Worksheet: Very Short Answer Questions
Worksheet: Very Short Answer Questions
Uploaded by
ssOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet: Very Short Answer Questions
Worksheet: Very Short Answer Questions
Uploaded by
ssCopyright:
Available Formats
worksheet
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
1. Arrange the following in increasing Order of Stability.
(CH3)3C +, CH3CH2CH2CH2 , CH3CH2CHCH3 ,CH3CH2 , CH3CH2CH2
(CH3)3C < CH3CH2CHCH3 < CH3CH2CH2CH2 < CH3CH2CH2 < CH3CH2.
2. Write the hybridized state of C atoms in the following
CH2 = CH – C N
Sp2 Sp2 Sp
3. Give the IUPAC name of the following compound.
2,5-dimethyl Heptane
4. Give an example for electrophile and nucleophile each.
Examples of nucleophiles are the halogen anions (I-, Cl-, Br-), the hydroxide ion
(OH-), the cyanide ion (CN-), ammonia (NH3), and water.
Examples of electrophiles are hydronium ion (H3O+, from Brønsted acids), boron
trifluoride (BF3), aluminum chloride (AlCl3), and the halogen molecules fluorine
(F2), chlorine (Cl2), bromine (Br2), and iodine (I2).
5. Identify the functional group present in the following compounds:
(a) 6- Methyloctan-3-ol (b) Aniline
(a) alcohol
(b) amino
6. Why are free radicals unstable?
The odd number of electron(s) of a free radical makes it unstable, short lived and
highly reactive. Because of their high reactivity, they can abstract electrons from
other compounds to attain stability.
7. Write the IUPAC name of the following compounds:
(a) Acetic acid (b) Acetone
(a) ethanoic acid
(b) propanone
8. Name two compounds showing functional group isomerism.
Aldehyde and ketone
Carboxylic acid and ester
9. Identify the electrophilic Centre in the following: CH3CH=O and CH3I.
The starred carbon atoms are electrophilic centres as they will have a partial
positive charge due to the polarity of the bond.
10. In which C – C bond of CH3CH2CH2Br, the inductive effect is expected to
be the least?
Magntitude of inductive effect diminishes as the number of intervening bonds
increases, Hence, the effect is least in the bond number 4.
11. Name the alkane present in LPG.
propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10)
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
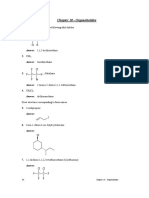
1. Draw the Structures of the following compounds.
a) Hex-3-enoic acid b) 2-chloro-2-ethylbutan-ol
2. Explain why (CH3 )3C+ is more stable than CH3C+H2.
CH33C+ has nine alpha hydrogens and has nine hyperconjugation structures while
CH3C+H2has three alpha hydrogens and has three hyperconjugation structures
therefore CH3 3C+ is more stable than CH3C+H2.
3. Give the number of Sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules
a) CH3NO2 b) HCONHCH3
(a) CH3NO2: there are 6 sigma bonds and 1 π bond.
(b) HCONHCH3: there are 8 sigma bonds and 1 π- bond.
4. Write the condensed and bond line formula of 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane.
Condensed formula
(CH3)2CHCH2C(CH3)3
Bond line formula
5. Which bond is more polar in the following pairs of molecules.
a) H3C-H, H3C-Br b) H3C-NH2, H2C-OH c) H3C-OH, H3C-SH
(a) C–Br, since Br is more electronegative than H
(b) C–O
(c) C–O
6. Define Isomerism. Explain position Isomerism and Functional Isomerism with
examples.
Two or more compounds having the same molecular formula but different
physical and chemical properties are called isomers and this phenomenon is
called isomerism.
Position Isomerism: Compounds which have the same structure of carbon chain
but differ in position of double or triple bonds or functional group are called
position isomers and this phenomenon is called Position Isomerism.
e g. CH3-CH2-CH=CH2
CH3-CH = CH –CH3
Functional Isomerism: Compounds which have the same molecular formula but
different functional group are called functional isomers and this phenomenon is
called functional Isomerism.
e g CH3 – CH2– OH
CH3 – O –CH3
7. Define Homologous series. Write the general formula of alkane, alkene and
alkynes.
Homologous Series: It is defined as group of similar organic compounds which
contains the similar functional groups and the two adjacent members of the
series is differ by a –CH2 group.
8. Define functional groups. Write the general formula of Carboxylic acids acid
chlorides.
Functional Groups :It is an atom or group of atoms bonded together ina unique
manner which is usually the site of chemical reactivity in an organic molecule. e
gCH3OH General formula of Carboxylic acids : CnH2n+1COOH General formula of
acid chlorides :RCOCl
9. Write a short note on Resonance effect.
The concept of resonance effect tells about the polarity induced in a molecule by
the reaction between a lone pair of electrons and a pi bond. It also occurs by the
interaction of 2 pi bonds in the adjacent atoms. Resonance, in simple terms, is the
molecules with multiple Lewis structures.
10. Give three points of differences between the inductive effect and resonance
effect.
Inductive Effect Resonance Effect
In inductive effect only partial In the resonance effect there is a
polarization of the sigma bond occurs complete displacement of π-bond or
due to electronegativity difference nonbonding electron pair from one part
due to which partial positive and of the conjugated system to the other
partial negative charge develops. part due to which complete positive and
It is a distance-dependent effect. negative charge develops.
Inductive effect is affected by the It is a distance independent effect.
electronegativity values of the atoms The resonance effect is affected by
conjugation.
You might also like
- The Girl Who Ate A Death God - (v3) (Complete) PDFDocument672 pagesThe Girl Who Ate A Death God - (v3) (Complete) PDFArkae Fortt100% (1)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Company Profile - IndoStarAviationDocument10 pagesCompany Profile - IndoStarAviationYamahaXD 01100% (1)
- AromaticsDocument5 pagesAromaticskinepela853No ratings yet
- Resonance and Inductive Effects PresentationDocument36 pagesResonance and Inductive Effects Presentationeagl33yeNo ratings yet
- ECF No. 0066 3 Exhibit B To Sooka Decl PDFDocument140 pagesECF No. 0066 3 Exhibit B To Sooka Decl PDFThavam RatnaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesHalimaNo ratings yet
- 11 Cbse Chemistry Organic ChemistryDocument22 pages11 Cbse Chemistry Organic ChemistryKrish KakkarNo ratings yet
- GOC NotesDocument43 pagesGOC NotesSudhanshu HedaNo ratings yet
- 11 ChemistryDocument12 pages11 ChemistryvirndrNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Principles of Organic ChemistryDocument74 pagesSome Basic Principles of Organic ChemistryprateekshadharaniNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12Document15 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12KrrishSPNo ratings yet
- University of Bahri Second Year Second Semester Main Exam 2015 Organic Reaction Type Date: / /2015 Time Allowed: 3 HrsDocument5 pagesUniversity of Bahri Second Year Second Semester Main Exam 2015 Organic Reaction Type Date: / /2015 Time Allowed: 3 HrsmanafadulNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry Important Questions 2022-23Document15 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry Important Questions 2022-23Divye DasNo ratings yet
- Effects StrengthsDocument36 pagesEffects StrengthsSesha Sai Kumar89% (9)
- Tutorial Letter 203/2/2018: General Chemistry 1BDocument17 pagesTutorial Letter 203/2/2018: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNo ratings yet
- GOC (Hints)Document2 pagesGOC (Hints)hchawla421No ratings yet
- Structure and FormulaeDocument64 pagesStructure and FormulaeLoveena SteadmanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 203/1/2018: General Chemistry 1BDocument12 pagesTutorial Letter 203/1/2018: General Chemistry 1BLeigh MakanNo ratings yet
- CH1O3 Questions PDFDocument52 pagesCH1O3 Questions PDFPrince T MashandaNo ratings yet
- CH1 C02-Structural and Molecular Organic Chemistry 2014Document22 pagesCH1 C02-Structural and Molecular Organic Chemistry 2014xapodi8776No ratings yet
- 12 - Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument9 pages12 - Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and TechniquesmohammedNo ratings yet
- Inductive EffectDocument6 pagesInductive EffectAyeshaNo ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry For IITDocument21 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry For IITParas Thakur83% (6)
- TextbookDocument42 pagesTextbookAarzoo KaziNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 DP2 HL T2 2019-MarkschemeDocument16 pagesPaper 2 DP2 HL T2 2019-MarkschemeconcessiozacharyNo ratings yet
- CHEM 331 Kraus Ihazlett 1 Chapter10Document10 pagesCHEM 331 Kraus Ihazlett 1 Chapter10Ahmed Sideeg100% (1)
- Aromatic Compounds: Y Y Y YDocument9 pagesAromatic Compounds: Y Y Y YCamille AdleNo ratings yet
- Diploe Moment and Inductive Effect Final VersionDocument45 pagesDiploe Moment and Inductive Effect Final VersionIqra BaigNo ratings yet
- Ch1 2 3 ExercisesDocument11 pagesCh1 2 3 ExercisesMancini100% (1)
- 8. Some basic concept in Organic ChemisrtyMCQ.... XI (2)Document10 pages8. Some basic concept in Organic ChemisrtyMCQ.... XI (2)Madhu MoniNo ratings yet
- TB Chapter15Document9 pagesTB Chapter15Luke SkywalkerNo ratings yet
- Long Exam 1Document8 pagesLong Exam 1Allan DNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesReasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryAasthaNo ratings yet
- 12-Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument2 pages12-Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesPadhai tak : by Dr.Aditya guptaNo ratings yet
- CHM 102 Past Test QuestionsDocument15 pagesCHM 102 Past Test Questionsalexapierre08No ratings yet
- 125 A Mid 2 Chemistry-1Document24 pages125 A Mid 2 Chemistry-1syeda ruqaiyah ashfaqNo ratings yet
- Anic Chemistry AK 2018-19Document22 pagesAnic Chemistry AK 2018-19XXXNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument21 pagesChapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesNitish MehraNo ratings yet
- Final Exam KeyDocument12 pagesFinal Exam KeykitthiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques PDFNitish MehraNo ratings yet
- Organic 2019Document24 pagesOrganic 2019xapodi8776No ratings yet
- XI CHE Final SAMPLE PAPER1Document4 pagesXI CHE Final SAMPLE PAPER1FIITJEE DPSNo ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry Theory 1Document28 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry Theory 1OasisEducation OesNo ratings yet
- Resonance and Induction Tutorial: Jack DeruiterDocument19 pagesResonance and Induction Tutorial: Jack DeruiterDanish AhmedNo ratings yet
- Complete GOC in One Shot by Singh SahabDocument122 pagesComplete GOC in One Shot by Singh Sahabhackr6828No ratings yet
- Key For Dec 2022 - Jan 2023 PaperDocument13 pagesKey For Dec 2022 - Jan 2023 PaperDivya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Halogenation of Alkanes t6tz2vh82vDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Halogenation of Alkanes t6tz2vh82vRiya NarangNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Organic ChemDocument12 pagesReasoning Organic ChemUtkarsh BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Orgnic ChemistryDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Orgnic ChemistryladybugNo ratings yet
- CHE 503 Organic Chemistry MSC I Term 1Document104 pagesCHE 503 Organic Chemistry MSC I Term 1omkar24march2011No ratings yet
- Combined OrganicDocument82 pagesCombined OrganicSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Goc and Isomerism Notes - PMDDocument46 pagesGoc and Isomerism Notes - PMDPritesh KakaniNo ratings yet
- Reactions of AlkanesDocument6 pagesReactions of AlkanesHamzaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument13 pagesOrganic ChemistryDhruv Raj 9 B 24No ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- 11: Free Radical Substitution and Addition ReactionsDocument39 pages11: Free Radical Substitution and Addition ReactionsCyrene MBolañosNo ratings yet
- Stereoelectronic Effects: A Bridge Between Structure and ReactivityFrom EverandStereoelectronic Effects: A Bridge Between Structure and ReactivityNo ratings yet
- Amorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesFrom EverandAmorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesNo ratings yet
- Legend - Vikings of Legend PDFDocument234 pagesLegend - Vikings of Legend PDFSamWissaNo ratings yet
- Stdin Tin PDF-job 336Document18 pagesStdin Tin PDF-job 336fubarNo ratings yet
- Readings in Pilippine History - Module 2Document26 pagesReadings in Pilippine History - Module 2Loki Balder BaldoviNo ratings yet
- Human Open Hand MonkDocument1 pageHuman Open Hand Monkcamilo duqueNo ratings yet
- PNP ValorDocument4 pagesPNP ValorigosseanNo ratings yet
- Defence Audit CodeDocument5 pagesDefence Audit Codekinnark100% (2)
- ALL THE KINGS HORSES Academia DRAFT20191022-29000-yp0ya3 PDFDocument15 pagesALL THE KINGS HORSES Academia DRAFT20191022-29000-yp0ya3 PDFRıdvan ÇeliközNo ratings yet
- Jtube Pull ForceDocument1 pageJtube Pull ForceferryNo ratings yet
- Руководство По Программе Mout Actd. Экспериментальная Тактика, Методы и Процедуры Для Пехотного Стрелкового Взвода и Отдедения в Городских Условиях. 1999 г.Document269 pagesРуководство По Программе Mout Actd. Экспериментальная Тактика, Методы и Процедуры Для Пехотного Стрелкового Взвода и Отдедения в Городских Условиях. 1999 г.Илья НикульшинNo ratings yet
- 3.x Style - The HomebreweryDocument9 pages3.x Style - The HomebreweryDxo DxoNo ratings yet
- National IntegrationDocument11 pagesNational IntegrationImman JohnNo ratings yet
- Cicero - Speech On Behalf of Publius Sestius (Oxford, 2006) PDFDocument510 pagesCicero - Speech On Behalf of Publius Sestius (Oxford, 2006) PDFsammiedearbornNo ratings yet
- Oil and The Great Powers Britain and Germany 1914 To 1945 First Edition Anand Toprani Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesOil and The Great Powers Britain and Germany 1914 To 1945 First Edition Anand Toprani Full Chapter PDFmurmelarriba100% (9)
- HSF-USA Statement On Passing of Leo RechterDocument3 pagesHSF-USA Statement On Passing of Leo RechterSamuel DubbinNo ratings yet
- The Force Awakens - (SWR09a) Character Folio - TirasDocument8 pagesThe Force Awakens - (SWR09a) Character Folio - TirasAlexNo ratings yet
- Denumire in Structura Form.J UR. Jud/Sec TDocument29 pagesDenumire in Structura Form.J UR. Jud/Sec Tcici1981No ratings yet
- Instant Download Sports Marketing A Strategic Perspective 5th Edition 5th Edition Ebook PDF PDF FREEDocument33 pagesInstant Download Sports Marketing A Strategic Perspective 5th Edition 5th Edition Ebook PDF PDF FREEmary.brinks380100% (60)
- ThewaroneducationingazaDocument14 pagesThewaroneducationingazaapi-735955672No ratings yet
- Total Warfare: Full ErrataDocument56 pagesTotal Warfare: Full ErrataManlio CipulloNo ratings yet
- CCH Group 1Document80 pagesCCH Group 1jessa lubayNo ratings yet
- Combat Flow ChartDocument1 pageCombat Flow ChartAzalnubizarNo ratings yet
- Aerial Bombardment Manual. Part 4. Flying Training For Pilots and Bombers (21 May 1920)Document24 pagesAerial Bombardment Manual. Part 4. Flying Training For Pilots and Bombers (21 May 1920)raheyo6168100% (1)
- Christopher Tomney TranscriptDocument70 pagesChristopher Tomney TranscriptDaily Kos100% (1)
- Public 61e7d650d5bfbb00260d28e3Document132 pagesPublic 61e7d650d5bfbb00260d28e3Mary Joy SeguiNo ratings yet
- Disrupt and Deny Spies Special Forces and The Secret Pursuit of British Foreign Policy Rory Cormac Full Chapter PDFDocument49 pagesDisrupt and Deny Spies Special Forces and The Secret Pursuit of British Foreign Policy Rory Cormac Full Chapter PDFyeenusegas100% (8)
- German Night Fighter Aces WW2Document17 pagesGerman Night Fighter Aces WW2Daniel Saboia75% (4)
- PT Rama Emerald MultiDocument12 pagesPT Rama Emerald MultiZarkasyi MudaNo ratings yet