0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
The Digestive System
The Digestive System
Uploaded by
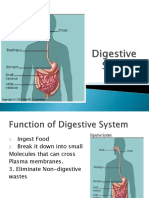
Luz Dianne SoloriaThe digestive system breaks down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. The process involves both mechanical and chemical stages. The mechanical stage uses the teeth, tongue, stomach contractions and intestinal movements to break food into smaller pieces. The chemical stage uses enzymes to break food down into even smaller molecules like glucose, amino acids and fatty acids. The major organs involved are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines and anus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
The Digestive System
The Digestive System
Uploaded by
Luz Dianne Soloria0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
The digestive system breaks down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. The process involves both mechanical and chemical stages. The mechanical stage uses the teeth, tongue, stomach contractions and intestinal movements to break food into smaller pieces. The chemical stage uses enzymes to break food down into even smaller molecules like glucose, amino acids and fatty acids. The major organs involved are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines and anus.
Original Title
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The digestive system breaks down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. The process involves both mechanical and chemical stages. The mechanical stage uses the teeth, tongue, stomach contractions and intestinal movements to break food into smaller pieces. The chemical stage uses enzymes to break food down into even smaller molecules like glucose, amino acids and fatty acids. The major organs involved are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines and anus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
The Digestive System
The Digestive System
Uploaded by
Luz Dianne SoloriaThe digestive system breaks down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. The process involves both mechanical and chemical stages. The mechanical stage uses the teeth, tongue, stomach contractions and intestinal movements to break food into smaller pieces. The chemical stage uses enzymes to break food down into even smaller molecules like glucose, amino acids and fatty acids. The major organs involved are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines and anus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1/ 3
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Chemical Stage
Enzymes found in the digestive
Food – body fuel. system constitute the chemical stage.
- Any substance that, when Digestive enzymes – are fluids that
absorbed into your body hasten the chemical reaction needed
tissues, yields materials for to break down starch into simpler
the production of energy. form called glucose, protein into
- Also provides materials for amino acids, fats into fatty acids, and
the growth, maintenance, glycerol.
and repair of body tissues. Alimentary canal - a long tube-like
structure where food passes.
Digestion – is the process of reducing
food to smaller molecules that can be The major organs of the digestive
absorbed by the body. tract are:
The process of digestion has two Mouth
main functions: Esophagus
1. To break down large pieces of Stomach
food into tiny particles. Small intestines
2. To break the tiny particles of Large intestines
food into molecules. Anus
The digestive process is divided into The Mouth
two stages: - Food passage begins in the
The mechanical phase mouth.
The chemical phase Mucus – which moistens the food,
comes from the cells lining the
Mechanical Stage mouth.
Mechanical stage – is performed by - It makes the food easier to
the teeth and tongue, through the swallow.
contractions of stomach, and through Saliva – like mucus, lubricates the
the movements of the intestines. food and it also contains the enzyme
Mechanical processes break up foods amylase.
by means of tearing, biting, cutting, Amylase – breaks down starch into
grinding and mashing them into very simpler sugar called maltose.
fine mixture. Tongue – is a muscular organ.
- It moves the food so it can
be chewed by the teeth.
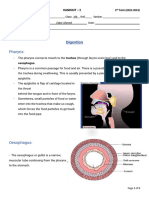
Pharynx – large area at the back of Gastric juice – formed by the
the mouth where food is being forced combinations of enzymes, water, and
into. hydrochloric acid.
Epiglottis – a structure that closes Hydrochloric acid – a strong acid
over the air passage each time you that helps break up the connective
swallow. tissue and cell membranes in food. It
also kills many harmful bacteria.
The Esophagus Proteases – break down proteins.
Esophagus – (also spelled as Pepsin – The principal stomach
oesophagus) is a tube that connects protease and it breaks down protein
the pharynx and stomach. into polypeptides.
- It carries food from the
mouth to the stomach. The Small Intestine
Mucosa – The layers of cells that line Three parts of the small intestine
the tube Duodenum
- These layers contain many Jejunum
mucus-secreting cells. Ileum
Lumen - The hollow interior space of
the alimentary canal. Duodenum – is the upper 20
Peristalsis – a rhythmic muscular centimeters connected to the
action. stomach.
Jejunum – is about 2.5 meters long.
The Stomach Ileum – is the longest half coiled
Stomach – a large J-shaped organ at through the abdominal cavity.
the end of the esophagus and on the
left side of the body. Villi – tiny finger like projections
When the food reaches the end of protruding out of the mucosal fold
the esophagus, it goes past a inside the intestines.
sphincter muscle. Microvilli – the plasma membrane of
each epithelial cell is folded into
Three kinds of cells in the stomach many tiny projections.
mucosa:
Secretes mucus The Pancreas and the Liver
Secretes enzymes Two functions of the pancreas:
Secretes hydrochloric acid and 1. It produces hormones that
water. regulate the homeostasis of
blood glucose.
2. It produces pancreatic juice esophagus, leaving a sour or bitter
that neutralizes the acidic taste in mouth.
stomach contents before they
move into the rest of the small
intestine.
Lipase – an enzyme that breaks down
fat molecules.
Liver – the largest gland in the body.
Bile – is the greenish-yellow liquid
produced in the liver where it is
stored in a small pouch called the
gallbladder.
The Large Intestine
- Also called as the colon,
large intestine is only about
two meters long but is twice
as wide as the small
intestine.
- One major function of the
large intestine is to absorb
water from the lumen.
Appendix – a small projection where
the small and large intestines joins. It
has no known function to humans.
Feces – Solid indigestible waste.
Rectum – The last 20 or 30
centimeters of the colon.
Indigestion or dyspepsia – another
name for an upset stomach.
- Happens when people eat too
much, too fast, or when they eat
foods that do not “agree” with them.
- Symptom is stomachache
Heartburn – chest pain
- Caused by stomach acid
splashing up and irritating the
You might also like
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam Sharma0% (1)Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam Sharma37 pages
- Digestive System Alimentary Tract of The Digestive System MouthNo ratings yetDigestive System Alimentary Tract of The Digestive System Mouth5 pages
- The Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8100% (2)The Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 844 pages
- Digestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1No ratings yetDigestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED13 pages
- L - 6 Life Processes - Heterotrophic NutritionNo ratings yetL - 6 Life Processes - Heterotrophic Nutrition7 pages
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemNo ratings yetAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive System5 pages
- Running Head: 1: The Process of Human DigestionNo ratings yetRunning Head: 1: The Process of Human Digestion5 pages
- Name: Santos, Lore Anne Mhae T. Date: - Instructor: Giovanni D. David, Edd, RN ScoreNo ratings yetName: Santos, Lore Anne Mhae T. Date: - Instructor: Giovanni D. David, Edd, RN Score4 pages
- Science 8 q4 Wk1 the Digestive System.cqa.Gqa.lrqa EditedNo ratings yetScience 8 q4 Wk1 the Digestive System.cqa.Gqa.lrqa Edited15 pages
- The Digestive System: Prepares Food For Use by All Body CellsNo ratings yetThe Digestive System: Prepares Food For Use by All Body Cells44 pages
- BIO103 Lec-17.46 ArIm Digestive System 220424No ratings yetBIO103 Lec-17.46 ArIm Digestive System 22042427 pages
- Nutrition in Humans: By: Khizar Hayat & Ade Bhai 10-ANo ratings yetNutrition in Humans: By: Khizar Hayat & Ade Bhai 10-A40 pages
- Mps Hong Kong Subscription Rates For 2009No ratings yetMps Hong Kong Subscription Rates For 20092 pages
- Mirjam Van Weissenbruch - Neonatal HypoglycaemiaNo ratings yetMirjam Van Weissenbruch - Neonatal Hypoglycaemia57 pages
- Alan Aragon Research Review - 2020 - 10 - OctNo ratings yetAlan Aragon Research Review - 2020 - 10 - Oct23 pages
- The Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) : Indicator Score DescriptionNo ratings yetThe Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) : Indicator Score Description6 pages
- Pediatric Neurology: David Dufresne MD, Lynn Dagenais BSC, Michael I. Shevell MD Repacq ConsortiumNo ratings yetPediatric Neurology: David Dufresne MD, Lynn Dagenais BSC, Michael I. Shevell MD Repacq Consortium4 pages
- Esclerosis Lateral Amiotrofica (Ela) : Tratamiento100% (1)Esclerosis Lateral Amiotrofica (Ela) : Tratamiento2 pages
- Vitamin C Deficiency Scurvy in Guinea PigsNo ratings yetVitamin C Deficiency Scurvy in Guinea Pigs3 pages
- Literature Review: Effect of Benson's Relaxation Therapy (BRT) On Post Caesarean Section Pain and StressNo ratings yetLiterature Review: Effect of Benson's Relaxation Therapy (BRT) On Post Caesarean Section Pain and Stress6 pages
- Name: Erika Novi Indriyanti NIM: 201701078 Class: 4B/ 33 Prodi: S1 KeperawatanNo ratings yetName: Erika Novi Indriyanti NIM: 201701078 Class: 4B/ 33 Prodi: S1 Keperawatan6 pages
- Wound Care: Dressing Changes, DVT Stockings, Etc Respiratory Care: Updrafts, Endotracheal Suctioning, Spirometry, Incentive Spirometer, EtcNo ratings yetWound Care: Dressing Changes, DVT Stockings, Etc Respiratory Care: Updrafts, Endotracheal Suctioning, Spirometry, Incentive Spirometer, Etc2 pages
- Download Full Current Diagnosis Treatment Geriatrics 2nd Edition Brie A. Williams PDF All ChaptersNo ratings yetDownload Full Current Diagnosis Treatment Geriatrics 2nd Edition Brie A. Williams PDF All Chapters77 pages
- Accidental Epidural Injection of Atropine: Case ReportNo ratings yetAccidental Epidural Injection of Atropine: Case Report2 pages