Sample Trans
Sample Trans
Uploaded by
NEIL NETTE S. REYNALDOCopyright:
Available Formats
Sample Trans
Sample Trans
Uploaded by
NEIL NETTE S. REYNALDOOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Sample Trans
Sample Trans
Uploaded by
NEIL NETTE S. REYNALDOCopyright:
Available Formats
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM bloodstream, rather than into a duct.
HORMONES
Hormones circulate through the bloodstream to
specific sites called target tissues, or effectors.
chemical signals produced by specialized cells
secreted into the blood stream
The hormones’ transport, interaction with its target,
and removal from the body is dependent to their
chemical structure. There are two major types of
hormones: lipidsoluble and water-soluble.
necessary for normal growth, development,
reproduction, and homeostasis
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
The endocrine system is one of the two important
control systems of the body
The endocrine system is composed of endocrine
glands and specialized endocrine cells located
throughout the body
Group of ductless glands that secrete hormones
Includes:
o Hypothalamus
o Pituitary gland
o Thyroid and Parathyroid Gland
o Adrenal Gland
The hormones’ transport, interaction with its target,
o Ovaries and Testes
and removal from the body is dependent to their
o Pancreas
chemical structure. There are two major types of
FUNCTIONS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM hormones: lipidsoluble and water-soluble.
1. Regulation of metabolism. The endocrine system
controls the rate of nutrient utilization and energy
production.
2. Control of food intake and digestion. The endocrine
system regulates the level of satiation (fullness) and the
breakdown of food into individual nutrients.
3. Modulation of tissue development. The endocrine
system influences the development of tissues, such as
those of the nervous system.
4. Regulation of ion levels. The endocrine system helps
monitor blood pH, as well as Na+, K+, and Ca2+
concentrations in the blood.
5. Control of water balance. The endocrine system
regulates water balance by controlling the solute
concentration of the blood.
6. Changes in heart rate and blood pressure. The
endocrine system helps regulate the heart rate and blood
pressure and prepare the body for physical activity.
7. Control of blood glucose and other nutrients. The
endocrine system regulates the levels of glucose and
other nutrients in the blood.
8. Control of reproductive functions. The endocrine
system controls the development and functions of the
reproductive systems in males and females.
9. Stimulation of uterine contractions and milk
release. The endocrine system regulates uterine
contractions during delivery and stimulates milk release
from the breasts in lactating females.
10. Modulation of immune system function. The
endocrine system helps control the production of
immune cells.
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Endocrine glands secrete very small amounts of
chemical messengers called hormones into the
NEIL NETTE REYNALDO 1
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
ACTION destined for secretion outside the cell
OTHER hydrophilic in nature
PROPERTI
ES
EXAMPLES
Glycoprotei carbohydrate-protein complex
n o Follicle stimulating hormone
(FSH)
o Human chorionic
gonadotropin (hCG)
o Thyroid-stimulating
hormone (TSH)
HORMONE ROLES o Erythropoietin
1 Stress response Polypeptides made entirely of protein
HORMONES SUCH AS: o Adrenocorticotropic hormone
1 Cortisol Known as fight (ACTH)
2 Epinephrine or flight hormones o Insulin
2 Homeostasis o Glucagon
HORMONES SUCH AS: o Somatostatin
1 Insulin For glucose o ADH
2 Glucagon homeostasis o Angiotensin
3 Cortisol o Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
4 Antidiuretic Involved in o Calcitonin
Hormone (ADH) regulating blood o Growth Hormone
volume
o Cholecystokinin
3 Sexual maturation and reproductive process
o Gastrin
HORMONES SUCH AS
o Oxytocin
1 Testosterone
o Prolactin
2 Estrogen
4 Growth and development of the body
STEROID HORMONES
HORMONES SUCH AS
SYNTHESI synthesized in the smooth ER
1 Growth Hormone
S derived from cholesterol as their
2 Tropic such as atropine, precursor substance
hormones corticotropin
STORAGE no storage form
5 Energy production and stabilize metabolic rate RECEPTOR nucleus of the target cell
6 Promote or inhibit other hormones SITE
HORMONES SUCH AS ACTION onset of action is slower than the
1 Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone peptide hormones and lasts longer
(GHRH) OTHER hydrophobic in nature
2 Dopamine PROPERTI
ES
COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE EXAMPLES
Include Mineralocorticoids
TYPES OF HORMONES o aldosterone
(1 Peptide/Protein Hormones Glucocorticoids
) o cortisol
(2 Steroid Hormones Androgens
) o testosterone
(3 Amino Acid Derived Hormones Estrogens
)
PEPTIDE/PROTEIN HORMONES AMINO ACID DERIVED HORMONES/ AMINES
SYNTHESI synthesized in the rough ER, in the SYNTHESI function similar to steroid or peptides
S ribosomes as a prehormone or a S synthesized in the cytoplasm
preprohormone (which means they are derived mainly from amino acid such
not yet activated) as:
STORAGE stored in vesicles of the cells of o Tyrosine
respective endocrine gland o Tryptophan
RECEPTOR in the cell membrane of the target EXAMPLES
SITE cell
Include Epinephrine
NEIL NETTE REYNALDO 2
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Norepinephrine EXAMPLE
o Peptide-like AA derived increase in prolactin
Triiodothyronine (T3) stimulates the secretion of
Thyroxine (T4) oxytocin
o Steroid-like AA derived INHIBITORY The presence of 1 hormone
REACTION inhibits the secretion of another
hormone
EXAMPLE
increase in prolactin inhibits
FSH/GnRH (Gonadotropin
releasing hormone)
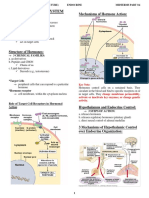
PATTERNS OF HORMONE COMMUNICATION
PATTERNS OF HORMONE COMMUNICATION
AUTOCRIN hormone secreted by a cell and acts on
E that cell
EXAMPLE
Insulin when secreted by the beta
NOTE cells of the pancreas, it will also act on
Hormones in the endocrine cell can only act on their the receptor of the beta cells itself
target cell via the receptors either in the cytoplasm or on
the nucleus
HORMONAL INTERACTION
TYPES OF HORMONAL INTERACTION
SYNERGISTIC 2 or more hormones are additive
or complementary in effect
EXAMPLE PARACRIN hormones secreted by a cell and acts
FSH and Luteinizing E on nearby cells
hormone (LH) complementary EXAMPLE
effect on the development of the Estrogen secreted by ovaries
ovaries Testosterone secreted by the Leydig
cells
ANTAGONISTI 1 hormone offsets another
C hormone
EXAMPLE
Insulin and Glucagon
increase in concentration of
insulin attenuates secretion of
glucagon and vice versa like a ENDOCRIN hormone secreted by glandular cell
“see saw” E into blood and acts on distant cells
PERMISSIVE 1 hormone enhance the EXAMPLE
responsiveness of a target to another Tropic hormones and
hormone Gonadotropins (FSH and LH)
EXAMPLE secreted by the distant pituitary gland
T3/T4 enhances the target and may act as far as the ovary
cells of epinephrine NEURO- hormone secreted by nerve cell
ENDOCRIN (neuron) into blood and acts on distant
POTENTIATIO 1 hormone increases the action of E target cells
N REACTION another hormone EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE Hypothalamic hormones
Testosterone enhances the (releasing hormones)
activity of the FSH
THYROID GLAND
STIMULATOR The presence of 1 hormone
Y REACTION stimulates the secretion of another
hormone’’
NEIL NETTE REYNALDO 3
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
A shield-shaped organs located inferior to the larynx. Divided into two portions: adrenal cortex (outer) and
Typically, it has two lobes, located laterally to the
trachea.
In 50% of the cases, it has a third lobe called
pyramidal lobe that extends superiorly to the isthmus.
adrenal medulla (inner).
WHAT HORMONES AND WHAT FOR?
Adrenal 1. Zona glomerulosa = mineralocorticoids
cortex 2. Zona fasciculata = glucocorticoids
3. Zona reticulata = androgens
1. Mineralocorticoids, mainly aldosterone,
regulates the homeostasis of two mineral ions:
sodium and potassium. It also promotes excretion
WHAT HORMONES AND WHAT FOR? of hydrogen via urination; thereby, preventing
Follicular cells T3 and T4 (thyroid hormone) acidosis. Its secretion is govern by the RAA
Parafollicular cells calcitonin pathway.
T3 (Triiodothyronine) Potent thyroxine
T4 (Tetraiodothyronine) Actual thyroxine
Calcitonin increase calcium absorption
by stimulating osteoblasts in
the bones.
PARATHYROID GLAND
Four, small, round structures that are partially
embedded in the posterior surface of the lateral lobes of the
thyroid gland. 2. Glucocorticoids, mainly cortisol
Chief/principal cells in the parathyroid gland produce (hydrocortisone), regulates metabolism and
the parathyroid hormone (PTH) or parathormone. resistance to stress. Functions include: protein
Parathormone is responsible for regulating the serum and lipid breakdown, glucose formation
levels of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate. (gluconeogenesis), stress resistance, anti-
It increases the calcium resorption by stimulating inflammatory response, and
osteoclast activity. immunosuppression.
PTH also increases the excretion of phosphate by the 3. Androgens, mainly
kidneys while decreasing the elimination of calcium and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), stimulates
magnesium in the urine. axillary and pubic hairs formation, female
↑Ca and ↑Mg while ↓HPO4 in the blood. libido, and is responsible for post-menopausal
Moreover, parathyroid hormone stimulates the kindey to estrogen production. All female estrogen
produce calcitriol (active vitamin D) that increases the comes from androgen. ACTH governs the
absorption of calcium by the intestines. regulation of androgens.
Adrenal modified sympathetic ganglion of the SNS.
medulla Instead of producing neurotransmitters, the
chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla secrete
hormones: Epinephrine and Norepinephrine.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) has a
direct control over the secretion of epinephrine
and norepinephrine that enhance the effect of
SNS.
During stressful situation or exercise, the
hypothalamus stimulates the sympathetic
preganglionic neurons to stimulate chromaffin
cells to produce epinephrine and norepinephrine.
ADRENAL GLAND PANCREAS
Two, flattened pyramidal glands located superior to Both endocrine and exocrine gland
each kidneys.
NEIL NETTE REYNALDO 4
MEDICAL-SURGICAL NURSING
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Located in the first curve of the duodenum and is Female: ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone
consist of head, tail, and body Male: testes synthesize testosterone
Endocrine tissues are called endocrine islets which Estrogen and progesterone is responsible for
include: A cells, B cells, D cells, and F cells. development and function of the female reproductive
organs and other female sexual characteristics
Cyclical release of estrogen and progesterone regulates
the menstrual cycle.
These two hormones promote development of
mammary glands and deposition of adipose tissue in
breast, hips, and thighs during puberty.
PINEAL GLAND
A small, pinecone-shaped structure located superior and
posterior to the thalamus of the brain.
It produces the hormone melatonin.
WHAT HORMONES AND WHAT FOR? Melatonin is thought to have two functions:
A (alpha) produce glucagon to increase glucose level in 1. Sleep-wake cycle
cells the blood and to stimulate insulin production. 2. Inhibits the functions of the reproductive system
B (beta) produce insulin to increase glucose uptake of
cells cells; thereby, lowering blood glucose level. It THYMUS
also inhibits glucagon production. A bilobed gland, roughly triangular in shape, located
D (delta) produce somatostatin that inhibits glucagon in the superior mediastinum, behind the sternum between
cells and insulin secretion. It also slows down the lungs.
nutrients absorption in the intestines. It produces the hormones: thymosin, thymi humoral
F cells produce pancreatic polypeptide which inhibits factor (THF), thymic factor (TF), and thymopoietin. All of
somatostatin secretion. which promotes the maturation of T cells
COMMON ENDOCRINE DISORDER AND
NURSING MANAGEMENT
GONADS
Gonads are organs that produce gametes and secretes
sex hormones.
NEIL NETTE REYNALDO 5
You might also like
- Immunology Lab Worksheet Student KEYDocument6 pagesImmunology Lab Worksheet Student KEYMar Yac100% (3)
- Clinical Chemistry 2: Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument3 pagesClinical Chemistry 2: Introduction To EndocrinologyYen BauzonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument5 pagesChapter 10 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- 11J Caybot Jashjovian Task12Document18 pages11J Caybot Jashjovian Task12JASH JOVIAN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System HandoutsDocument9 pagesEndocrine System HandoutsJosh ViñalonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 30-33 Endo Intro, Hypothalamus, PituitaryDocument44 pagesLecture 30-33 Endo Intro, Hypothalamus, PituitaryInshrah NazarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Effects Caused by HormonesDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Effects Caused by HormonesMa. Pia Lorein JacintoNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionHans Aldrin AbocNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument114 pagesReproductive SystembookaccountNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document10 pagesModule 5Jayvee VillaramaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM-Molecular Endocrinology 1Document14 pagesBIOCHEM-Molecular Endocrinology 1Std DlshsiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument14 pagesEndocrine System NotesSteven100% (1)
- Hormones, ClassificationDocument10 pagesHormones, ClassificationMenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Endocrine System NHR2021Document49 pagesChapter 3 - Endocrine System NHR2021h6qvqwvk2xNo ratings yet
- 1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineDocument36 pages1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- Endokrinologi DasarDocument33 pagesEndokrinologi DasarwadejackNo ratings yet
- Introduction - CC3: Mechanism of Hormonal ActionDocument40 pagesIntroduction - CC3: Mechanism of Hormonal ActionAl-hadad AndromacheNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Study GuideDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Study GuideCarla Andrea AbayaNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesEndocrinologyNathaniel Derige AndesNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Management of Male InfertilityDocument22 pagesHormonal Management of Male Infertilitydranibalurologoencancun.mxNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones and AgingDocument10 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones and AgingTushar ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones and AgingDocument10 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones and AgingTushar ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument76 pagesEndocrine Physiologykidusabeje7No ratings yet
- ENDOCRIONOLOGYDocument15 pagesENDOCRIONOLOGYmoepiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)Document31 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)arun231187100% (2)
- Endocrine System-1Document90 pagesEndocrine System-1markmuiruri581No ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Endocrine System 20231110 222858 0000Document87 pagesDrugs Acting On The Endocrine System 20231110 222858 0000Sameera DahamNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDocument32 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary Glandyararadwan56No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine SystemEthel May AlabastroNo ratings yet
- 10 - Hormonal AgentsDocument64 pages10 - Hormonal Agentsnica velanoNo ratings yet
- How Endocrine WorksDocument19 pagesHow Endocrine WorksSwad Abdul khalikNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument95 pagesEndocrine SystemUmar Ilyasu JibrilNo ratings yet
- Physio 2Document5 pagesPhysio 2amjadNo ratings yet
- Hormone GroupDocument35 pagesHormone GroupNeph VargasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Control and OordinationDocument5 pagesChemical Control and OordinationprimeeducationalinstituteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document8 pagesChapter 9Bea SeloterioNo ratings yet
- Hormones DR KhawlaDocument14 pagesHormones DR Khawlaحسين علاوي طاميNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument55 pagesHormonesAvinashNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument47 pagesHormonesSaad HassanNo ratings yet
- 10 - The Endocrine SystemDocument56 pages10 - The Endocrine SystemNickson OnchokaNo ratings yet
- Last ChapterDocument24 pagesLast ChapterVector AcademyNo ratings yet
- Ing - Sistem EndokrinDocument9 pagesIng - Sistem EndokrinWarman PurbaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemMark DimarucutNo ratings yet
- Sheena Khan: Biochemistry Generiic Bs NursingDocument22 pagesSheena Khan: Biochemistry Generiic Bs NursingsharmeenNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyNo ratings yet
- CHP 4 and 5Document22 pagesCHP 4 and 5Fatima Ejaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Regulasi Dan Mekanisme EndokrinDocument121 pagesRegulasi Dan Mekanisme Endokrinluthfiyya syafiqaNo ratings yet
- 5.endocrine System ++Document21 pages5.endocrine System ++fbn87rfm2jNo ratings yet
- NOTES Endocrinology ToxicologyDocument52 pagesNOTES Endocrinology ToxicologyRenz Gerard AmorNo ratings yet
- Module 22 HormonesDocument23 pagesModule 22 HormonesCrystal ManguneNo ratings yet
- Hormon Provided by Medico SlidesDocument31 pagesHormon Provided by Medico SlidesMuhammad NaveedNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ReviewerDocument5 pagesEndocrine ReviewerAshley MalolotNo ratings yet
- Endocrine 2Document13 pagesEndocrine 2Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- EndokrinDocument70 pagesEndokrinNur Hadi PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Week 13-16 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System Ms - Asma El-SharaDocument33 pagesWeek 13-16 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System Ms - Asma El-Sharalujainalshoubaki386No ratings yet
- 1 - Biokimia ReproduksiDocument56 pages1 - Biokimia ReproduksiTarissa Kartika EdwinNo ratings yet
- PD22 Hap1 L03Document33 pagesPD22 Hap1 L03Ka Yan LAUNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology: 100-Questions and Explanatory Answers for StudentsFrom EverandEndocrine Physiology: 100-Questions and Explanatory Answers for StudentsNo ratings yet
- MEDSURG 1 NotesDocument43 pagesMEDSURG 1 NotesNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- NCM 107N - MaternalDocument46 pagesNCM 107N - MaternalNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- NCM 113.Document5 pagesNCM 113.NEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- 2023 - Mood Disorders Lecture NotesDocument13 pages2023 - Mood Disorders Lecture NotesNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- Full Specification and Technical Data Sheet of Potato Dextrose AgarDocument2 pagesFull Specification and Technical Data Sheet of Potato Dextrose AgarKunal VermaNo ratings yet
- TS Glycobiology in Cancer EbookDocument8 pagesTS Glycobiology in Cancer EbookDaisy Joanna Castañeda MataNo ratings yet
- HEMA 1 LAB (Combined)Document24 pagesHEMA 1 LAB (Combined)Princess MikaNo ratings yet
- HashbrownDocument22 pagesHashbrownLeomill MendiolaNo ratings yet
- ZetamycinDocument6 pagesZetamycinelcapitano vegetaNo ratings yet
- Neglected Tropical DiseasesDocument84 pagesNeglected Tropical DiseasesAbhinesh Kr JhaNo ratings yet
- Thypus: Group 5 Adi Setiyo Nugroho Afif Ghariza Andriyanti A.G. Dewi Wulan Cahyani Muhammad IkhsanDocument11 pagesThypus: Group 5 Adi Setiyo Nugroho Afif Ghariza Andriyanti A.G. Dewi Wulan Cahyani Muhammad IkhsanikhsanNo ratings yet
- Agenda Prac Draft Agenda Meeting 7 10 February 2022 - enDocument69 pagesAgenda Prac Draft Agenda Meeting 7 10 February 2022 - ennegfbNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Biology Paper - 3 Solution: Section-I Answer 1 (A)Document7 pagesICSE Board Class IX Biology Paper - 3 Solution: Section-I Answer 1 (A)Narayanamurthy AmirapuNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Effectiveness of All Test Hbsag Rapid Test Kit Compared With Elisa SerologyDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Effectiveness of All Test Hbsag Rapid Test Kit Compared With Elisa SerologyHas SimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Use of Colony Morphology For The Presumptive Identification of MicroorganismDocument6 pagesChapter 8: Use of Colony Morphology For The Presumptive Identification of MicroorganismSamanthaNo ratings yet
- BacillusDocument7 pagesBacillusAHMED ZINEDDINENo ratings yet
- SDOM Promising TherapiesDocument16 pagesSDOM Promising TherapiesdarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document16 pagesWa0003.nikhilkumar6377311No ratings yet
- Role of Synthetic Proteins and Peptides in AnimalsDocument7 pagesRole of Synthetic Proteins and Peptides in AnimalsroniNo ratings yet
- Iron AbsorptionDocument3 pagesIron AbsorptionmaiiiNo ratings yet
- 928 12 Bio Botany Sliptest Questions emDocument10 pages928 12 Bio Botany Sliptest Questions emYazer ArafathNo ratings yet
- Vesicular, Ulcerative, and Necrotic Dermatitis of ReptilesDocument21 pagesVesicular, Ulcerative, and Necrotic Dermatitis of ReptilesAlice RmaNo ratings yet
- Ncbi Selulitis BulosaDocument3 pagesNcbi Selulitis BulosaHarefa TirtaNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument14 pagesAntiviral DrugsSunil100% (4)
- Physiology of Lactation: Clinics in Perinatology July 1999Document14 pagesPhysiology of Lactation: Clinics in Perinatology July 1999Muhammad SidiqNo ratings yet
- 11th Bio Botany Study Material emDocument9 pages11th Bio Botany Study Material emram28186428No ratings yet
- KDIGO 2024 ANCA Vasculitis GuidelineDocument47 pagesKDIGO 2024 ANCA Vasculitis GuidelineAlexis Villa VascoNo ratings yet
- ChromosomesDocument16 pagesChromosomesJan Lloyd Odrunia100% (2)
- Goodman Et Al 2013 Evaluation of Endogenous Allergens For The Safety Evaluation of Genetically Engineered Food CropsDocument16 pagesGoodman Et Al 2013 Evaluation of Endogenous Allergens For The Safety Evaluation of Genetically Engineered Food CropsZé Paulo PerestreloNo ratings yet
- Biological AgentsDocument83 pagesBiological AgentsEnderlys GarciaNo ratings yet
- PLASMIDSDocument24 pagesPLASMIDSAli HamzaNo ratings yet
- Parasites Transmission Infective Diagnostic StageDocument1 pageParasites Transmission Infective Diagnostic StageKaye NeeNo ratings yet
- Influenza: DR Sudipta Roy Asst - Prof, KPC Medical CollegeDocument10 pagesInfluenza: DR Sudipta Roy Asst - Prof, KPC Medical CollegeSudipto RoyNo ratings yet