299.08 - Renal Pathology) Chronic Kideny Disease (CKD)
299.08 - Renal Pathology) Chronic Kideny Disease (CKD)
Uploaded by
AnishilCopyright:
Available Formats
299.08 - Renal Pathology) Chronic Kideny Disease (CKD)
299.08 - Renal Pathology) Chronic Kideny Disease (CKD)
Uploaded by
AnishilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
299.08 - Renal Pathology) Chronic Kideny Disease (CKD)
299.08 - Renal Pathology) Chronic Kideny Disease (CKD)
Uploaded by
AnishilCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 11/12/2021
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD)
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Medical Editor: Donya Moslemzadeh
OUTLINE Mesangial cells
Interglomerular
I) INTRODUCTION Extraglomerular
II) CAUSES
o part of Juxtaglomerular complex
III) PATHOPHYSIOLOGY & CLINICAL FEATUERES
IV) DIAGNOSIS Overall function of Mesangial cells is protection of
V) TREATMENT Kidneys
VI) APPENDIX o Phagocytosis and Endocytosis
VII) REVIEW QUESTIONS o Structural Support
VIII) REFERENCES o Secretion of TGF-B and other Cytokines
o Etc.
I) INTRODUCTION
Juxtaglomerular Complex
Components
(i) Juxtaglomerular cells
Modified smooth muscle cells located in the
afferent arterioles
Renin Synthesis
(ii) Macula Densa
Monitors the NaCl concentration within the lumen
of the DCT
(iii) Extraglomerular Mesangial cells
Autoregulation of Blood flow
Afferent arteriole → Brings blood in
Efferent arteriole → Drains blood
(B) BASIC KIDNEY FUNCTIONS
Waste removal
o Drugs, Urea, Creatinine, etc.
Water balance
Electrolyte Balance
Figure 1. Structure of the Renal Corpuscle and the structures
o Ca2+, Na+, K+, PO43-
associated with it [Ross & Pawlina, 2015]
Acid-Base Balance
(A) REVIEW OF THE IMPORTATN KIDNEY Hormones
STRUCTURES o Erythropoietin
Nephron
(C) DEFINITIONS
Definition
Acute Kidney Injury, AKI
o Structural and Functional unit, o Abrupt Decrease in Renal Function
o composed of Renal Corpuscle and Renal Tubule
Chronic Kidney Disease, CKD
(i) Renal Corpuscle o ↓ Renal Function ≥ 3 months
o The renal corpuscle contains the filtration apparatus o ↓↓ Glomerular Filtration Rate =GFR (< 90)
of the kidney=Glomerular filtration barrier → 3
components
i. Glomerular Endothelium
ii. Glomerular Basement Membrane, GBM
iii. Visceral layer of Bowman's capsule
o Function: Filters fluid and produce ultrafiltrate
(ii) Renal Tubule
o Segments:
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Loop of Henle
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Connecting Tubule and collecting duct
o Function:
resorbs and secretes substances from the
ultrafiltrate, producing urine
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. 1 of 15
II) CAUSES
(A) HYPERTENSION (B) DIABETES
Second most common cause Most Common Cause
= Diabetic Nephropathy
Mechanism:
Mechanism:
High BP
(i) N.E.G
Non Enzymatic Glycosylation (also called Glycation) :
Consistent High BP o Glucose in the blood
(ii) Arteriolosclerosis
o Mesangial cells = Supportive cells o Diabetic Patients
Very sensitive to low O2
o Hyaline → protein deposition
o Atherosclerotic → fat deposition
(iii) Glomerulosclerosis
o arteriolosclerosis of the Efferent arteriole
(iv) Tubular Disease
o Arteriolosclerosis of the Efferent arteriole
Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules[Klatt, n.d.]
= Nodular glomerulosclerosis
Nodules of pink hyaline material form in regions of
glomerular capillary loops in the glomerulus. This is due
to a marked increase in mesangial matrix from damage
as a result of non-enzymatic glycosylation of proteins.
2 of 15 RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
(C) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS Glomerulosclerosis [AMBOSS, 2021]
A scarring of the renal glomeruli with deposition of
3 common cause
rd
extracellular matrix, which leads to impaired glomerular
Various Types filtration and proteinuria. Can occur in a segmental
pattern (e.g., in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis) or
o Secondary to autoimmune disease ,Lupus,
nodular pattern (e.g., in diabetic nephropathy).
rheumatoid arthritis
o Secondary to Infections like HIV, Hepatitis
Mechanism (D) POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE
Antigen-Antibody complex Inherited disorder
multiple cysts in the kidneys
2 Types:
o Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
(ADPKD)
Glomerular Endothelium o Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease
Glomerular Basement Membrane, GBM
Visceral layer of Bowman's capsule Mechanism:
• Contains Visceral Epithelial cells = o Cysts
Podocytes
↓ O2 Delivery to the tubular cells
↑ damage to GBM
↓Blood flow
(E) ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
Prolonged AKI
Frequent AKIs over time
Prostaglandins
Mechanism of NSAIDs
o Acts on COX enzyme
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. 3 of 15
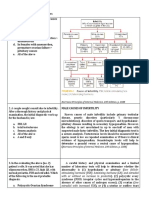
III) PATHOPHYSIOLOGY & CLINICAL FEATUERES
(A) ELECTROLYTE ABNORMALITIES (B) WATER IMBALANCE
Mechanism :
↓GFR
Lungs
Cardiovascular System
• Hypertension
Lower Extremities
• Peripheral Edema
Another mechanism that cause edema
o Albuminuria
• Pulmonary Edema
• Peripheral Edema
Albumin creates osmotic gradient to keep water in
(1) K+ and PO43- the vessels
Kidneys normally excrete two ions
o Potassium K+
o Phosphate PO43-
Hyperkalemia
o ↓GFR → ↓Excretion of K+→ Hyperkalemia
o Tubular damage → ↓Excretion of K+→ Hyperkalemia
Hyperphosphatemia
o ↓GFR →↓Excretion PO43- → Hyperphosphatemia
(2) Ca2+
Proximal Convoluted tubular cells Produce
Hypocalcemia
o ↓Kidney function
(3) Na+
Variable depending on the severity of CKD
Beginning → Stages Water retention → ↓sodium
Very Low GFR → Unable to Excrete Sodium
4 of 15 RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
(C) UREMIA (D) HORMONE IMBALANCE
Azotemia= Urea buildup without any organ damage (1) Erythropoietin
Uremia = Urea elevation with organ damage
Proximal Convoluted tubular cells
Clinical Features of Uremia
Encephalopathy
o Asterixis = Flapping Tremor
o Seizure
o Coma
o Fatigue CKD
o Nausea/vomiting o Damage of Proximal convoluted tubular cells
Uremic Pericarditis / Pericardial effusion
o Urea deposition in the pericardium
o Inflammation of the pericardium
o Normocytic and Normochromic Anemia
Uremic Frost
o Urea secreted in the sweat
Coagulopathy
o Uremia
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. 5 of 15
(2) Renin (3) PTH
CKD Vitamin D Synthesis:
o Renal Damage
o In skin
UV exposure
7 -Dehydrocholesterol → cholecalciferol (D3)
o liver
25-Hydroxylase
o kidney
1α-Hydroxylase
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone-ADH System
Components of RAAAS
Renin
o Enzyme produced by the kidneys
Angiotensinogen
o Protein produced by the liver §circulates in the blood
Angiotensin-I Figure 2. Vitamin D Metabolism. [ Brunton et al, 2017]
o precursor molecule ↓Kidney function
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)
o Mostly Produced by Capillary endothelial cells of the lungs
Angiotensin-II
o Extremely potent vasoconstrictive agent
Production of ANG-II ↓ Ca2+
↓Systemic BP, ↓ Blood Flow to the kidneys
If the kidney’s function was normal then PTH would
Renin converts Angiotensinogen made by the liver into increase the Calcium Reabsorption
Angiotensin-I PTH cannot increase Ca2+ by reabsorption from
Angiotensin-I circulates in the body and goes to lungs kidneys so it affects the bones → stimulate
Angiotensin-I in lungs reacts with Angiotensin Converting Osteoclasts →Bone Resorption → ↑ Ca2+
enzyme (ACE) High Bone turnover may cause various diseases:
ACE converts Angiotensin-I into Angiotensin o Renal Osteodystrophy
o Osteitis cystica fibrosa
Angiotensin-II Effects: o ↑ Risk of Fracture
Vasoconstriction
Angiotensin-II receptors on the vascular smooth muscle
Antidiuretic Hormone ADH
Angiotensin-II Stimulates Posterior Pituitary
Aldosterone
o Steroid Hormone produced by Zona Glomerulosa of the
adrenal medulla
o Angiotensin-II Stimulates Aldosterone Production from
Adrenal Cortex
o Aldosterone initiates K+ Excretion in the Urine
6 of 15 RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
(E) ACID-BASE IMBALANCE (F) ALBUMIN REGULATION
Mechanism : Mechanism:
↓Kidney function →↑ Albumin Excretion into the
Alpha-Intercalated cells in distal convoluted tubules Urine→↓ Albumin in the blood
and collecting duct
↓ Albumin in the blood
Kidney damage o →3rd spacing of Fluid
o → Stimulate Liver →↑ Protein production
→↑Lipoproteins →↑ TG and ↑LDL →
↓ Kidney function Hyperlipidemia
Third Spacing [UpToDate, 2021]
H+ retention+↑ HCO3- excretion
Third-spacing refers to the process of capillary leak
and extravasation of protein-rich serum into the
interstitial spaces of the soft tissues (e.g., skin, fat,
muscle), organs, deep space cavities (e.g., chest,
abdomen), or retroperitoneum.
Third-spacing into the soft tissue results in edema,
whereas fluid that leaks from the peritoneal or pleural
surfaces generates ascites or pleural effusion.
Hypoalbuminemia contributes to third-spacing; it is
theorized that the resultant intravascular oncotic
pressure, resulting from hypoalbuminemia, contributes
to the fluid shifting.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. 7 of 15
IV) DIAGNOSIS
History of (B) ALBUMINURIA
o Hypertension
o Diabetes Kidney damage marker
o Drugs Predictor of the severity of the disease
≥ 3 months Evidence of Kidney injury Urine analysis → Urine Albumin/Creatinine ratio
Table 2. Severity of the CKD based on albumin creatinine
o Markers → GFR, Albumin
ratio
(A) GFR Severity ACR (mg/g) Description
Normal GFR= 130 and 120 mL/min/1.73 m2 Normal to mildly
Mild <30
Best index of overall kidney function increased
Methods to Estimate GFR Moderate 30-299 Micro-Albuminuria
o Using Creatinine Severe ≥300 Macro-Albuminuria
o Serum cystatin C
Table 1. CKD staging based on GFR.
CKD GFR Description
Stages (mL/min/1.73 m2)
I >90 Normal or High
II 60-89 Mildly decreased
IIIa 45-59 Mildly to Moderately decreased
IIIb 30-44 Moderately to severely decreased
IV 15-29 Severely decreased
V <15 Kidney failure
Figure 3 Prognosis of CKD by GFR and Albuminuria
Category [KDIGO, 2012].
8 of 15 RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
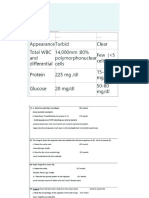
(C) RENAL ULTRASOUND (E) ADDITIONAL LAB TESTS
(1) Findings: Order BMP =Basic Metabolic Panel
o BMP measures: Glucose, Calcium, Sodium,
o Cysts → Diagnosis of polycystic kidney disease
Potassium, Bicarbonate, Chloride, BUN, Creatinine
(i) Small,
(ii) atrophic, Table 3. Additional Lab Tests for the Diagnosis of CKD.
(iii) fibrotic kidneys z
LAB Test Findings
o ↓perfusion, ↓vascularity (using Doppler Ultrasound)
Calcium Hypocalcemia
Sodium Hyponatremia or Hypernatremia
BMP
Potassium Hyperkalemia
Bicarbonate Low due to acidosis
Creatinine Use to estimate GFR
Phosphate Hyperphosphatemia
RBCs
Hb
Hct
Anemia
MCV
CBC
Normocytic= Normal MCV
MCH
MCHC
(D) RENAL BIOPSY + SEROLOGY WBC
Platelets
To Determine cause and types of Glomerulonephritis
(1) Renal Biopsy Serum Iron
May have Iron deficiency
Studies
Ferritin
Iron associated anemia
(2) Serology Transferrin
TIBC
(i) Antinuclear antibodies
ANA
(screening for Lupus) Bicarbonate
ABG
PaO2 Metabolic Acidosis
(ii) Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies SaO2
(ANCA;
for DX of Vasculitis, Goodpasture)
Lipid Panel
TG
(iii) RF (Rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis) LDL
(iv) Serology for hepatitis virus, and HIV ↑ TG and ↑LDL
HDL
Cholesterol
↑PTH
If Severe CKD and↑↑↑↑PTH →
PTH
Hypercalcemia
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. 9 of 15
V) TREATMENT
(A) SLOWING THE PROGRESSION OF CKD
Treat the underlying causes
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug (DMARD)
(1) HTN
Goal of Therapy: BP ≤ 130/80 A group of unrelated medications with
Treatment: immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory properties
that improve symptoms and prevent further disease
(i) RAAAS inhibitors progression. They are commonly used to treat
rheumatoid arthritis but may also be indicated in other
o ACEI diseases (e.g., malignancies, psoriatic arthritis, systemic
o ARBs lupus erythematosus). [AMBOSS, 2021]
o Potassium sparing diuretics
Table 4. Commonly Used DMARDs. [UpToDate, 2021]
(ii) Decrease H2O Retention
Traditional Biologic Other
o Diuretics
DMARDs DMARDs DMARDs
Loop Diuretics
o Sodium Intake Restriction → Low-Sodium Diet Etanercept Tofacitinib
Adalimumab Baricitinib
Infliximab
Methotrexate Upadacitinib
(2) Diabetes Certolizumab
Sulfasalazine Golimumab
Goal of Therapy: HbA1c < 6.5% Hydroxychloroquine Anakinra
Treatment: Leflunomide Abatacept
o Insulin Cyclosporine Rituximab
o Antidiabetic drugs Azathioprine
Metformin Tocilizumab
SGLT2 inhibitors Sarilumab
o Weight loss
o Diet Modification
(4) Polycystic Kidney Disease
(3) Glomerulonephritis
Treatment :
Treatment: o Control the secondary HTN and other complications
o Treat the underlying cause (e.g., Autoimmune
May lead to Renal Transplant
diseases, Inflammatory reactions)
o Steroids
o DMARDs (5) Discontinue Nephrotoxins
NSAIDs
Nephrotoxic Agents
10 of 15 RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
(B) MANAGING THE COMPLICATIONS OF CKD – ELECTROLYTES
May need Renal Replacement Therapy
(2) Hyperphosphatemia
(1) Hyperkalemia
Mechanism:
Mechanism: o ↓GFR →↑PO43- retention
o ↓GFR → ↓Excretion of K+→ Hyperkalemia
Treatment:
Treatment: o Dietary Phosphate Restriction
o Insulin o Phosphate binder
o Short-Acting Beta Agonists (SABA) Sevelamer Hydrochloride
Albuterol
(3) Hypocalcemia
o HCO3-
o Diuretics
Treatment:
Loop
Thiazide o Calcium
o Cation Exchanger o Vitamin D increase the calcium absorption
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (SPS) (4) Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
o If all failed → dialysis
Mechanism:
o If Severe CKD and ↑↑↑↑PTH → Hypercalcemia
Treatment:
o ↓ PTH production
Cinacalcet
o If Medications Fail → Parathyroidectomy
(C) MANAGING THE COMPLICATIONS OF CKD-HORMONES
(1) Anemia
Target : Hgb 8-10
(a) Mechanism:
o ↓EPO → ↓RBCs
Treatment:
o Synthetic Erythropoietin
(2) Secondary Hypertension
Goal of Therapy: BP ≤ 130/80
(a) Mechanism:
o ↓GFR
o Secondary HTN associated with elevated Renin
Treatment:
o ACEI
o ARBs
o Potassium sparing diuretics
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. 11 of 15
(D) MANAGING THE COMPLICATIONS OF CKD- (F) MANAGING THE COMPLICATIONS OF CKD-
WATER BALANCE ALBUMINURIA
Mechanism: Mechanism:
o ↑Albumin Excretion
o ↓GFR →↑H2O retention →↑volume overload
Manifestations:
• Pulmonary Edema
• Peripheral Edema Treatment:
• HTN o Proteinuria
ACEI (unknown mechanism)
Treatment: ARBs (unknown mechanism)
o Diuretics
Loop Diuretics Important ACEI and ARBs Side effects in CKD
Thiazide Diuretics patients
Potassium sparing diuretics o ↑ Creatinine
o Sodium Intake Restriction o Hyperkalemia
(G) MANAGING THE COMPLICATIONS OF CKD-
(E) MANAGING THE COMPLICATIONS OF CKD-
DYSLIPIDEMIA
ACIDOSIS
Mechanism: Mechanism:
o ↓ Albumin in the blood
o ↓Ability to excrete H → H retention
+ +
o ↑ HCO3- excretion
o H+ retention+↑ HCO3- excretion → Acidosis
o Acidosis → pH<7.2 → May affect
Cardiac System →↓Cardiac contractility
Electrolyte Abnormalities
Resistance to vasopressors Treatment:
Treatment: o Statins
o Sodium Bicarbonate (H) MANAGING THE COMPLICATIONS OF CKD-
PLATELET DSYFUNCTION
Mechanism:
o Uremia
Treatment:
o DDAVP = Desmopressin
Increase Platelets Activity
12 of 15 RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
(I) DIALYSIS
Need Dialysis if CKD worsening :
o Exacerbation of following conditions that are
refractory to medical therapies
Acidosis
Electrolyte abnormalities
Intoxication due to drug/waste accumulation
Volume Overload
Uremia
o Continuous reduction of GFR → Stage IV, V
Dialysis may be the bridge to Kidney Transplant
Different types of Dialysis :
o Peritoneal dialysis
o Hemodialysis
VI) APPENDIX
Table 5. Summary of CKD.
CKD
Decreased Kidney function for three or more months
Definition
Hypertension
Diabetes
Glomerulonephritis
Causes
Polycystic Kidney Disease
NSAID Overuse
Prolonged/ Recurrent AKI
Electrolyte Abnormalities Hyperkalemia
Hyperphosphatemia
Hypocalcemia
Water Imbalance Pulmonary Edema
o ↓H2O filtration Hypertension
o Albuminuria Peripheral Edema
Uremia Nervous System
o Encephalopathy
Asterixis
Pathophysiology & Clinical Features
Seizure
Coma
Cardiovascular System
o Uremic Pericarditis
Skin
o Uremic Frost
Platelets
o ↑ Risk of Bleeding
Hormone Imbalance Anemia
o EPO
o Renin Secondary Hypertension
o PTH
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism → CKD-related Bone Diseases
o Renal Osteodystrophy
o Osteitis cystica fibrosa
o Fractures
Acid-Base Imbalance Metabolic Acidosis
Albumin Imbalance Albuminuria → Hypoalbuminemia
o 3rd Spacing of fluids → Edema
o Hyperlipidemia
Additional Lab Tests
D
GFR
i
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. 13 of 15
CKD
Albumin o CBC
Ultrasound o BMP
Biopsy o ABG
Serology o Iron Studies
o Lipid Panel
o PTH
Slowing the progression of CKD HTN ACEI
ARBs
Diuretics
Low Sodium Intake
DM Insulin
Antidiabetic Drugs
Weight Loss
Diet Modification
Glomerulonephritis Steroids
DMARDs
PKD Treat Secondary HTN
Renal Transplant
Discontinue e.g., NSAIDs
Nephrotoxins
Managing the Complications Hyperkalemia
Insulin
Short-Acting Beta Agonists (SABA)
o Albuterol
HCO3-
Diuretics
o Loop
o thiazide
Cation Exchanger
Treatment
o Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (SPS)
If all failed → dialysis
Hyperphosphatemia Dietary Phosphate Restriction
Phosphate binder
o Sevelamer Hydrochloride
Hypocalcemia Calcium
Vitamin D
Secondary Cinacalcet
Hyperparathyroidism Parathyroidectomy
Anemia EPO
Volume Overload Diuretics
Low Sodium Intake
Acidosis Sodium Bicarbonate
Albuminuria ACEI
ARBs
Dyslipidemia Statins
Platelet Dysfunction DDAVP
Dialysis Exacerbation of following conditions that are refractory to medical therapies
o Acidosis
o Electrolyte abnormalities
o Intoxication due to drug/waste accumulation
o Volume Overload
o Uremia
Continuous reduction of GFR → Stage IV, V
14 of 15 RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
VII) REVIEW QUESTIONS
1) All the following conditions can cause CKD except:
a) Diabetes
b) Hypertension
c) Acute Kidney Injury less than 40 days
d) Polycystic kidney disease
2) The use of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
inhibitors is beneficial in patients with
a) Hypertension
b) Albuminuria
c) Hyperkalemia
d) A and B
3) The most common cause of CKD is
a) Diabetes
b) Hypertension
c) Glomerulonephritis
d) Polycystic Kidney Disease
4) A common marker of CKD is
a) Rash
b) Hematuria
c) Proteinuria
d) Bacteremia
5) Which statement is not true about the managing of
CKD complications:
a) Cation exchangers can be used to treat
Hyperkalemia.
b) Anemia in CKD patients is treated with Iron
Supplements only.
c) ARBs should Use cautiously in CKD patients with
Albuminuria.
d) Calcium and Vitamin D supplements can be used in
CKD patients with Hypocalcemia.
CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
VIII) REFERENCES
● Brunton, L., Knollman, B., & Hilal-Dandan, R. (2017). Goodman
and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13th
Edition. McGraw-Hill Education.
● AMBOSS: medical knowledge platform for doctors and students.
(n.d.). Amboss. Retrieved 2021, from https://www.amboss.com/
● UpToDate: Evidence-based Clinical Decision Support. (n.d.).
UpToDate.Com. Retrieved 2021, from
https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/solutions/uptodate
● Ross, M. H., & Pawlina, W. (2015). Histology: A Text and Atlas:
With Correlated Cell and Molecular Biology (7th ed.). Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins.
● Klatt, E. C. (n.d.). Renal Pathology. The Internet Pathology
Laboratory for Medical Education. Retrieved November 12, 2021,
from https://webpath.med.utah.edu/RENAHTML/RENAL027.html
● Lab Tests Online. (n.d.). Patient Education on Blood, Urine, and
Other Lab Tests. Retrieved August 22, 2021, from
https://labtestsonline.org/
● Le, T., Bhushan, V., & Sochat, M. (2021). First Aid for the
USMLE Step 1 2021, Thirty First Edition (31st ed.). McGraw-Hill
Education / Medical.
● Gabriel, D. (2019). USMLE Step 2 CK: A Student-to-student
Guide (Clinical Knowledge) (10th ed.). Independently published.
● Papadakis, M., McPhee, S., & Rabow, M. (2019). CURRENT
Medical Diagnosis and Treatment 2020 (59th ed.). McGraw-Hill
Education / Medical.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) RENAL PATHOLOGY: NOTE #8. 15 of 15
You might also like
- Derain Carla Elize-Group9 DXRDocument6 pagesDerain Carla Elize-Group9 DXRCarla Elize Derain100% (1)
- Kutesmart Case AnalysisDocument2 pagesKutesmart Case AnalysisRomen Samuel Wabina0% (1)
- OB-GYN Patient History and PEDocument4 pagesOB-GYN Patient History and PEAngelique TongsonNo ratings yet
- Ped Nephro 3rd Ed SchaeferDocument10 pagesPed Nephro 3rd Ed SchaeferAlonso Rodriguez EscobedoNo ratings yet
- CRD SubsampleDocument34 pagesCRD SubsampleFahmy Abo Walid Kseibi100% (3)
- Idoc - Pub Sketchy-MicroDocument2 pagesIdoc - Pub Sketchy-MicroCM NajitoNo ratings yet
- Nephrology - Proteinuria - SOAP Note - Manish Suneja PDFDocument4 pagesNephrology - Proteinuria - SOAP Note - Manish Suneja PDFΝίκος ΣυρίγοςNo ratings yet
- 2016 CPG Ent PDFDocument21 pages2016 CPG Ent PDFCamelle CelisNo ratings yet
- Roberts and Hedges: Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine (5th Edition)Document2 pagesRoberts and Hedges: Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine (5th Edition)Surya RajNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Henoch-Schönlein PurpuraDocument1 pageIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Henoch-Schönlein PurpuraMadelyn MedlingNo ratings yet
- MBR 2019 - Anes ENT Ophtha HandoutsDocument17 pagesMBR 2019 - Anes ENT Ophtha HandoutsNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- (PEDIA) Clerks Revalida Review 2022Document130 pages(PEDIA) Clerks Revalida Review 2022Sheila SantosNo ratings yet
- Determining The Cause: AnemiaDocument9 pagesDetermining The Cause: AnemiaSelina SubiasNo ratings yet
- Acute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument27 pagesAcute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisAlokh Saha RajNo ratings yet
- IM Ratio Endo 1 10 Charlie SamplexDocument3 pagesIM Ratio Endo 1 10 Charlie SamplexPaolo BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Nephrology Review NotesDocument6 pagesNephrology Review NotesEdilberto HernandezNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of The Passage-WilliamsDocument66 pagesAbnormalities of The Passage-Williamsapi-19641337100% (1)
- Gram Positive: NotesDocument37 pagesGram Positive: Notesgabb bbNo ratings yet
- Grace Medicial Reviewer Delivery 1233Document3 pagesGrace Medicial Reviewer Delivery 1233Jacob SamsonNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Glomerular DiseasesDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Glomerular DiseasesMaryam Fadah100% (1)
- Acute Pyelonephritis in Adults Rapid Evidence Review PDFDocument8 pagesAcute Pyelonephritis in Adults Rapid Evidence Review PDFMari aNo ratings yet
- Review of Pediatrics and NeonatologyDocument14 pagesReview of Pediatrics and Neonatologyrudraksh108108No ratings yet
- Emergencies For Onsite Revalida 2021 - 2022Document2 pagesEmergencies For Onsite Revalida 2021 - 2022Hal KingNo ratings yet
- Case Study 52 Cushing SyndromeDocument4 pagesCase Study 52 Cushing SyndromeAnonymous G7AdqnemziNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination ChecklistDocument5 pagesPhysical Examination ChecklistNiño Robert RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease AustrliaDocument63 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease AustrliaMuhammad Reza100% (3)
- Med History & PE GuideDocument7 pagesMed History & PE GuideStephanie GaerlanNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Clerks Revalida Review 2023Document106 pagesPEDIA Clerks Revalida Review 2023Raven Evangelista100% (1)
- Medical Case 1: Language Centre of Malahayati University at 2010Document16 pagesMedical Case 1: Language Centre of Malahayati University at 2010putri1114No ratings yet
- Nephrology ?Document52 pagesNephrology ?drxghamdiNo ratings yet
- RPGNDocument13 pagesRPGNArun GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Renal Tubular DisordersDocument40 pagesRenal Tubular DisordersHitesh Tanwar100% (1)
- Paeds Physical ExaminationDocument10 pagesPaeds Physical Examinationdrwra0% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWODocument6 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWOOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateDocument10 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateMirko S. León RguezNo ratings yet
- MED1 Samplex Rationale 6 - Endocrine DisordersDocument6 pagesMED1 Samplex Rationale 6 - Endocrine DisordersMartina GarciaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative EvaluationDocument4 pagesPreoperative EvaluationFadly Setiawirawan100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument6 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseAndrea GuidoteNo ratings yet
- Clinical Profile of Patients With Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric Age Group in Rural IndiaDocument7 pagesClinical Profile of Patients With Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric Age Group in Rural IndiaInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Alarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyDocument22 pagesAlarm Symptoms of Hematoonco in Pediatrics: Dr. Cece Alfalah, M.Biomed, Sp.A (K) Pediatric Hematology and OncologyMuhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Cardiology DR - Ahmed MowafyDocument150 pagesCardiology DR - Ahmed MowafyMohamed AlsaabNo ratings yet
- Identification of CKD: Algorithm ADocument3 pagesIdentification of CKD: Algorithm ArawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome 1: Eina Jane & Co. 2009Document11 pagesChapter 20: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome 1: Eina Jane & Co. 2009greenflames09No ratings yet
- CKD Algorithm EBG Approved April09Document1 pageCKD Algorithm EBG Approved April09Merry Aprila RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti-Epileptic DrugsKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- (Evidence-Based Medicine) Donald A. Molony, Jonathan C. Craig, Giovanni Strippoli - Evidence-Based Nephrology, 2 Volume Set-Wiley-Blackwell (2022)Document1,342 pages(Evidence-Based Medicine) Donald A. Molony, Jonathan C. Craig, Giovanni Strippoli - Evidence-Based Nephrology, 2 Volume Set-Wiley-Blackwell (2022)NMC NEPHROLOGYNo ratings yet
- Health HistoryDocument19 pagesHealth HistoryAngelene Caliva100% (1)
- Acute Medicine: Shock: Inadequate Tissue and Organ PerfusionDocument3 pagesAcute Medicine: Shock: Inadequate Tissue and Organ Perfusionmyat252No ratings yet
- Anemia SDocument5 pagesAnemia SGps PandetteNo ratings yet
- RAAS CKD ProgressionDocument86 pagesRAAS CKD ProgressionNikesh DoshiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Internal Medicine UKIDocument128 pages1 - Internal Medicine UKILewishoppusNo ratings yet
- List of Apmci Affiliated HospitalsDocument6 pagesList of Apmci Affiliated HospitalsJoy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- A To Z Diseases LISTS For NEETPGDocument5 pagesA To Z Diseases LISTS For NEETPGQworldNo ratings yet
- National Leaflet About CKD and eGFR For GPs (Updated September 2007)Document2 pagesNational Leaflet About CKD and eGFR For GPs (Updated September 2007)Dhika ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- AaDocument5 pagesAaYusril Marhaen100% (1)
- CKD Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesCKD Pocket GuideLutfi MalefoNo ratings yet
- Guide To The Comprehensive Pediatric H and P Write Up PDFDocument16 pagesGuide To The Comprehensive Pediatric H and P Write Up PDFnanaNo ratings yet
- Neurology Exam Checklist1Document6 pagesNeurology Exam Checklist1Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Pharmacology: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.Biomed Faculty of Medicine, UIIDocument27 pagesPediatric Pharmacology: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.Biomed Faculty of Medicine, UIIAfied Fitrah100% (1)
- P Harm Cheat SheetsDocument13 pagesP Harm Cheat SheetsJamielah Romano100% (1)
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Lesions of The EyeDocument4 pagesLesions of The EyeAnishilNo ratings yet
- Problem 3.12 Study Guide 1 Causes of Renal Failure 1. Discuss The Causes of Acute (Pre-Renal, Renal and Post-Renal) and Chronic Renal FailureDocument48 pagesProblem 3.12 Study Guide 1 Causes of Renal Failure 1. Discuss The Causes of Acute (Pre-Renal, Renal and Post-Renal) and Chronic Renal FailureAnishilNo ratings yet
- Pacific Access CategoryDocument1 pagePacific Access CategoryAnishilNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of 2018 SQ and Pac Pre Departure Settlement Information Pilot Final Report 08-01-0Document64 pagesEvaluation of 2018 SQ and Pac Pre Departure Settlement Information Pilot Final Report 08-01-0AnishilNo ratings yet
- Normal CXRsDocument19 pagesNormal CXRsAnishilNo ratings yet
- Pac Registration Guide For Fiji and TongaDocument18 pagesPac Registration Guide For Fiji and TongaAnishilNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 StatisticsDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 StatisticsAnishilNo ratings yet
- OSPEDocument6 pagesOSPEAnishilNo ratings yet
- Nihaal Sidhant Chand UU114 Report FinalDocument33 pagesNihaal Sidhant Chand UU114 Report FinalAnishilNo ratings yet
- Eye HXDocument2 pagesEye HXAnishilNo ratings yet
- Meningitis HXDocument2 pagesMeningitis HXAnishilNo ratings yet
- Bahan 3 SejarahDocument36 pagesBahan 3 SejarahSi Gam BatatNo ratings yet
- Carver 450 Voyager PilothouseDocument13 pagesCarver 450 Voyager PilothouseDenison Yacht SalesNo ratings yet
- Poultry LectureDocument15 pagesPoultry LectureLours LumapatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument3 pagesEndocrine Glandsdan 123No ratings yet
- 6.6 Notes - Trapezoids and KitesDocument12 pages6.6 Notes - Trapezoids and KitesAbrar DirdasawiNo ratings yet
- Manual Hota Heinner-DCH-650RIXDocument55 pagesManual Hota Heinner-DCH-650RIXIonescuTeodoraNo ratings yet
- Section 1: General ProvisionsDocument3 pagesSection 1: General Provisionsvictor mamaniNo ratings yet
- Bial T-2 Forecourt DBRDocument18 pagesBial T-2 Forecourt DBRShaileshRastogiNo ratings yet
- 50 Objective Questions For IT Officer With AnswerDocument6 pages50 Objective Questions For IT Officer With AnswerShuseel BaralNo ratings yet
- Honest Information About Your Septic System - YOU Make The Decision!Document4 pagesHonest Information About Your Septic System - YOU Make The Decision!Tally AnuNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Selected Human Resource Management Practices On Employees' Job Satisfaction in Ethiopian Public BanksDocument17 pagesThe Effect of Selected Human Resource Management Practices On Employees' Job Satisfaction in Ethiopian Public BanksRioBudiNo ratings yet
- Class 3 Computer StudiesDocument3 pagesClass 3 Computer StudiesTECHNO PASSPORTNo ratings yet
- Tag Question: 1. Positive Sentence, Negative TagDocument3 pagesTag Question: 1. Positive Sentence, Negative TagPanjul IdNo ratings yet
- Judicial Notice: The Law of Evidence II Notes Kobusinge K. Nyakoojo - Lectrurer UCU - Mukono 1Document4 pagesJudicial Notice: The Law of Evidence II Notes Kobusinge K. Nyakoojo - Lectrurer UCU - Mukono 1Moses MaiNo ratings yet
- Crown: To Wear or Not To Wear: Nora ShokrianDocument2 pagesCrown: To Wear or Not To Wear: Nora Shokrianoutdash2No ratings yet
- ATV320 ATV Logic Manual EN NVE71954 01Document66 pagesATV320 ATV Logic Manual EN NVE71954 01أبو أنس المسلمNo ratings yet
- CyberAces Module3-Python 3 ScriptsDocument16 pagesCyberAces Module3-Python 3 ScriptsCyrllandNo ratings yet
- How Many Calories Does Teen Girl Need - Google SearchDocument1 pageHow Many Calories Does Teen Girl Need - Google SearchdhsnskNo ratings yet
- CCNA Course Outline (R&S)Document6 pagesCCNA Course Outline (R&S)Akhtar MehmoodNo ratings yet
- 14132I White Mineral Oil SDS US V1 1Document6 pages14132I White Mineral Oil SDS US V1 1Fadhli KusumaNo ratings yet
- What Is VeneerDocument45 pagesWhat Is Veneeraliyah khalidNo ratings yet
- Discovering Tut The Saga ContinuesDocument9 pagesDiscovering Tut The Saga ContinuesAneesh RenuNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare and Psychology: Applying The Psychoanalytic Theory in A Midsummer Night's DreamDocument8 pagesShakespeare and Psychology: Applying The Psychoanalytic Theory in A Midsummer Night's DreamGabe Quintos100% (2)
- A Literature Review of Disaster Nursing Competencies in Japanese Nursing JournalsDocument14 pagesA Literature Review of Disaster Nursing Competencies in Japanese Nursing JournalsClaudya TamaNo ratings yet
- NSPC 2018 UpdatesDocument5 pagesNSPC 2018 UpdatesRahnelyn B BonillaNo ratings yet
- IEEE PDH (Modeling Vacuum Systems)Document1 pageIEEE PDH (Modeling Vacuum Systems)manuieeeNo ratings yet
- Microsoft TeamsDocument3 pagesMicrosoft TeamsHansika Weerasinghe100% (1)
- Understanding Units of Gas ConcentrationDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Units of Gas ConcentrationEnrique ArmandoNo ratings yet