Operation Management
Operation Management
Uploaded by
Zafar HafeezCopyright:
Available Formats
Operation Management
Operation Management
Uploaded by
Zafar HafeezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Operation Management
Operation Management
Uploaded by
Zafar HafeezCopyright:
Available Formats
M.
ZAFAR HAFEEZ
BSAF 5TH
213214
OPERATION MANAGEMENT
ASSIGMENT 01
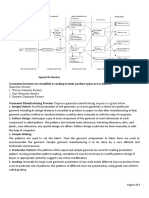
The supply chain process of textile sector
The textile sector's supply chain process involves a series of interconnected steps from sourcing raw
materials to distributing the final products. The process begins with raw material sourcing, which can
be local or global. The manufacturing of fabrics and textiles involves various processes, such as
ginning, spinning, weaving, knitting, or non-woven. Garment production involves cutting, sewing,
and assembly into clothing items. Quality control and testing ensure the products meet safety
regulations. Packaging and labeling are crucial for ensuring the products meet quality standards.
Distribution and logistics involve warehousing, transportation, and inventory management. Retailers
play a crucial role in merchandising and marketing the products. Consumer use and end of life
involve disposal, recycling, or repurposing. Returns and reverse logistics involve assessing, repairing,
or recycling returned items. Sustainability is increasingly important, leading to the exploration of
recycling and upcycling processes. Efficient management of each stage is essential for product
quality, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability in this competitive industry.
Inbound logistic Production process/System Out bound logistic
warehouse
HR QD FINANCE MM
Textile
Cotton
Farms Genning factory Spinning factory Weaving
Mills
Retailing
Brands Garments / Stitching
Dying & Finishing
units
M. ZAFAR HAFEEZ
BSAF 5TH
213214
Fashion Textile Cotton web
1. Sourcing Raw Materials
The process begins with the procurement of raw materials, primarily cotton or synthetic fibers. The
choice of materials depends on the type of fabric being produced.
2. Preparation of Raw Materials
Raw cotton is typically cleaned and processed to remove impurities, seeds, and other foreign
matter. In the case of synthetic fibers, they may need to be melted and extruded into filaments
before further processing.
3. Spinning
The cleaned and prepared fibers are spun into yarns through a process called spinning. This can be
done using various methods, including ring spinning, open-end spinning, or air jet spinning.
4. Weaving or Knitting
The yarns are then used to create fabric through either weaving or knitting. In weaving, the yarns
are interlaced at right angles to form a fabrics. In knitting, the yarns are looped together to create a
fabric.
5. Dyeing and Printing
After weaving or knitting, the fabric is often dyed to achieve the desired color. Printing may also be
done to add patterns or designs. Dyeing and printing processes can vary depending on the type of
fabric and the desired finish.
6. Finishing
The finished fabric may go through additional finishing processes, which can include treatments to
enhance texture, appearance, or performance. This may involve processes like calendering, heat-
setting, or chemical treatments.
7. Cutting and Sewing
Once the fabric is ready, it is cut into pieces according to a pattern or design. These pieces are then
sewn together by skilled workers to create the final clothing items.Garment manufacturing may
involve multiple steps, including cutting, stitching, pressing, and quality control checks.
8. Quality Control
At various stages of production, quality control checks are conducted to ensure that the clothing
meets the required standards in terms of size, stitching, color, and overall quality.
9. Packaging and Distribution
After the clothing items pass quality control, they are packaged and prepared for distribution.
Finished garments are usually packed in accordance with customer requirements and shipped to
retailers or distributors.
M. ZAFAR HAFEEZ
BSAF 5TH
213214
10.Marketing and Sales
The clothing items are then sold through various channels, including retail stores, online
marketplaces, or directly too hole salers and buyers.
11.Customer Feedback and Improvement: Feedback from customers and retailers is
valuable for making improvements in the production process, design, and quality of the
clothing.
This is all detail about the procedure or description of textile mills making clothes all our the country
and as well the whole world.
You might also like
- PNTV - The Power of Your Breath by Anders OlssonDocument22 pagesPNTV - The Power of Your Breath by Anders OlssonkontrakNo ratings yet
- The Only Recognized Trademarks For Textile Shrinkage ControlDocument8 pagesThe Only Recognized Trademarks For Textile Shrinkage ControlAditya Shrivastava100% (1)
- Garment Manufacturing Process: From Fabric To Finished Apparel ProductsDocument22 pagesGarment Manufacturing Process: From Fabric To Finished Apparel ProductsISHITA100% (1)
- Manufacturing Steps: 1.receiving FabricsDocument22 pagesManufacturing Steps: 1.receiving FabricsHaq ChandioNo ratings yet
- Garments Working ProcessDocument10 pagesGarments Working ProcessAbu UmarNo ratings yet
- Mis Presentation: Name Roll NoDocument30 pagesMis Presentation: Name Roll NoMansi PatelNo ratings yet
- Basics of Apparel ProductionDocument22 pagesBasics of Apparel ProductionJaswant Singh100% (1)
- Kura AaaaaaaDocument18 pagesKura AaaaaaaKurabachew BekeleNo ratings yet
- F2F PDFDocument8 pagesF2F PDFKalyani VaddepalliNo ratings yet
- Departments in RMG IndustryDocument80 pagesDepartments in RMG IndustryUtsash SarkerNo ratings yet
- Fashion Merchandising TasksDocument18 pagesFashion Merchandising TasksNitin VermaNo ratings yet
- Garments Factories Are Classified According To Their Product Types Are As FollowsDocument7 pagesGarments Factories Are Classified According To Their Product Types Are As Followsnainaa18No ratings yet
- Sourcing of Raymond'sDocument23 pagesSourcing of Raymond'sVibhav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Apparel ProductionDocument27 pagesApparel ProductionISHITANo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Unit IVDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Unit IVroselyn ayensaNo ratings yet
- Q & A-Unit 1 - Amt-IntroductionDocument117 pagesQ & A-Unit 1 - Amt-IntroductionISHITANo ratings yet
- MMSDocument23 pagesMMSDrBollapu SudarshanNo ratings yet
- AshimaDocument12 pagesAshimachins1289No ratings yet
- About The GarmentsDocument22 pagesAbout The GarmentsNisanthNo ratings yet
- Moi University School of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Production EngineeringDocument8 pagesMoi University School of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Production Engineeringhr maNo ratings yet
- Garments Manufacturing Process: Stepwise Garments ManufacturingDocument24 pagesGarments Manufacturing Process: Stepwise Garments ManufacturingAnamika Priyadarshini100% (1)
- Indra FileDocument41 pagesIndra FileVanika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Factory Layout, Labor Law & Compliance in RMG, AMM3203Document9 pagesFactory Layout, Labor Law & Compliance in RMG, AMM3203Syed Mahir AliNo ratings yet
- English Assingment GarmentsDocument8 pagesEnglish Assingment GarmentsKhalid abdiwasicNo ratings yet
- SRF Hosiery Manufacturing IndustryDocument14 pagesSRF Hosiery Manufacturing IndustryRija ImranNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument8 pagesSupply Chain ManagementyoginuluNo ratings yet
- Chapter One PDFDocument24 pagesChapter One PDFKibromGereNo ratings yet
- Marks N SpencerDocument22 pagesMarks N SpencerJyoti PathrejaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Planning and Designing Garment Collection For A SeasonDocument32 pagesUnit 1 - Planning and Designing Garment Collection For A Seasonmaya_muthNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Fashion Technology Patna: Time and Action CalenderDocument17 pagesNational Institute of Fashion Technology Patna: Time and Action CalenderKARISHMA RAJ100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Planning and Designing Garment Collection For A SeasonDocument30 pagesUnit 1 - Planning and Designing Garment Collection For A Seasonmaya_muth100% (2)
- Textile, Factory Marketing/merchandising, Buying House To RMGDocument13 pagesTextile, Factory Marketing/merchandising, Buying House To RMGsatexNo ratings yet
- Apparel Industry - Business OperationsDocument4 pagesApparel Industry - Business OperationsGopal Sinha100% (1)
- Garment Industry 1Document28 pagesGarment Industry 1Mega MegalaNo ratings yet
- Name: Mwendia Vincent MureaDocument11 pagesName: Mwendia Vincent Mureahr maNo ratings yet
- Cotton King ProjectDocument17 pagesCotton King ProjectPrajwal Gaikwad67% (9)
- Production and Quality Control in The Garment Industry: Learning ObjectivesDocument19 pagesProduction and Quality Control in The Garment Industry: Learning ObjectivesPratham PawarNo ratings yet
- Textile IndustryDocument11 pagesTextile IndustryPRATHIYUMAN JNo ratings yet
- FPQM DocumentDocument19 pagesFPQM DocumentSmritiNo ratings yet
- Garment Manufacturing Process Fabric To Finished ProductDocument12 pagesGarment Manufacturing Process Fabric To Finished ProductEmmanuel Tunde Renner100% (1)
- Quality Control in Apparel IndustryDocument16 pagesQuality Control in Apparel IndustryKrupa Reddy100% (1)
- XSRC AR-ETAPA3 IdnDocument16 pagesXSRC AR-ETAPA3 IdnCarlos Mon. T.No ratings yet
- Apparel Manufacturing ProcessDocument46 pagesApparel Manufacturing Processroselyn ayensa100% (1)
- Untitled 1Document21 pagesUntitled 1ShahiU28 UpskillingNo ratings yet
- GMT Unit 1 & 2 NotesDocument37 pagesGMT Unit 1 & 2 Notess.karansridharanNo ratings yet
- How Clothing Is Made in Developing CountriesDocument11 pagesHow Clothing Is Made in Developing CountriesenmimundodecolorNo ratings yet
- Production and Quality Control in The Garment IndustryDocument19 pagesProduction and Quality Control in The Garment IndustryZubair ShafqatNo ratings yet
- Sample Section:It Is The First Section Of: Garment Manufacturing ProcessDocument6 pagesSample Section:It Is The First Section Of: Garment Manufacturing ProcesssantumysoreNo ratings yet
- Fabric Carecteristics and InspectionDocument6 pagesFabric Carecteristics and Inspectionmohd gofranNo ratings yet
- Wool 482 582 12 T 15Document22 pagesWool 482 582 12 T 15KathirrveluSubramainanNo ratings yet
- Changes Automatically The Manufacturing Industry Is Getting More Fashionable in The Present Days and Arriving To The Organised Sector As WellDocument21 pagesChanges Automatically The Manufacturing Industry Is Getting More Fashionable in The Present Days and Arriving To The Organised Sector As WellSanthosh 8055No ratings yet
- Evince Textile Limited: Internship ExperienceDocument9 pagesEvince Textile Limited: Internship ExperienceAnik IslamNo ratings yet
- Time and Action Calendar or TNADocument17 pagesTime and Action Calendar or TNAruchi ratan100% (2)
- Cotton Sector Supply Chain GuidanceDocument9 pagesCotton Sector Supply Chain Guidancer246515gNo ratings yet
- Time and Action Calendar or TNADocument14 pagesTime and Action Calendar or TNAKARISHMA RAJ100% (2)
- Fashion Merchandising: Sourcing: AbstractDocument12 pagesFashion Merchandising: Sourcing: AbstractNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- Cotton Bale ManagementDocument9 pagesCotton Bale Managementchamp2357No ratings yet
- APM UNIT-1 FD: Ms. Liza NagpalDocument10 pagesAPM UNIT-1 FD: Ms. Liza NagpallizaNo ratings yet
- Carr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureFrom EverandCarr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureDavid J. TylerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- B2B BusinessDocument3 pagesB2B BusinessZafar HafeezNo ratings yet
- Pak - Study OutlineDocument5 pagesPak - Study OutlineZafar HafeezNo ratings yet
- Questions During IndDocument2 pagesQuestions During IndZafar HafeezNo ratings yet
- ML19 017Document8 pagesML19 017Zafar HafeezNo ratings yet
- Homescience - Intro & ScopeDocument41 pagesHomescience - Intro & Scopekcnit trainingNo ratings yet
- Dusk SequenceDocument15 pagesDusk SequenceGaston LaGaffeNo ratings yet
- Auditing Sukrisno Agoes PDFDocument7 pagesAuditing Sukrisno Agoes PDFNur Hidayah K. Fadilah50% (2)
- Bc-Prime SFDocument2 pagesBc-Prime SFrazcrete24No ratings yet
- (Stem - Pc11T-Iie-1) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 5Document7 pages(Stem - Pc11T-Iie-1) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 5Izaak CabigonNo ratings yet
- Nephrologist Numbers PDFDocument25 pagesNephrologist Numbers PDFsrv 9982% (11)
- 00 - Lesson 1 - Top 6 InventionsDocument3 pages00 - Lesson 1 - Top 6 InventionsNamelessNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science GR 7 q1 Week 4-5 Subtask 1Document9 pagesEnvironmental Science GR 7 q1 Week 4-5 Subtask 1Majin BuuNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Effectiveness of Using SQL-injection and PHP-including Mechanisms For SexDocument38 pagesAnalysis of The Effectiveness of Using SQL-injection and PHP-including Mechanisms For SexbamgbosesamueltofunmiNo ratings yet
- Murder On Orient ExpressDocument2 pagesMurder On Orient ExpressNagyBiankaNo ratings yet
- Chanakya National Law University: History Final Draft of Project On "Surat Settlement"Document21 pagesChanakya National Law University: History Final Draft of Project On "Surat Settlement"Diksha SinghNo ratings yet
- Bambalan v. Maramba, 51 Phil. 417 January 30, 1928Document2 pagesBambalan v. Maramba, 51 Phil. 417 January 30, 1928Ana BelleNo ratings yet
- Text EAPPDocument2 pagesText EAPPJayren CalzNo ratings yet
- ENE - Combined Updated For Use of AY2020Document2 pagesENE - Combined Updated For Use of AY2020Alzheimer RachNo ratings yet
- MOHD ZUKHAIRI ABD GHAPAR (AN INFANT SUING THROUGH HIS FATHER AND NEXT FRIEND, ABDUL GHAPAR BIN SAAD) V QUEK CHIAM KEE (2004) 5 MLJ 6Document7 pagesMOHD ZUKHAIRI ABD GHAPAR (AN INFANT SUING THROUGH HIS FATHER AND NEXT FRIEND, ABDUL GHAPAR BIN SAAD) V QUEK CHIAM KEE (2004) 5 MLJ 6Khairul IdzwanNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Analysis and Design of Reg PDFDocument8 pagesComparison of Analysis and Design of Reg PDFPacha Khan KhogyaniNo ratings yet
- Fanon and DevelopmentDocument16 pagesFanon and DevelopmentAlejandro De Oto100% (1)
- TO 2 Literasi Bahasa InggrisDocument9 pagesTO 2 Literasi Bahasa InggrisDedi Maman100% (2)
- IfA Diggers' Forum Away SurveyDocument103 pagesIfA Diggers' Forum Away SurveyRescue - The British Archaeological TrustNo ratings yet
- Lenovo ThinkPad T410 DatasheetDocument4 pagesLenovo ThinkPad T410 DatasheetSayed Ahmed NahinNo ratings yet
- Chapters 12 & 13 Practice Problems: Economy Probability Return On Stock A Return On Stock BDocument4 pagesChapters 12 & 13 Practice Problems: Economy Probability Return On Stock A Return On Stock BAnsleyNo ratings yet
- BE Professional!: Yoke S. FabiantoDocument17 pagesBE Professional!: Yoke S. FabiantoYokeS.FabiantoNo ratings yet
- First Conditional With BritishDocument14 pagesFirst Conditional With BritishValeria Rivera CarmonaNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Sample Paper (Pleasure Tests) PDFDocument30 pages12th Maths Sample Paper (Pleasure Tests) PDFBala Murugan.V100% (2)
- Hans Sluga - Politics and The Search For The Common Good (2014, Cambridge University Press)Document273 pagesHans Sluga - Politics and The Search For The Common Good (2014, Cambridge University Press)Carlos Eduardo Jiménez RubianoNo ratings yet
- Viiimaths 80 Marks Sample Paper First Term ExaminationDocument7 pagesViiimaths 80 Marks Sample Paper First Term Examinationsweetyappu88No ratings yet
- Meeting 10Document23 pagesMeeting 10Buddies 042No ratings yet
- Examguru Hindi Course BDocument128 pagesExamguru Hindi Course BHetal DhakadNo ratings yet
- JETIR2205718Document8 pagesJETIR2205718Faisal manzoorNo ratings yet