ED2
ED2
Uploaded by
jeffrey QuezoraCopyright:
Available Formats
ED2
ED2
Uploaded by
jeffrey QuezoraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
ED2
ED2
Uploaded by
jeffrey QuezoraCopyright:
Available Formats
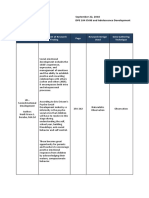
Theory related to learner Proposition Implications of Education
Development
1. Freud Freud's initial proposition was that the Freud's theory suggests that human
root causes of dysfunctional behavior is influenced by unconscious
psychological symptoms (neuroses) memories, thoughts, and urges. This
that interfered with normal human theory also proposes that the psyche
functioning were the continuing comprises three aspects: the id, ego,
harmful effects of traumatic and superego. The id is entirely
experiences that had been repressed unconscious, while the ego operates
from conscious awareness but in the conscious mind.
continued to control an individual's
conduct, feelings
2. Ericson By creating connections that make adhere to instructional materials
the unimaginable possible, we are matching individuals' developmental
helping to shape an exciting and stages. It should be expected that
positive future. A world where learners progress in their educational
limitless connectivity improves lives, needs in a certain approximate
redefines business and pioneers a structure, but with variations.
sustainable future.”
3. Piaget Piaget called this proposition Piaget's research has generated many
constructivism – individuals construct suggested implications for teaching,
their knowledge of the world based five issues have been selected for
on their experience. Learning requires discussion. These are stage-based
the resolution of conflicts between teaching, uniqueness of individual
dialectically opposed modes of learning, concep- tual development
adaptation to the world. Conflict, prior to language, experience in-
differences, and disagreement are volving action, and necessity of social
what drive the learning process. interaction.
4. Kohlberg Kohlberg’s theory suggests that moral By following Kohlberg's theory of
development occurs in a series of six moral development stages, teachers
stages and that moral logic is can understand their students best. As
primarily focused on seeking and the theory has contributed to every
maintaining justice. Here we discuss stage of growth of a child, teachers
how Kohlberg developed his theory can analyse their students' behaviour.
of moral development and the six It will help them change their
teaching methodology with the
stages he identified as part of this
children's growing age.
process
5. Vygotsky Vygotsky recognized the significant Human action is situated in
role of play in a child’s development, sociocultural, historical settings, and
particularly in the development of is mediated by tools and signs. All
self-regulation skills. Play allows human actions, including thinking,
children to engage in activities within are mediated by material and
their Zone of Proximal Development, symbolic objects (tools and signs) that
where they can practice and advance are culturally constructed and socially
used.
their self-regulatory abilities.
Additionally, through social
interactions during play, children
learn to manage their behavior,
emotions, and thoughts, enhancing
their overall self-regulation.
Therefore, play serves as a valuable
tool for children to develop essential
skills and abilities necessary for their
cognitive, social, and emotional
growth.
6. Brofenbrener Bronfenbrenner’s ecological systems Educational Implications of the
theory focuses on the quality and Ecological Systems TheoryThe
context of the child’s environment. school environment that occupies the
He states that as a child develops, the first layer of Bronfenbrenner model
interaction within these (microsystem) should work such,
environments becomes more that the key objective should be to
complex. This complexity can arise as make sure that a child's primary
relationships, which is the immediate
the child’s physical and cognitive
and larger famly, must last a lifetime.
structures grow and mature.
You might also like
- Theory PosterDocument2 pagesTheory PosterSonja LueNo ratings yet
- RCC 3.13Document25 pagesRCC 3.13Hayley Rose100% (1)
- Edu 530: The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument6 pagesEdu 530: The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesApple Apdian BontilaoNo ratings yet
- Osma, Emmarose - Bcaed-I (Child and Adolescent Development)Document4 pagesOsma, Emmarose - Bcaed-I (Child and Adolescent Development)Zane FavilaNo ratings yet
- Cereal Bar MachineryDocument7 pagesCereal Bar MachineryClaudia Lorena BuenoNo ratings yet
- ED2Document1 pageED2jeffrey QuezoraNo ratings yet
- PSY101-Sulibran-Activity 1Document3 pagesPSY101-Sulibran-Activity 1Kent VillelaNo ratings yet
- Report Kay Maam PriscillaDocument16 pagesReport Kay Maam PriscillaSheryl FajardpNo ratings yet
- Educ 201 - 2-Sedm1 - Domingo - Activity1Document3 pagesEduc 201 - 2-Sedm1 - Domingo - Activity1Crystal DomingoNo ratings yet
- Ece 15 - Module 1 - LacoDocument6 pagesEce 15 - Module 1 - LacoJELLAMIE LACONo ratings yet
- BlablablaDocument6 pagesBlablablaNathaniel AzulNo ratings yet
- Assessment 3Document3 pagesAssessment 3Vhlenky PortezaNo ratings yet
- Educ8 - Special and Inclusive Education Module5Document6 pagesEduc8 - Special and Inclusive Education Module5Giela S. DoriaNo ratings yet
- Bonajos, MiladyDocument7 pagesBonajos, MiladyMia ManayagaNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescen Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument15 pagesChild and Adolescen Learners and Learning PrinciplesLandz Buado IINo ratings yet
- Theories Related To The Learners DevelopmentDocument1 pageTheories Related To The Learners DevelopmentKim Timothy PinedaNo ratings yet
- ChildAndAdolescent ReviewerDocument5 pagesChildAndAdolescent ReviewerMichelle Villareal CuevasNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Educ70 Module 3-10Document17 pagesReviewer Educ70 Module 3-10Joyce Marielle SerratoNo ratings yet
- Child Development AssignmentDocument13 pagesChild Development AssignmentMAKABONGWE SHAQUILLE100% (1)
- Pde 505Document9 pagesPde 505PemarathanaHapathgamuwaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document5 pagesLesson 6Karen kaye De guzmanNo ratings yet
- 7 Domains of DevelopmentDocument35 pages7 Domains of DevelopmentJanet TarnateNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Development of Children Adolescents Written ReportDocument4 pagesCognitive Development of Children Adolescents Written ReportThrina DubbNo ratings yet
- Child Development Theories by SGH.JDocument13 pagesChild Development Theories by SGH.Jsgh education100% (1)
- Theories of DevelopmentDocument45 pagesTheories of DevelopmentZeeshan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Ed 1 MODULES 8-9Document13 pagesEd 1 MODULES 8-9Florence SenditoNo ratings yet
- Moral Development Theory: Y Awrence OhlbergDocument39 pagesMoral Development Theory: Y Awrence OhlbergDaryll Jim AngelNo ratings yet
- Areas Piaget Vygotsky: Theory ComparisonDocument1 pageAreas Piaget Vygotsky: Theory ComparisonJana Luz Dumam-ag PabalayNo ratings yet
- Hand Out PDFDocument6 pagesHand Out PDFJoanna Lyn PonceNo ratings yet
- ObservationDocument20 pagesObservationNurul KayNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Development of A ChildDocument18 pagesCognitive Development of A ChildLizze Agcaoili Arizabal100% (1)
- North Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteDocument14 pagesNorth Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteAnalyn FielNo ratings yet
- 64c6337d8ffaf AssignmentDocument8 pages64c6337d8ffaf AssignmentNgacha hitsNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingDocument4 pagesModule 9 - Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingSheila Mae Paltep100% (3)
- Activity 1 Child and Adolecence 1Document5 pagesActivity 1 Child and Adolecence 1Kim Jung UnNo ratings yet
- Field Study 1 ReviewersDocument13 pagesField Study 1 ReviewersJovie Dealca PratoNo ratings yet
- Human Growth &developmentDocument104 pagesHuman Growth &developmentMyka FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Learning TheoriesDocument19 pagesCognitive Learning TheoriesHibajene MweembaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Development From John W. Santrock - Educational Psychology-McGraw-Hill Education (2017) - 094427Document26 pagesCognitive Development From John W. Santrock - Educational Psychology-McGraw-Hill Education (2017) - 094427btsarmy1800No ratings yet
- Educational PsychologyDocument3 pagesEducational Psychologyirish xNo ratings yet
- Activity For Theories of DevelopmentDocument3 pagesActivity For Theories of DevelopmentYEEHSHIN JILL GAYONo ratings yet
- Social Constructivist TheoryDocument19 pagesSocial Constructivist TheoryDaniel Dube100% (1)
- Child DevelopmentDocument10 pagesChild DevelopmentMichael M. MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Significants LearningDocument6 pagesSignificants LearningMelvin SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Psychology For Language TeachersDocument4 pagesPsychology For Language TeachersLara Vigil GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3539437663596091703Document46 pagesInbound 3539437663596091703Sheila Mourine Tud BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2ramrom1975No ratings yet
- Module Ed1Document33 pagesModule Ed1Kyla Jelinne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 103 ReviewerDocument4 pagesProf Ed 103 ReviewerJenny May Jose TumabangNo ratings yet
- Human Developmental TheoriesDocument9 pagesHuman Developmental TheoriesAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- КСLecture 3-4Document17 pagesКСLecture 3-4Асилбек АружанNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1 Psic Educat YokastaDocument5 pagesTarea 1 Psic Educat YokastaMiguel LopezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document12 pagesAssignment 1G. B.No ratings yet
- Kohlberg Et. AlDocument7 pagesKohlberg Et. AlMay ann AntonioNo ratings yet
- Educ 211 W7 11Document47 pagesEduc 211 W7 11Eugene BaronaNo ratings yet
- FactSheet Group10HEDocument20 pagesFactSheet Group10HEaubreycanto4No ratings yet
- tionthroughBehavioralResponsesinAlgerianCollegeEducation-1Document15 pagestionthroughBehavioralResponsesinAlgerianCollegeEducation-1loverstak73No ratings yet
- Ped 101 ReviewerDocument8 pagesPed 101 ReviewerAliya JimenezNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1-Week 1 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument5 pagesMODULE 1-Week 1 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesMarsha MGNo ratings yet
- Educating the Whole Child: A Parent's Guide to Holistic DevelopmentFrom EverandEducating the Whole Child: A Parent's Guide to Holistic DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Reflective About Long LearningDocument4 pagesReflective About Long LearningDita DesalegnNo ratings yet
- AeroflexDocument4 pagesAeroflexPT. Bali Cukup MandiriNo ratings yet
- SANS 2505 Comparison 26-06-2023Document33 pagesSANS 2505 Comparison 26-06-2023pdzawarNo ratings yet
- Adam Smith: History of Economic ThoughtDocument14 pagesAdam Smith: History of Economic ThoughtBrendan RiceNo ratings yet
- Resilient File System (ReFS)Document40 pagesResilient File System (ReFS)Senthil Kumar MNo ratings yet
- 2020-10-22 Planning Guidline For MV ProtectionDocument62 pages2020-10-22 Planning Guidline For MV ProtectionThilina Rajapaksha100% (1)
- Perfil Fuerza-VelocidadDocument9 pagesPerfil Fuerza-Velocidadtasibem614No ratings yet
- What Is Forest School - Forest School AssociationDocument5 pagesWhat Is Forest School - Forest School AssociationLIM SENG CIN MoeNo ratings yet
- ConclusionGuidelines Lab ReportDocument2 pagesConclusionGuidelines Lab Reportxryceu100% (1)
- Precios AgostoDocument19 pagesPrecios AgostoLuis Alonso Vera VeraNo ratings yet
- User Report Remog ATLDocument3 pagesUser Report Remog ATLHugo NeriNo ratings yet
- Reflection On Evolutionism and Its TheoriesDocument9 pagesReflection On Evolutionism and Its TheoriesAdam Keth J. LaquioNo ratings yet
- Faust LibrariesDocument163 pagesFaust LibrariesItzá GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Etabloc Syt Operating InstructionsDocument50 pagesEtabloc Syt Operating InstructionsFayeez MukadamNo ratings yet
- Biological SafetyDocument14 pagesBiological SafetyTrường NhânNo ratings yet
- Traction Ferroviaire Electrique - Electronique de Puissance Et (PDFDrive)Document65 pagesTraction Ferroviaire Electrique - Electronique de Puissance Et (PDFDrive)lolaNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 6 - Patterns and Equations Unit PlanDocument8 pagesMath Grade 6 - Patterns and Equations Unit Planapi-242345831No ratings yet
- DMW Unit4Document39 pagesDMW Unit4Akshay RathodNo ratings yet
- Animated Scene PlanningDocument2 pagesAnimated Scene Planningapi-539931780No ratings yet
- Symmetrical ComponentsDocument32 pagesSymmetrical ComponentsReza SiavoshiNo ratings yet
- Ergonomic Risk Assessment of Workers in Garment IndustryDocument7 pagesErgonomic Risk Assessment of Workers in Garment IndustryEngrWasiAhmad100% (1)
- Nemis User Guide: Every Learner CountsDocument39 pagesNemis User Guide: Every Learner CountsEdwinNo ratings yet
- Miles Mathis - Ballooning Spiders As Proof of My Charge FieldDocument3 pagesMiles Mathis - Ballooning Spiders As Proof of My Charge FieldEvgyrt NesralNo ratings yet
- Working With Tabstrip WDADocument19 pagesWorking With Tabstrip WDAmcsrNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Disputed Moral Issues A Reader 5th Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Disputed Moral Issues A Reader 5th Edition PDF Scribdjason.martinez802100% (56)
- A Grammarian's Funeral SummeryDocument3 pagesA Grammarian's Funeral SummeryRajeev Choudhary100% (1)
- Descriptive TextDocument5 pagesDescriptive TextAvluz AdiansuhNo ratings yet
- Micrologus, Taylor, A New Inventory of Manuscripts of The Micrologus, 1998Document31 pagesMicrologus, Taylor, A New Inventory of Manuscripts of The Micrologus, 1998Hans ONo ratings yet
- Week4 Teacher Shaira NWM English 4Document5 pagesWeek4 Teacher Shaira NWM English 4reinzNo ratings yet