Blooms Taxonomy
Blooms Taxonomy
Uploaded by
api-3823878Copyright:
Available Formats
Blooms Taxonomy
Blooms Taxonomy
Uploaded by
api-3823878Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Blooms Taxonomy
Blooms Taxonomy
Uploaded by
api-3823878Copyright:
Available Formats
http://officeport.com/edu/blooms.
htm
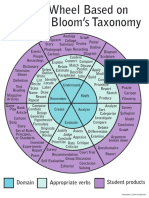
Bloom identified six levels within the cognitive domain, from the
simple recall or recognition of facts, as the lowest level, through
increasingly more complex and abstract mental levels, to the highest
order which is classified as evaluation.
Verb examples that represent intellectual activity on each level are listed
here.
1. Knowledge: arrange, define, duplicate, label, list, memorize,
name, order, recognize, relate, recall, repeat, reproduce state.
2. Comprehension: classify, describe, discuss, explain, express,
identify, indicate, locate, recognize, report, restate, review, select,
translate,
3. Application: apply, choose, demonstrate, dramatize, employ,
illustrate, interpret, operate, practice, schedule, sketch, solve, use,
write.
4. Analysis: analyze, appraise, calculate, categorize, compare,
contrast, criticize, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, examine,
experiment, question, test.
5. Synthesis: arrange, assemble, collect, compose, construct, create,
design, develop, formulate, manage, organize, plan, prepare,
propose, set up, write.
6. Evaluation: appraise, argue, assess, attach, choose compare,
defend estimate, judge, predict, rate, core, select, support, value,
evaluate.
http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/bloom.html
Learning Domains or Bloom's Taxonomy
Bloom identified three domains of educational activities:
• Cognitive: mental skills (K n o w l e d g e )
• Affective: growth in feelings or emotional areas (A t t i t u d e )
• Psychomotor: manual or physical skills (S k i l l s )
Bloom divides the three domains into subdivisions, starting from
the simplest behavior to the most complex. The divisions outlined
are not absolutes and there are other systems or hierarchies that have
been devised in the educational and training world. However,
Bloom's taxonomy is easily understood and is probably the most
widely applied one in use today.
Cognitive
The cognitive domain involves knowledge and the development of
intellectual skills. This includes the recall or recognition of specific
facts, procedural patterns, and concepts that serve in the development
of intellectual abilities and skills. There are six major categories,
which are listed in order below, starting from the simplest behavior to
the most complex. The categories can be thought of as degrees of
difficulties. That is, the first one must be mastered before the next one
can take place.
Category Example and Key Words
Knowledge: Recall data Examples: Recite a policy. Quote prices from
or information. memory to a customer. Knows the safety rules.
Key Words: defines, describes, identifies,
knows, labels, lists, matches, names, outlines,
recalls, recognizes, reproduces, selects, states.
Comprehension: Examples: Rewrites the principles of test
Understand the meaning, writing. Explain in one يs own words the steps
translation, interpolation, for performing a complex task. Translates an
and interpretation of equation into a computer spreadsheet.
instructions and problems.
State a problem in one's Key Words: Comprehends converts, defends,
own words. distinguishes, estimates, explains, extends,
generalizes, gives Examples, infers, interprets,
paraphrases, predicts, rewrites, summarizes,
translates.
Application: Use a Examples: Use a manual to calculate an
concept in a new situation employee يs vacation time. Apply laws of
or unprompted use of an statistics to evaluate the reliability of a written
abstraction. Applies what test.
was learned in the
classroom into novel Key Words: applies, changes, computes,
situations in the work constructs, demonstrates, discovers,
place. manipulates, modifies, operates, predicts,
prepares, produces, relates, shows, solves, uses.
Analysis: Separates Examples: Troubleshoot a piece of
material or concepts into equipment by using logical deduction.
component parts so that its Recognize logical fallacies in
organizational structure reasoning. Gathers information from a
may be understood. department and selects the required tasks for
Distinguishes between training.
facts and inferences.
Key Words: analyzes, breaks down,
compares, contrasts, diagrams, deconstructs,
differentiates, discriminates, distinguishes,
identifies, illustrates, infers, outlines, relates,
selects, separates.
Synthesis: Builds a Examples: Write a company operations or
structure or pattern from process manual. Design a machine to perform a
diverse elements. Put parts specific task. Integrates training from several
together to form a whole, sources to solve a problem. Revises and
with emphasis on creating
a new meaning or process to improve the outcome.
structure.
Key Words: categorizes, combines,
compiles, composes, creates, devises, designs,
explains, generates, modifies, organizes, plans,
rearranges, reconstructs, relates, reorganizes,
revises, rewrites, summarizes, tells, writes.
Evaluation: Make Examples: Select the most effective solution.
judgments about the value Hire the most qualified candidate. Explain and
of ideas or materials. justify a new budget.
Key Words: Appraises compares, concludes,
contrasts, criticizes, critiques, defends,
describes, discriminates, evaluates, explains,
interprets, justifies, relates, summarizes,
supports.
Affective
This domain includes the manner in which we deal with things
emotionally, such as feelings, values, appreciation, enthusiasms,
motivations, and attitudes. The five major categories are listed from the
simplest behavior to the most complex:
Category Example and Key Words
Receiving Examples: Listen to others with respect.
Phenomena: Listen for and remember the name of newly
Awareness, willingness to introduced people.
hear, selected attention.
Key Words: asks, chooses, describes,
follows, gives, holds, identifies, locates, names,
points to, selects, sits, erects, replies, uses.
Responding to Examples: Participates in class discussions.
Phenomena: Active Gives a presentation. Questions new ideals,
participation on the part of concepts, models, etc. in order to fully
the learners. Attends and understand them. Know the safety rules and
reacts to a particular practices them.
phenomenon. Learning
outcomes may emphasize Key Words: answers, assists, aids, complies,
compliance in responding, conforms, discusses, greets, helps, labels,
willingness to respond, or
satisfaction in responding performs, practices, presents, reads, recites,
(motivation). reports, selects, tells, writes.
Valuing: The worth or Examples: Demonstrates belief in the
value a person attaches to democratic process. Is sensitive towards
a particular object, individual and cultural differences (value
phenomenon, or diversity). Shows the ability to solve
behavior. This ranges problems. Proposes a plan to social
from simple acceptance to improvement and follows through with
the more complex state of commitment. Informs management on matters
commitment. Valuing is that one feels strongly about.
based on the
internalization of a set of Key Words: completes, demonstrates,
specified values, while differentiates, explains, follows, forms,
clues to these values are initiates, invites, joins, justifies, proposes,
expressed in the learner يs reads, reports, selects, shares, studies, works.
overt behavior and are
often identifiable.
Organization: Examples: Recognizes the need for balance
Organizes values into between freedom and responsible
priorities by contrasting behavior. Accepts responsibility for one يs
different values, resolving behavior. Explains the role of systematic
conflicts between them, planning in solving problems. Accepts
and creating an unique professional ethical standards. Creates a life
value system. The plan in harmony with abilities, interests, and
emphasis is on comparing, beliefs. Prioritizes time effectively to meet the
relating, and synthesizing needs of the organization, family, and self.
values.
Key Words: adheres, alters, arranges,
combines, compares, completes, defends,
explains, formulates, generalizes, identifies,
integrates, modifies, orders, organizes,
prepares, relates, synthesizes.
Internalizing values Examples: Shows self-reliance when
(characterization): working independently. Cooperates in group
Has a value system that activities (displays teamwork). Uses an
controls their objective approach in problem solving.
behavior. The behavior is Displays a professional commitment to ethical
pervasive, consistent, practice on a daily basis. Revises judgments
predictable, and most and changes behavior in light of new evidence.
importantly, characteristic Values people for what they are, not how they
of the look.
learner. Instructional
objectives are concerned Key Words: acts, discriminates, displays,
with the student's general influences, listens, modifies, performs,
patterns of adjustment
(personal, social, practices, proposes, qualifies, questions,
emotional). revises, serves, solves, verifies.
Psychomotor
The psychomotor domain includes physical movement,
coordination, and use of the motor-skill areas. Development of these
skills requires practice and is measured in terms of speed, precision,
distance, procedures, or techniques in execution. The seven major
categories are listed from the simplest behavior to the most complex:
Category Example and Key Words
Perception: The ability Examples: Detects non-verbal
to use sensory cues to communication cues. Estimate where a ball
guide motor activity. This will land after it is thrown and then moving to
ranges from sensory the correct location to catch the ball. Adjusts
stimulation, through cue heat of stove to correct temperature by smell
selection, to translation. and taste of food. Adjusts the height of the
forks on a forklift by comparing where the
forks are in relation to the pallet.
Key Words: chooses, describes, detects,
differentiates, distinguishes, identifies,
isolates, relates, selects.
Set: Readiness to act. It Examples: Knows and acts upon a sequence
includes mental, physical, of steps in a manufacturing process. Recognize
and emotional sets. These one يs abilities and limitations. Shows desire
three sets are dispositions to learn a new process (motivation). NOTE:
that predetermine a person This subdivision of Psychomotor is closely
يs response to different related with the "Responding to phenomena"
situations (sometimes subdivision of the Affective domain.
called mindsets).
Key Words: begins, displays, explains,
moves, proceeds, reacts, shows, states,
volunteers.
Guided Response: Examples: Performs a mathematical
The early stages in equation as demonstrated. Follows instructions
learning a complex skill to build a model. Responds hand-signals of
that includes imitation and instructor while learning to operate a forklift.
trial and error. Adequacy
of performance is Key Words: copies, traces, follows, react,
achieved by practicing. reproduce, responds
Mechanism: This is the Examples: Use a personal computer. Repair
intermediate stage in a leaking faucet. Drive a car.
learning a complex
skill. Learned responses Key Words: assembles, calibrates,
have become habitual and constructs, dismantles, displays, fastens, fixes,
the movements can be grinds, heats, manipulates, measures, mends,
performed with some mixes, organizes, sketches.
confidence and
proficiency.
Complex Overt Examples: Maneuvers a car into a tight
Response: The skillful parallel parking spot. Operates a computer
performance of motor acts quickly and accurately. Displays competence
that involve complex while playing the piano.
movement
patterns. Proficiency is Key Words: assembles, builds, calibrates,
indicated by a quick, constructs, dismantles, displays, fastens, fixes,
accurate, and highly grinds, heats, manipulates, measures, mends,
coordinated performance, mixes, organizes, sketches.
requiring a minimum of
NOTE: The Key Words are the same as
energy. This category
Mechanism, but will have adverbs or adjectives
includes performing
that indicate that the performance is quicker,
without hesitation, and
better, more accurate, etc.
automatic
performance. For
example, players are often
utter sounds of
satisfaction or expletives
as soon as they hit a tennis
ball or throw a football,
because they can tell by
the feel of the act what the
result will produce.
Adaptation: Skills are Examples: Responds effectively to
well developed and the unexpected experiences. Modifies instruction
individual can modify to meet the needs of the learners. Perform a
movement patterns to fit task with a machine that it was not originally
special requirements. intended to do (machine is not damaged and
there is no danger in performing the new task).
Key Words: adapts, alters, changes,
rearranges, reorganizes, revises, varies.
Origination: Creating Examples: Constructs a new theory.
new movement patterns to Develops a new and comprehensive training
fit a particular situation or programming. Creates a new gymnastic
specific problem. routine.
Learning outcomes
emphasize creativity Key Words: arranges, builds, combines,
based upon highly composes, constructs, creates, designs, initiate,
developed skills. makes, originates.
http://www.teachers.ash.org.au/researchskills/dalton.htm
Dalton, J. & Smith, D. (1986) “Extending Children’s Special Abilities – Strategies for
primary classrooms” pp36-7
Applying Bloom's taxonomy
Knowledge
Useful Sample Potential activities and
Verbs Question Stems products
tell - What happened - Make a list of the main
list after...? events..
describe - How many...? - Make a timeline of events.
relate - Who was it - Make a facts chart.
locate that...? - Write a list of any pieces of
write - Can you name information you can
find the...? remember.
state - Describe what - List all the.... in the story.
name happened at...? - Make a chart showing...
- Who spoke to...? - Make an acrostic.
- Can you tell - Recite a poem.
why...?
- Find the meaning
of...?
- What is...?
- Which is true or
false...?
Comprehension
Sample Potential activities and
Useful
Question products
Verbs
Stems
explain - Can you write - Cut out or draw pictures to
interpret in your own show a particular event.
outline words...? - Illustrate what you think the
discuss - Can you write a main idea was.
distinguish brief outline...? - Make a cartoon strip
predict - What do you showing the sequence of
restate think could of events.
translate happened next...? - Write and perform a play
compare - Who do you based on the story.
describe think...? - Retell the story in your
- What was the words.
main idea...? - Paint a picture of some
- Who was the aspect you like.
key character...? - Write a summary report of
- Can you an event.
distinguish - Prepare a flow chart to
between...? illustrate the sequence of
- What events.
differences exist - Make a colouring book.
between...?
- Can you
provide an
example of what
you mean...?
- Can you
provide a
definition for...?
Application
Useful Sample Potential activities and
Verbs Question Stems products
solve - Do you know - Construct a model to
show another instance demonstrate how it will work.
use where...? - Make a diorama to illustrate
illustrate - Could this have an important event.
construct happened in...? - Make a scrapbook about the
complete - Can you group areas of study.
examine by characteristics - Make a paper-mache map to
classify such as...? include relevant information
- What factors about an event.
would you change - Take a collection of
if...? photographs to demonstrate a
- Can you apply particular point.
the method used - Make up a puzzle game suing
to some the ideas from the study area.
experience of - Make a clay model of an item
your own...? in the material.
- What questions - Design a market strategy for
would you ask your product using a known
of...? strategy as a model.
- From the - Dress a doll in national
information costume.
given, can you - Paint a mural using the same
develop a set of materials.
instructions - Write a textbook about... for
about...? others.
- Would this
information be
useful if you had
a...?
Analysis
Useful Sample Question Potential activities
Verbs Stems and products
analyze - Which events could - Design a questionnaire
distinguish have happened...? to gather information.
examine - I ... happened, what - Write a commercial to
compare might the ending have sell a new product.
contrast been? - Conduct an
investigate - How was this similar investigation to produce
categorize to...? information to support a
identify - What was the view.
explain underlying theme - Make a flow chart to
separate of...? show the critical stages.
advertise - What do you see as - Construct a graph to
other possible illustrate selected
outcomes? information.
- Why did ... changes - Make a jigsaw puzzle.
occur? - Make a family tree
- Can you compare showing relationships.
your .... with that - Put on a play about the
presented in...? study area.
- Can you explain - Write a biography of
what must have the study person.
happened when...? - Prepare a report about
- How is ... similar the area of study.
to...? - Arrange a party. Make
- What are some of the all the arrangements and
problems of...? record the steps needed.
- Can you distinguish - Review a work of art in
between...? terms of form, colour
- What were some of and texture.
the motives behind...?
- What was the turning
point in the game?
- What was the
problem with...?
Synthesis
Useful Sample Potential activities and
Verbs Question Stems products
create - Can you design - Invent a machine to do a
invent a ... to...? specific task.
compose - Why not - Design a building to house
predict compose a song your study.
plan about...? - Create a new product. Give it
construct - Can you see a a name and plan a marketing
design possible solution campaign.
imagine to...? - Write about your feelings in
propose - If you had relation to...
devise access to all - Write a TV show, play,
formulate resources how puppet show, role play, song or
would you deal pantomime about...?
with...? - Design a record, book, or
- Why don't you magazine cover for...?
devise your own - Make up a new language
way to deal code and write material suing
with...? it.
- What would - Sell an idea.
happen if...? - Devise a way to...
- How many - Compose a rhythm or put
ways can you...? new words to a known melody.
- Can you create
new and unusual
uses for...?
- Can you write a
new recipe for a
tasty dish?
- Can you
develop a
proposal which
would...?
Evaluation
Sample Potential activities and
Useful
Question products
Verbs
Stems
judge - Is there a better - Prepare a list of criteria to
select solution to... judge a ... show. Indicate
choose - Judge the value priority and ratings.
decide of... - Conduct a debate about an
justify - Can you defend issue of special interest.
debate your position - Make a booklet about 5
verify about...? rules you see as important.
argue - Do you think ... - Convince others.
recommend is a good or a - Form a panel to discuss
assess bad thing? views, eg "Learning at
discuss - How would School."
rate you have - Write a letter to ... advising
prioritize handled...? on changes needed at...
determine - What changes - Write a half yearly report.
to ... would you - Prepare a case to present
recommend? your view about...
- Do you
believe?
- Are you a ...
person?
- How would
you feel if...?
- How effective
are...?
- What do you
think about...?
You might also like
- Blooms Taxonomy Verb WheelDocument1 pageBlooms Taxonomy Verb Wheelhansfarkas100% (1)
- Guidelines For TM 1 National AssessmentDocument7 pagesGuidelines For TM 1 National AssessmentIvy Rosell Buayaban100% (6)
- Kid Friendly Blooms TaxonomyDocument1 pageKid Friendly Blooms Taxonomytonybattista50% (2)
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument336 pagesBlooms TaxonomyMr100% (12)
- ASSURE ModelDocument29 pagesASSURE ModelAmelia Abdullah100% (1)
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument4 pagesBlooms TaxonomyJimmyconnors Chettipally100% (11)
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument37 pagesBlooms TaxonomySheryl Guimary Iballa100% (3)
- Active LearningDocument28 pagesActive Learningnainis100% (2)
- Bloom's Taxonomy - What's Old Is New Again - 2013Document53 pagesBloom's Taxonomy - What's Old Is New Again - 2013Victor Manuel Enriquez G100% (2)
- Three Domains of Learning: Cognitive Affective and PsychomotorDocument8 pagesThree Domains of Learning: Cognitive Affective and PsychomotorDr. M. Enamul Hoque100% (4)
- The New Bloom's TaxonomyDocument45 pagesThe New Bloom's Taxonomymllalaguna100% (10)
- Teaching Strategies, Approaches, and MethodsDocument47 pagesTeaching Strategies, Approaches, and MethodsMegs Mads100% (4)
- Bloom's Taxonomy in My ToolboxDocument6 pagesBloom's Taxonomy in My ToolboxCatholic Teacher DaydreamsNo ratings yet
- in Teaching English - Group 1Document50 pagesin Teaching English - Group 1Delos Santos Jainalyn M.No ratings yet
- ADDIE SampleDocument16 pagesADDIE SampleMuhamad Ridzuan100% (2)
- Blooms TexonomyDocument60 pagesBlooms TexonomyRajesh Sharma100% (2)
- Bruner - S Learning TheoriesDocument48 pagesBruner - S Learning TheoriesMazlan LannNo ratings yet
- Curriculum ImplementationDocument66 pagesCurriculum ImplementationCyrelOcfemiaNo ratings yet
- Constructivism Theory (Chemical Equation)Document49 pagesConstructivism Theory (Chemical Equation)Nurun Nadia MasromNo ratings yet
- TLS Blooms Taxonomy Jul2014Document3 pagesTLS Blooms Taxonomy Jul2014Guisella Infantes100% (1)
- PERENNIALISMDocument2 pagesPERENNIALISMJohn LloydNo ratings yet
- Constructivism: A Holistic Approach To Teaching and LearningDocument24 pagesConstructivism: A Holistic Approach To Teaching and LearningKogilavani Selvakumar100% (6)
- What Is Emergent LiteracyDocument4 pagesWhat Is Emergent Literacyelfe deramaNo ratings yet
- Quality Indicators of Multigrade Instruction in Southeast AsiaDocument108 pagesQuality Indicators of Multigrade Instruction in Southeast AsiaSEAMEO INNOTECH100% (5)
- ConstructivismDocument185 pagesConstructivismMark A. FosterNo ratings yet
- Domains of LearningDocument15 pagesDomains of LearningMichelle Lee100% (1)
- Assure ModelDocument28 pagesAssure ModelMae VisperasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CurriculumDocument9 pagesChapter 1 CurriculumLCC Library100% (2)
- Amirazizi Action Research-3Document22 pagesAmirazizi Action Research-3Faiz SarwaniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Teaching Listening and SpeakingDocument3 pagesSyllabus Teaching Listening and Speakingdaviqr100% (5)
- The Teaching ProcessDocument29 pagesThe Teaching ProcessFrancisAdonesR.Zaluaga100% (1)
- Knowles Antragogie PDFDocument4 pagesKnowles Antragogie PDFCorina Panfil100% (1)
- Developing and Using RubricsDocument33 pagesDeveloping and Using RubricsYudha Nawa Anggara100% (1)
- Instructional PlanningDocument42 pagesInstructional PlanningJAKELESTER BANGCASANNo ratings yet
- Teaching: Prepared by PayalDocument10 pagesTeaching: Prepared by PayalKAJAL RANINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Curriculum and Instruction-200313 - 095544Document12 pagesIntroduction To Curriculum and Instruction-200313 - 095544Norhafizah MuhaminNo ratings yet
- The Different Purposes of AssessmentDocument16 pagesThe Different Purposes of AssessmentAlter joy MoralNo ratings yet
- Behaviorist TheoriesDocument33 pagesBehaviorist Theoriesnasyratul100% (4)
- Early Athenian Education: TH THDocument4 pagesEarly Athenian Education: TH THMyla Mendiola JubiloNo ratings yet
- Lesson in Educ Tech 1 & Lecture OutlineDocument30 pagesLesson in Educ Tech 1 & Lecture OutlineRusty Ugay LumbresNo ratings yet
- Assessment As LearningDocument3 pagesAssessment As LearningIVy ViOlet ThOrnNo ratings yet
- 21st Century EducationDocument17 pages21st Century EducationJahseh OnfroyNo ratings yet
- Differentiated InstructionDocument5 pagesDifferentiated InstructionLu MendozaNo ratings yet
- Constructivist Teaching Methods - WikipediaDocument54 pagesConstructivist Teaching Methods - Wikipediatajum pullomNo ratings yet
- Designing The CurriculumDocument15 pagesDesigning The CurriculumJessica MarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cooperative Learning GroupsDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Cooperative Learning Groupsครูเอื้อย ครอบครัวตัวออNo ratings yet
- David AusubelDocument5 pagesDavid AusubelArt Dollosa100% (2)
- Affective Learning Competencies ReportDocument15 pagesAffective Learning Competencies ReportJulie Ann Sison100% (3)
- Teaching Approaches and Methods: Principles of Teaching: Chapter 2Document26 pagesTeaching Approaches and Methods: Principles of Teaching: Chapter 2Cres A LinogonNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Dyslexia PDFDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of Dyslexia PDFDaniel Garzia Aizrag100% (2)
- Formative Vs Summative AssessmentDocument50 pagesFormative Vs Summative AssessmentCarmen DelurintuNo ratings yet
- Week 6, Classroom ManagementDocument29 pagesWeek 6, Classroom ManagementSania MalikNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 - Motivation and LearningDocument16 pagesTopic 10 - Motivation and LearningTESL110621 Nur Zulaikha Binti ZahrollailNo ratings yet
- Nativist Theory: by Noam ChomskyDocument15 pagesNativist Theory: by Noam ChomskysakipitNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories Behaviourism, Cognitivism, Social ConstructivismDocument39 pagesLearning Theories Behaviourism, Cognitivism, Social ConstructivismJuan Miguel100% (3)
- Learning TheoriesDocument11 pagesLearning TheoriesPovesh PillayNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument5 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsHeksi Putri SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- All 3 Blooms 2015Document4 pagesAll 3 Blooms 2015Lenie Sang-olanNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument7 pagesBlooms Taxonomyutello100% (2)
- Learning Domains or Bloom's Taxonomy: The Three Types of LearningDocument8 pagesLearning Domains or Bloom's Taxonomy: The Three Types of Learningamber ariaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionapi-3823878No ratings yet
- Table of ContentDocument1 pageTable of Contentapi-3823878No ratings yet
- Needs AnalysisDocument1 pageNeeds Analysisapi-3823878No ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document1 pageLesson 5api-3823878No ratings yet
- RationaleDocument1 pageRationaleapi-3823878No ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document1 pageLesson 4api-3823878No ratings yet
- Appendix 1Document1 pageAppendix 1api-3823878No ratings yet
- Maritime Industry AuthorityDocument8 pagesMaritime Industry Authorityaolaya14No ratings yet
- SDLS301 Assignment 2-1Document4 pagesSDLS301 Assignment 2-1RoymadaNo ratings yet
- AA-As General Education 20-21Document2 pagesAA-As General Education 20-21abrahamNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument12 pagesAssignmentTenisha Knowles0% (1)
- ForkliftDocument19 pagesForkliftRiya MassoorNo ratings yet
- The Informed Investor A Hype Free Guide to Constructing a Sound Financial Portfolio 2nd Edition Armstrong Iii All Chapters Instant DownloadDocument75 pagesThe Informed Investor A Hype Free Guide to Constructing a Sound Financial Portfolio 2nd Edition Armstrong Iii All Chapters Instant Downloadindalglosezq100% (4)
- Week 2 2nd English Reinforcement Classes 2024-2025Document5 pagesWeek 2 2nd English Reinforcement Classes 2024-2025Mariisol TocteNo ratings yet
- 11.6 PoetryDocument5 pages11.6 PoetryMarilu Velazquez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Narrative Teachers Day 2018Document5 pagesNarrative Teachers Day 2018Evalyn M. SalvaNo ratings yet
- Walk in Interview Eligibility Criteria and Biodata Form - 0Document7 pagesWalk in Interview Eligibility Criteria and Biodata Form - 0karnadebabrata16No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document3 pagesUnit 1aung zinNo ratings yet
- Gen EdDocument7 pagesGen EdHannah Juanitas100% (1)
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument20 pagesTheoretical FrameworkDABI IBADNo ratings yet
- Week 2 & 3 Rizal LawDocument3 pagesWeek 2 & 3 Rizal LawChristine Joy DelaCruz CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Ed 435 Assessment Plan - 3Document7 pagesEd 435 Assessment Plan - 3api-545952718No ratings yet
- Language Art Lesson About ClothesDocument4 pagesLanguage Art Lesson About ClothesRosmalia KasanNo ratings yet
- Language and Construction of Gender A Fe PDFDocument19 pagesLanguage and Construction of Gender A Fe PDFattiqaNo ratings yet
- Charles Dunst ResumeDocument1 pageCharles Dunst ResumeCharles DunstNo ratings yet
- Development of SWPDocument8 pagesDevelopment of SWPJoniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Tools and Techniques of Knowledge ManagementDocument5 pagesUnit 2: Tools and Techniques of Knowledge ManagementRupaliNo ratings yet
- Pet-Past Simple VS Past ContinuousDocument22 pagesPet-Past Simple VS Past ContinuousTonaMosquedaNo ratings yet
- Educational Establishments For Geodesy: AustraliaDocument7 pagesEducational Establishments For Geodesy: AustraliaFaiz KarmaniNo ratings yet
- Education Related Texts 7Document13 pagesEducation Related Texts 7kamykamilia167No ratings yet
- IPA Cross-Border Programme "Greece - The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" 2007-2013Document18 pagesIPA Cross-Border Programme "Greece - The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" 2007-2013Zupan MartinovskiNo ratings yet
- Selecting A Method of Data Collection: Miss AlveenaDocument14 pagesSelecting A Method of Data Collection: Miss AlveenaMaria fayyazNo ratings yet
- Age of Technology Online Games and Its Effect To The Academic Performance of Junior and Senior High School StudentsDocument14 pagesAge of Technology Online Games and Its Effect To The Academic Performance of Junior and Senior High School StudentsJohn Cristoff MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4Document5 pagesLesson Plan 4api-357243074No ratings yet
- 20240322好好生物4bi1 2br 1120 quDocument16 pages20240322好好生物4bi1 2br 1120 qu中华雅思王No ratings yet
- Krauss - SummaryDocument2 pagesKrauss - Summaryashley scarlettNo ratings yet