0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 viewsCC Cheat Midsem
CC Cheat Midsem
Uploaded by
amsrivastava2002Computing involves using computer technology to complete goal-oriented tasks. A distributed system has multiple components located on different machines that communicate to appear as a single system. Distributed systems have advantages over centralized systems like increased speed and reliability. However, distributed systems are more difficult to develop for and faults can be harder to detect. Cluster computing involves grouping linked computers together to function like a single computer. It provides benefits like increased speed and optimized resource utilization but programming models can be complex. Grid computing pools unused resources from different locations for a common task and focuses on supplying isolated access to resources and coordinated processing control. Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources over the internet on a pay-per-use basis and offers flexibility and scalability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
CC Cheat Midsem
CC Cheat Midsem
Uploaded by
amsrivastava20020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views12 pagesComputing involves using computer technology to complete goal-oriented tasks. A distributed system has multiple components located on different machines that communicate to appear as a single system. Distributed systems have advantages over centralized systems like increased speed and reliability. However, distributed systems are more difficult to develop for and faults can be harder to detect. Cluster computing involves grouping linked computers together to function like a single computer. It provides benefits like increased speed and optimized resource utilization but programming models can be complex. Grid computing pools unused resources from different locations for a common task and focuses on supplying isolated access to resources and coordinated processing control. Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources over the internet on a pay-per-use basis and offers flexibility and scalability.
Original Title
CC CHEAT MIDSEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Computing involves using computer technology to complete goal-oriented tasks. A distributed system has multiple components located on different machines that communicate to appear as a single system. Distributed systems have advantages over centralized systems like increased speed and reliability. However, distributed systems are more difficult to develop for and faults can be harder to detect. Cluster computing involves grouping linked computers together to function like a single computer. It provides benefits like increased speed and optimized resource utilization but programming models can be complex. Grid computing pools unused resources from different locations for a common task and focuses on supplying isolated access to resources and coordinated processing control. Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources over the internet on a pay-per-use basis and offers flexibility and scalability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views12 pagesCC Cheat Midsem
CC Cheat Midsem
Uploaded by
amsrivastava2002Computing involves using computer technology to complete goal-oriented tasks. A distributed system has multiple components located on different machines that communicate to appear as a single system. Distributed systems have advantages over centralized systems like increased speed and reliability. However, distributed systems are more difficult to develop for and faults can be harder to detect. Cluster computing involves grouping linked computers together to function like a single computer. It provides benefits like increased speed and optimized resource utilization but programming models can be complex. Grid computing pools unused resources from different locations for a common task and focuses on supplying isolated access to resources and coordinated processing control. Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources over the internet on a pay-per-use basis and offers flexibility and scalability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
COMPUTING is the process of using computer technology to complete a
given goal-oriented task.
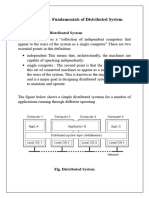
A DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM, also known as distributed computing, is a system
with multiple components located on different machines that communicate
and coordinate actions in order to appear as a single coherent system to the
end-user. • Example - Telecommunication networks: Telephone networks
and Cellular networks.Features: –1. No shared memory –2. Message-based
communication –3. Each runs its own local OS –4. Heterogeneity
CENTRALISED SYSTEM CHARACTERSTICS - 1.One component with Non-
autonomous parts 2.Components shared by users all the time 3.All Resources
accessible 4.Software runs in a single process 5.Single point of control
6.Single point of failure
DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM CHARACTERSTICS - 1.Multiple autonomous
components 2.Components are not shared by all users 3.Resources may not
be accessible 4.Software runs in concurrent processes on different
processors 5.Multiple points of control 6.Multiple points of failure
ADVANTAGES OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM OVER CENTRALIZED
SYSTEM - 1.Speed - distributed systems can achieve very high speed as
compared to the centralized 2.Inherent Distribution 3.Reliability(higher as
compared to centralized)
DISADVANTAGES OF DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM - 1.difficult to develop
software for distributed systems 2.Distribution of control 3.saturation, lossy
transmissions 4.easy access also applies to secret data 5.Hard to detect
faults 6.Administration issues.
CLUSTER COMPUTING - A computer cluster is a group of linked computers,
working together closely so that in many respects they form a single
computer,The components of a cluster are commonly, but not always,
connected to each other through fast local area networks.
CLUSTER CONSISTS OF -Nodes,network,OS,Cluster middleware:
Middleware such as MPI (Message Passing Interface) which permits compute
clustering programs to be portable to a wide variety of clusters
TYPES OF CLUSTER COMPUTING:- 1.High Availability (HA) and failover
clusters:These models are built to provide an availability of services and
resources in an uninterrupted manner through the use of implicit redundancy
to the system,If a cluster node fails (failover), applications or services may be
available in another node. .2.Load balancing (LB):This model distributes
incoming traffic or requests for resources from nodes that run the same
programs between machines that make up the cluster,If a node fails, the
requests are redistributed among the nodes available.3.HA &LB
combination – 1. As its name says, it combines the features of both types of
cluster, thereby increasing the availability and scalability of services
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF CLUSTER COMPUTING:
Advantages 1.Increasing speed – better performance 2.optimized resources
utilization 3.Can execute Large applications Disadvantages 1.Complex
programming models 2.Difficult for debug and development
GRID COMPUTING :a computing infrastructure that combines computer
resources spread over different geographical locations to achieve a common
goal. All unused resources on multiple computers are pooled together and
made available for a single task.Grids focus on two different but associated
objectives—supplying isolated access to IT resources and building up
processing control.
Grid Computing is a subset of distributed computing, where a virtual
super computer comprises of machines on a network connected by
some bus, mostly Ethernet or sometimes the Internet
Components in Grid : Control Node: • A computer, usually a server or a
group of servers which administrates the whole network and keeps the
account of the resources in the network pool. Provider: • The computer which
contributes it’s resources in the network resource pool. User: • The computer
that uses the resources on the network.
For controlling the network and it’s resources a software/networking
protocol is used generaly known as Middleware. ,middleware should ensure
that there is no unwanted task being executed on the network.,Another job of
the middleware is to authorize any process that is being executed on the
network
Layers of Grid System architecture are as follows: (i)Fabric Layer:
Lowest layer i. It comprises geographically distributed and sharable resources
such as storage devices, computing devices, high bandwidth networks and
scientific instruments, etc. ii. These resources are accessible from anywhere
in the internet. (ii)Connectivity Layer: i. It provides an easy and secure
access to the resources through some standardized protocols. ii. The
authentication protocols are used to provide proper verification of users and
resources. iii. The communication protocols provide a mechanism for
transmission of data between the fabric and the resource layer.(iii)Resource
Layer: i. It specifies the necessary protocols to operate among shared
resources. ii. It is primarily built upon the communication and authentication
protocols of connectivity layer. iii. It defines the APIs (Application Program
Interfaces) and SDK (Software Development Kit) to make secure the initiation,
accounting, negotiation, controlling and monitoring of resources.
(iv)Collective Layer: i. It is used for common functional utilities. ii. The
operations such as collaboration among the shared resources are performed
in this layer. iii. It provides services like brokering, monitoring, scheduling,
discovery, replication and co-allocation etc.(v)Application Layer: This layer
offers communication interfaces to the users and the administrators for
interacting with the Grid.
Types of Grid Systems :•Compute Intensive: i. Major functionality of this
Grid is to offer powerful CPU resources, whereas other characteristics are
trivial. ii. It intends to provide aggregated CPU cycles of several resources for
fulfilling computational need of a particular application. •Data-Intensive Grid:
It offers large storage space for data discovery, data management and data
processing. •Utility Grid: i. It pools dynamically available resources to match
the requirements of the applications. ii. This enables the Utility Grid to provide
services that cannot be provided by any single machine.•Self-Organized
Grid:includes some intelligence embedded into its infrastructure to automate
its control, organization, and monitoring procedure. iii. It can heal itself in
changing and uncertain environments for maximizing reliability and resource
utilization.•Real Time Grid: i. Traditional Grid could not support certain
requirements of many real time applications.
Mobile Computing is a technology that allows transmission of data, voice
and video via a computer or any other wireless enabled device without having
to be connected to a fixed physical link.
Difference between cluster and cloud computing (SCHOL) • Spanning
area -Cluster is a group of computers connected by a local area network
(LAN), whereas cloud and grid are more wide scale and can be
geographically distributed. • Coupling - cluster is tightly coupled, whereas a
grid or a cloud is loosely coupled. • Homogeneity -clusters are made up of
machines with similar hardware, whereas clouds and grids are made up of
machines with possibly very different hardware configurations. • Ownership:
A grid is a collection of computers which is owned by multiple parties in
multiple locations. Whereas a cloud is a collection of computers usually
owned by a single party. • Load distribution: In cluster the load is distributed
among all nodes but in case of Cloud, the resources are allocated as per the
request. The whole data center is not occupied by one job.
CLOUD COMPUTING:Cloud computing is the on-demand access of computing
resources—physical servers or virtual servers, data storage, networking
capabilities, application development tools, software, AI-powered analytic
tools and more—over the internet with pay-per-use pricing. This model offers
customers greater flexibility and scalability compared to traditional on-
premises infrastructure.Made of 5 characterstics,three service model and four
deployment model.
CHARACTERSTICS: 1.ON DEMAND SELF SERVICE--unilateral provision of
computing capabilities. 2.BROAD NETWORK ACCESS--available over the
network,access through standard mechanisim.3.RESOURCE POOLING--
multi tenant model,assigns and reassigns physical and virtual resources
based on demand preserving privacy and security.4.RAPID ELASTICITY--
cloud service can be elastically provisioned,, in some cases automatically to
quickly scale out and rapidly released to quickly scale in. .5.MEASURED
SERVICE--optimization of resource usage by leveraging a metering capability
at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service.
working models for cloud computing: 1.Deployment Models 2. Service
Models
Deployment Models
The Public Cloud allows systems and services to be easily accessible to the
general public. Public cloud may be less secure because of its openness, e.g.,
e-mail. • The Private Cloud allows systems and services to be accessible
within an organization. It offers increased security because of its private
nature.ex:-Amazon EC2, Gmail • Cummunity Cloud -The Community Cloud
allows systems and services to be accessible by group of organizations.ex:-
CityCloud • The Hybrid Cloud -is mixture of public and private cloud.
However, the critical activities are performed using private cloud while the
non-critical activities are performed using public cloud.
BENEFITS OF CLOUD COMPUTING : 1.Cost effective 2.High efficiency 3.
No software required 4. Resources availabe on network 5.On demand self
service.
Need for Cloud : 1.Flexibility, 2.Disaster recovery 3.Automatic software
updates: 4.Increased collaboration 5.Work from anywhere 6.Capital-
expenditure Free 7.Document control 8.Security 9.Competitiveness
10.Environmental friendly
COMPONENTS OF CLOUD COMPUTING: 1.Client Infrastructure is a Front
end component. It provides GUI (Graphical User Interface) to interact with the
cloud.2.The application may be any software or platform that a client wants
to access.3.A Cloud Services manages that which type of service you
access according to the client’s requirement.4.Runtime Cloud provides
the execution and runtime environment to the virtual machines.5.Storage
is one of the most important components of cloud computing. It provides a
huge amount of storage capacity in the cloud to store and manage
data.6.Cloud infrastructure includes hardware and software components
such as servers, storage, network devices, virtualization software, and other
storage resources that are needed to support the cloud computing
model.7.Management is used to manage components such as application,
service, runtime cloud, storage, infrastructure, and other security issues in the
backend and establish coordination between them.8.Security is an in-built
back end component of cloud computing. It implements a security mechanism
in the back end.9.The Internet is medium through which front end and back
end can interact and communicate with each other.
ELASTICITY IN CLOUD COMPUTING:1.VERTICAL SCALIBILITY:add more
resources to a single computation unit,move a workload to computation units
with more resources.2.HORIZANTAL SCALE:adding additional computation
units and having them act in concert,spitting workload across multiple
computation units
PURPOSE OF CLOUD ELASTICITY:helps users prevent over-provisioning or
under-provisioning system resources.
ADVANTAGES OF PUBLIC CLOUD:1. COST SAVING - The most prevalent
benefit in a public cloud is cost savings. Organizations do not buy, install,
operate or maintain servers or other equipment as they would with private
clouds.2.RELIABILITY Since public cloud employs large number of resources
from different locations, if any of the resource fail, public cloud can employ
another one.3.FLEXIBILITY It is also very easy to integrate public cloud with
private cloud, hence gives consumers a flexible approach.4.LOCATION
INDEPENDENCE Since, public cloud services are delivered through Internet
therefore ensures location independence. 5. UTILITY STYLE COSTING
Public cloud is also based on pay-per-use model and resources are
accessible whenever consumer needs it.
DISADVANTAGES OF PUBLIC CLOUD:1. Lacks proper controls: The
client has no control of data or infrastructure. There are issues of data privacy
and integrity. The service level policies and compliances are completely
enforced by the service provider. 2. Weak on Security: Since the hardware
resource is shared between multiple users, IT security issues are more
profound and data is vulnerable to thefts. 3. Performance: The performance
of the network depends on the speed of the internet connectivity.
ADAVANTAGES OF PRIVATE CLOUD:1.HIGHER SECURITY AND
PRIVACY • Private cloud operations are not available to general public and
resources are shared from distinct pool of resources, therefore, ensures high
security and privacy.2) Improved reliability: When compared to either
dedicated hardware or public cloud alternatives, private cloud offers a greater
degree of reliability thanks to a fault resilient and redundant architecture that
isn't shared in any way. 3) Increased flexibility: Unlike a physical machine, a
virtual machine can be scaled up and down seamlessly.4)Total CONTROL •
Private clouds have more control on its resources and hardware than public
cloud because it is accessed only within an organization5) Better
performance - A private cloud stays inside company's intranet network
behind a firewall. It provides access to the same resources as the public
model, but with less exposure to Internet security risks.
DISADVANTAGES OF PRIVATE CLOUD:1. RESTRICTED AREA • Private
cloud is only accessible locally and is very difficult to deploy globally. 2.
INFLEXIBLE PRICING & Higher Cost • In order to fulfill demand, purchasing
new hardware is very costly. private clouds are more expensive than public
because they require both hardware and maintenance.3. LIMITED
SCALABILITY • Private cloud can be scaled only within capacity of internal
hosted resources. 4. ADDITIONAL SKILLS • In order to maintain cloud
deployment, organization requires more skilled and expertise. 5. Under-
utilisation: With a private cloud, the cost of capacity under-utilisation is a cost
to you, not to your provider.
ADVANTAGES OF HYBRID CLOUD:1. SCALABILITY • It offers both
features of public cloud scalability and private cloud scalability. 2.
FLEXIBILITY • It offers both secure resources and scalable public resources.
3. COST EFFICIENCIES • Public cloud are more cost effective than private,
therefore hybrid cloud can have this saving.4. SECURITY • Private cloud in
hybrid cloud ensures higher degree of security.5. Speed – Though this model
is not as much as faster than public cloud but still it is better than private one.
DIADVANTAGES OF HYBRID CLOUD:NETWORKING ISSUES (complex
system architecture) • Networking becomes complex due to presence of
private and public cloud. SECURITY COMPLIANCE • It is necessary to
ensure that cloud services are compliant with organization's security policies.
COST - While the public cloud can offer an attractive option for its flexibility
and relatively low cost to operate, building a private enterprise cloud requires
significant expenditure and can become expensive very quickly with all the
physical hardware necessary. COMPATIBILITY - Compatibility across
infrastructure can prove itself to be a major issue when building a hybrid cloud
ADVANTAGES OF COMMUNITY CLOUD:COST EFFECTIVE • Community
cloud offers same advantage as that of private cloud at low cost. Flexibility &
Scalability – • The community cloud is very scalable and flexible as it is
mostly compatible with every user and they can modify as per their
use.Availability & Reliability – • The replication of data is done in the cloud
to protect it against the disaster SECURITY & COMPLIANCE • Community
cloud is comparatively more secure than the public cloud.
Disadvantages • Since all data is housed at one location, one must be
careful in storing data in community cloud because it might be accessible by
others. • It is also challenging to allocate responsibilities of governance,
security and cost. • Costly than public cloud.
Example of IaaS:DigitalOcean, • Linode, • Rackspace, • Amazon Web
Services (AWS), • Cisco Metacloud, • Microsoft Azure, and • Google Compute
Engine (GCE)
IaaS ADVANTAGES: 1.Full Control of the computing resources through
Administrative Access to VMs.2.Flexible and Efficient renting of Computer
Hardware 3.Portability, Interoperability with Legacy Applications 4.Cost
Saving & On Demand Scalability 5. No need to set up, maintain or update the
hardware 6. IaaS has greater reliability with the service provider.
IaaS DISADVANTAGES: 1.Changing the provider is very much complicated
2.Possible privacy issues due to the provider's server locations 3.enterprise
does not have any control over cloud security in an IaaS environment 4.Lack
of flexibility 5.Technical problems 6.Over Dependency 7.Upgrade &
Maintenance
EXAMPLES OF PaaS - • Google's App Engine, Force.com Microsoft Azure,
AWS, Aneka, salesforce.com, IBM Google
PaaS ADVANTAGES :1.AutomatedUpdates: • software updates are
automatically done and you get access to all the latest versions, updates
etc.2.LowInvestments: • You can use the software without having to make
any investment in infrastructure that otherwise they procure in an in-house
environment3.ReducedCosts: • Since the payment model is pay-as-you-use,
there is considerable savings for you without having to install the necessary
software like databases, server etc to run theapplications.4.Collaboration: •
Since it is an internet-based platform, it enables the employees to login and
work on the applications from anywhere, make their updates without
physically being present in the business premises.5.Focus: • Your IT team
can focus better on core applications rather than being diverted on
maintenance of the system
PaaS disadvantages : 1.Vendor lock-in:If you get locked in a specific
language, program, or interface that could affect you with some unnecessary
system that you do not require.2.Dependency on Vendor:great advantage
that a certain part of work is done by the provider without you having to make
an effort.3.Compatibility of Existing Infrastructure:4.Security Risks • As a
rule, PaaS software is available in a public environment where multiple end
users have access to the same basic resources.SaaS benefits: Reduced
Expences : SaaS removes the need for organizations to install and run
applications on their own computers or in their own data centers.Flexible
payments: Rather than purchasing software to install, or additional hardware
to support it, customers subscribe to a SaaS offering.Scalable usage: Cloud
services like SaaS offer high vertical scalability, which gives customers the
option to access more, or fewer, services or features on-demand. Trouble
Free Upgradation • It is a cumbersome task to upgrade your existing software
and hardware to the newer versions Modest Software Tools • The SaaS
application deployment requires a little or no client side software installation
which results in the following benefits:
SaaS disadvantages Insufficient Data SecurityConnectivity requirement –
since the SaaS model is based on web delivery, if your internet service fails,
you will lose access to your software or data Performance – SaaS may run at
somewhat slower speeds than on-premise client or server applications, so it's
worth keeping performance in mind your software isn't hosted on a local
machine. Difficulty with Regulations Compliance When your business critical
data is stored in the service provider's data center, it is difficult to comply with
the government's data protection regulations
Recovery as a service (RaaS), sometimes referred to as disaster recovery as
a service (DRaaS), is a category of cloud computing used for protecting an
application or data from a natural or human disaster or service disruption at
one location by enabling a full recovery in the cloud. • RaaS differs from
cloud-based backup services by protecting data and providing standby
computing capacity on demand to facilitate more rapid application recovery.
You might also like
- The Business of Sports: India - A Sporting Nation in The MakingDocument49 pagesThe Business of Sports: India - A Sporting Nation in The MakingIshan Shukla100% (1)
- Cloud Computing Lab Manual PDFDocument24 pagesCloud Computing Lab Manual PDFpradeepNo ratings yet
- Pob NotesDocument21 pagesPob NotesOneeka Plutoqueenbee Adams91% (11)
- Cloud Computing For Data ScienceDocument17 pagesCloud Computing For Data SciencedhanashreeNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing ReportDocument11 pagesCloud Computing ReportfebycvNo ratings yet
- Question Bank of Cloud computing KCS-713Document68 pagesQuestion Bank of Cloud computing KCS-713mohit9634155No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - KCS713 - UNIT-1 NotesDocument11 pagesCloud Computing - KCS713 - UNIT-1 NotesstealthyhistorianNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument33 pagesChapter OneUrgessa GedefaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesCloud Computingbc210402586 HAFIZA ANIQA IRFANNo ratings yet
- Distributed System IMP APYDocument210 pagesDistributed System IMP APYAryan PanchalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Cloud Computing FundamentalsDocument19 pagesUnit 1 - Cloud Computing FundamentalsKartik Pagariya.No ratings yet
- Distributed ComputingDocument40 pagesDistributed Computing014 CSE Devamruth AGNo ratings yet
- DS Unit-1Document31 pagesDS Unit-1ambatipudi praisy prasannaNo ratings yet
- CC - AB NotesDocument75 pagesCC - AB NoteskalpityonigNo ratings yet
- CSC - 406 - 1 - Intro To Distributed SystemDocument22 pagesCSC - 406 - 1 - Intro To Distributed SystemSamadNo ratings yet
- PPPDocument4 pagesPPPJames ComedianNo ratings yet
- 01 - Ch1Document25 pages01 - Ch1OmarallasasmhNo ratings yet
- CCT NotesDocument36 pagesCCT NotesBalaji .DNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing NotesDocument9 pagesCloud Computing Notesdumbthings1729No ratings yet
- Overview of Computing ParadigmDocument1 pageOverview of Computing Paradigmchirayush chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument89 pagesIntroductionMaaz SayyedNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing All Unit NotesDocument53 pagesCloud Computing All Unit NotesKritik BansalNo ratings yet
- U19ADS501 - CC U-1Document60 pagesU19ADS501 - CC U-1velrayappandiv7263No ratings yet
- Grid PlatformDocument4 pagesGrid PlatformShantru RautNo ratings yet
- L1.4_The World of ComputingDocument34 pagesL1.4_The World of Computingkrishnasribodduri07No ratings yet
- Notes - Cloud ComputingDocument34 pagesNotes - Cloud ComputingC Meenakshi MeyyappanNo ratings yet
- DC - Hand-WrittenDocument7 pagesDC - Hand-Writtenleebha.pushparajNo ratings yet
- Distributed Operating SystemDocument18 pagesDistributed Operating SystemRajni ShelkeNo ratings yet
- Module 6-Special Purpose OSDocument16 pagesModule 6-Special Purpose OSdevpgaonkar3No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesCloud Computingvotiho6842No ratings yet
- Parallel Computing - Unit IVDocument40 pagesParallel Computing - Unit IVshraddhaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Com Unit-01 (Dr. Laxman Singh)Document21 pagesCloud Com Unit-01 (Dr. Laxman Singh)abhinav.2226cseml108No ratings yet
- Distributed Systems-Question BankDocument16 pagesDistributed Systems-Question Bankkrishna7k7100% (1)
- 1.1 Overview: Cloud Computing Is The Use of Computing Resources (Hardware and Software)Document72 pages1.1 Overview: Cloud Computing Is The Use of Computing Resources (Hardware and Software)Samsul HuthaNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction of Distributed System PDFDocument23 pages01 Introduction of Distributed System PDFNắng Pha LêNo ratings yet
- Grid ArchitectureDocument19 pagesGrid ArchitectureBittu VermaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Working of Cloud ComputingDocument76 pages1.1 Working of Cloud ComputingTharun Theja ReddyNo ratings yet
- 1CC NotesDocument30 pages1CC Notesdarkxedits9No ratings yet
- KCS 713 Unit 1 Lecture 6Document38 pagesKCS 713 Unit 1 Lecture 6piyushpandat035No ratings yet
- CCunit 1Document69 pagesCCunit 1aman kumarNo ratings yet
- A) (I) A Distributed Computer System Consists of Multiple Software Components That Are OnDocument14 pagesA) (I) A Distributed Computer System Consists of Multiple Software Components That Are OnRoebarNo ratings yet
- 5-Distributed Systems EngineeringDocument42 pages5-Distributed Systems EngineeringRehan KhanNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Distributed Systems Ds Module1Document23 pagesCharacterization of Distributed Systems Ds Module1kalidassm.aimlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document117 pagesChapter 1snekarki80No ratings yet
- CHAPTER1 UpdateDocument20 pagesCHAPTER1 Updatemd5fxz9thsNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 90%Document9 pagesUnit-1 90%vishal roshanNo ratings yet
- Ref 6 ShivDocument7 pagesRef 6 ShivAkhilesh KhareNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Distributed SystemDocument12 pagesCH 1 Distributed Systemlucifer27meNo ratings yet
- Prof - Islam Overview of Cloud ComputingDocument32 pagesProf - Islam Overview of Cloud ComputingAdi Juliawan PawanaNo ratings yet
- Unit1notesccdocx 2024 08 15 13 40 15Document37 pagesUnit1notesccdocx 2024 08 15 13 40 15amitthakur25571No ratings yet
- CC 1Document102 pagesCC 1aniproductmailNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is The Use of Computing Resources (Hardware and Software) That AreDocument72 pages1.1 Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is The Use of Computing Resources (Hardware and Software) That AreShashi VardhanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Distributed SystemDocument13 pagesCH 1 Distributed SystemDesire MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument88 pagesCloud Computingmvd.offlNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument36 pagesClass NotesGentiyal BhumiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Cloud Architecture and ModelDocument9 pagesUnit - 1: Cloud Architecture and ModelRitu SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to CloudDocument57 pagesIntroduction to CloudSulochana jhaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Unit1Document53 pagesCloud Computing Unit1lioofficial.meNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction To Distributed SystemDocument68 pagesChapter-1 Introduction To Distributed SystemGUTAMA KUSSE GELEGLONo ratings yet
- CCunit 1Document57 pagesCCunit 1Manish RoyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Digital Transformation Project - RoughDocument5 pagesDigital Transformation Project - RoughSavita naikNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval DecanterDocument4 pagesAlfa Laval DecanterMTBNo ratings yet
- WSH Guidelines Managing Safety and Health For SME S in The Metalworking Industry Final 2 PDFDocument22 pagesWSH Guidelines Managing Safety and Health For SME S in The Metalworking Industry Final 2 PDFEmha AdamNo ratings yet
- Yupangco Cotton Mills, Inc. vs. Mendoza, 454 SCRA 386 (2005)Document12 pagesYupangco Cotton Mills, Inc. vs. Mendoza, 454 SCRA 386 (2005)Jahzel Dela Pena CarpioNo ratings yet
- MCQ of Microsoft ExcelDocument11 pagesMCQ of Microsoft ExcelNisha Agarwal 3No ratings yet
- Archiving Process in Sales DistributionDocument26 pagesArchiving Process in Sales DistributionkishorepanchakarlaNo ratings yet
- Kühlschrank/ Gefrierschrank Refrigerator: Bedienungsanleitung User ManualDocument48 pagesKühlschrank/ Gefrierschrank Refrigerator: Bedienungsanleitung User ManualFlorin CojocariuNo ratings yet
- 260-Article Text-875-1-10-20220728Document4 pages260-Article Text-875-1-10-20220728hasan andrianNo ratings yet
- ISM Lab FileDocument115 pagesISM Lab FileNidhi Rishabh Khare100% (1)
- Nelson/Salmo Pennywise July10, 2012Document56 pagesNelson/Salmo Pennywise July10, 2012Pennywise PublishingNo ratings yet
- Updated CB Report 22.9.16Document39 pagesUpdated CB Report 22.9.16ajaymatlaniNo ratings yet
- Systems Engineering ManagementDocument34 pagesSystems Engineering ManagementMadhvendra MishraNo ratings yet
- YANMAR Operation Manual YDG SeriesDocument92 pagesYANMAR Operation Manual YDG SeriesJufri AlfitriNo ratings yet
- QMS DeclarationDocument3 pagesQMS DeclarationMuhammad Saqib AsifNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument56 pagesMicroprocessors and MicrocontrollersAyush PatelNo ratings yet
- MCB-20-017 - 2023-2024 - 300 SIWES Assumption of Duty Letter For MCB - 20 - 017Document1 pageMCB-20-017 - 2023-2024 - 300 SIWES Assumption of Duty Letter For MCB - 20 - 017ayotundetundexNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Identity and Written Plea of Not GuiltyDocument1 pageAffidavit of Identity and Written Plea of Not GuiltyMyron BrandwineNo ratings yet
- ADMModule - STEM - GP12EU Ia 7Document27 pagesADMModule - STEM - GP12EU Ia 7Jel SuarezNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET Simple Equations For Entrance ExamsDocument2 pagesWORKSHEET Simple Equations For Entrance ExamsKeshav VaidNo ratings yet
- Murao vs. PeopleDocument18 pagesMurao vs. PeopleKenneth LimosneroNo ratings yet
- Medical Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in AdultsDocument17 pagesMedical Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Adultsduiennguyen262No ratings yet
- THE MISSIONARY SISTERS OF OUR LADY OF FATIMA vs. ALZONADocument3 pagesTHE MISSIONARY SISTERS OF OUR LADY OF FATIMA vs. ALZONAchaNo ratings yet
- Astm E1621-21Document9 pagesAstm E1621-21Tamara Silvana Cárcamo100% (2)
- Major Transactions Used in TRMDocument13 pagesMajor Transactions Used in TRMsapfico2k8100% (2)
- Prilog Chapter 1Document26 pagesPrilog Chapter 1Nuruddin AsyifaNo ratings yet
- N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFET: Product SummaryDocument5 pagesN-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFET: Product SummaryTony RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Leviton Industries V SalvadorDocument1 pageLeviton Industries V SalvadorAliw del RosarioNo ratings yet
- FCA Arrears Information SheetDocument2 pagesFCA Arrears Information SheetLee RamshawNo ratings yet