0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsQB CND
QB CND
Uploaded by
Ishwari JadhavThe document contains a question bank with questions and answers about data communication systems. It discusses topics like data communication characteristics, components of a data communication system including sender, receiver, transmission medium, protocols and messages. It also defines different types of data transmission such as synchronous, asynchronous, isochronous, serial and parallel transmission. Finally, it discusses concepts like data rate, bit rate, signaling rate, baud rate, different network topologies, advantages of networking, client-server architecture and layers of the TCP/IP protocol suite.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
QB CND
QB CND
Uploaded by
Ishwari Jadhav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views9 pagesThe document contains a question bank with questions and answers about data communication systems. It discusses topics like data communication characteristics, components of a data communication system including sender, receiver, transmission medium, protocols and messages. It also defines different types of data transmission such as synchronous, asynchronous, isochronous, serial and parallel transmission. Finally, it discusses concepts like data rate, bit rate, signaling rate, baud rate, different network topologies, advantages of networking, client-server architecture and layers of the TCP/IP protocol suite.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document contains a question bank with questions and answers about data communication systems. It discusses topics like data communication characteristics, components of a data communication system including sender, receiver, transmission medium, protocols and messages. It also defines different types of data transmission such as synchronous, asynchronous, isochronous, serial and parallel transmission. Finally, it discusses concepts like data rate, bit rate, signaling rate, baud rate, different network topologies, advantages of networking, client-server architecture and layers of the TCP/IP protocol suite.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views9 pagesQB CND
QB CND
Uploaded by
Ishwari JadhavThe document contains a question bank with questions and answers about data communication systems. It discusses topics like data communication characteristics, components of a data communication system including sender, receiver, transmission medium, protocols and messages. It also defines different types of data transmission such as synchronous, asynchronous, isochronous, serial and parallel transmission. Finally, it discusses concepts like data rate, bit rate, signaling rate, baud rate, different network topologies, advantages of networking, client-server architecture and layers of the TCP/IP protocol suite.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Question Bank:
1. What is data communication? List characteristics of data
communication.
Data communications means the exchange of data between two
devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire
cable.
For data communications to occur, the communicating devices
must be part of a communication system made up of a
combination of hardware (physical equipment) and software
(programs).
Characteristics of Data Communication –
1. Delivery:
The system must deliver data to the correct destination. Data
must be received by the intended device or user and only by
that device or user.
2. Accuracy:
The system must deliver the data accurately. Data that have
been altered in transmission and left uncorrected are unusable.
3. Timeliness:
The system must deliver data in a timely manner. Data
delivered late are useless.
4. Jitter:
Jitter refers to the variation in the packet arrival time. It is the
uneven delay in the delivery of audio or video packets.
2. Draw basic block diagram of Data Communication system.
3. List and describe the components of data communication.
1. Sender –
It is simply a device that sends data messages. It can be a
computer, mobile, telephone, laptop, video camera, or
workstation, etc.
2. Receiver –
It is a device that receives messages. It can be a computer,
telephone mobile, workstation, etc.
3. Transmission Medium / Communication Channels -
Communication channels are the medium that connect two
or more workstations. Workstations can be connected by
either wired media or wireless media.
4. Set of rules (Protocol) –
When someone sends the data (The sender), it should be
understandable to the receiver also otherwise it is
meaningless.
5. Message -
A message is a piece of information that is to be transmitted
from one person to another. It could be a text file, an audio
file, a video file, etc.
4. Define Synchronous, Asynchronous, Isochronous, Serial and
Parallel data transmission.
1. Synchronous data transmission –
In Synchronous Transmission, data is sent in form of blocks
or frames. Between sender and receiver, synchronization is
compulsory. In Synchronous transmission, there is no time-
gap present between data.
2. Asynchronous data transmission –
In Asynchronous Transmission, data is sent in form of byte
or character. In this transmission start bits and stop bits are
added with data. It does not require synchronization.
3. Isochronous data transmission –
It is combination of both Synchronous and Asynchronous
data transmissions. Here the transmission has a time
constraint meaning, data must be delivered within time and
at regular intervals.
4. Serial data transmission –
In this, data-bit flows from one computer to another
computer in bi-direction. In this transmission, one-bit flows
at one clock pulse. In Serial Transmission, 8 bits are
transferred at a time having a start and stop bit.
5. Parallel data transmission –
In this, many bits are flow together simultaneously from one
computer to another computer. Parallel Transmission is
faster than serial transmission to transmit the bits. Parallel
transmission is used for short distance.
5. Define Data rate, Bit rate, Signaling rate, Baud rate.
1. Data rate –
Data Rate is defined as the amount of data transmitted
during a specified time period over a network. It is the speed
at which data is transferred from one device to another.
2. Bit rate –
Bit rate is defined as the transmission of a number of bits per
unit time (seconds). Bit rate emphasized computer efficiency.
3. Signaling rate –
Data signaling rate, is the aggregate rate at which data
passes a point in the transmission path of a data
transmission system.
4. Baud rate –
Baud rate is defined as the number of signal units per
second. Baud rate emphasized data transmission.
6. What are examples of point-to-point and multipoint connection?
1. Point-to-point connection examples –
Star Topology, Ring Topology, Mesh Topology.
2. Multipoint connection examples –
Bus Topology, Tree Topology, Hybrid Topology.
7. Outline the diagram of Ring, Bus Topology.
Ring topology –
Bus topology –
8. Name the advantages of Networking.
1. Resource sharing –
Devices can share resources between each other
interconnected through a network.
2. Remote management –
With a network, one can effortlessly manage their team from
even the remotest location virtually.
3. Cloud Computing –
Not everyone has access to high end hardware, so using a
network to access cloud computing serves as a solution.
4. Collaboration –
Collaboration can be improved if a team is just few clicks
away and network aids that.
5. Communication –
Similar to collaboration, communication also improves once
a network.
6. Competitive advantage –
If you have a network setup, to integrate your teams, you
have a better competitive advantage.
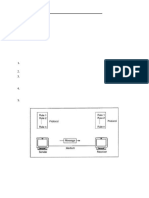
9. Examine Client-Server Architecture.
Diagram –
This is a model built to distribute workload between clients and
servers.
Client -
Client refers to any entity or organisation using a particular
service.
Server –
Server refers to a medium or person that serves something with a
specific purpose in mind.
Methodology -
1. A request is sent to the server by the client, through the
internet.
2. The server accepts the requests and sends data packets to the
client as per request.
3. Clients don’t share any resources but can share credentials if
required.
4. Example – World Wide Web, E-Mail.
10.Discuss Tree topology in detail.
1. The topology which has tree like structure and all the
devices are connected in branches is a Tree topology.
2. It is a combination of bus and start topology.
3. It is highly flexible and has a better scalability than
individual topologies.
4. Most popular topology among all.
Diagram –
11.Name two disadvantages of Mesh Topology.
1. Installation of this is extremely difficult.
2. Setup is a Complex process.
3. Power requirement is high.
4. Maintenance needs are challenging.
5. Each new devices adds significant cost.
12.Name two disadvantages of Hybrid Topology.
1. Design is a complex process.
2. Hybrid structures are larger in scale and hence require more
cables.
3. Hubs used to connect two structures are very costly, because
they are more intelligent than usual hubs.
4. Changes are to be made in hardware to connect one
topology to another.
13.Discuss Transport Layer.
Transport Layer –
It is responsible for giving services to application layer. Each
transport layer protocol has a specified protocol.
14.Discuss Application Layer.
Application Layer –
It is the logical end-to-end connection between two layers. It
includes a lot of predefined protocols over the internet.
15.Rewrite two protocols briefly.
1. TCP/IP Protocol –
Also known as Transmission Control Protocol/Internet
Protocol, developed by US Dept. of Defence to connect
multiple networks and preserve integrity.
2. ISO-OSI Model –
The International Standard Organisation developed this
architecture to allow different devices of varying
manufacturers to work together to communicate with
different operating systems.
16.Outline basic layers in TCP/IP Protocol Suite.
There are 5 basic layers in TCP/IP Suite as below –
1. Physical Layer -
It is lowest layer in a network model and is responsible for
carrying individual bit in a frame across the link. It deals
with the mechanical and electrical interface and medium.
2. Data Link Layer –
It is responsible for taking datagram and moving it across
the link. The link can be wired/wireless.
3. Network Layer -
It is responsible for connecting source computer to
destination computer. Routers are responsible to choose the
best path.
4. Transport Layer –
It is responsible for giving services to application layer. Each
transport layer protocol has a specified protocol.
5. Application Layer –
It is the logical end-to-end connection between two layers. It
includes a lot of predefined protocols over the internet.
You might also like
- Assignment BBPP1103 Principles of ManagementDocument8 pagesAssignment BBPP1103 Principles of ManagementNajib Roslan67% (3)
- Worksheet Torque Revised 2013 W KeyDocument2 pagesWorksheet Torque Revised 2013 W KeyRyan TomeldenNo ratings yet
- Road Safety Audit REPORTDocument99 pagesRoad Safety Audit REPORTayaz ali khan100% (7)
- Computer Networks and SecurityDocument184 pagesComputer Networks and SecurityPadma SankarNo ratings yet
- E Discovery OutlineDocument2 pagesE Discovery Outlinejackojidemasiado100% (1)
- 4915536Document123 pages4915536josephvanbac89% (18)
- DCN Notes - Unit 1 To 5 PDFDocument105 pagesDCN Notes - Unit 1 To 5 PDFM.tamil arasiNo ratings yet
- Networking Notes PDFDocument30 pagesNetworking Notes PDFMahi MudgalNo ratings yet
- Network Model ArchitectureDocument27 pagesNetwork Model ArchitectureS M AkashNo ratings yet
- CN (UNIT-1)Document60 pagesCN (UNIT-1)shivkumarbhardwaj043No ratings yet
- CN Unit 1Document52 pagesCN Unit 1megha.bhoityNo ratings yet
- Components of Data CommunicationDocument10 pagesComponents of Data CommunicationVinit KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument13 pagesComputer NetworkParidhi GaurNo ratings yet
- Cs3591 CN Unit 1Document79 pagesCs3591 CN Unit 1sgshanu121No ratings yet
- BCAI 302 computer networks UNIT 1Document25 pagesBCAI 302 computer networks UNIT 1raghav gourNo ratings yet
- Advance Computer NetworkDocument15 pagesAdvance Computer NetworkIffat KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document37 pagesChapter 1divyanshya03No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Advance Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument21 pagesUnit 2 - Advance Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inprince keshriNo ratings yet
- CS8591 CN Unit 1Document61 pagesCS8591 CN Unit 1Nagu StudyNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Network Assignment PDFDocument5 pagesData Communication and Computer Network Assignment PDFeyasuNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Xii CsDocument74 pagesComputer Networks Xii CsMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking Basics Questions and AnswersDocument19 pagesData Communication and Networking Basics Questions and AnswersaksumgereNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and NetworkingDocument55 pagesData Communications and NetworkingnadritzyNo ratings yet
- TYBCom Sem V CSA Unit I DCNI 1 PDFDocument5 pagesTYBCom Sem V CSA Unit I DCNI 1 PDFAditya KothariNo ratings yet
- Cosc 0160 NotesDocument25 pagesCosc 0160 NotesIANNo ratings yet
- Physical TopologyDocument7 pagesPhysical Topologyahraf jalaluddinNo ratings yet
- IctdipNetworking NotesDocument86 pagesIctdipNetworking NotesJoshua Kioko100% (1)
- PART (1) : Assignment Brief and Guidance: (Scenario)Document15 pagesPART (1) : Assignment Brief and Guidance: (Scenario)Minh Tuấn NgôNo ratings yet
- Data Comunication CH 1Document22 pagesData Comunication CH 1Desalegn sirnaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and NetworkingDocument38 pagesData Communication and NetworkingY CreationNo ratings yet
- CT 4Document10 pagesCT 4mj porrasNo ratings yet
- III B.SC DCN NOTESDocument172 pagesIII B.SC DCN NOTESMalathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemDocument10 pagesComputer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemShepherd AndoliniNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Data Communication and Computer NetworkDocument27 pagesFundamentals of Data Communication and Computer NetworkYash raundalNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Data Communication & NetworksDocument9 pages1 - Introduction To Data Communication & NetworksLakshmi NarayananNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networks: PerformanceDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networks: PerformancealokNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument32 pagesComputer NetworkTony StarkNo ratings yet
- All Unit ChatgptDocument75 pagesAll Unit ChatgptSAKSHAM PRASADNo ratings yet
- Unit I Computer Networks 16SCCCS6Document69 pagesUnit I Computer Networks 16SCCCS6Rajapradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Q1. Explain All Design Issues For Several Layers in Computer. What Is Connection Oriented and Connectionless Service?Document8 pagesQ1. Explain All Design Issues For Several Layers in Computer. What Is Connection Oriented and Connectionless Service?Shabbir KahodawalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument109 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksTejaswi SuryaNo ratings yet
- DC Lec1Document32 pagesDC Lec1malkmoh781.mmNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Cs Notes-083-1 (1)Document9 pagesClass Xii Cs Notes-083-1 (1)legendgaming161207No ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument133 pagesComputer NetworksAnusha MeenakshiNo ratings yet
- DCN-unit-1 ModifiedDocument112 pagesDCN-unit-1 ModifiedMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- cn chp 1Document73 pagescn chp 1pangerkarkaustubhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksIshan MengiNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemDocument5 pagesComputer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemShepherd AndoliniNo ratings yet
- Cs Unit 2 Test1 AnsDocument2 pagesCs Unit 2 Test1 AnsnjragavendaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Basics of Internet and The World Wide WebDocument11 pagesLesson 1-Basics of Internet and The World Wide WebLukania BoazNo ratings yet
- Computer Network AssignmentDocument17 pagesComputer Network AssignmentMohd Sadik KhanNo ratings yet
- CACS101 CFA Unit 5Document15 pagesCACS101 CFA Unit 5Shaikh YasmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1_Computer NetworkingDocument15 pagesChapter 1_Computer NetworkinglipungdrNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 - EditedDocument29 pagesModule - 1 - EditedPrathiksha GowdaNo ratings yet
- Cs1302 Computer Networks Full NotesDocument135 pagesCs1302 Computer Networks Full NotesRengabilla100% (6)
- Computer NetworksDocument172 pagesComputer NetworksOptimistic zenithNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Telecommunication Network Model and TypesDocument19 pagesLecture - Telecommunication Network Model and TypesMOHAMMED FAYEZ KHANNo ratings yet
- BCS 041Document28 pagesBCS 041priyanshu kNo ratings yet
- CN UNIT1 - Network FundamentalsDocument59 pagesCN UNIT1 - Network FundamentalsDamodhar BalireddyNo ratings yet
- Week 03 LecturesDocument21 pagesWeek 03 LecturesHamzah AkhtarNo ratings yet
- DCN ManualDocument465 pagesDCN ManualMiriam KautemwaNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- OTDRDocument2 pagesOTDRIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument12 pagesQuestion BankIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Dse Round 1 Cutoff 2021 For VjtiDocument3 pagesMaharashtra Dse Round 1 Cutoff 2021 For VjtiIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Free Education To Girl-Students Upto 12th STD (1994-95)Document9 pagesFree Education To Girl-Students Upto 12th STD (1994-95)Ishwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- EST Micro Project Group ListDocument2 pagesEST Micro Project Group ListIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Bpe MicroprojectDocument8 pagesBpe MicroprojectIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Exp EnergyConservationDocument5 pagesExp EnergyConservationMyla ToqueNo ratings yet
- Postmodification by Infinitive and - Ing Non-Finite ClausesDocument3 pagesPostmodification by Infinitive and - Ing Non-Finite Clausesscribd3No ratings yet
- (Cliqueapostilas - Com.br) Rudimentacao de BateriaDocument3 pages(Cliqueapostilas - Com.br) Rudimentacao de BateriaLuan TavaresNo ratings yet
- Bickford Et Al - 2010Document20 pagesBickford Et Al - 2010Lucas GrandinettiNo ratings yet
- Ecrime Identification Using Face Matching Based Using PHPDocument18 pagesEcrime Identification Using Face Matching Based Using PHPLogaNathanNo ratings yet
- Solve Tomorrow TnC2024Document21 pagesSolve Tomorrow TnC2024Harsh ChitaliyaNo ratings yet
- CLASS - 12th CAMPION SCHOOL, BHOURI, BHOPAL PT-2 EXAMINATION SUBJECT - CHEMISTRY MM - 50Document22 pagesCLASS - 12th CAMPION SCHOOL, BHOURI, BHOPAL PT-2 EXAMINATION SUBJECT - CHEMISTRY MM - 50Harshil NagwaniNo ratings yet
- PSM-ADV FlowchartDocument2 pagesPSM-ADV FlowchartCedric YabyabinNo ratings yet
- ME EXTC 1st Year PortionDocument96 pagesME EXTC 1st Year PortionHannan SatopayNo ratings yet
- Dbms Project ReportDocument93 pagesDbms Project Reportkenchalo100% (2)
- 1st Exam 2nd yDocument3 pages1st Exam 2nd yChekchek ImibashNo ratings yet
- MT105b Commentary 2021Document22 pagesMT105b Commentary 2021Tamara TopicNo ratings yet
- PEHEL - 2022 - Ward Wise ListDocument27 pagesPEHEL - 2022 - Ward Wise Listsameer143waghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Motion in A Plane Introduction To Polar CoordinatesDocument11 pagesLecture 11 Motion in A Plane Introduction To Polar CoordinatesAnonymous yorzHjDBdNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument11 pagesEpithelial TissueFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- 424 Eletrical CircutDocument4 pages424 Eletrical CircutveereshNo ratings yet
- 2 A Norma A 185 - 02Document5 pages2 A Norma A 185 - 02Kenvi AlarconNo ratings yet
- Aghorastra Mantra Sadhna Vidhi in Hindi & Sanskrit PDFDocument12 pagesAghorastra Mantra Sadhna Vidhi in Hindi & Sanskrit PDFsumit girdharwal80% (5)
- PolicyDocument3 pagesPolicylisayanfoNo ratings yet
- How To Repair A Dead Hard Disk Drive To Recover DataDocument20 pagesHow To Repair A Dead Hard Disk Drive To Recover DataDragan Fića FilipovićNo ratings yet
- 2 CIBG - Volume27 - Issue1 - Pages3450-3458Document10 pages2 CIBG - Volume27 - Issue1 - Pages3450-3458sabir aliNo ratings yet
- Paris BurningDocument2 pagesParis BurningKelsey KeulemanNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 10 Test QDocument5 pagesMath Grade 10 Test QDulce M. LupaseNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Class 9 - Atoms and MoleculesDocument28 pagesMCQ - Class 9 - Atoms and Moleculesget2maniNo ratings yet
- Christmas Meals MenuDocument3 pagesChristmas Meals Menufrankieellis04No ratings yet