International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences: Corresponding Author
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences: Corresponding Author
Uploaded by
editorofijtosCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences: Corresponding Author
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences: Corresponding Author
Uploaded by
editorofijtosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences: Corresponding Author
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences: Corresponding Author
Uploaded by
editorofijtosCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
REVIEW ARTICLE MICROBIOLOGY
BAD BUGS NO DRUGS-A REVIEW ON NDM-I
Corresponding Author
MR. M. SENTHIL KUMAR
Department of pharmaceutics, Annai Veilankanni’s Pharmacy
College, Saidapet, Chennai-15, India.
Co Authors
MR. J. BALASUBRAMANIAN2, MS. GARGEYI PAVULURI2, MS.
HAREESHA CHAMARTHI 1 AND MS MADHURI.K2.
1
Department of pharmaceutics, Annai Veilankanni’s Pharmacy College, Saidapet, Chennai-15,
India.
2
Department of pharmaceutical Bio technology, Annai Veilankanni’s Pharmacy College, Saidapet,
Chennai-15, India.
ABSTRACT
A dangerous new mutation that makes some bacteria resistant to almost all antibiotics has
become increasingly common throughout the world. Experts in antibiotic resistance called
the gene mutation, named NDM-1(New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase), “worrying” and
“ominous” and they feared it would spread globally. The spreading of this is increasing day
by day. So, the scarcity of the antibiotics and the need of these in the present condition
show the target to the world. The potential of NDM-1 to be a worldwide public health
problem is great, and co-ordinated international surveillance is needed.
This article can be downloaded from www.ijpbs.net
B-2
B - 62
2
KEYWORDS
NDM-1, Antibiotics, bacteria and superbug.
INTRODUCTION
Homosapiens is an alien species on earth. This unless we have divine powers to bring the
planet belongs to bacteria. There are more dead back to the life3.
bacteria on earth than all other living organisms.
The human body contains more number of The new superbug
bacteria than human cells themselves. We lived Experts have warned that a new type of
with arrogant optimism that we had conquered drug resistant super bug, they have called
infections, at least the bacterial infections, if not NDM-1 and it could spread worldwide.
the viruses. How wrong we were! Bacteria have
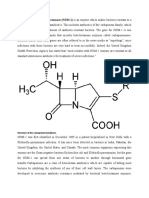
finally reclaimed their premier status and New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM-1)4
superiority and won the war against humans. is a gene that makes bacteria resistant to
They are literally mocking our intellect, antibiotics of the carbapenem family12. It
knowledge and antibiotic weaponry1. encodes a type of beta-lactamase enzyme
When we are called to manage patients called a carbapenemase10. It is found on
with severe infections due to pan resistant bugs, plasmids - DNA structures that can be easily copied
we do really wonder whether we are living in pre- and transferred between different bacteria -
Alexander Fleming years without antibiotics and suggesting "an alarming potential to spread and
then with a shock, but no surprise, realize that diversify among bacterial populations"5. Bacteria
we have reached the end of antibiotic era2. Still, that carry this gene are often referred to by
the Indian medical community remains in a state news reporters as "super bugs"6. There are
of denial. We have not yet taken the issue of currently no new drugs in the research
antibiotic resistance seriously. We believe that pipelines that aim to stop NDM-1. Some strains
Dr. Fleming has discovered penicillin only early of E.coli and Klebsiella pneumonia8 are known
this morning and consider antibiotic resistance a carriers of the gene, but the gene can be
problem of next century where in fact antibiotics transmitted from one strain of bacteria to
are dead and the foul smell of decay is already another through horizontal gene transfer.
around us, It is too late to save antibiotics,
This article can be downloaded from www.ijpbs.net
B-3
B - 63
3
Function pneumoniae, E cloacae, Pseudomonas
The gene produces a metallo-beta- aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii10.
lactamase, an enzyme that hydrolyzes and
inactivates antibiotics in the beta-lactam family7. Can it be treated?
This modification makes bacteria completely Other treatment options are available to
resistant to all known antibiotics-even to the fight these infections but they present major
“WEAPON OF LAST RESORT”, a group of challenges for clinicians and will often demand
drugs called the CARBAPENEMS, which are combinations of antibiotics are used. Scientists
usually held in reverse for grave emergencies have identified some strains that have been
and infections by highly-resistant bacteria such resistant to all known antibiotics.
as MRSA8. Those antibiotics were, until recently,
capable of killing most bacteria by inhibiting the How would I know if I had it?
synthesis of one of their cell wall layers. The The infections have ranged from mild to
resistance conferred by this gene therefore aids severe - and some have been fatal. Two types
the expansion of bacteria that carry it throughout of bacteria have been host to NDM-1: the gut
a human host, since they will face less bacterium E.coli and another that can invade
opposition/competition from populations of the lungs called Klebsiella pneumonia8. Both
antibiotic-sensitive bacteria, which will be can lead to urinary tract infections and blood
diminished by the original antibacterial treatment. poisoning.
Regular queries regarding this issue Can its spread be stopped?
What is ndm-1? Experts say the way to stop it is through
New Delhi metallo-ß-lactamase-14 is a surveillance, rapid identification and isolation of
gene carried by bacteria that makes the strain any hospital patients who are infected. Normal
resistant to carbapenem antibiotics. This is infection control measures, such as disinfecting
concerning because these antibiotics are some hospital equipment and doctors and nurses
of the most powerful ones, used on hard-to-treat washing their hands with antibacterial soap,
infections that evade other drugs. can stop the spread. And they say we now
need new drugs to treat resistant strains.
Why is this a problem?
NDM-14 (or more precisely the DNA code Are there new antibiotics that could help?
for this enzyme) is “extremely mobile” can easily While there is a great deal of investment
now jump from one strain of bacteria to another in research to find new antibiotics, experts say
& it may end up in another bacterium which is that most of the drugs currently in the pipeline
already resistant to many other antibiotics. will be useless for treating NDM-1 positive
Ultimately, it could produce dangerous infections patients. This is because the bacteria that carry
that would spread rapidly from person to person NDM-1 are Gram-negative, while most of the
and be almost impossible to treat. work is being carried out for Gram-positive
bugs like MRSA11. The Health Protection
What are all the bacterial strains bearing Agency says "multi-resistant Gram-negative
this? bacteria pose a notable public health risk and it
K pneumoniae8, Escherichia coli, remains important that the pharmaceutical
Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae, and industry continues to work towards developing
Morganella morganii9. Other classes of new treatment options".
carbapenemases have already been found in K
This article can be downloaded from www.ijpbs.net
B - 64
B-4 4
What will happen now? such as burgers, so make sure you cook
The government said HPA (health them thoroughly and they are not left
protection agency) would continue to monitor the bloody.
situation and would regularly review the data and
the need for further action. In the meantime, Ndm-1, is it a global scare
hospitals should ensure they continue to provide Already 40 types of bugs similar to
good infection control to prevent any spread, and NDM-1 are existing globally, that also includes
consider whether patients have recently been the German Imipenem Resistant Metallurgical
treated abroad and send samples to HPA for Strain. The Indian variant is just the 41st strain.
testing if necessary. A day after the Lancet report5 on a drug-
resistant super bug NDM-1 created a global
What you can do to protect yourself? scare, It’s quite concerning because there are
So what steps can you take to minimise the risk? very limited treatment options. "The risk is that
Simply, don’t get it that’s your best bet. we have an enzyme with very major resistant
Wearing a mask or respirator like the Critical and if it combined with a particularly nasty
Cover Micro breathe Mask and the Critical Cover bacterium, then that would be a concern". As it
PFL N-95 Particulate Respirator will go very far is spreading alarmingly i.e. several cases are
to keep you from contacting the virus. identified 44 isolates with NDM-1 in Chennai,
• Use an antibacterial body wash/shampoo 26 in Haryana, 37 in the UK, and 73 in other
such as Hibiscrub before, during and after a sites in India and Pakistan5. NDM-1 was mostly
hospital stay. found among Escherichia coli (36) and
• If you’re fitted with a catheter, ask for it to be Klebsiella pneumoniae (111), which were
removed as soon as clinically possible, says highly resistant to all antibiotics except to
Professor Mervyn Bibb, a molecular tigecycline and colistin. K pneumoniae isolates
microbiologist at the John Innes Institute, from Haryana were clonal but NDM-1
Norwich. ‘It is a potential source of infection.’ producers from the UK and Chennai were
• Ask hospital staff and visitors to use clonally diverse. The potential of NDM-1 to be
antiseptic hand gel. a worldwide public health problem is great, and
• Take your antibiotics as prescribed: If you co-ordinate international surveillance is
don’t finish the course or take them at needed.
reduced dose there is a risk you won’t kill all It is a wakeup call for microbiologists, an
the bacteria, says Professor Bibb. ‘Finishing extremely serious situation and our health
the course will ensure all pathogens are authorities are not able to realize the gravity of
killed. Taking less than the prescribed amount it19.
could lead to incrementally resistant strains
developing.’ Linking india to superbug is unfair and
• Watch for signs of redness, swelling and pain wrong15
around wounds and report it to medical staff. The Ministry of Health protested against
• At home, practice good hand hygiene. Wash the British study blaming India for exporting a
your hands after going to the loo and before drug-resistant super bug to the rest of the
preparing food. Regularly clean door handles, world. “India strongly refutes the naming of this
light switches and flushes on loos. Avoid enzyme as New Delhi metallo beta lactamase
sharing towels. Be vigilant about food (NDM-1) and also refutes that hospitals in India
hygiene: E. coli can colonise meat products, are not safe for treatment, including medical
This article can be downloaded from www.ijpbs.net
B - 65
B-5 5
tourism,” read a statement from the Union Health are the world's best in liver transplantation and
ministry24. also at the very top in endoscopic procedures.
“It is ridiculous to call it NDM-1 when none In fact American doctors are coming here to
of the samples that tested positive were picked learn the procedure from us.
in New Delhi,” it is a commercially motivated Several super bugs are surviving in
campaign to hurt India’s Rs 1,200-crore medical nature and they have been reported from
tourism industry. countries like Greece, Israel, the US, Britain,
The Indian health ministry has Brazil, Puerto Rico and many others and it is
disputed the conclusion that the gene originated unfair to link the super bug to India,' said V.M.
in India or Pakistan, describing this conclusion Katoch, director general, Indian Council of
as "unfair" and stating that Indian hospitals are Medical Research (ICMR).
perfectly safe for treatment 13, 14. Indian
politicians have described linking this new drug CONCLUSION
resistance gene to India as “malicious
propaganda” and blamed multinational
We have a bleak window of may be ten
corporations for what they describe as selective
years, where we are going to have to use the
malignancy 20, 21. The Indian Ministry of Health
antibiotics very wisely, but also grapple with
released a statement "strongly refuting" naming
the reality that we have nothing to treat these
the enzyme "New Delhi" 22.
infections with. It is the first time it has got to
The primary author of the 2010 Lancet
this stage with these types of bacteria. 'Every
study, who is based in the University of Madras,
time we throw enough antibiotics at enough
has stated that he does not agree with the part of
people, we encourage the evolution of drug-
the article that advises people to avoid elective
resistant mutants.' So, now there're no
surgeries in India17.
antibiotics in the pipeline to treat this.
Bajaj described the statements by
Ultimately, we will need new antibiotics -
British medical experts as being politically
and even completely new ways of killing
motivated. 'They might have been alarmed by
bacteria. Professor Enright's team at Biocontrol
the prospect of losing business to Indians’.
Ltd is working on a new take on an old idea -
Medical tourism in India is expected to be worth
using natural viruses to attack bacteria instead
$2.3 billion by 2012, according to an estimate25.
of antibiotics.
Health experts said it was politically
Clinical trials are under way and we
motivated as Western doctors were alarmed at
could have a new weapon in our armory within
the prospect of losing business to India's
a few days.
booming health tourism. As the 'Indian surgeons
REFERENCES
1. Abdul Ghafur.K.K, Journal of the Association Report on Development Pipeline. Clin Infcet
of Physicians of India, March 2010, vol 58. Dis 2009; 48:1-12.
2. Cesar A. Arias. Antibiotic-Resistant Bugs in 4. Kumarasamy et. al. (2010). "Emergence of
the 21st Century —A Clinical Super- a new antibiotic resistance mechanism in
Challenge.NEJM 2009, 360:439-443. India, Pakistan, and the UK: a molecular,
3. Helen W. Boucher, et al. Bad Bugs, No biological, and epidemiological study". The
Drugs: No ESKAPE! An Update from the Lancet Infectious Diseases doi:
Infectious Diseases Society of America -IDSA 10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70143-2.
This article can be downloaded from www.ijpbs.net
B - 66
B-6 6
5. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, Early Online 13. Pandey, Geeta (12 August 2010). "India
Publication, 11 August2010 doi: rejects UK scientists' 'superbug' claim". BBC
10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70143-2. News. Retrieved 13 August 2010.
6. Unattributed report, CNN "World Update", 14. Telegraph.co.uk: Indian Government angry
August 11, 2010. over claims its hospitals are fuelling global
7. http://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/article- superbug.
1302358/NDM-1-Were-blame-indestructible- 15. "Linking India to superbug unfair and wrong,
Indian-superbug. says India". Hindustan Times. 12 August
8. Young D, Toleman MA, Giske CG, Cho HS, 2010. Retrieved 13 August 2010.
Sundman K,Lee K, et al.Characterization of a 16. http://en.wikipedia.org
new metallo-beta-lactamase gene, bla(NDM- 17. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chenn
1), and a novel erythromycin esterase gene ai/Indian-author-says-superbug-report-is-
carried on a unique genetic structure in fudged/articleshow/6302479.cms
K.Pneumoniae sequence type14 from India. 18. http://promo.expressindia.com
Antimicrobe Agents Chemother2009; 19. http://ijmm.org,August
53:5046-54. 13,2010,IP:122.174.183.206
9. Health protection agency.National resistance 20. http://www.hindustantimes.com/Linking-
alert: Carbapenamase in India-to-superbug-unfair-and-wrong-says-
Enterobacteriaceae.Health protection report India/Article1-585840.aspx
2009; 3: news. 21. http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-south-
10. Walsh TR. Clinically significant asia-10954890
Carbapenamase: An update. Curr Opin 22. http://www.hindustantimes.com/Don-t-
Infect Dis2008; 21:367-71. blame-superbug-on-India-it-s-
11. McNeil Jr., Donald G. (11 August everywhere/Article1-585926.aspx
2010). "Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Moving 23. http://www.the
From South Asia to U.S.". The New York lancet.com/journals/lonint/article/PIIS1473-
Times. Retrieved 13 August 2010. 3099(10)70143-2/fulltext
12. Karthikeyan K, Thirunarayan MA, Krishnan P 24. “Don’t blame superbug on India, it’s
(July 2010). "Coexistence of blaOXA-23 with everywhere”. Hindustan Times. 13 August
blaNDM-1 and armA in clinical isolates of 2010.
Acinetobacter baumannii from India". J 25. Indo-Asian,News-Service.New-Delhi,
AntimicrobChemother. doi:10.1093/jac/dkq27 August12,2010.
3. PMID 20650909.
This article can be downloaded from www.ijpbs.net
7
B - 67
B-7
You might also like
- Fast Track Guide To Effective Parasite CleansingDocument17 pagesFast Track Guide To Effective Parasite CleansingCátia Vilas-BoasNo ratings yet
- This Test Method Is Not For ResaleDocument3 pagesThis Test Method Is Not For Resaletomellefsen100% (3)
- Ozone Uses in Medicine - Renate Viebahn HanslerDocument8 pagesOzone Uses in Medicine - Renate Viebahn HanslerAdrian Alex100% (3)
- Ap Evolution Gizmo WriteupDocument2 pagesAp Evolution Gizmo Writeupapi-522349089No ratings yet
- Pharmacology MCQDocument30 pagesPharmacology MCQLokesh Mahata82% (11)
- Study Drug Resistance in Bacteria Using AntibioticsDocument47 pagesStudy Drug Resistance in Bacteria Using Antibioticskioilui;lphio961% (18)
- Bactomin Product MonographDocument43 pagesBactomin Product MonographVivek AlaiNo ratings yet
- NDM 1 SuperbugDocument14 pagesNDM 1 SuperbugVinisha Reddy100% (1)
- Nuevos Antibioticos Vs Gram NegativosDocument11 pagesNuevos Antibioticos Vs Gram NegativosbrenpmNo ratings yet
- 1 Vol. 11 Issue 4 Apr 2020 IJPSR RE 3287Document21 pages1 Vol. 11 Issue 4 Apr 2020 IJPSR RE 3287Veydant NandaNo ratings yet
- New Delhi Metallo-Beta-Lactamase (NDM-1) Is An Enzyme Which Makes Bacteria Resistant To ADocument7 pagesNew Delhi Metallo-Beta-Lactamase (NDM-1) Is An Enzyme Which Makes Bacteria Resistant To AantioxidantsNo ratings yet
- Super BugDocument22 pagesSuper BugRahul NetragaonkarNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument9 pagesArticlesathish.sure20No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Resistance, Problem Pathogens and Clinical CountermeasuresDocument514 pagesAntimicrobial Resistance, Problem Pathogens and Clinical CountermeasuresPutri Amirah100% (3)
- Morgan 2011Document10 pagesMorgan 2011recklesspeshal2058No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Resistance A Tale of The Past Becomes A Terrorfor The PresentDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial Resistance A Tale of The Past Becomes A Terrorfor The PresentdssgssNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Resistance: The Indian ScenarioDocument14 pagesAntimicrobial Resistance: The Indian Scenariosungita_kNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria: A Global Challenge: Saswati Sengupta and Madhab K ChattopadhyayDocument15 pagesAntibiotic Resistance of Bacteria: A Global Challenge: Saswati Sengupta and Madhab K Chattopadhyaysourav dasNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics 10 00672 v2Document23 pagesAntibiotics 10 00672 v2Reem AliNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Combination Approaches To Combat Multi-Drug Resistant BacteriaDocument15 pagesNIH Public Access: Combination Approaches To Combat Multi-Drug Resistant BacteriaValentina RoznovNo ratings yet
- AMR - Current Scenario and ChallangesDocument37 pagesAMR - Current Scenario and ChallangesShonit SharmaNo ratings yet
- History of Antimicrobial Agents & Resistant BacteriaDocument6 pagesHistory of Antimicrobial Agents & Resistant BacteriaAnurrag KumarNo ratings yet
- StewardshipDocument19 pagesStewardshipJorge David LopezNo ratings yet
- Bio Project Drug Resistance in BacteriaDocument18 pagesBio Project Drug Resistance in BacteriaAKASH ALAMNo ratings yet
- Hello Bio InvestDocument16 pagesHello Bio InvestAadrica WaliaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Tushar Kapur Ranbir Negi Samarth Agarwal Prakhar DubeyDocument16 pagesPharmaceutical Biotechnology: Tushar Kapur Ranbir Negi Samarth Agarwal Prakhar DubeyRanbir100% (1)
- A Bioinspired Peptide Scaffold With High Antibiotic Activity and Low in Vivo ToxicityDocument11 pagesA Bioinspired Peptide Scaffold With High Antibiotic Activity and Low in Vivo ToxicityMaria Eduarda de MeloNo ratings yet
- Biology Project XiiDocument14 pagesBiology Project XiiSagayaraniNo ratings yet
- The Role of Clinical Pharmacist in Combating Antibiotic ResistanceDocument4 pagesThe Role of Clinical Pharmacist in Combating Antibiotic ResistanceAnto BijuNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Antibiotic ResistanceDocument5 pagesResearch Paper Antibiotic Resistancegvyns594100% (1)
- 2021 IDSA Amr Guidance v2.0Document92 pages2021 IDSA Amr Guidance v2.0Thithuyngan DangNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Use: Present and Future: Stephen H. ZinnerDocument5 pagesAntibiotic Use: Present and Future: Stephen H. Zinnermbilouzi589No ratings yet
- Ajay AgrawalDocument17 pagesAjay Agrawalharsh raizadaNo ratings yet
- Carbapenem-Resistant EnterobacteriaceaeDocument16 pagesCarbapenem-Resistant EnterobacteriaceaeOG3 PolizuNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Antibiotics AntimicrobialDocument12 pagesMicrobiology Antibiotics AntimicrobialSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Peptides From Scorpion Venoms PDFDocument23 pagesAntimicrobial Peptides From Scorpion Venoms PDFOrlando Pérez DelgadoNo ratings yet
- The Prehistory of Antibiotic ResistanceDocument9 pagesThe Prehistory of Antibiotic ResistanceErick Antonio Castillo GurdianNo ratings yet
- Antitubercular Isoniazid and Drug Resistance of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis - A ReviewDocument16 pagesAntitubercular Isoniazid and Drug Resistance of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis - A ReviewNini FarmNo ratings yet
- Polishing The Tarnished Silver Bullet The Quest FoDocument12 pagesPolishing The Tarnished Silver Bullet The Quest FoTamas ZefferNo ratings yet
- Bacteriophage TherapyDocument5 pagesBacteriophage TherapyMário FernandesNo ratings yet
- P6 HsaDocument37 pagesP6 HsaAndreNo ratings yet
- Review On Cephalosporins Re ModifiedDocument6 pagesReview On Cephalosporins Re Modifiedramirezgrisel966No ratings yet
- TX Carbapenem Resistent MoDocument11 pagesTX Carbapenem Resistent MoInes MendonçaNo ratings yet
- Sabtu 2015Document9 pagesSabtu 2015Felicia BulaiNo ratings yet
- Global Spread of Antibiotic Resistance: The Example of New Delhi Metallo-B-Lactamase (NDM) - Mediated Carbapenem ResistanceDocument15 pagesGlobal Spread of Antibiotic Resistance: The Example of New Delhi Metallo-B-Lactamase (NDM) - Mediated Carbapenem ResistanceDon Marcos Quintela BalujaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of In-Vitro Efficacy of Vanc, LNZ and Dapto Angainst MRSA.Document6 pagesComparison of In-Vitro Efficacy of Vanc, LNZ and Dapto Angainst MRSA.Nawwal NaeemNo ratings yet
- Report 1Document6 pagesReport 1api-484300781No ratings yet
- Inhibiting The Growth of Pathogens in Vivo Using Antimicrobial AgentsDocument6 pagesInhibiting The Growth of Pathogens in Vivo Using Antimicrobial AgentsronneldeleyvaNo ratings yet
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Vitro Activity of 12 AMDocument5 pagesMycobacterium Tuberculosis in Vitro Activity of 12 AMyves.cosnuauNo ratings yet
- The Resistance Mechanism of Escherichia Coli Induced by Ampicillin in LaboratoryDocument11 pagesThe Resistance Mechanism of Escherichia Coli Induced by Ampicillin in Laboratorylitbang.pbperdosri4No ratings yet
- Microorganisms 11 01474Document19 pagesMicroorganisms 11 01474hawamasfufahNo ratings yet
- Review: Antimicrobial Resistance in Hospitals: How Concerned Should We Be?Document8 pagesReview: Antimicrobial Resistance in Hospitals: How Concerned Should We Be?Victor GodwinNo ratings yet
- Multidrug Resistant Gram Negative BacteriaDocument6 pagesMultidrug Resistant Gram Negative BacteriaAniAliciaOrtizCastleNo ratings yet
- Niños Clin - Infect - Dis - 2014 - May - 15 - 58 (10) - 1439-48Document10 pagesNiños Clin - Infect - Dis - 2014 - May - 15 - 58 (10) - 1439-48mariangelNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2.editedDocument13 pagesDiscussion 2.editedmutisya johnboscoNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Resistensi Antibiotik - 2014Document10 pagesMekanisme Resistensi Antibiotik - 2014ArdieNo ratings yet
- Art - Antimicrobial Resistance and Respiratory InfectionsDocument11 pagesArt - Antimicrobial Resistance and Respiratory InfectionsjoshalmartzNo ratings yet
- NDM 1Document8 pagesNDM 1m.purbashaNo ratings yet
- Khvi 19 2175519Document23 pagesKhvi 19 2175519Robert StryjakNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2.editedDocument11 pagesDiscussion 2.editedmutisya johnboscoNo ratings yet
- Treatment Options For Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial InfectionsDocument11 pagesTreatment Options For Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial InfectionsCesar Augusto Cardona OspinaNo ratings yet
- Seukep Et al.2022-Antibiotics-ReviewDocument26 pagesSeukep Et al.2022-Antibiotics-ReviewArmel J. SeukepNo ratings yet
- Aslm 2018 Role of The Laboratory in AmrDocument37 pagesAslm 2018 Role of The Laboratory in Amrphuong mai leNo ratings yet
- Fbrio 02 1304444Document15 pagesFbrio 02 1304444walidNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics – Are They Curing Us or Killing Us?: The Catastrophic Impact of the Over-prescription of Antibiotics on Our HealthFrom EverandAntibiotics – Are They Curing Us or Killing Us?: The Catastrophic Impact of the Over-prescription of Antibiotics on Our HealthNo ratings yet
- JWC EWMA Supplement NPWT Jan 2018 AppendixDocument155 pagesJWC EWMA Supplement NPWT Jan 2018 AppendixirwanchemNo ratings yet
- Intracanal Medicaments: Presented By: DR - Suruchi Sisodia Dept. of Conservative Dentistry and EndodonticsDocument106 pagesIntracanal Medicaments: Presented By: DR - Suruchi Sisodia Dept. of Conservative Dentistry and Endodonticsrasagna reddy100% (1)
- 47161-Article Text-129163-1-10-20210606Document8 pages47161-Article Text-129163-1-10-20210606Yulia MargarethaNo ratings yet
- лекция 8 Phlegmon of the floor of the mouth. Topographic anatomy of the floor of the mouth, sources of infection, possible ways of spreading the infection. Clinic, differential diagnostics. Surgery. PDocument41 pagesлекция 8 Phlegmon of the floor of the mouth. Topographic anatomy of the floor of the mouth, sources of infection, possible ways of spreading the infection. Clinic, differential diagnostics. Surgery. Ptalalelsherif92No ratings yet
- Ijerph 18 06796 v2Document24 pagesIjerph 18 06796 v2paolaNo ratings yet
- WHO Methodology For A Global Programme On Surveillance of Antimicrobial ConsumptionDocument44 pagesWHO Methodology For A Global Programme On Surveillance of Antimicrobial ConsumptionKharisma GynaNo ratings yet
- Tugas KompreDocument6 pagesTugas KompreNadilla islamiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Clinical Pharmacology - An Important Aspect in Homoeopathic ReDocument16 pagesPre-Clinical Pharmacology - An Important Aspect in Homoeopathic ReSandhiya GustinNo ratings yet
- Genomic Analysis of Phylogroup D Assembly: Escherichia Coli Strains Using Novel De-Novo Reference-Based GuidedDocument9 pagesGenomic Analysis of Phylogroup D Assembly: Escherichia Coli Strains Using Novel De-Novo Reference-Based GuidedRecto SutismaNo ratings yet
- The Truth About Colloidal Silver and Gold PDFDocument153 pagesThe Truth About Colloidal Silver and Gold PDFIgor Genov100% (2)
- An Update On Prunus Armeniaca Phytochemical Composition and Biological ActivitiesDocument7 pagesAn Update On Prunus Armeniaca Phytochemical Composition and Biological ActivitiesDenice JercqueNo ratings yet
- Mikroorganisma Dan Kesannya Terhadap Benda Hidup Mikroorganism Terhadap Bend TDocument33 pagesMikroorganisma Dan Kesannya Terhadap Benda Hidup Mikroorganism Terhadap Bend TElleya AsnibamedaYasaNo ratings yet
- MrsaDocument63 pagesMrsaRAHULNo ratings yet
- Infection and ResponseDocument26 pagesInfection and ResponseStefaniya Dmitrievna “Stef” DeminetsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Environmental and Applied MicrobiologyDocument44 pagesChapter 10 Environmental and Applied MicrobiologySherinne Jane CariazoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Moist Exposed Burn Ointment (MEBO) With Silver Sulfadiazine (Ag-S) For The Treatment of Deep Burn InjuryDocument89 pagesComparison of Moist Exposed Burn Ointment (MEBO) With Silver Sulfadiazine (Ag-S) For The Treatment of Deep Burn InjuryElis Sri AlawiyahNo ratings yet
- ваппывDocument82 pagesваппывizmailovraimNo ratings yet
- BetaStar 1206Document2 pagesBetaStar 1206api-3697331No ratings yet
- Apteka Participants Profile1Document26 pagesApteka Participants Profile1satyam pathakNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document15 pagesChap 4Rayner AbuegNo ratings yet
- Paket ADocument14 pagesPaket AAgnes Magda Dewi S.Pd. (Guru)No ratings yet
- SEM 6 - 10 - BA-BSc - HONS - MICROBIOLOGY - CC-14 - MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY - 10329Document2 pagesSEM 6 - 10 - BA-BSc - HONS - MICROBIOLOGY - CC-14 - MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY - 10329soumyadip shitNo ratings yet
- Regulations: The TheDocument5 pagesRegulations: The Thekaris delcastilloNo ratings yet