Heredity and Evolution
Heredity and Evolution
Uploaded by
Kartik MishraCopyright:
Available Formats
Heredity and Evolution
Heredity and Evolution
Uploaded by
Kartik MishraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Heredity and Evolution
Heredity and Evolution
Uploaded by
Kartik MishraCopyright:
Available Formats
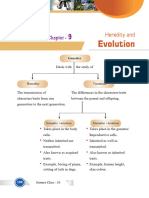
HEREDITY
Introduction
- All living organisms give rise to new individuals (offspring) by a
process of reproduction.
- The offspring produced as a result is similar to their parent but not
identical i.e. they also show some differences.
- The mechanism of transmission of character is called Heredity or
Inheritance while the differences seen among individuals is called
variations
Accumulation of Variation during Reproduction
Variation
- The differences in the characters (or traits) among the parents and
their offspring, the offspring or the individuals of same specs is
called as variation.
- Some amount of variation is produced during asexual reproduction
while the number of successful variations are maximized by the
process of Sexual Reproduction.
Importance of Variation
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
- Depending on the nature of variation, different individuals of a
species can have different advantages. E.g; Bacteria that can
withstand heat will survive better in a heat wave.
- Main advantage of variation to a species is that it increases the
chances of its survival in a changing environment.
Heredity
- The transmission of characters from parents to offspring is
called heredity.
Traits
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Rule of Inheritance of Traits -
Gregor Mendel
- Considered as the "Father of Genetics".
- He was the first Scientist to make a
systematic study of patterns of inheritance.
- He used pea plants Pisum sativum for his
experiments.
Tall Short Round Yellow Green
Wrinkled Seed Color
Plant Height
Important Terms
Factor/Gene - It is a segment of DNA that determines a particular
character. Genes are represented by letters. A capital letter shows that
the gene is dominant, and a small one that it is recessive.
Alleles - Alternate forms of a gene. E.g, Pea plant height - Tall(T) & Short
(t) Allele
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Dominant Allele - A dominant allele expresses itself in the presence or
absence of recessive allele. Example - Allele for tallness (T).
Recessive Allele - A recessive allele is able to express itself only in the
absence of a dominant allele. Example – Allele for shortness (t)
Genotype – It is the genetic composition of an individual. Example TT, Tt
or tt
Phenotype – It is the characteristic which is visible in an organism.
Example Tall or Short plant height.
Homozygous – An individual having identical alleles. Example TT or tt
Heterozygous – An individual having contrasting alleles. Example Tt
Monohybrid Cross
- In monohybrid cross, we consider one pair of contrasting trait.
1. Mendel selected true breeding tall pea plant (TT) and crossed
it with Short (tt) plant.
2. The plants formed as a result of the cross represented first
filial or F1 generation.
3. All the F1 plants obtained were tall.
4. Mendel self-pollinated the F1 plants (selfing) and observed that
plants in the F2 generation were 75% tall and 25% Short i.e.
phenotypic ratio 3:1
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Parental Generation Tall X Short
TT tt
Gametes T T t t
F1 Generation Tt Tt Tt Tt
Phenotype – All tall Genotype - Tt
Selfing F1 Tall X Tall
Generation Tt Tt
Gametes T t T t
F2 Generation
Phenotypic Ratio - 3 Tall : 1 Short Genotypic Ratio - 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt
3:1 1:2:1
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
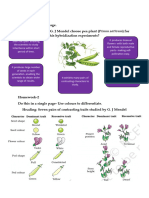
Dihybrid Cross
- In Dihybrid cross, We consider two pairs of contrasting traits.
(Seed shape and Seed Colour)
Experiment
1) Mendel crossed pea plants bearing Round & Yellow seeds (Rryy)
with wrinkled green (rryy).
2) He obtained F1 generation with all pea plants having Round and
Yellow seeds (RrYy).
3) On Selfing F1 offspring, Mendel obtained 4 different types of
progeny in F2 generation: Round & Yellow, Round and Green,
Wrinkled & green and Wrinkled green in the ratio 9:3:3:1
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Parental Generation Round & Yellow X Wrinkled & Green
RRYY rryy
Gametes RY Ry ry ry
F1 Generation
Phenotype –
Round & Yellow
Selfing F1 RrYy X RrYy
Generation
Gametes RY Ry rY ry RY Ry rY ry
F2 Generation RY Ry rY ry
Round & Yellow 9
RY
Round & Green 3
Wrinkled & Yellow 3
Ry Wrinkled & Green 1
rY Phenotype Ratio-
9:3:3:1
ry
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Mendel's Laws
Law of Dominance -
Mendel's Law of dominance states that in a heterozygote, one
trait will conceal the presence of another trait.
E.g. Tall (TT) X Short (tt)
Tall (Tt)
Law of Segregation -
When an organism makes gametes, each gamete receives just one
gene copy, which is randomly. This is known as the law of
Segregation.
E.g. - Tall (Tt)
Gamete T t
Law of Independent Assortment -
Mendel's law of independent assortment that the alleles of two
more (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes
independently of one another.
E.g. - In a dihybrid cross, the shape of seed doesn't depend on
the colour of seed.
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
How do traits get expressed?
- Cellular DNA is the information source for making proteins in the
cell.
- A part of DNA that provides information for one particular
protein is called a gene for that protein.
- Example
Height of a plant depends upon growth hormone which in turn is
controlled by the gene. If the gene is efficient and more growth
hormone is s ecreted, the plant will grow tall. If the gene gets
altered and less hormone is secreted, then the plant will remain
short. Thus, genes control characteristics or traits.
Sex Determination
- The process by which sex of a new born individual is determined is
called Sex Determination.
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
Factors determination Sex Determination
Non - Genetically Genetically
- Environmental cues : In - In humans, genes inherited
turtles, Alligators, Crocodile, from parents decide the sex
temperature at which of the offspring.
fertilized eggs are kept
determines sex.
- In Snails, individuals can
change sex.
Sex determination in humans
- In humans, sex of the child depends on the
father or we can say, the male gamete that
fuses with the female gamete.
- Humans possess 23 pairs of chromosomes
out of which one pair comprises the sex
chromosomes.
(XX in females - perfect pair)
(XY in males - Mis-matched pair)
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
- At the time of fertilization, the egg cell
fuses with sperm resulting in the formation
of Zygote.
- During fertilization,
i) If the egg cell carrying X chromosome
fuses with sperm carrying X
chromosome, the offspring would be a
girl.
ii) If the egg cell carrying X chromosome
fuses w ith sperm carrying Y
chromosome, the offspring would be a
boy.
Subscribe to my YT channel - https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSuthar
You might also like
- CSEC Biology - Monohybrid Cross Worksheet 1Document2 pagesCSEC Biology - Monohybrid Cross Worksheet 1Tamicka Bonnick100% (3)
- Heredity and Evolution - RemovedDocument11 pagesHeredity and Evolution - Removedashika2731No ratings yet
- Heredity Notes by Gaurav SutharDocument13 pagesHeredity Notes by Gaurav SutharVinayak ParasharNo ratings yet
- Heredity NotesDocument13 pagesHeredity Notesashwinsachdeva22No ratings yet
- HEREDITY - Important Questions& AnswersDocument7 pagesHEREDITY - Important Questions& Answerskfjg47zq26No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument9 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationShalini JhaNo ratings yet
- POWERED BY MR NOTES CLASS 10th NOTES FOR STUDENTS For 2023Document7 pagesPOWERED BY MR NOTES CLASS 10th NOTES FOR STUDENTS For 2023ayushnagraj76No ratings yet
- JK BW QJEQFM4 WHFG LQ FAlDocument17 pagesJK BW QJEQFM4 WHFG LQ FAlxedop66649No ratings yet
- HeredityDocument24 pagesHereditythemidnightismNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document18 pagesWa0004.Mouth LessNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Heredity and EvolutionDocument7 pagesChapter 8 - Heredity and Evolutionrohitnpatil9021No ratings yet
- Evolution HereditaryDocument54 pagesEvolution HereditaryaidonveliyilNo ratings yet
- Experiments Conducted by Mendel: (F,-Generation UndergoDocument3 pagesExperiments Conducted by Mendel: (F,-Generation Undergosi5416119No ratings yet
- Ln-9 BOOK EXERCISEDocument10 pagesLn-9 BOOK EXERCISEsusrudhansNo ratings yet
- ch9 Heredity & Evolution.10thDocument18 pagesch9 Heredity & Evolution.10thnotstutibutlucyNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument6 pagesGenetics NotesTRIANGULAR CLASSNo ratings yet
- CH-9-HEREDITYDocument11 pagesCH-9-HEREDITYannlov2laugh45No ratings yet
- Homework Chapter-8 HeredityDocument10 pagesHomework Chapter-8 HereditydivyanagarajjNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument19 pagesHeredity and EvolutionJames Bond 007No ratings yet
- Velammal Bodhi Campus, Ponneri Velammal Iit/Neet Academy: Class: Xii Sub: Biology Book Back QuestionsDocument10 pagesVelammal Bodhi Campus, Ponneri Velammal Iit/Neet Academy: Class: Xii Sub: Biology Book Back QuestionsKaviya NNo ratings yet
- Heredityan12092024121625 0Document6 pagesHeredityan12092024121625 0nmathur505No ratings yet
- Biology Form 5: 5.1: MENDEL'S ExperimentDocument29 pagesBiology Form 5: 5.1: MENDEL'S Experimentveronica francisNo ratings yet
- Heredity Notes Class XDocument9 pagesHeredity Notes Class Xwefomo9108No ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics:: The Laws of InheritanceDocument16 pagesMendelian Genetics:: The Laws of InheritanceCaro Torres GaleanoNo ratings yet
- Heredity NotesDocument7 pagesHeredity Notessofia khanumNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution Notes PDFDocument17 pagesHeredity and Evolution Notes PDFsofiyajamadar15No ratings yet
- 2nd Term Biology Ss3Document20 pages2nd Term Biology Ss3Wisdom Lawal (Wizywise)No ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument30 pagesMendelian GeneticsChleo Princess Aporbo EscolNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 NotesDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 NotesHenry SathyanNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 8 - Variation & InheritanceDocument27 pagesBiology Grade 8 - Variation & InheritanceMokshitha Reddy YanamalNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 3Document16 pagesScience 8 - Q4 - Week 3AlfielAquino100% (1)
- Elegant Planner Cover DesignDocument41 pagesElegant Planner Cover Designharibharathan007No ratings yet
- Heredity Class 10Document40 pagesHeredity Class 10ChaithraNo ratings yet
- Principle of InheritanceDocument8 pagesPrinciple of Inheritanceganishgakannan05100% (1)
- Heredity by Sr Maharana Kv2,BbsrDocument5 pagesHeredity by Sr Maharana Kv2,BbsrBISWANATH BEHERANo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument15 pagesHeredity and Evolutionrvharshini31No ratings yet
- Class 10 HeredityDocument7 pagesClass 10 HeredityInsiya HuzefaNo ratings yet
- GeneticsA LevelDocument38 pagesGeneticsA Levelezraariho01No ratings yet
- 14 PDFDocument38 pages14 PDFAbdullah Saad Al-AbashNo ratings yet
- Geneticso LevelDocument25 pagesGeneticso Levelrobertoryema4No ratings yet
- Heredity Class 10 NEETDocument25 pagesHeredity Class 10 NEETPixcasso 21100% (1)
- Mendel's Law of Inheritance 24Document10 pagesMendel's Law of Inheritance 24darktomal920No ratings yet
- Genetics by Garima Mam Lecture 2Document99 pagesGenetics by Garima Mam Lecture 2MOHD zAIDNo ratings yet
- UNIYTFOUR2Document91 pagesUNIYTFOUR2stevenguaduNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument53 pagesGeneticspkyliejane30No ratings yet
- Importance of VariationDocument15 pagesImportance of VariationRAJESH MEENANo ratings yet
- Notes of HERIDITY2020Document5 pagesNotes of HERIDITY2020Shubham VermaNo ratings yet
- q4 Mod 3 w3 Mendelian GeneticsDocument52 pagesq4 Mod 3 w3 Mendelian GeneticsBaja, Ysabelle Rose B.No ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 5 Part IDocument5 pagesNotes Chapter 5 Part IRida ShareefNo ratings yet
- X 9 Heredity and EvolutionDocument29 pagesX 9 Heredity and Evolutionrenugoyal1920No ratings yet
- Chapter 5-2Document30 pagesChapter 5-2parisinghg098No ratings yet
- 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation-NCERT Questions N AnswersDocument3 pages5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation-NCERT Questions N AnswersJustin SajuNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology - Principles of Inheritance and Variations - Notes (Part I)Document13 pages12 Biology - Principles of Inheritance and Variations - Notes (Part I)Jayadevi Shanmugam100% (1)
- HeredityDocument4 pagesHeredityneko -samaNo ratings yet
- Mendel's DiscoveriesDocument39 pagesMendel's DiscoveriesponnambhuviNo ratings yet
- 10th Heredity (1)Document7 pages10th Heredity (1)chetnabisht003No ratings yet
- Class 10 Heredity and Evolution Study NotesDocument13 pagesClass 10 Heredity and Evolution Study Notesi like cowsNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument28 pagesMendelian Geneticsjamaicaubpon5No ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and VariationAfzal MohammedNo ratings yet
- Notes - Heredity and EvolutionDocument16 pagesNotes - Heredity and EvolutionweirdoNo ratings yet
- CH14 Study QuestionsDocument24 pagesCH14 Study QuestionsShuba SalvamNo ratings yet
- Heredity - Inheritance and VariationDocument25 pagesHeredity - Inheritance and VariationPhilpNil8000No ratings yet
- Drosophila ExperimentDocument8 pagesDrosophila Experimenteizzah asriNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 5 InheritanceDocument52 pagesBIOLOGY Form 5 Chapter 5 InheritanceCabdicasiis Maxamuud Guuleed100% (1)
- Science Class 10 Term 2 Sample Paper 2Document5 pagesScience Class 10 Term 2 Sample Paper 2Sangeeta SharmaNo ratings yet
- 05 - Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument35 pages05 - Principles of Inheritance and Variationporape8561No ratings yet
- Study MaterialDocument36 pagesStudy MaterialAngelNo ratings yet
- Bio511 c2.3Document51 pagesBio511 c2.3Athirah JeffryNo ratings yet
- Document Camera and PunnettDocument4 pagesDocument Camera and PunnettJohn Kevin NocheNo ratings yet
- Open Genetics PDFDocument513 pagesOpen Genetics PDFSagenxNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Chapter 14 - Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocument3 pagesAP Biology Chapter 14 - Mendel and The Gene IdeawaterforlifeNo ratings yet
- Tiffany Shoham - UntitledDocument2 pagesTiffany Shoham - Untitledknoblock_michaelNo ratings yet
- Quarter3 Syllabus StudentDocument4 pagesQuarter3 Syllabus Studentapi-232311174No ratings yet
- Biology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 7 AnswersDocument10 pagesBiology For CAPE Unit 1 Chapter 7 AnswersFiveLimaRomeo100% (1)
- Endel S AWS OF Nheritance: Figure 4.1 Seven Pairs of Contrasting Traits in Pea Plant Studied by MendelDocument23 pagesEndel S AWS OF Nheritance: Figure 4.1 Seven Pairs of Contrasting Traits in Pea Plant Studied by Mendeldhruvingandhi0002No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Genetics Guided Notes Page 7 Non-MendellanDocument11 pagesUnit 5 Genetics Guided Notes Page 7 Non-MendellanCurt NormanNo ratings yet
- Cmap 9Document7 pagesCmap 9Emmanuel John PonioNo ratings yet
- Definition of Gene (Repaired)Document107 pagesDefinition of Gene (Repaired)Ananda PreethiNo ratings yet
- Cot-Biology Science-DlpDocument16 pagesCot-Biology Science-DlpMarisol Ann de Leon100% (1)
- Bio428L - Exercise 9 - VillamancaDocument5 pagesBio428L - Exercise 9 - VillamancaJohn Jerald VillamancaNo ratings yet
- +2 Previous Year Zoology QP 2023 UpdatedDocument52 pages+2 Previous Year Zoology QP 2023 UpdatedLena AlbertNo ratings yet
- 9 InheritanceDocument6 pages9 InheritancePeter TingNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell) Chapter 9 Patterns of InheritanceDocument16 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell) Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritanceabeer khawwamNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics PDFDocument7 pagesMendelian Genetics PDFKaiyama AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 12th Science HSC Perfect Biology I PDFDocument31 pages12th Science HSC Perfect Biology I PDFSamyak TelmoreNo ratings yet
- All Kerala Bhavans Biology 2010Document14 pagesAll Kerala Bhavans Biology 2010SajeevNo ratings yet
- GENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedDocument310 pagesGENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedHarshit VermaNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics: - Mendel & The - Monohybrid Cross - Law - Dihybrid Cross - Law ofDocument20 pagesMendelian Genetics: - Mendel & The - Monohybrid Cross - Law - Dihybrid Cross - Law ofPawan MahiyaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and GeniticsDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and GeniticsVaishakhi MuraliNo ratings yet