materials, offering patients a quick and that combines ultra-high strength with good
permanent cure.[23-25] deformability, corrosion resistance, and surface
Nanocomposites finish in contrast to current molar up righting
Tooth durability and appearance may be techniques, which require weeks or months to
improved by replacing upper enamel layers with complete.[27]
pure sapphire and diamond which can be made Impression materials
more fracture resistant as part of a nanostructured Nanofillers are integrated into vinylpolysiloxanes,
composites material that possibly including producing a unique siloxane impression material
embedded carbon nanotubes.[21] Microfillers in that has a better flow, improved hydrophilic
composites and microcore materials have long properties, and enhanced precision detail.[26]
been in use and nanocomposite particles are Dental implants: structure, chemistry, and
minute enough to be synthesized at the molecular biocompatibility
level and improve the compressive strength of the Bone is a natural nanostructure that is composed
material. Zirconium dioxide used as filler of of organic compounds (mainly collagen) and
submicron size, are necessary to improve reinforced with inorganic ones. Nanotechnology
polishability and esthetics. However, when aims to emulate this natural structure for
particles of this size are used, the material may be orthopedic and dental applications and, more
more prone to brittleness and cracking or particularly, for the development of nanobone.
fracturing after curing. To address this issue, The determining factors for successful
IJOCR July - Sep 2015; Volume 3 Issue 9 3
Nanodentistry Jaya AR, Umapathy T, Nihal NK, Bhat PK, Vora MS, Ramya BJ
osseointegration are surface contact area and and their installation. Complete dentition
surface topography. However, bone bonding and replacement was the basis for research by Chan et
stability also play a role. Bone growth and al., who recreated dental enamel, the hardest
increased predictability can be effectively tissue in the human body, by using highly
expedited with implants by using organized microarchitectural units of nanorods.[21]
nanotechnology. The addition of nanoscale CONCLUSION
deposits of hydroxyapatite and calcium phosphate Nanodentistry still faces many significant
creates a more complex implant surface for challenges in realizing its tremendous potential.
osteoblast formation. Extensive research on the Basic engineering problems from precise
effects and subsequent optimization of positioning and assembly of molecular scale parts
microtopography and surface chemistry has to economical mass production techniques, to
produced ground-breaking strides in material biocompatibility and the simultaneous
engineering. These new implants are more coordination of the activities of large number of
acceptable, because they enhance the integration independent micrometer scale robots. In addition,
of nanocoatings resembling biological materials there are larger social issues of public acceptance,
to the tissues.[30,31] ethics, regulations and human safety that must be
Nanoencapsulation addressed before molecular nanotechnology can
Trials on controlled drug release has been best enter the modern medical armamentarium.
experimented in Nano materials with hollo However, there is equally powerful motivation to
spheres, nanotubes, core-shell structure and surmount these various challenges such as the
nanocomposite.[8,9] Target delivery system has possibility of providing high quality dental care to
been developed successfully by SWRI [South 80% of the world’s population that currently
West Research Institute] that involves receives no significant dental care. Time, specific
nanocapsules including antibiotics ,vaccines and advances, financial and scientific resources and
drug delivery. Targeted release systems that human needs will determine which of the
encompass nanocapsules are under trial for applications to be realized first. However,
inclusion in vaccines and antibiotics.[28,29] researchers have predicted that high-tech and
Treatment of Oral Cancer effective management at the microscopic level,
Nanoshells, which are miniscule beads, are termed nanotechnology, will become an
specific tools in cancer therapeutics. Nanoshells important part of future dental and periodontal
have an outer metallic layer that selectively health.
destroys cancer cells, while leaving normal cells CONFLICT OF INTEREST & SOURCE OF
intact. Brachytherapy is an advanced form of FUNDING
cancer treatment. Still under trial are The author declares that there is no source of
nanoparticle-coated, radioactive sources placed funding and there is no conflict of interest among
close to or within the tumor to destroy it. Other all authors.
uses of nanovectors include drug delivery across BIBLIOGRAPHY
the blood–brain barrier in the treatment of 1. Kaehler T, Nanotechnology. Basic Concepts
Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.[19,20] and Definitions, Clinical Chemistry
Photosensitizers and Carriers 1994;40[9]:1797-9.
Quantum dots can be used as photosensitizers and 2. Freitas RA Jr. Nanomedicine, Volume I:
carriers. They can bind to the antibody present on Basic Capabilities, Georgetown, TX:
the surface of the target cell and when stimulated Landes. Bioscience 1999;345-50.
by UV light, they can give rise to reactive oxygen Feynman R. There's Plenty of Room at the
species and thus will be lethal to the target cell.[26] Bottom, In: Gilbert HD (Ed.),
Major Tooth Repair Miniaturization, New York: Rein hold
Nanodental techniques for major tooth repair may 1961;282-96.
evolve through several stages of technological 3. Taniguchi N. On the Basic Concept of
development, first using genetic engineering, 'Nano-Technology'," Proc. Intl. Conf. Prod.
tissue engineering and regeneration, and later Eng. Tokyo, Part II, Japan Society of
involving the growth of whole new teeth in-vitro Precision Engineering, 1974.
IJOCR July - Sep 2015; Volume 3 Issue 9 4
Nanodentistry Jaya AR, Umapathy T, Nihal NK, Bhat PK, Vora MS, Ramya BJ
4. Robert A. Freitas Jr., “Nanodentistry”. J 19. Wong DT. Salivary diagnostics powered by
Amer Dent Assoc 2000;131:1559-66. nanotechnologies, proteomics and genomics.
5. Shi H, Tsai WB, Garrison MD, Ferrari S, J Am Dent Assoc 2006;137:313-21.
Ratner BD. Template-imprinted 20. Shetty NJ, Swati P, David K. Saudi Dent J
nanostructured surfaces for protein 2013;25(2):49-52.
recognition. Nature 1999;398(6728):593-7. 21. Kleinberg I, Codipilly M. Modeling of the
6. West JL, Halas NJ. Applications of oral alodour system and methods of
nanotechnology to biotechnology. Curr Opin analysis. Quintessence Int 1999;30:357-69.
Biotechnol 2000;11(2):215-7. 22. Mjör IA, Nordahl I. The density and
7. Pruzansky S. Effect of molecular genetics branching of dentinal tubules in human
and genetic engineering on the practice of teeth. Arch Oral Biol 1996;41(5);401-12.
orthodontics. Am J Orthod 1972;62(5):539- 23. Sumikawa DA, Marshall GW, Gee L.
42. Microstructure of primary tooth dentin.
8. Farr C. Biotech in periodontics: molecular Paediatric Dentistry 1999;21(7);439-44.
engineering yields new therapies. Dent 24. Freitas RA Jr. Exploratory design in medical
Today 1997;16(10):92, 94-7. nanotechnology: A mechanical artificial red
9. Slavkin HC. Entering the era of molecular cell. Artificial Cells Blood Substitute
dentistry. JADA 1999;130(3):413-7. Immobile Biotechnology 1998;26(4):30-2.
10. Sims MR. Brackets, epitopes and flash 25. Saravana RK, Vijayalaksmi R.
memory cards: a futuristic view of clinical Nanotechnology in dentistry. Ind J Dent Res
orthodontics. Aust Orthod J 1999;15(5):260- 2006;17(2):
8. 26. Shellhart WC, Oesterle LJ. Uprighting
11. Baum BJ, Mooney DJ. The impact of tissue molars without extrusion. JADA
engineering on dentistry. JADA 1999;130:381-5.
2000;131:309-18. 27. Piρσn-Segundo E, Ganem-Quintanar A,
12. Buckley MJ, Agarwal S, Gassner R. Tissue Alonso-Pιrez V, Quintanar-Guerrero D.
engineering and dentistry. Clin Plast Surg Preparation and characterization of triclosan
1999;26(4):657-62. nanoparticles for periodontal treatment. Int J
13. Freitas RA Jr. Nanomedicine. Vol. 1.Basic Pharm 2005;294(1-2):217-32.
capabilities. Georgetown, Texas: Landes 28. Paquette DW, Hanlon A, Lessem J,
Bioscience; 1999. Available Williams RC. Clinical relevance of
at:“www.nanomedicine.com”. Accessed adjunctive minocycline microspheres in
Sept. 26, 2000. patients with chronic periodontitis:
14. Bumb SS, Bhaskar DJ, Punia H. Nanorobots secondary analysis of a phase 3 trial. J
& challenges faced by Nanodentistry. Periodontol 2004;75(4):531-6.
Guident 2013;6(10):67-9. 29. Albrektsson T, Sennerby L, Wennerberg A.
15. Babel S, Mathur S. Nanorobotics: Headway State of the art of oral implants.
Towards Dentistry. International Journal of Periodontology 2008;47:15-26.
Research in Science And Technology 30. Goene RJ, Testori T, Trisi P. Influence of a
2011;1(3):1-9. nanometerscale surface enhancement on de
16. Nagpal A, Kaur J, Sharma S, Bansal B, novo bone formation on titanium implants: a
Sachdev P. Nanotechnology: the Era Of histomorphometric study in human maxillae.
Molecular Dentistry. Indian Journal of Int J Periodontics Restor Dent 2007;27:211-
Dental Sciences 2011;3(5):80-2. 9.
17. Lampton C. Nanotechnology promises to 31. Li Y, Denny P, Ho CM. The Oral Fluid
revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of MEMS/NEMS Chip (OFMNC): Diagnostic
diseases. Genet Eng News 1995;15:23-5. and Translational Applications. Adv Dent
18. Song JM, Kasili PM, Griffin GD, Vo-Dinh Res 2005;18(1):3-5.
T. Detection of cytochrome C in a single 32. Gau V, Wong D. Oral fluid nanosensor test
cell using an optical nanobiosensor. Anal (OFNASET) with advanced electrochemical
Chem 2004;76(9):2591-4. -based molecular analysis platform. Ann NY
IJOCR July - Sep 2015; Volume 3 Issue 9 5
Nanodentistry Jaya AR, Umapathy T, Nihal NK, Bhat PK, Vora MS, Ramya BJ
33. Acad Sci 2007;1098:401-10.
34. Dalai DR, Bhaskar DJ, Agali RC, Singh N,
Gupta D, Bumb SS. International Journal of
Advanced Health Sciences 2014;1(3):16-20.
IJOCR July - Sep 2015; Volume 3 Issue 9 6
View publication stats
You might also like
- The Immediacy Concept: Treatment Planning from Analog to DigitalFrom EverandThe Immediacy Concept: Treatment Planning from Analog to DigitalNo ratings yet
- Is Endodontic Re-Treatment Mandatory For Every Relatively Old Temporary Restoration?: A Narrative ReviewDocument7 pagesIs Endodontic Re-Treatment Mandatory For Every Relatively Old Temporary Restoration?: A Narrative ReviewARTNo ratings yet
- Ijn 6 2799Document7 pagesIjn 6 2799MizalunaNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Prevention Dentistry 2 PicDocument25 pagesNanotechnology in Prevention Dentistry 2 Picpxb8dhqgs9No ratings yet
- Nanotechnology and Its Application in DentistryDocument10 pagesNanotechnology and Its Application in DentistryAbirame SivasNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology and Its Application in Dentistry: Go ToDocument9 pagesNanotechnology and Its Application in Dentistry: Go ToMoni PopNo ratings yet
- 74-Article Text-127-1-10-20180408Document5 pages74-Article Text-127-1-10-20180408Fira SafiraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2414644723000337 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S2414644723000337 Mainivanguevarallatas31No ratings yet
- THE ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF NANOTECHNOLOGY Ed PDFDocument7 pagesTHE ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF NANOTECHNOLOGY Ed PDFHareeshaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Drug Delivery Science and TechnologyDocument15 pagesJournal of Drug Delivery Science and TechnologyvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Dentistry - Soon To Be Called NanodonticsDocument12 pagesNanotechnology in Dentistry - Soon To Be Called NanodonticsIJAR JOURNAL100% (1)
- Nanorobotics - A Novel Shift Towards An Era of Hands Free DentistryDocument4 pagesNanorobotics - A Novel Shift Towards An Era of Hands Free DentistryShyambhavi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Medical Aspects of Nanomaterial ToxicityDocument17 pagesMedical Aspects of Nanomaterial ToxicityP. MihailNo ratings yet
- Nanoperiodontics: A New Era in The Management of Periodontal DiseaseDocument8 pagesNanoperiodontics: A New Era in The Management of Periodontal DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology For Dentistry Prospects and ApplicationsDocument60 pagesNanotechnology For Dentistry Prospects and ApplicationsbiihterbayrakNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary StudiesDocument8 pagesInterdisciplinary Studiesp.maheswariopenventioNo ratings yet
- Molecules 28 06624Document30 pagesMolecules 28 06624Himanshu PalNo ratings yet
- SaudiEndodJ83163-4719541 130635 PDFDocument7 pagesSaudiEndodJ83163-4719541 130635 PDFAmrutha DasariNo ratings yet
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios 134Document10 pagesCentro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios 134Gabii ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology and Its Application in DentistryDocument7 pagesNanotechnology and Its Application in Dentistrydr parveen bathlaNo ratings yet
- Nanodentistry The Benefits of NanotechnologyDocument7 pagesNanodentistry The Benefits of NanotechnologyDellar Arciantika CahyaniNo ratings yet
- NANOMEDICINEDocument5 pagesNANOMEDICINEabhinav.kumar61opNo ratings yet
- Theranostic Nanoparticles A Recent Breakthrough in Nanotechnology 2157 7439.1000e114Document1 pageTheranostic Nanoparticles A Recent Breakthrough in Nanotechnology 2157 7439.1000e114Demouthie EsmeraldoNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology: The Emerging Science in Dentistry: Fundamental ConceptsDocument0 pagesNanotechnology: The Emerging Science in Dentistry: Fundamental ConceptsMarian TavassoliNo ratings yet
- S Under The MicroscopeDocument41 pagesS Under The MicroscopeBruno SarmentoNo ratings yet
- Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy: Fian, Jabar Zaman Khan Khattak, Shahzad Yousaf, Muhammad Suleman Rana MarkDocument6 pagesPhotodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy: Fian, Jabar Zaman Khan Khattak, Shahzad Yousaf, Muhammad Suleman Rana MarkMariaAlejandraChanciNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Medicine and Relevance To Dermatology: Present ConceptsDocument7 pagesNanotechnology in Medicine and Relevance To Dermatology: Present ConceptsGaurav GargNo ratings yet
- Materials Horizons From Nature To Nanomaterials Sabu Thomas, R MDocument264 pagesMaterials Horizons From Nature To Nanomaterials Sabu Thomas, R MAgnes ratu langitNo ratings yet
- Nano Material As Biological Sensors or Nano in Medical Therapy or Nano in Medical UseDocument19 pagesNano Material As Biological Sensors or Nano in Medical Therapy or Nano in Medical UsestyleashNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Dentistry: Present and FutureDocument6 pagesNanotechnology in Dentistry: Present and FutureManuNo ratings yet
- Nanomedicine, Nanotechnology in MedicineDocument17 pagesNanomedicine, Nanotechnology in Medicinejro840% (1)
- Costas Demetzos (Auth.) - Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology - Fundamentals and Practical Applications-ADIS (2016)Document224 pagesCostas Demetzos (Auth.) - Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology - Fundamentals and Practical Applications-ADIS (2016)Lê Nhất LinhNo ratings yet
- Ramesh Amitha Local Drug Delivery in PeriodontalDocument6 pagesRamesh Amitha Local Drug Delivery in Periodontalsobhan hajianNo ratings yet
- Stimuli Based NanomaterialDocument12 pagesStimuli Based NanomaterialnidhiNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Medical FieldDocument6 pagesNanotechnology in Medical FieldIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Binalbagan Catholic College: Course Guide Science, Technology and Society (STS)Document5 pagesBinalbagan Catholic College: Course Guide Science, Technology and Society (STS)Away To PonderNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Medicine and Healthcare PossibilDocument5 pagesNanotechnology in Medicine and Healthcare PossibilJesubori SojobiNo ratings yet
- Nanoparticles in Drug DeliveryDocument26 pagesNanoparticles in Drug Deliveryقصة مع أحمدNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Dentistry Present and Future Perspectives on Dental Nanomaterials (4)Document36 pagesNanotechnology in Dentistry Present and Future Perspectives on Dental Nanomaterials (4)moking083No ratings yet
- Nanomedicine: Application of Nanotechnology: ArticleDocument9 pagesNanomedicine: Application of Nanotechnology: ArticleAndres GomezNo ratings yet
- Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews: P. CouvreurDocument3 pagesAdvanced Drug Delivery Reviews: P. CouvreurVanessa HernandezNo ratings yet
- 8 Nanotechnology in Healthcare DR Sunita SinghDocument3 pages8 Nanotechnology in Healthcare DR Sunita Singhmanendra lakraNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Medicine and Biosciences: ISSN 2319 - 2739Document3 pagesInternational Journal of Medicine and Biosciences: ISSN 2319 - 2739Mohammed NabeelNo ratings yet
- Nanomaterials 12 01676Document20 pagesNanomaterials 12 01676Dea NandaNo ratings yet
- Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery PAst Present and FutureDocument3 pagesNanoparticles in Drug Delivery PAst Present and FutureDEVYANI KADAMNo ratings yet
- Lague, Inah Krizia O. BSN - 2ADocument3 pagesLague, Inah Krizia O. BSN - 2Ainah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Application of Nanotechnology For Animal HealthDocument9 pagesApplication of Nanotechnology For Animal HealthDr. Adnan Al-KanaanNo ratings yet
- Current Trends of "Nanotechnology" in PharmaceuticalDocument6 pagesCurrent Trends of "Nanotechnology" in PharmaceuticalEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in Healthcare ApplicationDocument6 pagesNanotechnology in Healthcare ApplicationNjehia MwauraNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical NanotechnologyDocument49 pagesPharmaceutical NanotechnologyAlaa SiNo ratings yet
- Application of Dental Nanomaterials: Potential Toxicity To The Central Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesApplication of Dental Nanomaterials: Potential Toxicity To The Central Nervous SystemOny WulandariNo ratings yet
- BALLOCANAG, Jessica, BSN1i, STS JournalReadingFinalsDocument13 pagesBALLOCANAG, Jessica, BSN1i, STS JournalReadingFinalsJessica Saludar BallocanagNo ratings yet
- Aiomt 94Document5 pagesAiomt 94AyestinNo ratings yet
- Case Study Analysis On Nanotechnology STSDocument4 pagesCase Study Analysis On Nanotechnology STSE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Unit XDocument2 pagesUnit XDanna Mae MirandaNo ratings yet
- CN NanoDocument9 pagesCN NanoDương TrươngNo ratings yet
- Gold Nanoparticles:A Boon To Drug Delivery System: December 2015Document7 pagesGold Nanoparticles:A Boon To Drug Delivery System: December 2015Andreea TudorascuNo ratings yet
- Gold Nanoparticles:A Boon To Drug Delivery System: December 2015Document7 pagesGold Nanoparticles:A Boon To Drug Delivery System: December 2015Andreea TudorascuNo ratings yet
- Applications of Bionanotechnology in Nanomedicine: A Theoretical AnalysisDocument6 pagesApplications of Bionanotechnology in Nanomedicine: A Theoretical AnalysisPhilip KpaeNo ratings yet
- Nitrous Oxide in Pediatric Dentistry: A Clinical HandbookFrom EverandNitrous Oxide in Pediatric Dentistry: A Clinical HandbookKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ismail 25 5Document6 pagesIsmail 25 5Shivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Enamel.2Document49 pagesSingle Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Enamel.2Shivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Foreign Body AspirationDocument4 pagesForeign Body AspirationShivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Diet and Dental Caries The Psychological.1Document2 pagesDiet and Dental Caries The Psychological.1Shivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Laser in Pediartic DentistryDocument12 pagesLaser in Pediartic DentistryShivani Dubey100% (1)
- THEORIES OF Tooth Eruption 1st SeminarDocument50 pagesTHEORIES OF Tooth Eruption 1st SeminarShivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Accidental File SwallowingDocument6 pagesAccidental File SwallowingShivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Diet and Dental CariesDocument38 pagesDiet and Dental CariesShivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries PresentationDocument97 pagesDental Caries PresentationShivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Diet and Dental CariesDocument113 pagesDiet and Dental CariesShivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Eleanor SlidesCarnivalDocument83 pagesEleanor SlidesCarnivalShivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument4 pagesArgumentative Essayraxllorente080409No ratings yet
- LTE Autoclaves Floor Standing Front Loading TouchClave-R Series ManualDocument35 pagesLTE Autoclaves Floor Standing Front Loading TouchClave-R Series ManualAyungNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration-Systems Part 1Document11 pagesRefrigeration-Systems Part 1Sean GuanzonNo ratings yet
- PD1 - Assignment Brief - Trimester 1Document6 pagesPD1 - Assignment Brief - Trimester 1Fahad MunirNo ratings yet
- An Agile Methodology For Ontology Development - AbdelghanyDocument13 pagesAn Agile Methodology For Ontology Development - AbdelghanyproconteNo ratings yet
- WI 04 PrEN 15203 Assessment of Delivered Energy Use of BuildDocument49 pagesWI 04 PrEN 15203 Assessment of Delivered Energy Use of BuildPascariu FlorinNo ratings yet
- RT Interpretation-SignedDocument7 pagesRT Interpretation-Signedhamdi hamdiNo ratings yet
- Lucifer.S02E03.HDTV.x264 LOL - TorrentDocument8 pagesLucifer.S02E03.HDTV.x264 LOL - TorrentLuis Paulo CamargoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English Proficiency Sample Paper 1 Listening v2Document8 pagesCambridge English Proficiency Sample Paper 1 Listening v2kwmkb6jffzNo ratings yet
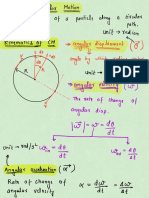
- Circular MotionDocument23 pagesCircular MotionAnkit PatidarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Your Role - Final Action PlanDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Your Role - Final Action Planshadow21No ratings yet
- Astungkara Way - Tree To SeaDocument2 pagesAstungkara Way - Tree To Searuiqi zhouNo ratings yet
- MSA Freestanding Constant Force Post Data Sheet-EnDocument3 pagesMSA Freestanding Constant Force Post Data Sheet-EnPedro Cortes CallejasNo ratings yet
- Rolando Tolentino - Piracy Regulation and The Filipino's Historical ResponseDocument25 pagesRolando Tolentino - Piracy Regulation and The Filipino's Historical ResponseGwyneth PatamNo ratings yet
- Technical Datasheet For Monorail With Chain HoistDocument5 pagesTechnical Datasheet For Monorail With Chain Hoistvuong100% (1)
- Morocco Ifr FeedbackDocument6 pagesMorocco Ifr FeedbackcscNo ratings yet
- English For BeginnersDocument18 pagesEnglish For Beginnersbojanak123No ratings yet
- Sovereign Bonds - The FundamentalsDocument1 pageSovereign Bonds - The FundamentalsJasvinder JosenNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Light Engineering SectorDocument50 pagesPakistan Light Engineering Sectortest12341No ratings yet
- 1098 T UWM 2017 PDFDocument2 pages1098 T UWM 2017 PDFsolrak9113No ratings yet
- Chapter4 TransDocument104 pagesChapter4 TransAbdul Shukor100% (1)
- Midterm DAM 2014 CommonDocument2 pagesMidterm DAM 2014 CommonSachi SurbhiNo ratings yet
- TOOL AND DIE STEEL FinalDocument73 pagesTOOL AND DIE STEEL FinalSapan KansaraNo ratings yet
- Vandelay: Implementing An ERP SystemDocument1 pageVandelay: Implementing An ERP SystemBernie ClintonNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra For Machine LearningDocument5 pagesLinear Algebra For Machine LearningGeeta SinghNo ratings yet
- Declaratie de Conformitate CE Camera Supraveghere Exterior IP Dahua IPC-HFW5541T-ASE-0280BDocument2 pagesDeclaratie de Conformitate CE Camera Supraveghere Exterior IP Dahua IPC-HFW5541T-ASE-0280BLaurentiu LutaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Why Tall Parents Don't Have Even Taller Children: The Department of Obvious ConclusionsDocument1 pageChapter 7. Why Tall Parents Don't Have Even Taller Children: The Department of Obvious ConclusionsMiguel OlmoNo ratings yet
- Top Up Jateng 13.12.23Document1 pageTop Up Jateng 13.12.23AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ebooks File The Complete Vegan Cookbook Over 150 Whole Foods Plant Based Recipes and Techniques Natural Gourmet Center All ChaptersDocument34 pagesEbooks File The Complete Vegan Cookbook Over 150 Whole Foods Plant Based Recipes and Techniques Natural Gourmet Center All Chaptersbundocheou76No ratings yet