S - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - Light
S - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - Light
Uploaded by
Vector HuntCopyright:
Available Formats
S - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - Light
S - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - Light
Uploaded by
Vector HuntOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
S - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - Light
S - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - Light
Uploaded by
Vector HuntCopyright:
Available Formats
SUBJECT: SCIENCE
CLASS VIII
SESSION 2021-22
CH 16: LIGHT
HANDOUT – 16.3
General Instructions:
• The questions given herewith are for self-practice and are to be done in school notebook.
Recapitulation:
Discussion
At the end of the handout, you will be able to
Elaborate on defects of eyes.
Methodology:
Flipped classroom
SUBTOPIC: Internal Structure of Eye
• The human eye is a light-sensitive organ, which enables us to see the beautiful world around us.
• The eyes absorb the light rays and form a visual image and transform this information of the image to the
brain.
• The eye has a spherical structure which is called the eyeballs. The eyeballs are attached in the eye socket
and various muscles are connected to them called the eye muscles. These are muscles allow the movement
of the eyeballs.
• The eyes are protected with eyelids. The eyelids act as the shutters of the eyes and protect them from
shocks, injuries bright light and save the eyes from any outer objects.
Let’s find how our eyes enables us to see things.
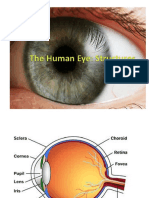
The parts of the human eye & their working
Cornea –
• It is a transparent covering present on the outer side of the
eyes. It consists of 6 layers.
• Lacrimal glands covers cornea, It secretes tear fluid to wash
away the dust particles etc. out of the eyes.
Iris
• It is a dark coloured muscular structure in the center of the
cornea.
• The Iris gives the eye its distinctive colours like grey, blue,
black, green, brown etc.
• The iris has a hole at its center which is called pupil. Pupil
appears like a dark spot in the center of iris because no light is
reflected from it.
• Iris controls the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting
the size of the pupil with the help of the muscles.
• The adjustment of the size of pupil takes time.
Lens –
• The eye lens is located behind the Pupil.
• The eye-lens is a convex lens made of a transparent, flexible,
living cells which allows light to converge through them and this
helps in the formation of a real and inverted image in the eye.
GURUKUL THE SCHOOL, GHAZIABAD 1
• A thin eye-lens has less converging power whereas a thick
eye-lens has greater converging power on the rays of light Flow of Light Inside the Eyes
coming from an object.
Ciliary muscles- Light enters
• The eye-lens is held in position by ciliary muscles whose Cornea
one side is attached to the eye-lens and the other side is
Iris
attached to the eye-ball.
• When the eye is looking at a distant object, the ciliary Pupil
muscles are relaxed due to which the eye-lens is thin (or less Lens controlled by cilliary muscles
convex). The thin eye-lens has smaller converging power
which is sufficient to converge the parallel rays of light Light falls on Retina
coming from a distant object to form its image on the retina. Activation of sensory cells (rods & cones)
• When the same eye is looking at a nearby object, the ciliary
muscles get stretched due to which the eye-lens becomes Formation of image on retina
thick (or more convex). The thick eye-lens has greater Electrical impulse generated
converging power which is required to converge the
Optic nerve sends impulse to brain
diverging rays of light coming from a nearby object to form
its image on the retina.
Retina-
• The retina is behind the eye-lens, at the back part of the eye.
• The eye-lens focusses the image of an object on the retina. The retina is a screen on which the image is
formed.
• The retina has a large number of light sensitive cells to generate electrical signals.
• There are two types of vision cells in the retina are:
Rods - They get activated in darkness or dim-light and the responsible for dark vision.
Cones - They react to bright light hence responsible for light vision and they can sense colour of an
object.
Optic nerve-
• The retina is attached to optic nerve. The optic nerve carries the image formed on retina to the brain in the
form of electrical signals and we are able to see the object. The image of the object formed is inverted.
Aqueous humour- The space between cornea and eye-lens is filled with a viscous liquid called aqueous humour.
Vitreous humour- The space between eye-lens and retina is filled with another liquid called vitreous humour.
Blind spot - There is a point in the eye located at the junction of the retina and the optic nerve where no sensory
cells are present. This spot is therefore called the blind spot as it does not support any vision.
Read Activity 16.9 given in NCERT Pg. No. 206 related to blind spot.
Persistence of Image on the Retina
• The image that is formed on the retina persists for 1/16th of a second.
• Therefore, if one tries to move 16 still images per second of a moving object in front of our eye it appears
as if the object is moving. This is how animation films and movies work. They are a collection of separate
pictures which are moved in a sequence.
• However, this movement is so fast, around 24 pictures in a second, that it appears as if they are moving.
Range of Vision of a Normal Human Eye
• The farthest point from the eye at which an object can be seen clearly is known as the “far point” of the
eye. The far point of a normal human eye is at infinity.
GURUKUL THE SCHOOL, GHAZIABAD 2
• The nearest point up to which the eye can see an object clearly without any Strain, is called the “near point”
of the eye. The near point of a normal human eye is at a distance of 25 centimeters from the eye. It is also
known by another name as the least distance of distinct vision.
Defects of Eyes
• Sometimes with old age, the lens of the
eye can become cloudy or foggy as the
proteins gets collected. This condition
is called cataract with results in loss of
vision.
• However, this defect can be rectified by
removing the old lens from the eye and
inserting an artificial lens at that place
The Braille system
• Braille is a tactual aid for visually challenged people that allow them to read and write. It was developed by
a visually challenged person called Louis Braille.
• In the Braille code, there are 63 Dots or 63 Characters.
• These are arranged in a cell of two vertical rows having three dots each.
• The patterns are embossed on a Braille Sheet that allows a person to read by touching the pattern. Each
character in the Braille system can represent: a letter, a combination of letters or a word a grammatical sign.
How to take care of the eyes?
• One should go for a regular eye check-up.
• Wear spectacles if the eyesight is found weak.
• Always study or watch TV in a sufficient light. Excess or insufficient light both can lead to problems.
Insufficient light can cause strain and leads to a headache.
• Do not look at the sharp source of light like the sun directly. Excess of light can damage the eyes.
• If dust enters into the eye one should not rub them and rather wash them straightway.
• Maintain a normal distance while reading or watching TV. Keep at least 5 times the distance from the
screen as the screen is wide. For example, if your television is 32 inches wide, the optimal viewing distance
is 160 inches or about 13 feet.
• Take a balanced diet to ensure that you get the right nutrients.
NOTEBOOK WORK:
A. Answer the following questions in 30-50 words:
8. What are the roles of ciliary muscles in the eyes?
9. People find difficulty in seeing when they move from dark to enlighten room. Give reason for the same.
B. Answer the following questions in 50-80 words:
10. Elaborate on any three defects of eyes and also mention how can they be corrected?
00000
GURUKUL THE SCHOOL, GHAZIABAD 3
You might also like
- Asvs 04 0267Document7 pagesAsvs 04 0267T KNo ratings yet
- Physiology of VisionDocument49 pagesPhysiology of VisionPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- Waves Aranoco Ppt-Anatomy of The EyeDocument40 pagesWaves Aranoco Ppt-Anatomy of The EyeARNOLD ARANOCONo ratings yet
- Sense of VisionDocument34 pagesSense of VisionqqqqqNo ratings yet
- 11 2 LS EyeDocument63 pages11 2 LS EyeAdhi PandayNo ratings yet
- Structure of Human Eye DipiyDocument10 pagesStructure of Human Eye Dipiyvineet_knwrNo ratings yet
- Chapter-11 Human Eye Final - B9juwtwg7s3bon6atwxsDocument15 pagesChapter-11 Human Eye Final - B9juwtwg7s3bon6atwxsSarveshyaNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye PowerPointDocument69 pagesThe Human Eye PowerPointKemoy Francis100% (1)
- The Human Eye PowerPointDocument69 pagesThe Human Eye PowerPointfathul rahmanNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Sense OrganDocument8 pages3.2 Sense OrganMod HollNo ratings yet
- Light - Class NotesDocument6 pagesLight - Class Noteskirankarnawat29No ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colorful WorldDocument31 pagesHuman Eye and Colorful WorldmuniraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Light at Work: Lesson 7.1: The Human EyeDocument25 pagesChapter 7: Light at Work: Lesson 7.1: The Human EyeMar SelaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement 3Document12 pagesAcknowledgement 3dankymemey96No ratings yet
- Vision FXNDocument11 pagesVision FXNIrene VuremyNo ratings yet
- Light 8thDocument8 pagesLight 8thalikrushna1979No ratings yet
- Ch-10 Human Eye Notes FinalDocument27 pagesCh-10 Human Eye Notes Finalkilemas494No ratings yet
- The Human Eye PowerPointDocument64 pagesThe Human Eye PowerPointmogessisayNo ratings yet
- Light-The Human and The Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesLight-The Human and The Colourful WorldTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Optics10 PhysicsDocument10 pagesOptics10 PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Power PointDocument36 pagesHuman Eye Power Pointlourdescuaresma838No ratings yet
- Resumen Semana 1 Clase de OftalmologiaDocument3 pagesResumen Semana 1 Clase de OftalmologiaIsis MartinezNo ratings yet
- Physics of Eye and Vision - Updated DR Bakhtiar 2023Document46 pagesPhysics of Eye and Vision - Updated DR Bakhtiar 2023mhamadmhamad1184No ratings yet
- 187 RefractionDocument5 pages187 RefractionShabir KhanNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument8 pagesThe Human EyemandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument26 pagesSense OrgansArpan AdhikariNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye PowerPointDocument69 pagesThe Human Eye PowerPointEmerito Perez100% (1)
- Ch-11-Human Eye and The Colouful World 285-307 Physics Sem-1Document22 pagesCh-11-Human Eye and The Colouful World 285-307 Physics Sem-1MAYUR DESAI II BeingMD in PHYSICS IINo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument14 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful Worldsanch.kadam08No ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument24 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful Worldharsha999901No ratings yet
- Human Eye 2023Document5 pagesHuman Eye 2023arpitashekhawat2No ratings yet
- L-2A Human EyeDocument53 pagesL-2A Human EyedancelikeangelNo ratings yet
- An Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainDocument59 pagesAn Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainIsarra AmsaluNo ratings yet
- OLD Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesOLD Human Eye and The Colourful WorldRadhika GargNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument21 pagesThe Human EyeMichel ThorupNo ratings yet
- 11.human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument22 pages11.human Eye and Colourful WorldMalancha high school HSNo ratings yet
- Human Eye PDF 2Document27 pagesHuman Eye PDF 2Satish singhNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Structure and Defects of VisionDocument25 pagesHuman Eye Structure and Defects of Visionmailansh904No ratings yet
- Worksheet (Textual Excercises Based) Grade - 8 LightDocument4 pagesWorksheet (Textual Excercises Based) Grade - 8 LightwafaNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore-East Chapter Notes Physics Topic-The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument7 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore-East Chapter Notes Physics Topic-The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldcatalystdelegationNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument25 pagesThe Eyey2mvfp9wdyNo ratings yet
- 6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Document35 pages6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Lazare ChNo ratings yet
- اخطاء انكسار 3&4Document6 pagesاخطاء انكسار 3&4Hassan AljaberiNo ratings yet
- Eye and VisionDocument20 pagesEye and VisionshyanNo ratings yet
- Human Eye PresentationDocument15 pagesHuman Eye PresentationDipanshu Nagar93% (14)
- Eyes Health AssessmenttDocument34 pagesEyes Health AssessmenttMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- HUMAN EYE Class XDocument25 pagesHUMAN EYE Class Xsai projectNo ratings yet
- SSTDocument2 pagesSSTkWaNgyANo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument11 pagesHuman EyeblehblehdadaNo ratings yet
- CL X Physics Ch-11 The Human EyeDocument12 pagesCL X Physics Ch-11 The Human EyeDeepanshu BindalNo ratings yet
- Human Senses: Monique MavronicolasDocument10 pagesHuman Senses: Monique MavronicolasMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs NotesDocument13 pagesSense Organs NotesVijay Laxmi MundhraNo ratings yet
- Parts of The EYE: Group IiDocument49 pagesParts of The EYE: Group IiJay GregorioNo ratings yet
- Class VIII 15-31 October PhysicsDocument4 pagesClass VIII 15-31 October Physicssateesh kumarNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument9 pagesThe EyeJada MillerNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Human EyeDocument6 pagesStructure and Function of The Human EyeAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Eye PPT For Nursing Students by DR - Reshma AjayDocument46 pagesEye PPT For Nursing Students by DR - Reshma AjayDR RESHMA AJAY100% (2)
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- How Can My Eyes See? Sight and the Eye - Biology 1st Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Can My Eyes See? Sight and the Eye - Biology 1st Grade | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- October Time Table PDFDocument1 pageOctober Time Table PDFVector HuntNo ratings yet
- E - 8 - CH3 - HO3.1 - Macavity The Mystery CatDocument3 pagesE - 8 - CH3 - HO3.1 - Macavity The Mystery CatVector HuntNo ratings yet
- TAMBOLADocument1 pageTAMBOLAVector HuntNo ratings yet
- S - 8 - CH6 - Ho6.4 - Combustion and FlameDocument4 pagesS - 8 - CH6 - Ho6.4 - Combustion and FlameVector HuntNo ratings yet
- Ocular Fundus DrawingDocument33 pagesOcular Fundus DrawingguhanNo ratings yet
- Opd and Clinic Sedule - 3!11!22Document2 pagesOpd and Clinic Sedule - 3!11!22Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EyeDocument96 pagesPhysiology of EyePhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (1)
- Eye Care IntroductionDocument66 pagesEye Care IntroductionEdeti RoneNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The EyeDocument1 pageVocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The EyeOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Tajam Penglihatan Dan Komplikasi Pasca Implantasi Lensa Intraokular SekunderDocument11 pagesTajam Penglihatan Dan Komplikasi Pasca Implantasi Lensa Intraokular SekunderYayayayaya Hmm123No ratings yet
- Presentation1 (2) 4Document10 pagesPresentation1 (2) 4Shokunbi TolaniNo ratings yet
- The Eye - PrintedDocument4 pagesThe Eye - PrintedGabriel RiderNo ratings yet
- Shalakya Udaya ShankarDocument82 pagesShalakya Udaya ShankarDivya MakhareNo ratings yet
- Small Incision Cataract SurgeryDocument249 pagesSmall Incision Cataract SurgeryAillen YovitaNo ratings yet
- Bionic Eye EB KNS 2019Document58 pagesBionic Eye EB KNS 2019Lalitaditya DivakarlaNo ratings yet
- Eye Scanning Ophthalmology PowerPoint TemplateDocument49 pagesEye Scanning Ophthalmology PowerPoint TemplateChing MacarubboNo ratings yet
- Keratitis and Corneal Ulcers in Patients Visiting at Hospital Dr.H.Abdoel Moeloek Lampung Province in 2013-2014Document10 pagesKeratitis and Corneal Ulcers in Patients Visiting at Hospital Dr.H.Abdoel Moeloek Lampung Province in 2013-2014Alif OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Fisio - Faal Special SenseDocument107 pagesFisio - Faal Special SensetiffsbronteNo ratings yet
- The Eye - Grade11Document4 pagesThe Eye - Grade11joshua NaulthyNo ratings yet
- Ace Achievers: The OrbitDocument4 pagesAce Achievers: The OrbitaditryjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The First Steps in Vision: Seeing Stars: Test BankDocument5 pagesChapter 2: The First Steps in Vision: Seeing Stars: Test BankSakata AyameNo ratings yet
- ProP Ophthalmic Examination Made EasyDocument5 pagesProP Ophthalmic Examination Made EasyRosario AyalaNo ratings yet
- Your Eye AnatomyDocument4 pagesYour Eye AnatomyAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 30 - Histology of Special Sensory Organs - EyeDocument53 pagesLecture 30 - Histology of Special Sensory Organs - Eyespitzmark2030No ratings yet
- RETINADocument4 pagesRETINAElizabeth Anne Loto100% (1)
- PP15. Receptors The EyeDocument108 pagesPP15. Receptors The Eyelebohangcandy8No ratings yet
- Ex17 Sense Organs Histology LabDocument6 pagesEx17 Sense Organs Histology LabRod Daniel CalistonNo ratings yet
- Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Padjadjaran Pusat Mata Nasional Rumah Sakit Mata Cicendo BandungDocument12 pagesFakultas Kedokteran Universitas Padjadjaran Pusat Mata Nasional Rumah Sakit Mata Cicendo BandungSri Hudaya WidihasthaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Human EyeDocument4 pagesCH 11 Human EyekniFe VisualzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of RetinaDocument39 pagesAnatomy of Retinadr_dev100% (1)
- EyesDocument3 pagesEyesShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument10 pagesThe Human Eyemargaretziaja1997No ratings yet