1819-F4-Physics-final Exam
1819-F4-Physics-final Exam
Uploaded by
Chan KyleCopyright:
Available Formats
1819-F4-Physics-final Exam
1819-F4-Physics-final Exam
Uploaded by
Chan KyleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
1819-F4-Physics-final Exam
1819-F4-Physics-final Exam
Uploaded by
Chan KyleCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheng Kung Hui Tang Shiu Kin Secondary School
Final Examination
2018 - 2019
Physics
Time allowed: 2 hours
F.4 June 2019
Name :________________________
Class : _____________ (Class No.: ________)
General Instructions :
1. There are TWO sections, A and B, in this Paper. Section A consists of multiple-choice
questions, while Section B contains conventional questions.
2. Answers to Section A should be marked on the Multiple-choice Answer Sheet while answers
to Section B should be written in the spaces provided in Question-Answer scripts. The
Answer Sheet for Section A and the Question-Answer scripts for Section B must be handed
in separately at the end of the examination.
SECTION A (MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS)
INSTRUCTIONS FOR SECTION A (40% of the paper)
1. All questions carry equal marks.
2. ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. You should use an HB pencil to mark all your answers on the
Answer Sheet. Wrong markings must be completely erased.
3. You should mark only ONE answer for each question. If you mark more than one answer,
you will receive NO MARKS for that question.
4. No marks will be deducted for wrong answers.
5. Pages 13 and 14 of this question paper contain a list of data, formulae and relationships
which you may find useful.
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 1
1. Ben is 0.2 m in front of a vertical plane mirror in length h. His eyes E are 1.5 m above the floor. A vase XY
of height 0.6 m sits on the floor and is 0.5 m behind Ben.
What is the min. value of h such that Ben can see the whole vase?
A. 0.13 m B. 0.24 m C. 0.3 m D. 0.9 m
2. The figure shows the path of a light ray passing through a right-angled glass prism in air. What is the
refractive index of the glass?
3. Media X and Y have refractive indices of nX and nY respectively, where nx <nY. Which of the following
statements are correct?
(1) Light travels faster in X than in Y .
(2) The critical angle of X in air is larger than that in Y.
(3) Total internal reflection CANNOT occur on a boundary formed by X and Y if light is
travelling in X initially.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 2
4. A red ray and a blue ray enter a glass prism with the same angle of incidence. Which of the
following diagrams may shows the correct emergent rays?
5. A convex lens of focal length 10 cm is placed 15 cm from a plane mirror as shown. When
an object is placed in front of the convex lens, an image is formed between the lens and the mirror.
What is the range of the object distance?
A. smaller than 30 cm
B. greater than 30 cm
C. between 15 cm and 30 cm
D. greater than 15 cm
6. The graph shows how the linear magnification m of an image varies with its distance from the lens v.
A lens of a longer focal length is used instead. Which of the following graphs is correct? (The original
graph is shown by the dotted line.)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 3
7. A car is travelling along a straight road. The figure below shows its velocity-time (v-t) graph.
Which of the following statements is/are INCORRECT?
(1) From t = 0 to 10 s, the displacement of the car is zero.
(2) From t = 0 to 10 s, the average speed of the car is 12 m s-1.
(3) From t = 8 to 10 s, the acceleration of the car is - 10 m s-2.
A. (1) only
B. (3) only
C. (1) and (2) only
D. (2) and (3) only
8. A car accelerates from rest to a speed of 40 m s-1 in 20 s. If the car travels along a straight line and the
distance travelled by the car is 300 m, which of the following graphs may show the variation
of the velocity v of the car against time t?
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 4
9.
An object accelerates uniformly from rest. The figure above shows the variation of its displacement
and the square of the time. Find the acceleration of the object.
A. 2 m s-2
B. 4 m s-2
C. 8 m s-2
D. 16 m s-2
10. A driver driving at 90 km h -1 on a straight highway sees a road-block 100 m in front of him.
If the car decelerates uniformly at 4 m s -2 during braking, what is the maximum reaction time of
the driver so that he can stop in front of the block?
A. 0.35 s
B. 0.5 s
C. 0.625s
D.0 . 8 7 5s
11. Which of the following statements about mass and weight is/are correct?
(1) Mass is scalar while weight is vector.
(2) Both the mass and weight of an object may vary from place to place.
(3) The weight of an object at a particular place on the earth is proportional to its mass.
A. (3) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (1) and (2) only
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 5
12. An elastic ball is dropped from a height. When it touches the ground, it rebounds to its original
position. Which of the following graphs may be the correct net force-time graph of the ball?
13. Two blocks are connected by an inextensible string as shown in the figure.
The objects are moved together by an external force of 17 N. The frictional forces acting on the
blocks A and B are 2 N and 3 N respectively. Find the tension in the string.
A. 4.0 N
B. 5.7 N
C. 6.0 N
D. 7.0 N
14.
The above diagram shows a block resting on the ground.
Let W be the weight of the block,
F be the gravitational force acting on the earth by the block, and
R be the force acting on the block by the ground.
Which of the following pairs of forces is/are action and reaction pair(s) according to Newton’s
third law of motion ?
(1) R and W
(2) W and F
(3) F and R
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 6
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1) and (3) only
15. A helicopter of weight W is moving horizontally to the left with uniform velocity as shown. Its rotating
blades are providing a lifting force L, which makes an angle of 15° with the vertical.
Find the drag R on the helicopter.
A. W tan 15o B. W / tan 15o C. W sin 15° cos 15° D. W / (sin 15° cos 15°)
16. Force F is the resultant of F1, F2 and F3. The figure below shows F, F1 and F2.
Which of the following figures best represents F3?
A. B.
C. D.
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 7
17. Which of the following objects is/are in equilibrium?
(1) an object falling with terminal velocity
(2) a boy standing on a scale (reading 600 N) at rest
(3) a merry-go-round which is coming to a stop
A. (1) only
B. (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1) and (2) only
18. On a straight horizontal road, a car of mass 1400 kg travels a distance of 96 m with a uniform
acceleration of 12 m s-2. What is the work done on the car?
A. 1.12 × 104 J B. 1.01 × 105 J C. 1.61 × 106 J D. 1.61 × 107 J
19. An object is released from rest in the air. Neglect air resistance. Which of the following graphs best
shows how its potential energy EP changes with its height s from the ground?
20. As shown in the figure, a truck of weight 12 000 N climbs up an inclined plane at a constant speed of
15 m s-1. If the average friction and the air resistance acting on the truck is 2000 N, what is the
average power output of the truck?
A. 30 000 W B. 60 000 W C.120 000 W D. 210 000 W
21. A 20 g bullet travelling at 400 m s -1 hits a 2 kg block which is placed on a table. The bullet embeds
itself in the block and moves the block. The block then slows down with constant deceleration
and eventually stops after 2.0 s.
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 8
Assume that air resistance is negligible. Find the average friction between the block and the surface
of the table.
A. 4.0 N
B. 8.5 N
C. 18.4 N
D. 40.2 N
22. On a smooth horizontal ground, ball A is travelling at a velocity of 2 m s-1 towards ball B which is at rest.
A and B have mass of 1 kg and 4 kg respectively.
The collision is elastic. What are the velocities of A and B afterwards?
ball A ball B
A. -1.2 m s-1 0.8 m s-1
B. -0.4 m s-1 1.6 m s-1
C. 0.4 m s-1 0.4 m s-1
-1
D. 1.2 m s 0.8 m s-1
23. Two identical cars A and B crash into different barriers and are brought to stop. The graph below
shows how the force F acting on each car changes with time t during the collision.
Which of the following statements about the two cars is/are correct?
(1) the speed of car A just before the collision is equal to that of car B.
(2) The change in momentum acting on car A is greater than that on car B.
(3) The average force acting on car A during collision has the same magnitude as that on car B.
A. (2) and (3) only
B. (1) and (2) only
C. (3) only
D. (1) only
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 9
24. The diagram below shows two balls X and Y. The mass of X is twice that of Y.
X is released to fall vertically at the same moment as Y is projected horizontally. Neglecting air
resistance, which of the following is / are correct?
(1) The vertical component of velocity of X when it hit s the ground is t he sam e as
t hat of Y.
(2) X hits floor before Y.
(3) The vertical acceleration of X is half that of Y.
A. (1) only
B. (3) only
C. (1) and (2) only
D. (2) and (3) only
25. In the figure, an aeroplane is travelling horizontally at constant velocity. Three bombs are dropped
from rest relative to the plane in equal time intervals.
If the air resistance is negligible, which of the foll owing diagrams correctl y s hows
the positions of the bombs as observed by people on the ground?
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 10
26. An object is projected at an angle from the ground. If the air resistance is negligible, which of the
following descriptions about the object at its highest position must be correct?
(1) The net force acting on the object reaches its maximum value.
(2) The speed of the object reaches its minimum value.
(3) The time taken for the object to reach its highest position is equal to one-half of the total time
of travel.
A. (1), (2) and (3)
B. (1) and (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
27. A bullet is fired horizontally towards a vertical wall 1.0 m away. It hits the wall at a point 0.5 m below
the point of projection. At what speed does the bullet hit the wall? Neglect air resistance.
A. 3.13 m s–1
B. 3.95 m s–1
C. 4.43 m s–1
D. 4.95 m s–1
28. A ball is kicked from O with an initial velocity u at an angle θ above the horizontal, as shown in the
figure below. The dotted line shows the trajectory A if there was no air resistance and the solid line
shows the actual trajectory B.
u
A
B
O
Which of the following statements are correct?
(1) The vertical speed of the ball at its maximum height is greater for trajectory A than that for
trajectory B.
(2) The initial horizontal speed of the ball is u cos for both trajectories.
(3) The horizontal speed of the ball at its maximum height is greater for trajectory A than that for
trajectory B.
A. (1), (2) and (3)
B. (1) and (2) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1) and (3) only
29. A stone is projected at an angle of 45° to the horizontal with an initial kinetic energy E. Neglect air
resistance. When the stone is at the highest position, its kinetic energy is
E 3E E
A. . B. . C. . D. E.
2 4 2
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 11
30. Ball A is situated on one end of a rail, while another ball B of the same mass is released from rest at the
other end of the rail.
When ball B falls to the end of the rail, two balls collide elastically, and ball A is projected outwards and
hits the ground at a horizontal distance x from its initial position. Find the distance x.
A. 0.13 m B. 0.30 m C. 1.00 m D. 3.13 m
End of Section A
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 12
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 13
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 14
Name: _________________________ Class: ________ No: _______
Section B Question-Answer Scripts
INSTRUCTIONS FOR SECTION B (60% of the paper)
Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your answers in the spaces provided. All numerical
answers should be either exact or correct to three significant figures. Marks will be deducted for
unclear presentation or incomplete sentences. The diagrams in this section are NOT necessarily
drawn to scale.
1. Sam stands on a weighing scale calibrated in Newtons in a lift. The graph below (figure 1) shows how
the reading of the scale varies with time t. The lift starts at t = 5 s.
reading / N
673
Figure 1
600
530
0 t/s
5 10 30 35
(a) Does the lift go up or down? (1 mark)
(b) Find Sam’s acceleration at t = 8 s. (3 marks)
(c) Find Sam’s acceleration at t = 32 s. (2 marks)
(d) Find Sam’s velocity at t = 20 s. (2 marks)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 15
2. A luggage of mass 20 kg moves with a constant velocity down a rough inclined plane as shown in
figure 2.
luggage Figure 2
40
(a) Draw the free-body diagram for the luggage. (2 marks)
(b) What is the magnitude of the normal reaction acting on the luggage? (2 marks)
(c) What is the magnitude of the friction acting on the luggage? (2 marks)
(d) If the plane is smooth, what is the acceleration of the luggage when it moves down? (2 marks)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 16
3.
Figure 3
A uniform metre rule with a small hole bored in the middle is pivoted by a pin inserted into the
hole, as shown in Figure 3. The weight of the metre rule is 1 N. An object P of weight 12 N
is suspended on the left-hand side of the metre rule at a distance of 0.12 m from the pin.
Another object Q is suspended on the right-hand side at a distance of 0.48 m, from the pin to balance
the metre rule.
(a) What is the moment of the weight of P about the pin ? (1 mark)
(b) Find the weight of Q. (2 marks)
(c) Find the force acting on the metre rule by the pin. (2 marks)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 17
4.
Figure 4
Kenneth, of mass 60 kg, falls vertically from rest from a 10 m platform into a swimming
pool (see Figure 4). In the following calculations, you may neglect the size of Kenneth.
(a) Find the potential energy of Kenneth when he stands on the platform, taking potential
energy at the water surface as zero. (1 mark)
(b) Find the speed of Kenneth at the instant he reaches the water surface. (2 marks)
(c) If Kenneth reaches a maximum depth of 3 m in the water, estimate the average resistive
force exerted by the water on Kenneth. (3 marks)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 18
5.
figure 5a
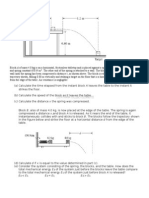
Fi gu re 5 a shows a c annon of m ass 1000 kg. It fires a metal ball off mass 10 kg in order to
destroy a fixed target. Assume the ball travels with a constant horizontal speed of 100 m s' towards
the target.
(a) Suppose that the minimum energy required to destroy the target is 60 000 J. Shown with
calculation, explain whether the ball will destroy the target. (2 marks)
(b) The cannon recoils as the ball is fired.
(i) Find the recoil speed of the cannon. (2 marks)
(ii)
Figure 5b
(c) To stop the cannon, a smooth plane inclined at 15° to the horizontal is placed behind the
cannon. (See Figure 5b) How far will the cannon move up along the inclined plane? (3 marks)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 19
(d) The ball hits the target and becomes embedded in it.
(i) If the ball takes 0.05 s to come to a rest inside the target, find the average force exerted by
the target on the ball. (2 marks)
(ii) A student thinks that as the ball and the target are both at rest after the impact, momentum
has been lost. He asks why the law of conservation of momentum does not apply in this
process. If you were a teacher, how could you answer this question? (3 marks)
6. In a data -logging experiment, a trolley of mass 0.5 kg moves on a smooth hori zontal
surface. It collides with a rigid wall and then moves backwards in the opposite direction. The
variation of the velocity of the trolley is recorded by a motion sensor and is shown in the figure 6.
Figure 6
(a) Find
(i) the change in momentum of the trolley in the collision, (2 marks)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 20
(ii) the time of impact, and (1 mark)
(iii) the average force acting on the trolley during the collision. (2 marks)
(b) Is the magnitude of average force acting on the wall during the collision equal to
that of the average force acting on the trolley? Explain briefly. (2 marks)
(c) Is total kinetic energy conserved in this collision? Show your justification with calculation.
(4 marks)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 21
7. Figure 7 shows a volleyball court in which a player is serving. The player jumps upwards and strikes the
ball so that it starts to move horizontally. When the ball is struck, the bottom of the ball is at a height of
2.70 m from the ground. It falls by 0.30 m to just clear the top of the net. Neglect air resistance.
Figure 7
(a) When the ball is struck, it is vertically above the service line
(i) Calculate the time the ball takes to fall 0.30 m. (2 marks)
(ii) The net is midway between the service line and the back line. Calculate the initial speed of
the ball if it is to just clear the net. (2 marks)
(b) (i) Determine whether the ball will land in the court, i.e. land between the back line and the net. (3 marks)
(ii) Suggest one technique the player may apply to ensure the ball lands in the court. ( 1 mark)
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 22
8. A car turns a corner on a level road with a constant speed as shown in Figure 8. The radius of curvature
of the road is 100 m. The car takes 10 s to move from X to Y.
Figure 8
(a) (i) Find the magnitude of the angular velocity of the car. (2 marks)
(ii) Hence, find the linear speed of the car. (1 mark)
(iii) Find the magnitude of the car’s angular displacement in 25 s. (1 mark)
(b) Find the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the car. (3 marks)
THE END
2018-19 F.4 Physics Final Examination Page 23
You might also like
- The Best Sports Training Book Ever - D.B. HammerDocument136 pagesThe Best Sports Training Book Ever - D.B. HammerJaron Kung100% (5)
- Fiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class 11th), Jee Advance Paper 1Document12 pagesFiitjee Phase Test 1 (Class 11th), Jee Advance Paper 1Shlok Sah73% (80)
- 1st Exam FinDocument18 pages1st Exam Finduncan pengchew limNo ratings yet
- Elegantia College (Sponsored by Education Convergence) Second Term Examination (2018 - 2019) Form 5 Combined Science - Physics (Section A)Document10 pagesElegantia College (Sponsored by Education Convergence) Second Term Examination (2018 - 2019) Form 5 Combined Science - Physics (Section A)edmond 黃No ratings yet
- Phy 2022-2023 F5 Term 2 MCDocument10 pagesPhy 2022-2023 F5 Term 2 MCElm TutchNo ratings yet
- 2009T1Document8 pages2009T1smk1992No ratings yet
- A Projectile Is Fired Horizontally From A Launching DeviceDocument10 pagesA Projectile Is Fired Horizontally From A Launching DeviceharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SJPO 2015 General Round - QuestionDocument23 pagesSJPO 2015 General Round - QuestionZleepNo ratings yet
- Final 1a03 Winter 2017 Version 1 WatermarkDocument18 pagesFinal 1a03 Winter 2017 Version 1 Watermarkproplayer910No ratings yet
- F4 - Phy P1 - 2018 End of YrDocument18 pagesF4 - Phy P1 - 2018 End of YrblueegofxNo ratings yet
- 4 VMXQ J9 R Qyj 7 Xo XUaj EBDocument49 pages4 VMXQ J9 R Qyj 7 Xo XUaj EBAhxhsNo ratings yet
- 2001 Newington Trial - Text.markedDocument25 pages2001 Newington Trial - Text.markedomhreemaimhreemNo ratings yet
- 2013 JC1 H2 Promo Sect ADocument8 pages2013 JC1 H2 Promo Sect AVarshLokNo ratings yet
- Iit PaceDocument19 pagesIit PaceabhishekjanjalkarNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample Finals Answer KeyDocument9 pagesPhysics Sample Finals Answer KeyChinny SabadoNo ratings yet
- Cranbrook 2000 Physics Prelim YearlyDocument7 pagesCranbrook 2000 Physics Prelim YearlyInferno Bros132No ratings yet
- F6 Physics Mock P1 AEXDocument14 pagesF6 Physics Mock P1 AEXporter100% (1)
- Physics HSSC 1 Paper IDocument8 pagesPhysics HSSC 1 Paper Ikirshnadembra44No ratings yet
- SJPO General Round SampleDocument19 pagesSJPO General Round SampleToh Qin KaneNo ratings yet
- Tampines Junior College JC 2 Semestral Assessment 2010: Physics H2 9646Document25 pagesTampines Junior College JC 2 Semestral Assessment 2010: Physics H2 9646Lelouch1337No ratings yet
- STPM 2018 Term 1 Trial MHSDocument13 pagesSTPM 2018 Term 1 Trial MHSchoichiangNo ratings yet
- Unit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice TestDocument11 pagesUnit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice TestChristian Firsching0% (1)
- India Outgoing SR (Y Programme) (2012 PAPER - 1 MODEL) Iitjee Model Exam Date: Time: 3:00 Max Marks: 210 Id - NoDocument9 pagesIndia Outgoing SR (Y Programme) (2012 PAPER - 1 MODEL) Iitjee Model Exam Date: Time: 3:00 Max Marks: 210 Id - Nojagan9912342495No ratings yet
- 1626957029Rituparna-SAT Physics Practice Paper 13Document15 pages1626957029Rituparna-SAT Physics Practice Paper 13dodo.thetruelegionNo ratings yet
- 2nd LE Sample ExamDocument13 pages2nd LE Sample ExamElla CardenasNo ratings yet
- HSSC 2011Document10 pagesHSSC 2011Rateeb AsmarNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Final QPDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Final QPfazeelm24No ratings yet
- Physics PAPER 2024Document7 pagesPhysics PAPER 2024Aditya GautamNo ratings yet
- Secondary Physics - TPT - Revised Tool - After PilotDocument14 pagesSecondary Physics - TPT - Revised Tool - After PilotTony MorerwaNo ratings yet
- F4 Final Exam 2122Document19 pagesF4 Final Exam 21225B04 CHOW HOI LAMNo ratings yet
- SJPO General Round 2008Document19 pagesSJPO General Round 2008shilgNo ratings yet
- AS Trial - 2004 Mar - P1Document14 pagesAS Trial - 2004 Mar - P1Syafiq Shazwan100% (1)
- Physics PahangDocument20 pagesPhysics PahangJuen LohNo ratings yet
- 2009 F-MaDocument9 pages2009 F-MaGeorge KongNo ratings yet
- SJPO General Round SampleDocument19 pagesSJPO General Round Sampleronghui009No ratings yet
- CareerPoint Iit JEE 2007 Paper I Question and SolutionsDocument15 pagesCareerPoint Iit JEE 2007 Paper I Question and Solutionsblue_l1No ratings yet
- Baulkham Hills 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument30 pagesBaulkham Hills 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & SolutionsTharanga MudaligeNo ratings yet
- A B CD A B CD A B CD 1oooo 6 Oooo11Oooo 2oooo 7 Oooo12Oooo 3oooo 8 Oooo13Oooo 4oooo 9 Oooo14Oooo 5Oooo10Oooo15OoooDocument5 pagesA B CD A B CD A B CD 1oooo 6 Oooo11Oooo 2oooo 7 Oooo12Oooo 3oooo 8 Oooo13Oooo 4oooo 9 Oooo14Oooo 5Oooo10Oooo15Oooominh nguyễnNo ratings yet
- NJC 2022 H2 Physics Prelim P1 QPDocument16 pagesNJC 2022 H2 Physics Prelim P1 QPYong JieNo ratings yet
- Physice IX First Term 2020 Paper I A (Answer Key)Document12 pagesPhysice IX First Term 2020 Paper I A (Answer Key)Haseeb MirzaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam A1Document3 pagesMidterm Exam A1Bá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- 2017 Sem 1 - Physics 1 Test 2 & MemoDocument8 pages2017 Sem 1 - Physics 1 Test 2 & MemomphoNo ratings yet
- Sec 4 Phy 2009Document368 pagesSec 4 Phy 2009Adrian100% (1)
- Form Three New FormatDocument7 pagesForm Three New FormatShomariNo ratings yet
- SG Physics PaperDocument18 pagesSG Physics Paperfyzc76tbdxNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1Document14 pagesPhysics Paper 1Mwape KeXiana MukukaNo ratings yet
- 2014 DSE Phy 1ADocument18 pages2014 DSE Phy 1AJetco LawNo ratings yet
- SC f3 CHP 7Document7 pagesSC f3 CHP 7ROSNI BINTI ISMAIL MoeNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument48 pagesJames Ruse 2020 Physics Prelim Yearly & Solutionsfortnitegamerpro123451No ratings yet
- PHY105 20182 Midterm2 VersionaDocument8 pagesPHY105 20182 Midterm2 Versionaemreno514No ratings yet
- Topics 1,2,6 Summative SLDocument14 pagesTopics 1,2,6 Summative SLAhmad OmarNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C 1998 With AnswersDocument16 pagesAP Physics C 1998 With AnswersjhbmleeNo ratings yet
- 1604025581SAT Physics Subject Test Question Paper 2Document28 pages1604025581SAT Physics Subject Test Question Paper 2hacksufi47No ratings yet
- University of Waterloo Physics 115 Final ExamDocument13 pagesUniversity of Waterloo Physics 115 Final ExamAashish GauravNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Review - DynamicsDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Review - DynamicsPremkumar NaikarNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 《論仁論孝論君子》Document7 pages《論仁論孝論君子》Chan KyleNo ratings yet
- Ch.23 Plastics and Addition PolymersDocument5 pagesCh.23 Plastics and Addition PolymersChan KyleNo ratings yet
- Ch.10 Transpiration, Transport and SuppoDocument15 pagesCh.10 Transpiration, Transport and SuppoChan KyleNo ratings yet
- Ch.21 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesCh.21 Introduction To Organic ChemistryChan KyleNo ratings yet
- Ch.9 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantDocument8 pagesCh.9 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantChan KyleNo ratings yet
- 香港特別行政區的法治Document3 pages香港特別行政區的法治Chan KyleNo ratings yet
- Meachanics and LightDocument12 pagesMeachanics and LightSomeone AroundNo ratings yet
- LeaP-Science-G4-Weeks 3-4-Q3Document4 pagesLeaP-Science-G4-Weeks 3-4-Q3Diana Marie Vidallon AmanNo ratings yet
- Doppler QuestionDocument3 pagesDoppler QuestionJohnNo ratings yet
- PS11BRDDocument7 pagesPS11BRDPreda AndreiNo ratings yet
- DAE ElectricalDocument194 pagesDAE Electricalalibanker100% (1)
- 1 Vortice de Agua PDFDocument4 pages1 Vortice de Agua PDFLechu SallesNo ratings yet
- HspsebssDocument48 pagesHspsebssdeepakNo ratings yet
- 24 IndoDocument34 pages24 IndoFebrina RahayuNo ratings yet
- Ncert Class 12 Physics Magnetism and MatterDocument35 pagesNcert Class 12 Physics Magnetism and MatterChandraMohanNo ratings yet
- 15ee73 Module 4Document39 pages15ee73 Module 4ethanNo ratings yet
- Phys 111 Final Exam Formulas - Fall 2011: DT DWDocument1 pagePhys 111 Final Exam Formulas - Fall 2011: DT DWVenkataramanan SureshNo ratings yet
- 1976013282Document88 pages1976013282luis900000No ratings yet
- Sediment TransportDocument75 pagesSediment Transportpooneh777No ratings yet
- Eddy Currents 3dDocument7 pagesEddy Currents 3dcik_sya87No ratings yet
- 9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument7 pages9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersbobNo ratings yet
- 7 Mechanical PrinciplesDocument2 pages7 Mechanical Principleszeyadahmedza24No ratings yet
- Crystal Test OscillatorsDocument3 pagesCrystal Test OscillatorsmathurashwaniNo ratings yet
- Topics Problem Set 5 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies (Final) 2nd Term 2020-2021Document1 pageTopics Problem Set 5 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies (Final) 2nd Term 2020-2021Franz SantosNo ratings yet
- Electromagetics Matlab ProjectDocument11 pagesElectromagetics Matlab ProjectSaloni AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Sunny Boy SWR 2500U: Installation and Operator's ManualDocument60 pagesSunny Boy SWR 2500U: Installation and Operator's ManualDavid Alessandro EspinosaNo ratings yet
- 1015 Modeling and Simulation of Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) Used in Power SystemDocument6 pages1015 Modeling and Simulation of Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) Used in Power SystemFajar Ari100% (1)
- Cable Sizing PDFDocument8 pagesCable Sizing PDFkumarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22jad obaidNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument22 pagesNewton's First LawJayPee BasiñoNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET AP Projectile MotionDocument2 pagesPROBLEM SET AP Projectile MotionmariniabrahanNo ratings yet
- Installation Operation Manual: Growatt New EnergyDocument33 pagesInstallation Operation Manual: Growatt New Energysteven6diaz-2No ratings yet
- Dire Dawa University: Institute of TechnologyDocument49 pagesDire Dawa University: Institute of TechnologyAsed ZakirNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines EE-260 Lecture-04: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamDocument12 pagesElectrical Machines EE-260 Lecture-04: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamSaif Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Phase-Shifting Transformers - July 2008Document34 pagesPhase-Shifting Transformers - July 2008paisanckNo ratings yet