0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsPROTEINS
PROTEINS
Uploaded by
VaibhavMittalThis document contains a chemistry test on biomolecules with 22 multiple choice and short answer questions covering topics like:
- The definition of a peptide linkage and the linkage joining amino acids
- How hydrogen bonding helps stabilize the alpha helix structure of proteins
- The difference between essential and non-essential amino acids
It also includes questions about:
- Nucleotides, nucleosides, and the structural differences between DNA and RNA
- Fat soluble vitamins and the diseases caused by their deficiency
- The mechanism of DNA replication
- The primary and secondary structures of proteins
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
PROTEINS
PROTEINS
Uploaded by
VaibhavMittal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThis document contains a chemistry test on biomolecules with 22 multiple choice and short answer questions covering topics like:
- The definition of a peptide linkage and the linkage joining amino acids
- How hydrogen bonding helps stabilize the alpha helix structure of proteins
- The difference between essential and non-essential amino acids
It also includes questions about:
- Nucleotides, nucleosides, and the structural differences between DNA and RNA
- Fat soluble vitamins and the diseases caused by their deficiency
- The mechanism of DNA replication
- The primary and secondary structures of proteins
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document contains a chemistry test on biomolecules with 22 multiple choice and short answer questions covering topics like:
- The definition of a peptide linkage and the linkage joining amino acids
- How hydrogen bonding helps stabilize the alpha helix structure of proteins
- The difference between essential and non-essential amino acids
It also includes questions about:
- Nucleotides, nucleosides, and the structural differences between DNA and RNA
- Fat soluble vitamins and the diseases caused by their deficiency
- The mechanism of DNA replication
- The primary and secondary structures of proteins
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pagePROTEINS
PROTEINS
Uploaded by
VaibhavMittalThis document contains a chemistry test on biomolecules with 22 multiple choice and short answer questions covering topics like:
- The definition of a peptide linkage and the linkage joining amino acids
- How hydrogen bonding helps stabilize the alpha helix structure of proteins
- The difference between essential and non-essential amino acids
It also includes questions about:
- Nucleotides, nucleosides, and the structural differences between DNA and RNA
- Fat soluble vitamins and the diseases caused by their deficiency
- The mechanism of DNA replication
- The primary and secondary structures of proteins
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
EIGHTTEENTH TEST OF CHEMISTRY (BIOMOLECULES – II)
M.M:40 TIME:1.30 hrs
1. Define a peptide linkage. 1
2. Write the name of linkage joining two amino acids. 1
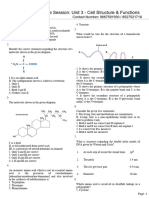
3. What type of bonding helps in stabilising the 𝛼- helix structure of proteins? 1
4. The deficiency of which vitamin causes the disease, pernicious anaemia? 1
5. Define the Zwitter ion with an example. 1
6. What is the biological effect of denaturation of proteins? 1
7. Where does the water of egg goes on boiling? 1
8. Amino acids may be acidic, alkaline or neutral. How does this happen? 1
9. Name the location where proteins are synthesize. 1
10.Why vitamin C cannot be stored in our body? 1
11.Write the name of the vitamin responsible for the coagulation of blood. 1
12.The two strands of DNA are not identical but are complementary. Explain. 2
13.What is a nucleotide? 2
14.Describe what do you understand by primary & secondary structure of proteins? 2
15.Name two fat soluble vitamins, their sources & the diseases caused due to their deficiency in
diet. 2
16.What are essential & non-essential amino acids? Give one example of each type. 2
17.What is the difference between a nucleoside & a nucleotide? 2
18.Difference between globular & fibrous proteins. 2
19.What is a dinucleotide & phosphodiester linkage? 3
20.Write the main structural difference b/w DNA & RNA. Of the four bases which are those
which are common to both DNA & RNA? 3
21.Describe the mechanism of replication of DNA. 3
22.Mention type of linkages responsible for the formation of the following: 4
a. Primary structure of protein
b. Cross linking of polypeptide chains
c. 𝛼- helix formation
d. 𝛽- sheet structure
You might also like
- Unit 1 Bozeman WorksheetsDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Bozeman Worksheetsa accountNo ratings yet
- Slide Paparan - Dicky - Potensi Genomik DM BGSIDocument27 pagesSlide Paparan - Dicky - Potensi Genomik DM BGSIFebrian DewiNo ratings yet
- Semester-II Paper-VI: Computer Aided Drug Designing (CADD) : Practicals Pertaining To Above TopicsDocument12 pagesSemester-II Paper-VI: Computer Aided Drug Designing (CADD) : Practicals Pertaining To Above Topicschandan kumarNo ratings yet
- Core Practical Notes 1Document14 pagesCore Practical Notes 1Books100% (1)
- Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules TestDocument3 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Biomolecules Testankitsingh90No ratings yet
- GR 11 Biomolecules Study Materials - Case Study (2023)Document9 pagesGR 11 Biomolecules Study Materials - Case Study (2023)salvatoreelena039No ratings yet
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Document9 pagesUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)percivalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Chemistry of LifeDocument44 pagesUnit 1: Chemistry of Life(25) Yahya Kagan AksunNo ratings yet
- 185954.mswordDocument3 pages185954.mswordlosim3125No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ap Biology Review GuideDocument12 pagesUnit 1 Ap Biology Review Guideapi-605991044No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Biomolecules)Document6 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Biomolecules)SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Part - VDocument5 pagesPart - Vmonika1009moniNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Review GuideDocument4 pagesBiochemistry Review Guidegeorginametcalf1No ratings yet
- Biology Summer WorkDocument2 pagesBiology Summer WorkPinkiPonki2No ratings yet
- Biomolecules WorksheetDocument3 pagesBiomolecules WorksheetksvyamunaaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Atoms Covalently Bond-Ed To Each OtherDocument10 pagesCarbon Atoms Covalently Bond-Ed To Each OtherlayanhaliloNo ratings yet
- The World of Chemistry Genetic Code SGDocument3 pagesThe World of Chemistry Genetic Code SGowls_1102No ratings yet
- StudyGuide Lecture1 4 Chapter2 5Document4 pagesStudyGuide Lecture1 4 Chapter2 5Eunice Kellin QuinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Work Sheet Ch10Document2 pagesChemistry Work Sheet Ch10jinop79764No ratings yet
- 07b Biochemistry Review WorkDocument6 pages07b Biochemistry Review Workututoringunion1No ratings yet
- G10 Q4 Week4finalDocument12 pagesG10 Q4 Week4finalANALYN DEL CASTILLONo ratings yet
- MC 2 Worksheet Week 4Document3 pagesMC 2 Worksheet Week 4Leah Mariz RocaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Outline and Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesCH 2 Outline and Practice Questionsk4cx7gpgmkNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Past PapersDocument2 pagesBiomolecules Past Papersharshiiiii352No ratings yet
- 2.4 ProteinsDocument18 pages2.4 ProteinsMohammad Ali Al-IadyNo ratings yet
- Bio Mole CuleDocument13 pagesBio Mole CuleaayanNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESSDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESScse.220840131017No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument1 pageBiomoleculesbarinasafdar10No ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument7 pagesBIOMOLECULESMasum AhmedNo ratings yet
- XI Board QsDocument25 pagesXI Board Qssadiau270No ratings yet
- AP+Bio 042+Biological+Molecules+Worksheet WLDocument2 pagesAP+Bio 042+Biological+Molecules+Worksheet WLSabrina LouiseNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure: Group Based Learning Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesProtein Structure: Group Based Learning Learning Objectiveskxng crockedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument2 pagesChapter 14 BiomoleculesAaryaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules OCR EditDocument242 pagesBiological Molecules OCR Editteeb1826No ratings yet
- Tutorial Study Guide: NSC 1110 - BiologyDocument14 pagesTutorial Study Guide: NSC 1110 - BiologyKalinda MondeNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Biology Important Short &long QuestionsDocument4 pages1st Year Biology Important Short &long Questionsbdigitalacademy3367No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region Xii Division of Sultan KudaratDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region Xii Division of Sultan KudaratMaribel membradoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Work Sheet Ch10Document2 pagesChemistry Work Sheet Ch10jinop79764No ratings yet
- Chap5 ChemcomposeDocument20 pagesChap5 ChemcomposeatynzatyNo ratings yet
- Faq in Acids, Bases, PH Short Answer QuestionsDocument5 pagesFaq in Acids, Bases, PH Short Answer QuestionsransinghNo ratings yet
- SLG Chem 3 LG 5.11 Biomolecules As Natural PolymersDocument10 pagesSLG Chem 3 LG 5.11 Biomolecules As Natural PolymersfranzachilleslindayagNo ratings yet
- 12 Qa-BiomoleculesDocument6 pages12 Qa-BiomoleculesSUMIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Proteins Ib Biology PresentationDocument33 pages2.4 Proteins Ib Biology PresentationIker GNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules WorksheetDocument10 pagesMacromolecules WorksheetShaira BautistaNo ratings yet
- 3 ProteinsDocument42 pages3 ProteinsTeam BEENo ratings yet
- 3.6 (Lesson 1) Proteins LPDocument22 pages3.6 (Lesson 1) Proteins LP4qx55wxzxrNo ratings yet
- Super Live Session - Unit 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionsDocument6 pagesSuper Live Session - Unit 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionsAvishek tiadiNo ratings yet
- Identification of Macromolecules LabDocument10 pagesIdentification of Macromolecules Labapi-318129862No ratings yet
- CH 3 NotesDocument40 pagesCH 3 Notesbaileigh5995No ratings yet
- Easter Revision Day 1 Work Book 1712165354Document31 pagesEaster Revision Day 1 Work Book 1712165354robinsonbryNo ratings yet
- Molecule La BMGDocument4 pagesMolecule La BMGKevin KocotNo ratings yet
- Las Sci10 Q4W4Document5 pagesLas Sci10 Q4W4Stephen Zachary SilagaNo ratings yet
- Bio 151 Exam 1 PracticeDocument5 pagesBio 151 Exam 1 PracticehNo ratings yet
- Learning Targets Unit 1Document3 pagesLearning Targets Unit 1api-522789883No ratings yet
- Biomolecules WorksheetDocument2 pagesBiomolecules WorksheetakhilmattayNo ratings yet
- 2 4proteinsDocument35 pages2 4proteinsKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study Guide - TaggedDocument3 pagesExam 1 Study Guide - Taggedjlconnors941No ratings yet
- Protein StructureDocument11 pagesProtein Structurelol heyNo ratings yet
- Essential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismsDocument29 pagesEssential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismshzunigaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Chemistry and the Body: Things You Should Know (Questions and Answers)From EverandAnatomy and Physiology: Chemistry and the Body: Things You Should Know (Questions and Answers)No ratings yet
- Molecular System Bioenergetics: Energy for LifeFrom EverandMolecular System Bioenergetics: Energy for LifeValdur SaksNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Oxidative Stress: Chemistry, Mechanisms, and Disease PathogenesisFrom EverandMolecular Basis of Oxidative Stress: Chemistry, Mechanisms, and Disease PathogenesisNo ratings yet
- PH.D Engineering ProgrammeDocument5 pagesPH.D Engineering ProgrammeVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- Revision Tests - MathsDocument6 pagesRevision Tests - MathsVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- Revision TestsDocument8 pagesRevision TestsVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- Revision Test III MathsDocument7 pagesRevision Test III MathsVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- (Asce) CF 1943-5509 0001738Document1 page(Asce) CF 1943-5509 0001738VaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- Revision Test II ChemistryDocument8 pagesRevision Test II ChemistryVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- Maths ObjectiveDocument4 pagesMaths ObjectiveVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- 2021 Priyanka Clay Subgrade PracticePeriodical ASCEDocument13 pages2021 Priyanka Clay Subgrade PracticePeriodical ASCEVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- Micro MCQDocument26 pagesMicro MCQabdulNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer A Review of Risk FactorsDocument7 pagesBreast Cancer A Review of Risk FactorsKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On LiverDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Liverhyzypif0gif3100% (1)
- Biology Semester 2 ExamDocument4 pagesBiology Semester 2 ExamMaaz MinhasNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 4 Staining Techniques Answer SheetsDocument2 pagesExercise No. 4 Staining Techniques Answer SheetsRhyn Ruz DohilagNo ratings yet
- Clinical Immunology Nima Rezaei Full ChapterDocument51 pagesClinical Immunology Nima Rezaei Full Chaptertim.morrison630100% (18)
- SOP Final UpdatedDocument4 pagesSOP Final UpdatedKesehoNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Lab Manual Term-Ii Practical Content 2021-22Document11 pagesClass 12 Biology Lab Manual Term-Ii Practical Content 2021-22MY - Moody YashNo ratings yet
- How The Body WorksDocument221 pagesHow The Body WorksNada Al Baridi100% (3)
- Red Dragon Fruit As Natural DyeDocument7 pagesRed Dragon Fruit As Natural DyeKiersten GabatoNo ratings yet
- ALL EST REAL Biology Exams BY DR. MAI ABD EL SalamDocument152 pagesALL EST REAL Biology Exams BY DR. MAI ABD EL Salamminhpham90012No ratings yet
- Midterm Topics Hema 1 LecDocument37 pagesMidterm Topics Hema 1 Lec4jzbxz64kqNo ratings yet
- Frac Code List 2020 FinalDocument15 pagesFrac Code List 2020 FinalIoan GugNo ratings yet
- Biodegradable PolymerDocument33 pagesBiodegradable PolymerMohamed Abu-BakrNo ratings yet
- The C. Elegans F-box/WD-repeat Protein LIN-23 Functions To Limit Cell Division During DevelopmentDocument12 pagesThe C. Elegans F-box/WD-repeat Protein LIN-23 Functions To Limit Cell Division During DevelopmentStrahil NikolovNo ratings yet
- Book PDFDocument569 pagesBook PDFprabhudevmvNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Physiology BLOODDocument50 pagesVeterinary Physiology BLOODGagan shri Bankira roll-43No ratings yet
- Dickins & Dickins (Eds.) (2023) Evolutionary Biology - Contemporary and Historical Reflections Upon Core TheoryDocument606 pagesDickins & Dickins (Eds.) (2023) Evolutionary Biology - Contemporary and Historical Reflections Upon Core TheoryFabregasAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 TestDocument8 pagesChapter 7 Testkwilliams1994No ratings yet
- Lipolysis and Aerobic ExerciseDocument11 pagesLipolysis and Aerobic ExerciseAna Flávia SordiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 2 LectureDocument46 pagesClinical Chemistry 2 LectureGillian Joy Pagaling100% (1)
- Reproduction in VertebratesDocument18 pagesReproduction in Vertebratesapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Animal BreedingDocument423 pagesAnimal BreedingShuguta LatiNo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Zoology Research Paper TopicsDocument7 pagesVertebrate Zoology Research Paper Topicsafmcuvkjz100% (1)
- 24 Angelaki Nature 2004Document5 pages24 Angelaki Nature 2004sebNo ratings yet
- Importance of MetamorphosisDocument3 pagesImportance of MetamorphosisAfrid BaigNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledSaurav sharmaNo ratings yet