Looping in Python
Uploaded by
Shahid MandokhailLooping in Python
Uploaded by
Shahid MandokhailCode & Debug
WHILE LOOP
A while loop in python runs a bunch of code or statements again and again
until the given condition is true when the condition becomes false, the loop
terminates its repetition.
We must use the keyword “while”, along with it we have to put a condition in
parenthesis and after that, a colon is placed. The condition could be either true
or false. Until the condition is true, the loop will keep on executing again and
again. If we use a certain sort of condition in our while loop that, it never
becomes false then the program will keep on running endlessly, until we stop it
by force. So, this kind of mistake in our syntax is known as logical/human error.
To terminate an infinite loop, you can press CTRL+C on your system.
Syntax
while condition:
Body of your While Loop
Example
count = 0
while count < 9:
print("The count is : ", count)
count = count + 1
print("Good bye!")
Output
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
The infinite Loop
A loop becomes infinite loop if a condition never becomes FALSE. You must use
caution when using while loops because of the possibility that this condition
never resolves to a FALSE value.
This results in a loop that never ends. Such a loop is called an infinite loop.
Example 1
x = 1
while x == 1: # This shows an infinite loop
num = input("Enter a number :")
print("You entered: ", num)
print("Good bye!")
Example 2
num = 10
while num > 1:
print("Hello")
Using WHILE loop with IF and BREAK statement
Break statement helps us to stop the execution of any loop at that position.
count = 0
while count < 9:
if count == 3:
break
print('The count is:', count)
count = count + 1
print("Good bye!")
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
Using WHILE loop with IF and CONTINUE statement
Continue statement skips all the code written below that and goes to next
loop.
count = 0
while count < 9:
count = count + 1
if count == 4:
continue
print('The count is:', count)
NESTED WHILE Loop
Python programming language allows to use one loop inside another loop
which is known as Nested Loop.
The syntax for a nested while loop statement in Python programming language
is as follows:
while expression:
while expression:
statement(s)
statement(s)
Example
i = 1
j = 5
while i < 4:
while j < 8:
print(i, ",", j)
j = j + 1
i = i + 1
Output
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
Practice Examples (WHILE-LOOP)
1. Print first 10 Natural numbers.
2. Print all the even numbers from 1 to 100.
3. Find sum of N numbers where N is input from User.
4. Check whether number entered by User is Prime or Not.
5. Check whether number entered by User is Armstrong or not.
6. Find Factorial of a number entered by User.
7. Print the first 10 multiples of a number entered by User.
8. Count the number of digits in a number that is entered by User.
9. Write a Program to Reverse a number.
For solutions, check the end of the book.
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
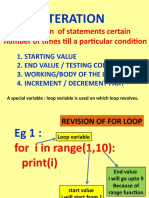
FOR LOOP
Like all the other functions we have seen so far, for loop is also just a
programming function that iterates a statement or several statements based
on specific boundaries under certain defined conditions, that are the basis of
the loop.
Note that the statement that the loop iterates must be present inside the body
of the loop.
Regarding loops, iteration means going through some code again and again. In
programing it has the same meaning, the only difference is that the iteration
depends upon certain conditions and upon its fulfillment, the iteration stops,
and the compiler moves forward.
The concept of the loop could be easily understood using an example of songs
playlist. When we like a song, we set it on repeat, and then it automatically
starts playing again and again. The same concept is used in programming, we
set a part of code for looping and the same part of the code executes until the
certain condition that we provided is fulfilled. You must be thinking that in
song playlist the song keeps on playing until we stop it, the same scenario can
be made in case of loops, if we put a certain condition that the loop could not
fulfill, then it will continue to iterate endlessly until stopped by force.
An example of where loop could be helpful to us could be in areas where a lot
of data must be printed on the screen and physically writing that many printing
statements could be difficult or in some cases impossible.
Advantages of Loops:
• Complex problems can be simplified using loops
• Less amount of code required for our program
• Lesser code so lesser chance or error
• Saves a lot of time
• Can write code that is practically impossible to be written
• Programs that require too many iterations such as searching and sorting
algorithms can be simplified using loops
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
Example 1
Print 0 to 10 using for loop.
for i in range(11):
print(i)
We have typed 11 because any number at the end is excluded in FOR-LOOP.
Example 2
Print 5 to 20 using for loop.
for x in range(5, 21):
print(x)
We have typed 21 because any number at the end is excluded in FOR-LOOP.
Example 3
Calculate sum of numbers from 1 to 10.
total = 0
for x in range(1, 11):
total = total + x
print(total)
Using FOR-LOOP with IF and BREAK Statement
Break statement stops the Loop at that Position.
for i in range(1, 20):
if i == 5:
break
print(i)
Output
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
Using For-Loop with IF and CONTINUE Statement
Continue statement skips all the code written below that and goes to next
loop.
for i in range(1, 10):
if i == 5:
continue
print(i)
Output
Steps in FOR-LOOP
Suppose we want to print numbers from 1 to 20, but by adding +2 every time.
Ex. We need to print -> 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19
Example
for i in range(1, 21, 2):
print(i, end=" ")
Try out these examples on your own
for i in range(1, 21, 5):
print(i, end=" ")
for i in range(55, 100, 5):
print(i, end=" ")
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
Negative FOR-LOOP
Print all the numbers from 1 to 10, in reverse order.
for i in range(10, 0, -1):
print(i)
See some more examples below:
for i in range(10, 5, -1):
print(i)
for i in range(100, 20, -13):
print(i)
for i in range(20, -20, -2):
print(i)
for i in range(-10, -100, -20):
print(i)
Practice Examples (FOR-LOOP)
10. Print first 10 Natural numbers.
11. Print all the even numbers from 1 to 100.
12. Find sum of N numbers where N is input from User.
13. Check whether number entered by User is Prime or Not.
14. Check whether number entered by User is Armstrong or not.
15. Print multiplication table of a number entered by user.
16. Program to display all the prime numbers within a range.
For solutions, check the end of the book.
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
Nested FOR-LOOP
Loops defined within another Loop are called Nested Loops. Nested loops are
used to iterate matrix elements or to perform complex computation.
When an outer loop contains an inner loop in its body it is called Nested
Looping.
for <expression>:
for <expression>:
Body
Example
Print the following pattern
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
Solution
for i in range(5):
for j in range(5):
print("*", end=" ")
print()
Example
Print the following pattern:
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
Solution
for i in range(1, 6):
for j in range(i):
print("*", end=" ")
print()
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
Practice Examples (NESTED-FOR-LOOP)
17. Make the following Patterns:
a. *
**
***
****
*****
b. 1
12
123
1234
12345
c. 5
54
543
5432
54321
d. 5 5 5 5 5
4444
333
22
1
e. 1
21
321
4321
54321
f. 5
45
345
2345
12345
18. Write a program to display following Output
a. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
b. 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
c. 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
Code & Debug
d. 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40
e. 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
For solutions, check the end of the book.
Contact: +91-9712928220 | Mail: info@codeanddebug.in
Website: codeanddebug.in
You might also like
- 03 Python - Decision Making and LoopingNo ratings yet03 Python - Decision Making and Looping52 pages
- Loops and Iteration (Python For Beginners)No ratings yetLoops and Iteration (Python For Beginners)7 pages
- FALL WIN SEM (2023-24) CSE0106 ETH AP2023243000534 Reference Material I 02-Nov-2023 Module3No ratings yetFALL WIN SEM (2023-24) CSE0106 ETH AP2023243000534 Reference Material I 02-Nov-2023 Module382 pages
- L06 - Flow Control - While Loop and Basic For LoopNo ratings yetL06 - Flow Control - While Loop and Basic For Loop32 pages
- Report On Loops in Python and Their UtilityNo ratings yetReport On Loops in Python and Their Utility4 pages
- Python Loop Statement: By: Abhishek Saikia Class: 12 (C) Roll No: 17No ratings yetPython Loop Statement: By: Abhishek Saikia Class: 12 (C) Roll No: 1712 pages
- Flow of Control: Loops: Introduction To Programming and Problem SolvingNo ratings yetFlow of Control: Loops: Introduction To Programming and Problem Solving21 pages
- Two Steps Forward One Step Back The Presence of FeNo ratings yetTwo Steps Forward One Step Back The Presence of Fe12 pages
- Question8: Identify 3 Social Issues Along With Causes and Effect and Legal RemedyNo ratings yetQuestion8: Identify 3 Social Issues Along With Causes and Effect and Legal Remedy2 pages
- Odoo Book by Cybrosys Technologies 9 19No ratings yetOdoo Book by Cybrosys Technologies 9 1911 pages
- DB Manual - Operational DB3-5.5 OIM (107599)No ratings yetDB Manual - Operational DB3-5.5 OIM (107599)17 pages
- Boeing RFP - Vfs SDC 2020 - Final - 1.2No ratings yetBoeing RFP - Vfs SDC 2020 - Final - 1.220 pages
- Complete Download Mastering UX Design with Effective Prototyping Apurvo Ghosh PDF All Chapters100% (2)Complete Download Mastering UX Design with Effective Prototyping Apurvo Ghosh PDF All Chapters39 pages
- COAL Assignment (Y86 Processor Architecture)100% (1)COAL Assignment (Y86 Processor Architecture)32 pages
- Madras University Bca Syllabus Ebcfd3186baf63904d42bba6f1d54f91No ratings yetMadras University Bca Syllabus Ebcfd3186baf63904d42bba6f1d54f915 pages
- Police Clearance Cerificate Character VerificationNo ratings yetPolice Clearance Cerificate Character Verification2 pages
- Fully Automatic Self-Calibrated Conductivity Measurement System PDFNo ratings yetFully Automatic Self-Calibrated Conductivity Measurement System PDF7 pages
- LM107/LM207/LM307 Operational Amplifiers: General DescriptionNo ratings yetLM107/LM207/LM307 Operational Amplifiers: General Description10 pages